当前位置:网站首页>f.grid_sample
f.grid_sample
2022-07-31 02:20:00 【love CV】
SPATIAL TRANSFORMER NETWORKS TUTORIAL
Author: Ghassen HAMROUNI

In this tutorial, you will learn how to augment your network using a visual attention mechanism called spatial transformer networks. You can read more about the spatial transformer networks in the DeepMind paper
Spatial transformer networks are a generalization of differentiable attention to any spatial transformation. Spatial transformer networks (STN for short) allow a neural network to learn how to perform spatial transformations on the input image in order to enhance the geometric invariance of the model. For example, it can crop a region of interest, scale and correct the orientation of an image. It can be a useful mechanism because CNNs are not invariant to rotation and scale and more general affine transformations.
grid_sample,A sketch was drawn as an explanation.
- 图像尺寸归一化:First normalize the size of the image,(-1,-1)represents the original image(0,0)位置,(1,1)represents the original image(H-1,W-1)位置,这样一来,The positions of the feature points are also normalized to the corresponding positions.
- 构建grid:List the normalized feature points,constitutes a scale of 1*1*K*2的张量,其中K表示特征数量,2分别表示xy坐标.
- The feature point positions are denormalized:according to the input tensorH与W对grid(1,1,0,:)(represents the first feature point,The rest of the feature points are similar)进行反归一化,In fact, it is scaled proportionally+平移,Get the denormalized feature points in a tensor of a certainslice(通道)上的位置;But this location may not be a whole pixel,At this point, it needs to be filled with bilinear interpolation,然后其余sliceDo bilinear interpolation in the same way.注:What is actually in the code is bilinear interpolation,It is not the bicubic interpolation mentioned in the text;
- 输出维度:1*C*1*K.

One of the best things about STN is the ability to simply plug it into any existing CNN with very little modification.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# In[ ]:
# get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')
#
# Spatial Transformer Networks Tutorial
# =====================================
# **Author**: `Ghassen HAMROUNI <https://github.com/GHamrouni>`_
#
# .. figure:: /_static/img/stn/FSeq.png
#
# In this tutorial, you will learn how to augment your network using
# a visual attention mechanism called spatial transformer
# networks. You can read more about the spatial transformer
# networks in the `DeepMind paper <https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02025>`__
#
# Spatial transformer networks are a generalization of differentiable
# attention to any spatial transformation. Spatial transformer networks
# (STN for short) allow a neural network to learn how to perform spatial
# transformations on the input image in order to enhance the geometric
# invariance of the model.
# For example, it can crop a region of interest, scale and correct
# the orientation of an image. It can be a useful mechanism because CNNs
# are not invariant to rotation and scale and more general affine
# transformations.
#
# One of the best things about STN is the ability to simply plug it into
# any existing CNN with very little modification.
#
# In[ ]:
# License: BSD
# Author: Ghassen Hamrouni
# from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.ion() # interactive mode
# Loading the data
# ----------------
#
# In this post we experiment with the classic MNIST dataset. Using a
# standard convolutional network augmented with a spatial transformer
# network.
#
#
# In[ ]:
from six.moves import urllib
opener = urllib.request.build_opener()
opener.addheaders = [('User-agent', 'Mozilla/5.0')]
urllib.request.install_opener(opener)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# Training dataset
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(root='.', train=True, download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])), batch_size=64, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
# Test dataset
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(root='.', train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])), batch_size=64, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
# Depicting spatial transformer networks
# --------------------------------------
#
# Spatial transformer networks boils down to three main components :
#
# - The localization network is a regular CNN which regresses the
# transformation parameters. The transformation is never learned
# explicitly from this dataset, instead the network learns automatically
# the spatial transformations that enhances the global accuracy.
# - The grid generator generates a grid of coordinates in the input
# image corresponding to each pixel from the output image.
# - The sampler uses the parameters of the transformation and applies
# it to the input image.
#
# .. figure:: /_static/img/stn/stn-arch.png
#
# .. Note::
# We need the latest version of PyTorch that contains
# affine_grid and grid_sample modules.
#
#
#
# In[ ]:
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10)
# Spatial transformer localization-network
self.localization = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 8, kernel_size=7),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(8, 10, kernel_size=5),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(True)
)
# Regressor for the 3 * 2 affine matrix
self.fc_loc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(10 * 3 * 3, 32),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(32, 3 * 2)
)
# Initialize the weights/bias with identity transformation
self.fc_loc[2].weight.data.zero_()
self.fc_loc[2].bias.data.copy_(torch.tensor([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0], dtype=torch.float))
# Spatial transformer network forward function
def stn(self, x):
xs = self.localization(x)
xs = xs.view(-1, 10 * 3 * 3)
theta = self.fc_loc(xs)
theta = theta.view(-1, 2, 3)
grid = F.affine_grid(theta, x.size())
x = F.grid_sample(x, grid)
return x
def forward(self, x):
# transform the input
x = self.stn(x)
# Perform the usual forward pass
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2))
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2))
x = x.view(-1, 320)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
model = Net().to(device)
# Training the model
# ------------------
#
# Now, let's use the SGD algorithm to train the model. The network is
# learning the classification task in a supervised way. In the same time
# the model is learning STN automatically in an end-to-end fashion.
#
#
# In[ ]:
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
def train(epoch):
model.train()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % 500 == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
#
# A simple test procedure to measure the STN performances on MNIST.
#
def test():
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
output = model(data)
# sum up batch loss
test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, size_average=False).item()
# get the index of the max log-probability
pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'
.format(test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
# Visualizing the STN results
# ---------------------------
#
# Now, we will inspect the results of our learned visual attention
# mechanism.
#
# We define a small helper function in order to visualize the
# transformations while training.
#
#
# In[ ]:
def convert_image_np(inp):
"""Convert a Tensor to numpy image."""
inp = inp.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
inp = std * inp + mean
inp = np.clip(inp, 0, 1)
return inp
# We want to visualize the output of the spatial transformers layer
# after the training, we visualize a batch of input images and
# the corresponding transformed batch using STN.
def visualize_stn():
with torch.no_grad():
# Get a batch of training data
data = next(iter(test_loader))[0].to(device)
input_tensor = data.cpu()
transformed_input_tensor = model.stn(data).cpu()
in_grid = convert_image_np(
torchvision.utils.make_grid(input_tensor))
out_grid = convert_image_np(
torchvision.utils.make_grid(transformed_input_tensor))
# Plot the results side-by-side
f, axarr = plt.subplots(1, 2)
axarr[0].imshow(in_grid)
axarr[0].set_title('Dataset Images')
axarr[1].imshow(out_grid)
axarr[1].set_title('Transformed Images')
for epoch in range(1, 20 + 1):
train(epoch)
test()
# Visualize the STN transformation on some input batch
visualize_stn()
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
pytorch的grid_sampleReturns an incorrect value - 问答 - 腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云 (tencent.com)
There are forward mappings in the neural network framework/Is warpage realized?
A deep learning featureSuperPoint
How to use optical flow and grid_sample对图像进行扭曲?
Convolutional network solves affine transformation parameters
边栏推荐
- Project development software directory structure specification
- Simple confession page
- Teach you how to configure Jenkins automated email notifications
- rpm install postgresql12
- Static route analysis (the longest mask matching principle + active and standby routes)
- Force buckled brush the stairs (7/30)
- 【AcWing 第62场周赛】
- Linux下redis7的安装,启动与停止
- To write good test cases, you must first learn test design
- PDF split/merge
猜你喜欢
Nacos

加密生活,Web3 项目合伙人的一天
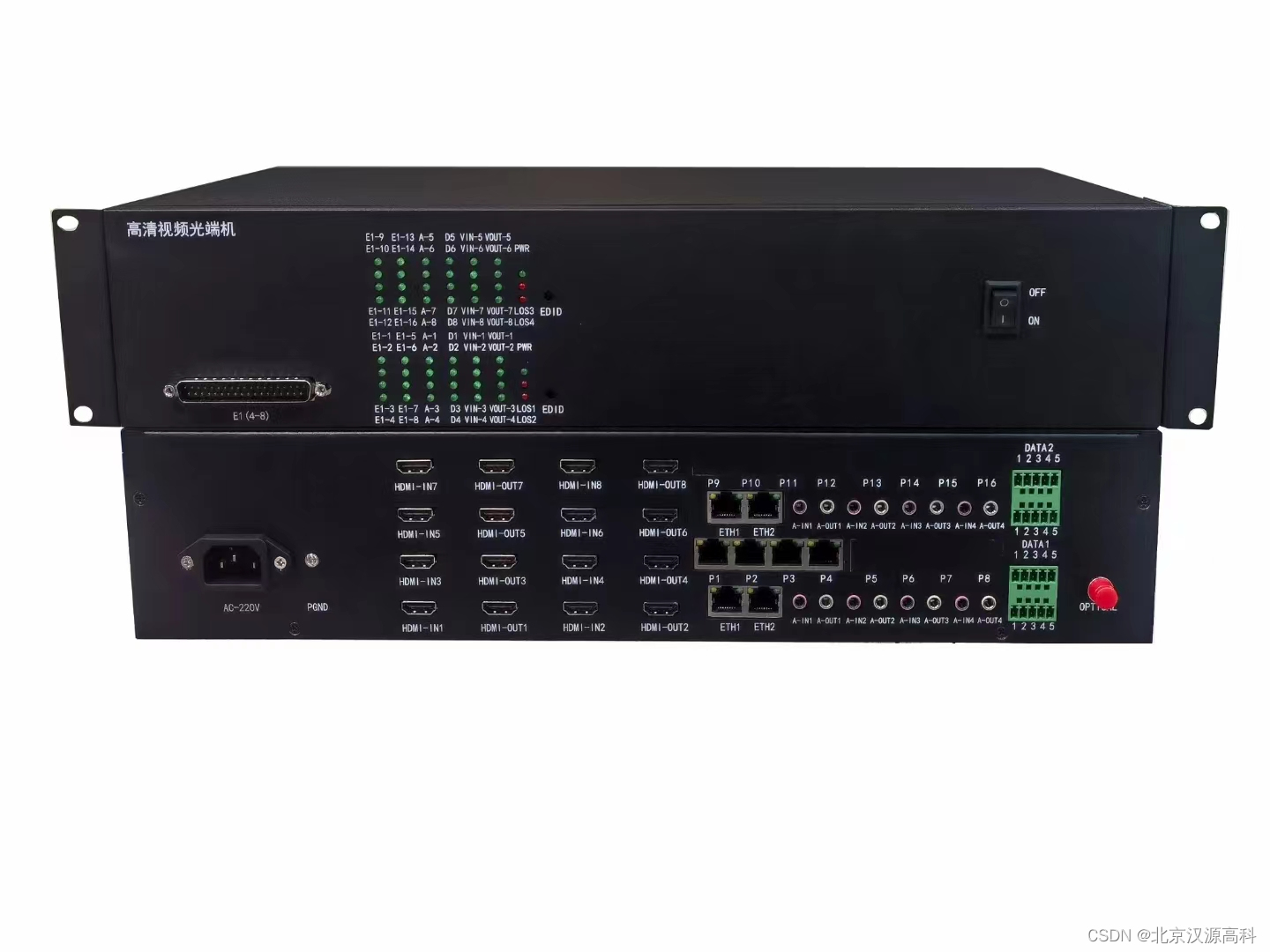

汉源高科8路HDMI综合多业务高清视频光端机8路HDMI视频+8路双向音频+8路485数据+8路E1+32路电话+4路千兆物理隔离网络

How to do a startup CTO?
![LeetCode 1161 The largest element in the layer and the LeetCode road of [BFS binary tree] HERODING](/img/56/fcc8ee6f592abf0a374fc950a3362f.png)
LeetCode 1161 The largest element in the layer and the LeetCode road of [BFS binary tree] HERODING
Are you still working hard on the limit of MySQL paging?

What does a software test report contain?

What level of software testing does it take to get a 9K job?

16. Registration Center-consul
StringJoiner详解
随机推荐
PDF split/merge
The effective square of the test (one question of the day 7/29)
汉源高科8路HDMI综合多业务高清视频光端机8路HDMI视频+8路双向音频+8路485数据+8路E1+32路电话+4路千兆物理隔离网络
汉诺塔问题
Drools WorkBench的简介与使用
用户交互+格式化输出
leetcode-952: Calculate max component size by common factor
AtCoder Beginner Contest 261 Partial Solution
Manchester City confuses fans with smart scarf that detects emotions
FPGA-based vending machine
There is a problem with the multiplayer-hlap package and the solution cannot be upgraded
keep-alive cache component
BAT卖不动「医疗云」:医院逃离、山头林立、行有行规
经典链表OJ强训题——快慢双指针高效解法
最大路径和
基于opencv实现人脸检测
ShardingJDBC usage summary
PDF 拆分/合并
Drools基本介绍,入门案例,基本语法
Layer 2 broadcast storm (cause + judgment + solution)