当前位置:网站首页>RAID disk redundancy queue
RAID disk redundancy queue
2022-07-06 00:42:00 【Riding the waves】
RAID brief introduction
As servers are more and more widely used in enterprises , Data security , data storage , Data recovery , Storage speed and other aspects are becoming more and more important for enterprise users , and RAID Cards play a vital role in this process ,RAID The performance and characteristics of the card itself are often ignored by some users , In order to save costs, server manufacturers will also match some relatively elementary or even small brands RAID Card products , When there are problems in the use process, users just focus on the hard disk
RAID( Independent redundant disk array ) It's a kind of multi independent hard disk ( Physical hard disk ) Combine them in different ways to form a hard disk group ( Logical hard disk ), So as to provide higher storage performance and data backup capability than a single hard disk .
soft RAID And hard RAID
We want to implement on the server RAID, You can use disk array cards (RAID card ) To form a RAID, That is, hard RAID.RAID There is a special chip on the card for RAID Mission , So the performance is much better , And does not occupy the system performance , The disadvantage is that RAID Cards are expensive
If we don't want to spend money and want to use RAID, Then only use soft RAID 了 . soft RAID It refers to the realization through software RAID function , There is no extra cost , But it costs more server system performance , And the writing speed of data is faster than that of hard RAID slow
RAID It features N Block hard disk simultaneously accelerates reading speed and provides fault tolerance . Redundant disk array technology was born in 1987 year , Proposed by the University of California, Berkeley . According to different combinations of disk display , Can be RAID Divided into different levels . The level does not represent the level of Technology , Choose which one RAIDlevel Our products depend solely on the user's operating environment and Application , It has nothing to do with the level
RAID advantage :
1、 Improve I/O Ability , Disk parallel read and write
2、 Improve durability , Disk redundancy
3、 Level : Multiple disks work in different ways
4、raid How to achieve :
External disk array : Provide adaptability through expansion card
Built in raid: motherboard integrated raid controller , In the installation OS Before BIOS It's equipped with
Software raid: adopt OS To achieve , Hardware is used in production raid To achieve
raid The shortcomings of :
raid In the later stage of the array group, new members cannot be added to expand the overall capacity . for example : use 2 Block hard disk creation raid 0, Later cannot be in raid 0 Add a new hard disk . And that's where LVM Logical volume management function
RAID It can be divided into levels 0 To level 6, Often referred to as :RAID0、RAID1、RAID2、RAID3、RAID4、RAID5、RAID6
More classic RAID0、RAID1、RAID5、RAID6、RAID10 (RAID0+RAID1)
| Grade | name | Number of hard disks | Total capacity | The number of bad sets allowed ( Maximum ) | function |
| RAID0 | Banding | >=2 block | 2n+n | 0 block ( redundancy ) | High read-write performance , Capacity combination |
| RAID1 | Mirror image | =2 block | n | 1 block ( redundancy ) | Synchronous backup , Data security |
| RAID5 | Striping of distributed parity | >=3 block | 3n-n | 1 block ( redundancy ) | High read-write performance |
| RAID6 | Striping of two groups of distributed parity | >=4 block | 4n-2n | 2 block ( redundancy ) | High read-write performance , Data security |
| RAID10 | Mirror image + Banding | 4+2n block | Total capacity 50% | The bad half ( redundancy ) | Quantity combination + Synchronous backup |
mdadm command
linux Software in the system raid Management tool software :mdadm
| Parameters | explain |
| -D | Show RAID Device details |
| -A | Add a previously defined RAID |
| -B | Create one without super blocks RAID equipment |
| -F | Option monitoring mode |
| -G | change RAID Size or shape of equipment |
| -I | Add device to RAID in , Or from RAID Delete device from |
| -z | To form a RAID1、RAID4、RAID5、RAID6 After each RAID Space capacity acquired by members |
| -s | Scan configuration files or /proc/mdstat Search for lost information |
| -C | establish RAID equipment , hold RAID Information is written to each RAID Member super block |
| -v | Show RAID Details of the creation process |
| -B | establish RAID Another way , Not put RAID Information is written to each RAID In the super block of members |
| -l | Appoint RAID The level of |
| -n | Appoint RAID Number of active devices in |
| -f | hold RAID Members are listed as having problems , To remove the member |
| -r | hold RAID Members move out RAID equipment |
| -a | towards RAID Add a member to the device |
| --re-add | Put the recently removed RAID Members are added back to RAID In the device |
| -E | see RAID Member details |
| -c | Appoint chunk size , Create a RAID It defaults to 512kb |
| -R | Start partial assembly RAID |
| -S | Discontinue use RAID equipment , Release all resources |
| -x | Specify initial RAID Number of spare members of the device |
| --zero-superblock | If RAID The device contains a valid superblock , This block uses zero coverage |
Practice preparation
take linux Virtual machine shutdown , Add 5 block SCSI Interface 2GB The hard disk of , Create a snapshot “5 block 2G Hard disk ”, Then boot the virtual machine , perform lsblk The command displays a list of disk block devices
Raid practice : The request will linux Of system virtual machine 5 block 2G Hard disk for raid 5 Conduct management , Before the 4 The hard disk is organized into a file named md5 Of Raid5, among raid 5 The active disk of is the first 3 Block hard disk , The first 4 Hard disk as hot standby ( Spare tire 、 As a substitute ) disk .
