当前位置:网站首页>A complete tutorial for getting started with redis: transactions and Lua
A complete tutorial for getting started with redis: transactions and Lua
2022-07-04 22:53:00 【Gu Ge academic】
To ensure the atomicity of multiple command combinations ,Redis It provides simple transaction functions and sets
become Lua Script to solve this problem . This section begins with a brief introduction Redis How to use transactions in and
Its limitations , After that, we will focus on the following Lua The basic use of language , And how to Redis and
Lua Script integration , Finally gives Redis management Lua Related commands of the script .
3.4.1 Business
Readers familiar with relational databases should be familiar with transactions , In short , Transaction representation one
Group action , Or all , Or none at all . For example, on social networking sites, users A Pay attention to the
user B, Then you need to A Add users to the following list of B, And in the user B In the fan list of
Add users A, These two actions are either executed in full , Or none at all , Otherwise, data will appear
A situation of inconsistency .
Redis Simple transaction functionality is provided , Place a set of commands that need to be executed together multi and
exec Between the two commands .multi An order represents the beginning of a business ,exec The order represents the end of the transaction , they
The commands between are executed in atomic order , For example, the following operation realizes the above user concerns .
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd user:a:follow user:b
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd user:b:fans user:a
QUEUED
You can see sadd The return result of the command at this time is QUEUED, Represents that the order is not really carried out
That's ok , But for the time being Redis in . If another client performs sismember user:
a:follow user:b The return result should be 0.
127.0.0.1:6379> sismember user:a:follow user:b
(integer) 0
Only when exec After execution , user A Focus on users B Your behavior is complete , Return as follows
The two results of correspond sadd command .
127.0.0.1:6379> exec
1) (integer) 1
2) (integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sismember user:a:follow user:b
(integer) 1
If you want to stop the execution of the transaction , have access to discard Command instead of exec Command is enough .
127.0.0.1:6379> discard
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> sismember user:a:follow user:b
(integer) 0
If there is an error in the command in the transaction ,Redis The processing mechanism is also different .
1. Wrong command
For example, the following operation will be wrong set It has been written. sett, It's a syntax error , It will make the whole transaction impossible
perform ,key and counter The value of has not changed :
127.0.0.1:6388> mget key counter
1) "hello"
2) "100"
127.0.0.1:6388> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6388> sett key world
(error) ERR unknown command 'sett'
127.0.0.1:6388> incr counter
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6388> exec
(error) EXECABORT Transaction discarded because of previous errors.
127.0.0.1:6388> mget key counter
1) "hello"
2) "100"
2. Runtime error
For example, users B When adding a fan list , Mistake sadd The order is written zadd command , This kind of
Is a runtime command , Because the grammar is correct :
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd user:a:follow user:b
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd user:b:fans 1 user:a
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> exec
1) (integer) 1
2) (error) WRONGTYPE Operation against a key holding the wrong kind of value
127.0.0.1:6379> sismember user:a:follow user:b
(integer) 1
You can see Redis Rollback is not supported ,sadd user:a:follow user:b The order has been
After successful execution , Developers need to fix such problems themselves .
Some application scenarios need to be before the transaction , Make sure that the key Not repaired by other clients
Changed , To execute a transaction , Otherwise, do not execute ( Like optimistic lock ).Redis Provides watch Order it
Solve these kinds of problems , surface 3-2 It shows the sequence of two clients executing commands .
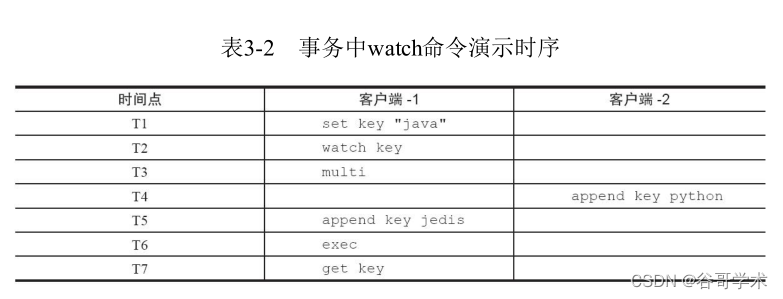
You can see “ client -1” In execution multi It was done before watch command ,“ Customer
End -2” stay “ client -1” perform exec It was modified before key value , Cause the transaction not to be executed (exec result
by nil), The whole code looks like this :
#T1 : client 1
127.0.0.1:6379> set key "java"
OK
#T2 : client 1
127.0.0.1:6379> watch key
OK
#T3 : client 1
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
#T4 : client 2
127.0.0.1:6379> append key python
(integer) 11
#T5 : client 1
127.0.0.1:6379> append key jedis
QUEUED
#T6 : client 1
127.0.0.1:6379> exec
(nil)
#T7 : client 1
127.0.0.1:6379> get key
"javapython"
Redis Provides a simple transaction , The reason why it is simple , Mainly because it does not support transactions
Rollback feature in , At the same time, the relationship between commands cannot be calculated , Of course, it also reflects
Redis Of “keep it simple” Characteristics of , The next section introduces Lua Scripts can also implement transactions
Related functions , But it's much more powerful .
3.4.2 Lua Brief introduction to usage
Lua Language is in 1993 Invented by a university research group in Brazil , Its design goal is to serve as
Transplant embedded programs to other applications , It is from C The realization of language , Simple and small, but
Powerful , So many applications use it as a scripting language , Especially in the field of games , for example
The famous blizzard company will Lua Language is introduced to “ World of warcraft ” In this game ,Rovio The company will
Lua Language as “ Angry birds ” This hot game level upgrade engine ,Web The server Nginx
take Lua Language as an extension , Enhance your own capabilities .Redis take Lua As a scripting language, it can help develop
You can customize your own Redis command , before this , You have to change the source code . In the introduction of how in Redis in
Use Lua Before the script , It is necessary to Lua Make a basic introduction to the use of language .
1. Data types and their logical processing
Lua The language provides the following data types :booleans( Boolean )、numbers( Count
value )、strings( character string )、tables( form ), Compared with many advanced languages , Relatively simple
single . The following will combine examples with Lua The basic data types and logical processing are described .
(1) character string
The following defines a string type of data :
local strings val = "world"
among ,local representative val Is a local variable , without local The representation is a global variable .
print Function to print out the value of a variable , For example, the following code will print world, among "--" yes Lua
Language notes .
-- The result is "world"
print(hello)
(2) Array
stay Lua in , If you want to use functions like arrays , It can be used tables type , The following code makes
It defines a tables Variable of type myArray, But unlike most programming languages ,
Lua The array subscript of is from 1 Start calculating :
local tables myArray = {"redis", "jedis", true, 88.0}
--true
print(myArray[3])
If you want to traverse this array , have access to for and while, These keywords and many programming languages
Words are consistent .
(a)for
The following code will calculate 1 To 100 And , keyword for With end As an end sign :
local int sum = 0
for i = 1, 100
do
sum = sum + i
end
-- The output is 5050
print(sum)
To traverse the myArray, The first thing you need to know is tables The length of , Just add one... Before the variable #
No :
for i = 1, #myArray
do
print(myArray[i])
end
besides ,Lua There are also built-in functions ipairs, Use for index,value
ipairs(tables) Can traverse all index subscripts and values :
for index,value in ipairs(myArray)
do
print(index)
print(value)
end
(b)while
The following code will also calculate 1 To 100 And , It just USES while loop ,while Follow
The ring is also end As an end sign .
local int sum = 0
local int i = 0
while i <= 100
do
sum = sum +i
i = i + 1
end
-- The output is 5050
print(sum)
(c)if else
To determine if the array contains jedis, Print if you have true, Be careful if With end ending ,if after
Following the then:
local tables myArray = {"redis", "jedis", true, 88.0}
for i = 1, #myArray
do
if myArray[i] == "jedis"
then
print("true")
break
else
--do nothing
end
end
(3) Hash
If you want to use a hash like function , It can also be used tables type , For example, the following code
Defined a tables, Each element contains key and value, among strings1..string2 Yes, two
String to connect :
local tables user_1 = {age = 28, name = "tome"}
--user_1 age is 28
print("user_1 age is " .. user_1["age"])
If you want to traverse user_1, have access to Lua Built in functions for pairs:
for key,value in pairs(user_1)
do print(key .. value)
end
2. Function definition
stay Lua in , Function to function start , With end ending ,funcName Is the function name , The middle
Cent is a function body :
function funcName()
...
end
contact Function to splice two strings :
function contact(str1, str2)
return str1 .. str2
end
--"hello world"
print(contact("hello ", "world"))
Be careful
This book only introduces Lua Some functions , because Lua The full function of has gone beyond the scope of this book
around , Readers can buy corresponding books or go to Lua Official website (http://www.lua.org/)
To study .
