当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode 450 deleting nodes in a binary search tree
Leetcode 450 deleting nodes in a binary search tree
2022-07-06 00:18:00 【Hello, I'm Boger】
source : Power button (LeetCode)
link :https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst
The question :
Given the root node of a binary search tree root And a value key, Delete the key Corresponding node , And keep the property of binary search tree unchanged . Back to binary search tree ( May be updated ) Reference to the root node of .
Generally speaking , Deleting a node can be divided into two steps :
First find the node to be deleted ;
If you find it , Delete it .
Example 1: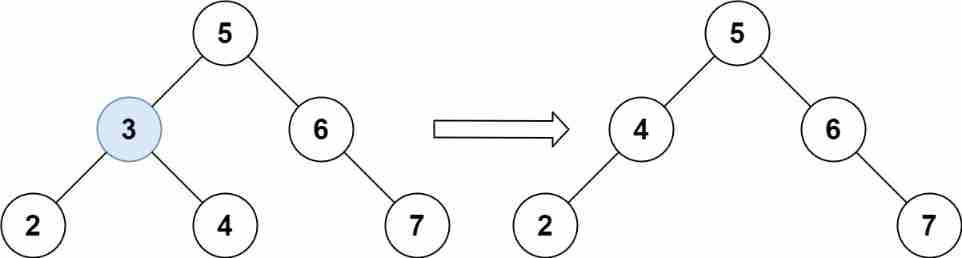
Input :root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3
Output :[5,4,6,2,null,null,7]
explain : Given the node value to be deleted is 3, So first we found 3 This node , Then delete it .
The right answer is [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], As shown in the figure below .
The other correct answer is [5,2,6,null,4,null,7].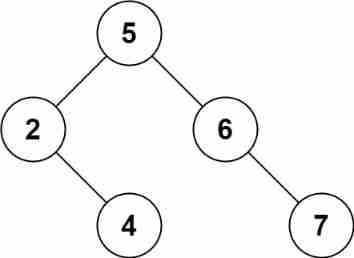
Example 2:
Input : root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0
Output : [5,3,6,2,4,null,7]
explain : Binary tree does not contain a value of 0 The node of
Example 3:
Input : root = [], key = 0
Output : []
Tips :
Range of nodes [0, 104].
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
Unique node value
root Is a legitimate binary search tree
-105 <= key <= 105
Advanced : The time complexity of the algorithm is required to be O(h),h Is the height of the tree .
Ideas :
In fact, the operation of deleting binary search tree nodes was written in the data structure experiment class before , What I did at that time was , First find the deleted node in the tree , Then, the leftmost node in the right subtree of the deleted node will replace the position of the deleted node . Based on this idea, I wrote the following code :
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
TreeNode parent = null, parent1 = null, deleteNode = null, cur = root;
int leftOrRight = 0;// This variable is used to record whether the deleted node is the left node or the right node of the parent node ,0 Is the root node ,1 Represents the left node ,2 Represents the right node
// First find the node to delete
while (cur != null && cur.val != key) {
parent = cur;
if (cur.val > key) {
cur = cur.left;
leftOrRight = 1;
} else if (cur.val < key) {
cur = cur.right;
leftOrRight = 2;
}
}
if (cur == null) return root;// There are no nodes to delete
deleteNode = cur;
if (deleteNode.right == null) {
// The deleted node has no right subtree
if (leftOrRight == 0) return deleteNode.left;
else if (leftOrRight == 1) parent.left = deleteNode.left;
else parent.right = deleteNode.left;
return root;
}
// Find the leftmost node in the right subtree of the node to be deleted
cur = deleteNode.right;
if (cur.left == null) {
// The right subtree of the node to be deleted has no left son
cur.left = deleteNode.left;
if (leftOrRight == 0) return cur;
else if (leftOrRight == 1) parent.left = cur;
else parent.right = cur;
return root;
}
while (cur.left != null) {
parent1 = cur;
cur = cur.left;
}
parent1.left = cur.right;
cur.left = deleteNode.left;
cur.right = deleteNode.right;
if (leftOrRight == 0) return cur;
else if (leftOrRight == 1) parent.left = cur;
else parent.right = cur;
return root;
}
}
The above code can really meet the requirements of the problem , But it's too tedious , Because you need to consider all kinds of situations .
After I read the reference article , The idea is to delete the head node of the left subtree of the node ( Left the child ) Put it on the left child of the leftmost node of the right subtree of the deleted node , The process can be seen in the figure below ( Picture transferred from code Capriccio ), Then modify the above code , The code is under the picture :
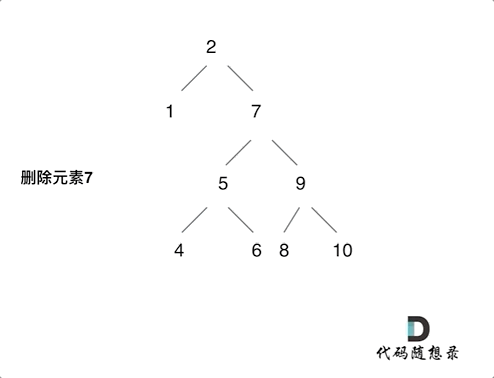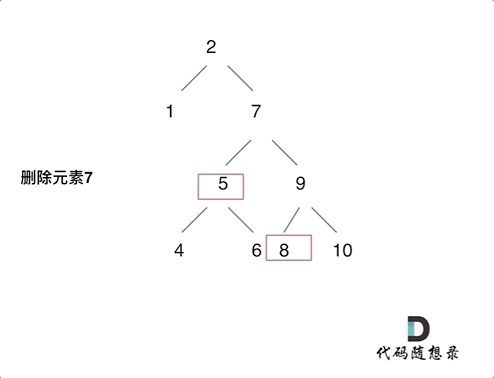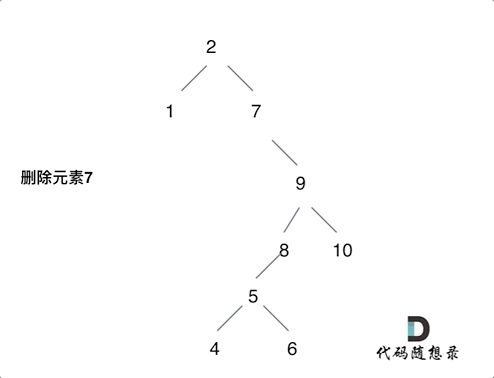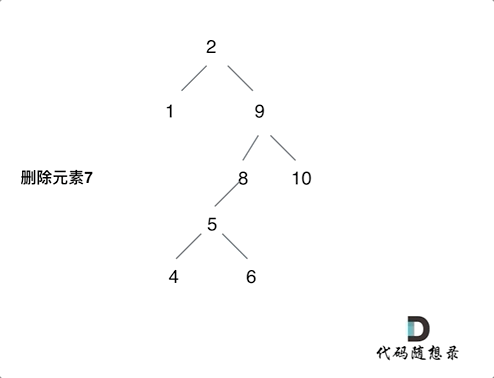
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
TreeNode parent = null, deleteNode = null, cur = root;
int leftOrRight = 0;// This variable is used to record whether the deleted node is the left node or the right node of the parent node ,0 Is the root node ,1 Represents the left node ,2 Represents the right node
// First find the node to delete
while (cur != null && cur.val != key) {
parent = cur;
if (cur.val > key) {
cur = cur.left;
leftOrRight = 1;
} else if (cur.val < key) {
cur = cur.right;
leftOrRight = 2;
}
}
if (cur == null) return root;// There are no nodes to delete
deleteNode = cur;
if (deleteNode.right == null) {
// The deleted node has no right subtree
if (leftOrRight == 0) return deleteNode.left;
else if (leftOrRight == 1) parent.left = deleteNode.left;
else parent.right = deleteNode.left;
return root;
}
// Find the leftmost node in the right subtree of the node to be deleted
cur = deleteNode.right;
while (cur.left != null) cur = cur.left;
cur.left = deleteNode.left;
if (leftOrRight == 0) return deleteNode.right;
else if (leftOrRight == 1) parent.left = deleteNode.right;
else parent.right = deleteNode.right;
return root;
}
}
It can be seen that the code is concise , Some variables are also reduced .
Then I saw another wonderful approach in the reference article ( Refer to the deletion method of ordinary binary tree in the article ).
The idea of this approach is , Constantly exchange the value of the deleted node with the value of the leftmost node in the right subtree of the deleted node , Until the leftmost node in the exchanged right subtree does not have a right subtree , In this case, the left subtree of the node will be replaced directly .
Look at the code in detail , Note that this process may exchange values more than once , And the recursive method is used , It's also very concise .
If you don't understand the process , You can draw a picture on paper , You can understand the subtlety of this idea .
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root.val == key) {
if (root.right == null) return root.left;
TreeNode cur = root.right;
while (cur.left != null) cur = cur.left;
root.val = cur.val;
cur.val = key;
}
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
return root;
}
}
边栏推荐
- FPGA内部硬件结构与代码的关系
- [Luogu p3295] mengmengda (parallel search) (double)
- Configuring OSPF load sharing for Huawei devices
- Key structure of ffmpeg -- AVCodecContext
- 【DesignMode】适配器模式(adapter pattern)
- FFT learning notes (I think it is detailed)
- [binary search tree] add, delete, modify and query function code implementation
- Problems encountered in the database
- QT QPushButton details
- Notepad + + regular expression replace String
猜你喜欢
Problems encountered in the database
Key structure of ffmpeg - avframe
Configuring OSPF GR features for Huawei devices

数据库遇到的问题
提升工作效率工具:SQL批量生成工具思想

China Jinmao online electronic signature, accelerating the digitization of real estate business
教你在HbuilderX上使用模拟器运行uni-app,良心教学!!!
Multithreading and high concurrency (8) -- summarize AQS shared lock from countdownlatch (punch in for the third anniversary)
How to solve the problems caused by the import process of ecology9.0
![Atcoder beginer contest 254 [VP record]](/img/13/656468eb76bb8b6ea3b6465a56031d.png)
Atcoder beginer contest 254 [VP record]
随机推荐
LeetCode 1189. Maximum number of "balloons"
Hudi of data Lake (2): Hudi compilation
7.5模拟赛总结
Effet Doppler (déplacement de fréquence Doppler)
Extracting profile data from profile measurement
MySql——CRUD
Global and Chinese markets of universal milling machines 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Key structure of ffmpeg -- AVCodecContext
MySQL存储引擎
2022.7.5-----leetcode.729
Learn PWN from CTF wiki - ret2libc1
mysql-全局锁和表锁
Room cannot create an SQLite connection to verify the queries
Atcoder beginer contest 258 [competition record]
Hudi of data Lake (1): introduction to Hudi
China Jinmao online electronic signature, accelerating the digitization of real estate business
Global and Chinese markets for hinged watertight doors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
JS 这次真的可以禁止常量修改了!
MySql——CRUD
电机的简介