lsblk # Display the list of disk devices
mdadm -Dsv # Show raid The equipment list
mdadm -C md5 -l 5 -n 3 -x 1 /dev/sd{b..e} # Create name as md5 Of raid 5 equipment
mdadm -D /dev/md/md5 # The display name is md5 Of raid 5 Device details
mdadm -Dsv # Show raid The equipment list
mdadm -Dsv > /etc/mdadm.conf # Generate raid The configuration file
——————————————————————————————————————
lsblk # Display the list of disk devices
mdadm -S /dev/md/md5 # Discontinue use md5 This raid equipment
mdadm -A /dev/md/md5 # Enable md5 This raid equipment
Be careful : To deactivate raid Enable the device later , Must ensure mdadm.conf The configuration file exists practice : simulation md5 This Raid5 In the equipment sdc The hard disk is damaged , And then from md5 Remove from the array sdc This member , However, check md5 Device details . take sdc Remove the hard disk from the server , Install a new hard disk to Sdc On the slot of the hard disk . then sdf Hard disk added to md5 This raid 5 In the device group
mdadm -D /dev/md/md5 # The display name is md5 Of raid 5 Device details
mdadm /dev/md/md5 -f /dev/sdc # Appoint sdc The hard disk is bad (fail)
mdadm -D /dev/md/md5 # The display name is md5 Of raid 5 Device details
mdadm /dev/md/md5 -r /dev/sdc # take sdc Hard disk from md5 This raid Remove from group (remove)
mdadm /dev/md/md5 -a /dev/sdf # take sdf Hard disk add (add) To md5 This raid In the group
mdadm -D /dev/md/md5 # The display name is md5 Of raid 5 Device details 边栏推荐
- Keepalive component cache does not take effect
- 小程序技术优势与产业互联网相结合的分析
- For a deadline, the IT fellow graduated from Tsinghua suddenly died on the toilet
- Basic introduction and source code analysis of webrtc threads
- Spark DF adds a column
- synchronized 和 ReentrantLock
- Notepad + + regular expression replace String
- Spark AQE
- Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)【比赛记录】
- Set data real-time update during MDK debug
猜你喜欢
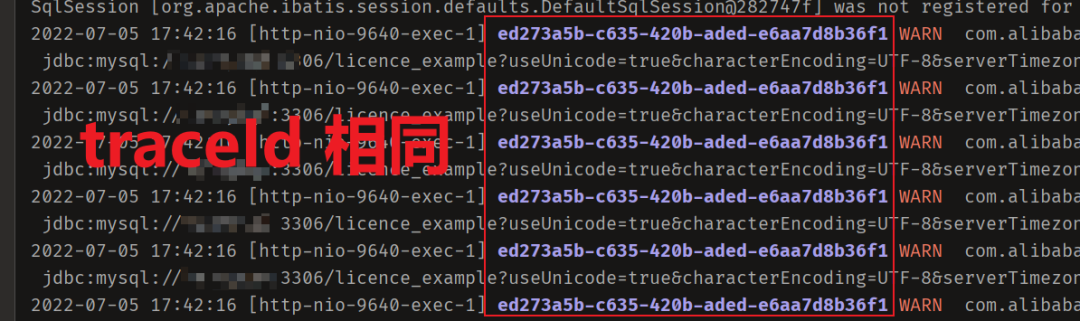
Starting from 1.5, build a micro Service Framework - call chain tracking traceid

KDD 2022 | 脑电AI助力癫痫疾病诊断
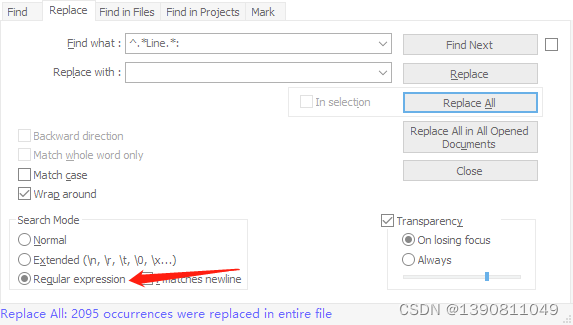
Notepad + + regular expression replace String
常用API类及异常体系

State mode design procedure: Heroes in the game can rest, defend, attack normally and attack skills according to different physical strength values.
Spark AQE
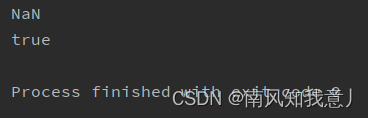
Spark SQL null value, Nan judgment and processing
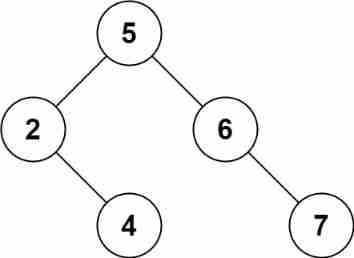
Leetcode 450 deleting nodes in a binary search tree
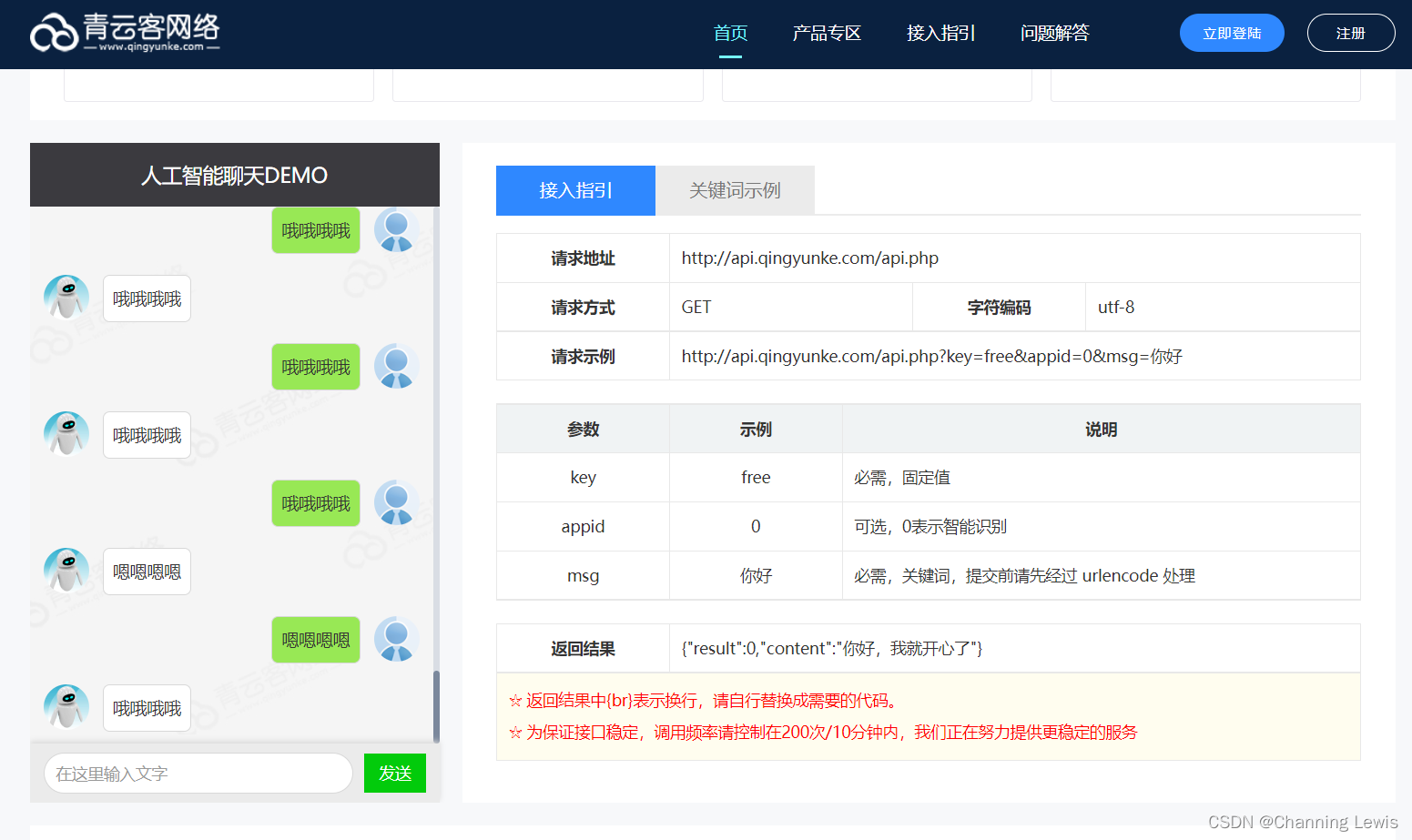
免费的聊天机器人API
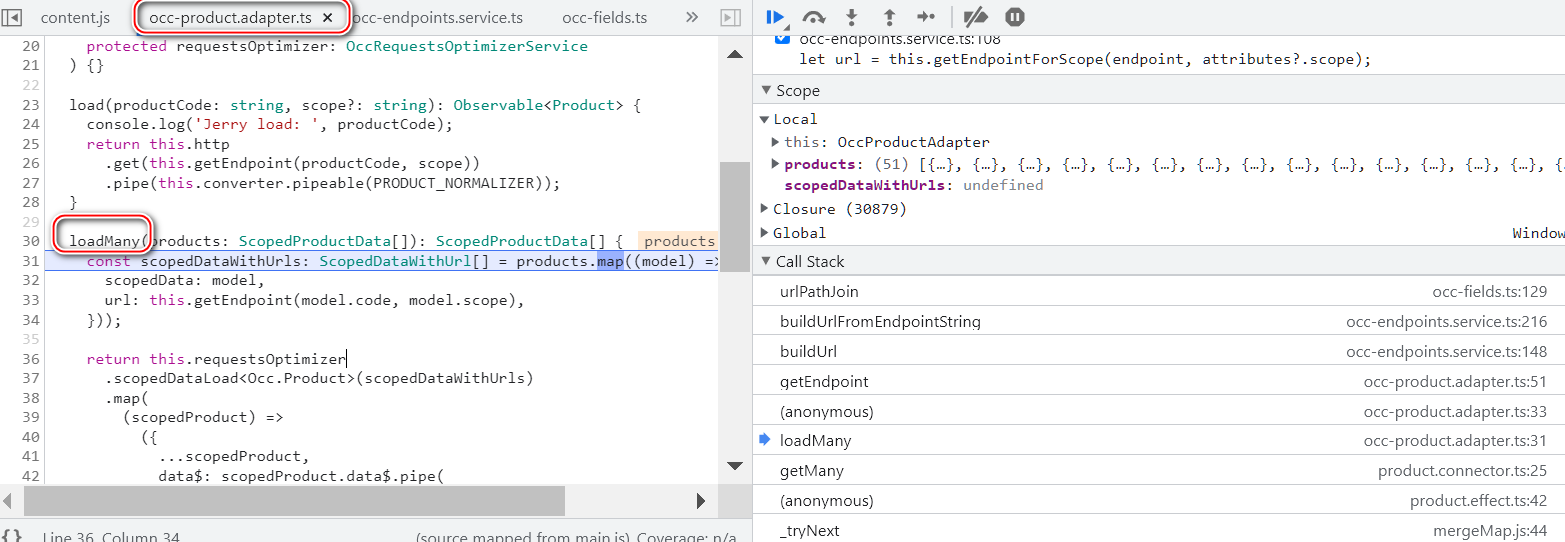
SAP Spartacus home 页面读取 product 数据的请求的 population 逻辑
随机推荐
Yolov5, pychar, Anaconda environment installation
LeetCode 6006. Take out the least number of magic beans
Free chat robot API
免费的聊天机器人API
新手入门深度学习 | 3-6:优化器optimizers
Spark DF增加一列
Model analysis of establishment time and holding time
[groovy] XML serialization (use markupbuilder to generate XML data | create sub tags under tag closures | use markupbuilderhelper to add XML comments)
STM32 key chattering elimination - entry state machine thinking
Promise
Classic CTF topic about FTP protocol
Leetcode:20220213 week race (less bugs, top 10% 555)
MYSQL GROUP_ The concat function realizes the content merging of the same ID
About the slmgr command
The value of applet containers
Keepalive component cache does not take effect
Room cannot create an SQLite connection to verify the queries
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)【比赛记录】
《编程之美》读书笔记
curlpost-php