当前位置:网站首页>Masterless replication system (1) - write DB when node fails
Masterless replication system (1) - write DB when node fails
2022-07-31 16:39:00 【Huawei cloud】
The idea of single-master and multi-master replication is that the client sends a write request to a master node, and the DB system is responsible for copying the write request to other replicas.The master node decides the write order, and the slave nodes apply the write logs sent by the master node in the same order.
Some data storage systems use a different design: abandoning the primary node, allowing any replica to accept writes directly from clients.The earliest replicated data systems were masterless (or called decentralized replication, centerless replication), but later in the era of relational database dominance, this idea was almost forgotten.After Amazon used it for its in-house Dynamo system[^vi], it was once again a popular DB architecture.Riak, Cassandra, and Voldemort are all open source data stores with a masterless replication model inspired by Dynamo, so such databases are also known as Dynamo style.
[^vi]: Dynamo is not available for users outside of Amazon.Confusingly, AWS offers a managed database product called DynamoDB that uses a completely different architecture: it's based on single-leader replication.
In some unowned implementations, the client sends write requests directly to multiple replicas, while in other implementations, there is a coordinator node that writes on behalf of the client, but unlike the master node's database,The coordinator is not responsible for maintaining write order.This design difference has profound implications for how DBs are used.
4.1 Write DB when node fails
Assuming a three-replica DB, one of which is currently unavailable, perhaps rebooting to install system updates.Under the primary node replication model, to continue processing writes, a failover needs to be performed.
Without a master model, there is no such switch.
Figure-10: Client (user 1234) sends write requests to three replicas in parallel, two available replicas accept writes, and the unavailable replica cannot handle it.Assuming two successful confirmations of the three copies, the user 1234 can consider the writing to be successful after receiving the two confirmation responses.The case where one of the replicas cannot be written can be completely ignored.
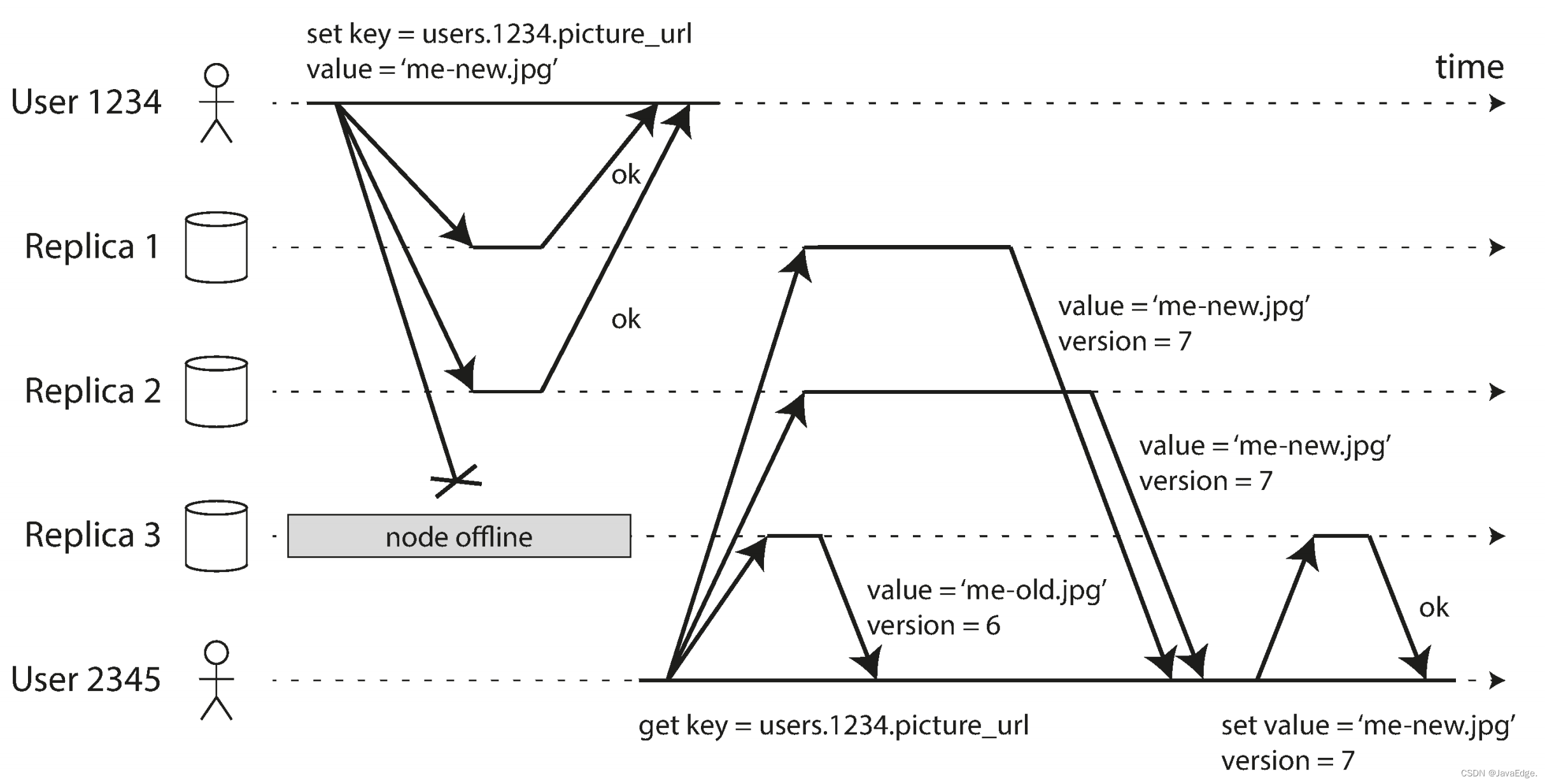
The failed node comes back online and clients start reading it.Any writes that occur during a node failure are not yet synchronized at that node, so reads may get stale data.
To solve this problem, when a client reads data from the DB, it does not send a request to 1 replica, but to multiple replicas in parallel.Clients may get different responses from different nodes, i.e. the latest value from one node and the old value from another node.The version number can be used to determine which value is updated.
4.1.1 Read Repair and Anti-Entropy
The replication model should ensure that all data is eventually replicated to all replicas.After a failed node comes back online, how does it catch up with missed writes?
Dynamo-style data storage system mechanism:
Read repair
When a client reads multiple copies in parallel, an expired return value can be detected.As shown in Figure-10, user 2345 gets version 6 from R3 and version 7 from replicas 1 and 2.The client can determine that replica 3 is the expired value, and then write the new value to that replica.Suitable for read-intensive scenarios
Anti-entropy process
Some data stores have background processes that constantly look for data differences between replicas, copying any missing data from one replica to another.Unlike replicated logs based on primary replication, this anti-entropy process does not guarantee any particular order of replicated writes and introduces significant synchronization lag
Not all systems implement either scheme.For example, Voldemort currently has no anti-entropy process.If there is no anti-entropy process, because [read repair] is only possible to perform repair when a read occurs, those rarely accessed data may be lost in some replicas and can no longer be detected, thus reducing the durability of writes.
边栏推荐
- Huawei's top engineers lasted nine years "anecdotal stories network protocol" PDF document summary, is too strong
- 深度学习机器学习理论及应用实战-必备知识点整理分享
- Qt实战案例(54)——利用QPixmap设计图片透明度
- SHELL内外置命令
- 百度网盘网页版加速播放(有可用的网站吗)
- 动态规划(一)
- Dialogue with Zhuang Biaowei: The first lesson of open source
- 动态规划之线性dp(上)
- 动态规划之线性dp(下)
- 第二届中国PWA开发者日
猜你喜欢
阿里三面:MQ 消息丢失、重复、积压问题,如何解决?
Graham‘s Scan法求解凸包问题

【网络通信三】研华网关Modbus服务设置
Design and Implementation of Compiler Based on C Language
使用 Postman 工具高效管理和测试 SAP ABAP OData 服务的试读版

联邦学习:联邦场景下的多源知识图谱嵌入

Implementing DDD based on ABP

EF Core 2.2中将ORM框架生成的SQL语句输出到控制台

华为顶级工程师历时9年总结的“趣谈网络协议”PDF文档,太强了
组合学笔记(六)局部有限偏序集的关联代数,Möbius反演公式
随机推荐
网站漏洞修复服务商关于越权漏洞分析
How C programs run 01 - the composition of ordinary executable files
C language - function
Mariabackup实现Mariadb 10.3的增量数据备份
关于柱状图的经典画法总结
最后写入胜利(丢弃并发写入)
The arm button controls the flashing of the led light (embedded button experiment report)
复杂高维医学数据挖掘与疾病风险分类研究
使用 Postman 工具高效管理和测试 SAP ABAP OData 服务的试读版
[pytorch] pytorch automatic derivation, Tensor and Autograd
牛客 HJ17 坐标移动
动态规划之线性dp(上)
【pytorch】1.7 pytorch与numpy,tensor与array的转换
Foreign media right, apple on May be true in inventory
Design and Implementation of Compiler Based on C Language
【7.29】代码源 - 【排列】【石子游戏 II】【Cow and Snacks】【最小生成数】【数列】
无主复制系统(1)-节点故障时写DB
What is the difference between BI software in the domestic market?
Three aspects of Ali: How to solve the problem of MQ message loss, duplication and backlog?
【C语言】LeetCode27.移除元素