3.4.3 Redis And Lua
1. stay Redis Use in Lua
stay Redis In the implementation of Lua There are two ways to script :eval and evalsha.
(1)eval
eval The script content key Number key list parameter list
The following example uses key List and parameter list for Lua Scripts provide more flexibility :
127.0.0.1:6379> eval 'return "hello " .. KEYS[1] .. ARGV[1]' 1 redis world
"hello redisworld"
here KEYS[1]="redis",ARGV[1]="world", So the final return result
yes "hello redisworld".
If Lua The script is longer , You can also use redis-cli--eval Direct execution of documents .
eval Command and --eval The parameters are essentially the same , If the client wants to execute Lua Script , First
Write it on the client Lua Script code , Then send the script as a string to the server , service
The client will return the execution result to the client , The whole process is as shown in the figure 3-7 Shown .
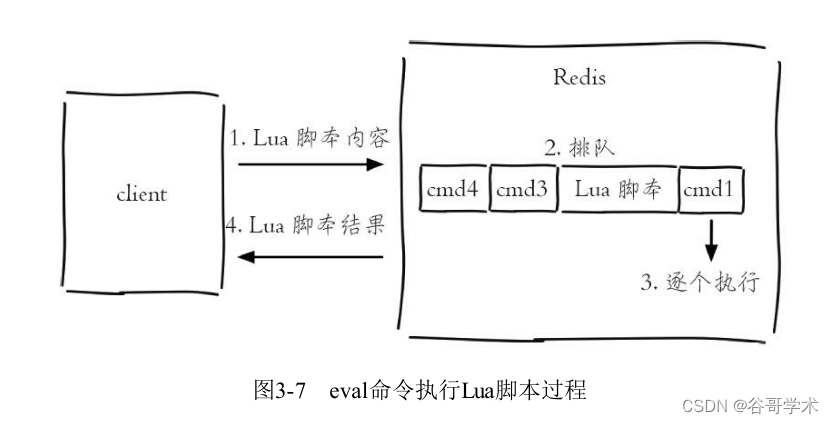
(2)evalsha
Besides using eval,Redis It also provides evalsha Command to execute Lua Script . Pictured 3-8 the
in , First of all to Lua The script is loaded into Redis Server side , Get the SHA1 The checksum ,
evalsha Command to use SHA1 As a parameter, you can directly execute the corresponding Lua Script , Avoid sending... Every time
Lua The cost of the script . So the client doesn't need to execute the script content every time , And the script will be resident
On the server , Script functions are reused .
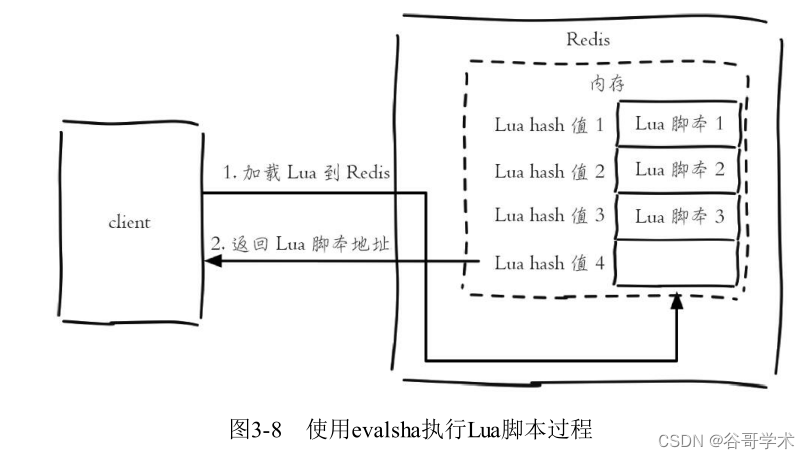
Load script :script load Command to load the script content into Redis In the memory , For example, next
Face will lua_get.lua Load into Redis in , obtain SHA1
by :"7413dc2440db1fea7c0a0bde841fa68eefaf149c"
# redis-cli script load "$(cat lua_get.lua)"
"7413dc2440db1fea7c0a0bde841fa68eefaf149c"
Execute the script :evalsha Is used as follows , Parameters use SHA1 value , Executive logic and
eval Agreement .
