当前位置:网站首页>[Verilog tutorial]
[Verilog tutorial]
2022-07-02 23:29:00 【Wenhua Wuying】
Verilog course
1.Verilog brief introduction
Verilog Language is a hardware description language for modeling electronic systems , This hardware description language is mostly used for register transfer level modeling and verification of digital circuit systems , At the same time, some modeling and verification circuits of digital analog hybrid circuits such as biological circuits .Verilog The grammatical rules of language and C There are many similarities in language .Verilog The standardized content of language is IEEE 1364 Specified in the standard .
2. Verilog Grammar explanation
Verilog Hardware description language has variables and constants , Next, we will introduce variables and constants respectively .
2.1 Verilog Variable data type
2.1.1 Wire network data (Nets)
Wire network data represents the direct physical connection between different circuit structures . This type of variable does not store data , The value of the variable changes instantaneously with the change of the driving signal . This data type uses keywords wire To define .
The following table is wire The value of the type variable , The next section will introduce reg Type values are similar .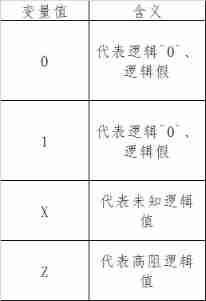
2.1.2 Register data (Reg)
Register type variables are often used in sequential circuits . This type of variable can store the value of data . When the trigger signal arrives , The value of the variable changes with the drive signal . When the trigger signal does not arrive , The value of the variable does not change . Register type data uses keywords reg To define .
2.1.3 Other data types :(integer、real、time)
integer、real、time These three variables are actually register type variables .integer The variable is usually a 32bit Shaping data .real The variable is a IEEE The standard 64bit Floating point data .time It's a 64 Unsigned integer variable of bit . Represents the simulation run time . You can use system functions $time see time Variable of type .
2.1.4 Vector data structure
2.1.1 and 2.1.2 Mentioned in the two sections wire The type and reg Types are 1 bit data .Verilog There is a vector type in (Vector), The vector variable type represents a variable that contains multiple bit A data type of data .
The following code defines a network type wire Vector of type data signal,signal The variable contains 32bit data .[31:0] On behalf of 32bit The highest angular position of the data 31, The lowest angle is 0.
wire [31:0] signal
The following code defines a network type reg Vector of type data signal,signal The variable contains 32bit data .[31:0] On behalf of 32bit The highest angular position of the data 31, The lowest angle is 0.
reg [31:0] signal
2.1.5 Memory type data
The array composed of register variables is memory type data . The definition statement is as follows :
reg [15:0] memo [7:0];
The above statement defines a storage class memo, Yes 8 Storage unit , Each storage unit has 16 position .
2.1.6 Verilog A constant represents
Verilog Constants in mainly include integer constants and parameter constants
The most complete description of integer constants is < A wide >< Number system >< The number >. The bit width and number system can be specified or omitted as needed . The number system types of integer data mainly include binary (b or B Express )、 octal (o or O Express )、 Hexadecimal (h or H Express ). It can be expressed in the following form :
// Indicates the data bit width , binary data
4‘b1011
// Indicates the data bit width 、 Hexadecimal representation
4’hFF
// Negative said , The symbol is marked in the front
-4'b1001
Parametric constants use keywords parameter To claim , It is called parametric variable .parameter The right side of a type constant assignment statement must be a constant expression . Example of parameter type definition :
parameter msb =7;
2.2 Verilog The operator
Verilog Operators can be divided into 10 Two categories: .
2.2.1 Arithmetic operator
+ // Add
- // Subtraction
* // Multiplication
/ // to be divisible by
% // Remainder
** // Power operation
Hint:
When performing arithmetic operations , As long as one of the operands is x and z, Then the result is x.
2.2.2 Assignment operator
Detailed see 2.4 section
2.2.3 Relational operator
Relational operators are used to determine the size of two operands . When the relationship between operands is true, it returns 1, When false, the return value is 0.
> // Greater than
>= // Greater than or equal to
< // Less than
<= // Less than or equal to
Hint:
Relational operators take precedence over arithmetic operators . When performing relational operation , As long as one of the operands is x and z, Then the result is x.
2.2.4 Equality operators
The equality operator is used to determine whether two operands x. When the relationship between operands is true, it returns 1, When false, the return value is 0.
== // equal
!= // It's not equal
=== // Congruence
!== // Incongruence
Operator ==,!= When comparing , value x and ’z’ It has physical significance , The operand contains x and z, Then the comparison result of logical equality is x.
Operator ===,!==, It can be compared with x and z The number of operations , When comparing , Don't consider x and z The physical meaning of , Compare strictly according to the character value , If the result is non-zero, it is one .
The following example can be used to illustrate the problem .
a=4'b10x0
b=4'b10x0
(a==b) The result is x
(a===b) The return is 1
2.2.5 Logical operators
&& Logic and
|| Logic or
! Logic is not
2.2.6 Conditional operator
The conditional operator selects one of the two expressions according to the value of the conditional expression , The grammar format is :( Conditional expression )? expression 1: expression 2
Indicates if the conditional expression is true , Then return the expression 1 Value , If the conditional expression is false , Then return the expression 2 Value .
wire y;
assign y=(sel==1)?a:b;
2.2.7 An operator
Bitwise operators share 7 Kind of :
& // And
| // or
~ // