当前位置:网站首页>Granularity of blocking of concurrency control
Granularity of blocking of concurrency control
2022-07-05 21:59:00 【Short section senior】
The size of the blocking object is called blocking granularity (Granularity)
Blocked objects : Logical unit , Physical unit
example : In a relational database , Block the object :
Logical unit : Property value 、 A collection of attribute values 、 Tuples 、 Relationship 、 Index entry 、 The whole index 、 The whole database, etc
Physical unit : page ( Data page or index page )、 Physical records, etc
Choose the principle of blocking granularity
Blocking granularity is closely related to the concurrency of the system and the overhead of concurrency control .
The greater the granularity of the blockade , The fewer data units a database can block , The less concurrency , The lower the system overhead ;
The smaller the size of the blockade , High concurrency , But the more overhead there is
example
If blocking granularity is data page , Business T1 Tuples need to be modified L1, be T1 Must include L1 The entire data page A Lock . If T1 Yes A After lock transaction T2 To be modified A Zhongyuan group L2, be T2 Forced to wait , until T1 Release A.
If the blocking granularity is tuple , be T1 and T2 Can be right at the same time L1 and L2 Lock , There's no need to wait for each other , The parallelism of the system is improved .
And so on , Business T You need to read the entire table , If blocking granularity is tuple ,T Every tuple in the table must be locked , It costs a lot
Multi granularity blocking (Multiple Granularity Locking)
Multiple blocking granularity are supported in one system for different transaction choices
Select block granularity
Consider both blocking overhead and concurrency , Select appropriate blocking granularity
User transactions that need to handle a large number of tuples of multiple relationships : Take the database as the blocking unit
User transactions that need to handle a large number of tuples : Take the relationship as the blocking unit
Handle user transactions with only a small number of tuples : In tuples
Multi granularity blocking
Multi granularity tree
Multi level blocking granularity is represented by tree structure
The root node is the entire database , Represents the maximum data granularity
Leaf nodes represent the smallest data granularity
example : Three level granularity tree . The root node is the database , The child nodes of the database are relationships , The child node of the relationship is tuple .
Multi granularity blocking protocol
Allow each node in the multi granularity tree to be locked independently
Locking a node means that all descendant nodes of the node are also locked of the same type
In multi granularity blocking, a data object may be blocked in two ways : Explicit blocking and implicit blocking
Explicit blocking and implicit blocking
Explicit blocking : A block directly added to a data object
Implicitly block : The data object is not locked independently , The data object is locked because its parent node is locked
Explicit blocking has the same effect as implicit blocking
When the system checks for blocking conflicts
To check for explicit blocking
Also check for implicit blocking
Such as transaction T To the relationship R1 Add X lock
The system must search its parent node database 、 Relationship R1
And search R1 Child node of , namely R1 Every tuple in
If one of the data objects has an incompatible lock , be T Must wait
Lock a data object , The system needs to be checked
The data object
Whether there is an explicit blockade conflict with it
All parent nodes
Check whether the explicit blocking of this transaction conflicts with the implicit blocking on the data object :( Caused by the blockade added by the parent node )
All child nodes
See whether the above explicit blocking is different from the implicit blocking of this transaction ( The block that will be added to the child node ) Conflict
Intent locks
Introduction of intention lock (intention lock) Purpose
Improve the efficiency of system checking when a data object is locked
If you add intention lock to a node , It means that the lower node of the node is being locked
Add a basic lock to any node , You must first add intention lock to its upper node
for example , When locking any tuple , You must first add an intentional lock to the database and relationship it is in
Common intention locks
Intention sharing lock (Intent Share Lock, abbreviation IS lock )
Intention exclusive lock (Intent Exclusive Lock, abbreviation IX lock )
Sharing intention exclusive lock (Share Intent Exclusive Lock, abbreviation SIX lock )
IS lock
If you add... To a data object IS lock , Represents its descendant node ( Intention ) Add S lock .
for example : Business T1 Right R1 Add... To a tuple in S lock , First of all, the relationship R1 And database plus IS lock
IX lock
If you add... To a data object IX lock , Represents its descendant node ( Intention ) Add X lock .
for example : Business T1 Right R1 Add... To a tuple in X lock , First of all, the relationship R1 And database plus IX lock
SIX lock
If you add... To a data object SIX lock , To add to it S lock , add IX lock , namely SIX = S + IX.
example : Add... To a watch SIX lock , It means that the transaction needs to read the whole table ( So add S lock ), Individual tuples are also updated ( So add IX lock ).
Consistency matrix of intention lock

The strength of the lock
The strength of a lock is its rejection of other locks
It is safe for a transaction to replace weak lock with strong lock when applying for blocking , Otherwise 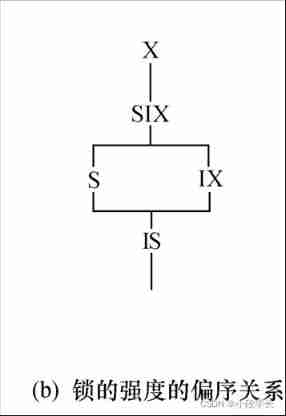
Multi granularity blocking method with intention lock
When applying for a blockade, it should be done in a top-down order
The release of the blockade should be done in a bottom-up order
for example : Business T1 To the relationship R1 Add S lock
First, add... To the database IS lock
Check the database and R1 Whether incompatible locks have been added (X or IX)
No more searching and checking R1 Whether the tuples in are locked with incompatible locks (X lock )
Multi granularity blocking method with intention lock
It improves the concurrency of the system
Reduce the cost of locking and unlocking
It is widely used in practical database management system products
Welcome to join me for wechat exchange and discussion ( Please note csdn Add )
边栏推荐
- 【愚公系列】2022年7月 Go教学课程 003-IDE的安装和基本使用
- Huawei game multimedia service calls the method of shielding the voice of the specified player, and the error code 3010 is returned
- The American Championship is about to start. Are you ready?
- Detailed explanation of memset() function usage
- Kingbasees v8r3 cluster maintenance case -- online addition of standby database management node
- Evolution of large website architecture and knowledge system
- Shell script, awk uses if, for process control
- Lightweight dynamic monitorable thread pool based on configuration center - dynamictp
- The Blue Bridge Cup web application development simulation competition is open for the first time! Contestants fast forward!
- 854. 相似度为 K 的字符串 BFS
猜你喜欢
MMAP learning
Analysis and test of ModbusRTU communication protocol
Exercise 1 simple training of R language drawing
DBeaver同时执行多条insert into报错处理

2.2.3 output of documents
递归查询多级菜单数据
Reptile practice

Type of fault

An exception occurred in Huawei game multimedia calling the room switching method internal system error Reason:90000017
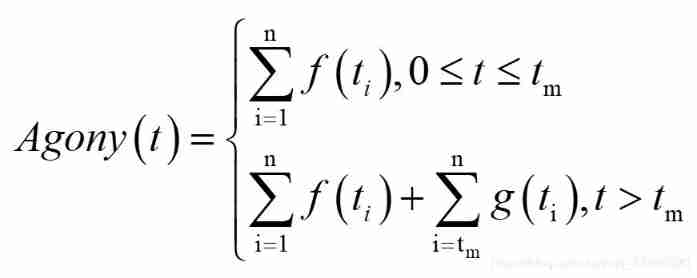
Cold violence -- another perspective of objective function setting
随机推荐
资深电感厂家告诉你电感什么情况会有噪音电感噪音是比较常见的一种电感故障情况,如果使用的电感出现了噪音大家也不用着急,只需要准确查找分析出什么何原因,其实还是有具体的方法来解决的。作为一家拥有18年品牌
Meituan dynamic thread pool practice ideas, open source
PyGame practical project: write Snake games with 300 lines of code
Ad637 notes d'utilisation
How to organize an actual attack and defense drill
Three components of openpyxl
[Yugong series] go teaching course 003-ide installation and basic use in July 2022
多家呼吸机巨头产品近期被一级召回 呼吸机市场仍在增量竞争
Xlrd common operations
Installation of VMware Workstation
Official clarification statement of Jihu company
NET中小型企业项目开发框架系列(一个)
Implementing Lmax disruptor queue from scratch (IV) principle analysis of multithreaded producer multiproducersequencer
Some common processing problems of structural equation model Amos software
ICMP introduction
Yolov5 training custom data set (pycharm ultra detailed version)
HDU 4391 Paint The Wall 段树(水
华为游戏多媒体调用切换房间方法出现异常Internal system error. Reason:90000017
SQL knowledge leak detection
MySQL连接断开报错MySQLdb._exceptions.OperationalError 4031, The client was disconnected by the server