evalsha Script SHA1 value key Number key list parameter list
So just do the following , You can call lua_get.lua Script :
127.0.0.1:6379> evalsha 7413dc2440db1fea7c0a0bde841fa68eefaf149c 1 redis world
"hello redisworld"
2.Lua Of Redis API
Lua have access to redis.call Function implementation to Redis The interview of , For example, the following code is Lua Use
redis.call Called Redis Of set and get operation :
redis.call("set", "hello", "world")
redis.call("get", "hello")
Put it in Redis The implementation effect is as follows :
127.0.0.1:6379> eval 'return redis.call("get", KEYS[1])' 1 hello
"world"
besides Lua You can also use redis.pcall Function implementation to Redis Call to ,redis.call and
redis.pcall The difference is , If redis.call Execution failure , Then the end of script execution will return to
Back to the wrong , and redis.pcall Will ignore the error and continue to execute the script , So in the actual development, we should base on
Specific application scenarios for function selection .
Development tips
Lua have access to redis.log Function will Lua The log of the script is output to Redis In the log file of ,
But be sure to control the log level .
Redis3.2 Provides Lua Script Debugger Functions are used to debug complex Lua Script , Specifically
You can refer to :http://redis.io/topics/ldb.
3.4.4 Case study
Lua The script function is Redis There are three benefits for developers and operators :
·Lua Script in Redis It's atomic execution , No other commands are inserted during execution .
·Lua Scripts can help developers and operators create their own customized commands , And you can put this
Some orders reside in Redis In the memory , Realize the effect of reuse .
·Lua Scripts can package multiple commands at one time , Effectively reduce network overhead .
Here is an example of Lua Use of scripts , The current list records popular users id,
Suppose this list has 5 Elements , As shown below :
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hot:user:list 0 -1
1) "user:1:ratio"
2) "user:8:ratio"
3) "user:3:ratio"
4) "user:99:ratio"
5) "user:72:ratio"
user:{id}:ratio Represents the popularity of users , It itself is a string type key :
127.0.0.1:6379> mget user:1:ratio user:8:ratio user:3:ratio user:99:ratio
user:72:ratio
1) "986"
2) "762"
3) "556"
4) "400"
5) "101"
Now all the keys in the list should be added to the corresponding heat 1 operation , And it's guaranteed to be atomic execution ,
This function can take advantage of Lua Script to achieve .
1) Remove all elements from the list , Assign a value to mylist:
local mylist = redis.call("lrange", KEYS[1], 0, -1)
2) Defining local variables count=0, This count It's the end incr The total number of times :
local count = 0
3) Traverse mylist All elements in , Every time I finish count Self increasing , Finally back to count:
for index,key in ipairs(mylist)
do
redis.call("incr",key)
count = count + 1
end
return count
Write the above script lrange_and_mincr.lua In file , And do the following , Return knot
Fruit 5.
redis-cli --eval lrange_and_mincr.lua hot:user:list
(integer) 5
After execution, the popularity of all users increases 1:
127.0.0.1:6379> mget user:1:ratio user:8:ratio user:3:ratio user:99:ratio
user:72:ratio
1) "987"
2) "763"
3) "557"
4) "401"
5) "102"
This section is just a simple example , In actual development , Developers can play self
Your imagination creates more new commands .
3.4.5 Redis How to manage Lua Script
Redis Provides 4 A command is implemented to Lua Script management , Here are the introduction .
(1)script load
script load script
This command is used to Lua The script is loaded into Redis In the memory , I have already introduced and used ,
No more details here .
(2)script exists
scripts exists sha1 [sha1 … ]
This command is used to determine sha1 Whether it has been loaded into Redis In the memory :
127.0.0.1:6379> script exists a5260dd66ce02462c5b5231c727b3f7772c0bcc5
1) (integer) 1
The returned result represents sha1[sha1…] Be loaded to Redis Number of memory .
(3)script flush
script flush
This command is used to clear Redis All the memory that has been loaded Lua Script , In execution script flush
after ,a5260dd66ce02462c5b5231c727b3f7772c0bcc5 No longer exist :
127.0.0.1:6379> script exists a5260dd66ce02462c5b5231c727b3f7772c0bcc5
1) (integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> script flush
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> script exists a5260dd66ce02462c5b5231c727b3f7772c0bcc5
1) (integer) 0
(4)script kill
script kill
This command is used to kill the executing Lua Script . If Lua The script is time consuming , even to the extent that Lua
There is a problem with the script , So at this time Lua The execution of the script will block Redis, Until the script is executed or
External intervention to end it . Now let's simulate a Lua Script blocking
bright .
The following code will make Lua Into the dead cycle :
while 1 == 1
do
end
perform Lua Script , The current client will block :
127.0.0.1:6379> eval 'while 1==1 do end' 0
Redis Provides a lua-time-limit Parameters , The default is 5 second , It is Lua The script “ Overtime
Time ”, But this timeout is only when Lua Script time exceeds lua-time-limit after , To the other
Command call send BUSY The signal of , But it will not stop the script execution of the server and client
That's ok , So when it comes to lua-time-limit The value of , When other clients execute normal commands , take
Will receive “Busy Redis is busy running a script” error , And prompt to use script kill perhaps
shutdown nosave Order to kill this busy Script for :
127.0.0.1:6379> get hello
(error) BUSY Redis is busy running a script. You can only call SCRIPT KILL or
SHUTDOWN NOSAVE.
here Redis It's blocked , Unable to process normal call , You can choose to wait ,
But more often, you need to kill the script quickly . Use shutdown save Obviously not , So choose
Choose script kill, When script kill After performing , The client call will resume :
127.0.0.1:6379> script kill
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get hello
"world"
But there is one caveat , If at present Lua The script is performing a write operation , that script
kill It won't work . for example , We simulate a continuous write operation :
while 1==1
do
redis.call("set","k","v")
end
At this point, if you execute script kill, You will receive the following exception message :
(error) UNKILLABLE Sorry the script already executed write commands against the
dataset. You can either wait the script termination or kill the server in a
hard way using the SHUTDOWN NOSAVE command.
The above tips Lua The script is sending Redis Execute write order , Either wait for the script execution to end or
Use shutdown save Stop Redis service . so Lua Although the script is easy to use , But if you don't use it properly
Bad sex is also unimaginable .
边栏推荐
- 剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- Attack and defense world misc advanced grace-50
- 繁华落尽、物是人非:个人站长该何去何从
- 攻防世界 MISC 进阶区 3-11
- Redis démarrer le tutoriel complet: Pipeline
- [OpenGL] note 29 anti aliasing (MSAA)
- 醒悟的日子,我是怎么一步一步走向软件测试的道路
- 企业如何跨越数字化鸿沟?尽在云原生2.0
- [machine learning] handwritten digit recognition
- Detailed explanation of flask context
猜你喜欢
串口数据帧

Wake up day, how do I step by step towards the road of software testing
PMO: compare the sample efficiency of 25 molecular optimization methods
Attack and defense world misc advanced zone 2017_ Dating_ in_ Singapore
攻防世界 MISC 高手进阶区 001 normal_png
On-off and on-off of quality system construction
MYSQL架构——用户权限与管理

都说软件测试很简单有手就行,但为何仍有这么多劝退的?
The new version judges the code of PC and mobile terminal, the mobile terminal jumps to the mobile terminal, and the PC jumps to the latest valid code of PC terminal
Business is too busy. Is there really no reason to have time for automation?
随机推荐
Redis入门完整教程:键管理
攻防世界 MISC 进阶区 Ditf
Deployment of JVM sandbox repeater
Sword finger offer 68 - ii The nearest common ancestor of binary tree
【烹饪记录】--- 青椒炒千张
The table is backed up in ODPs. Why check m in the metabase_ Table, the logical sizes of the two tables are inconsistent, but the number of
[machine learning] handwritten digit recognition
安装人大金仓数据库
On-off and on-off of quality system construction
The new version judges the code of PC and mobile terminal, the mobile terminal jumps to the mobile terminal, and the PC jumps to the latest valid code of PC terminal
The overview and definition of clusters can be seen at a glance
POM in idea XML dependency cannot be imported
企业如何跨越数字化鸿沟?尽在云原生2.0
Redis入门完整教程:有序集合详解
How to reset the password of MySQL root account
NFT Insider #64:电商巨头eBay提交NFT相关商标申请,毕马威将在Web3和元宇宙中投入3000万美元
常用技术指标之一文读懂BOLL布林线指标
LOGO特訓營 第三節 首字母創意手法
How to manage 15million employees easily?
Redis入门完整教程:Bitmaps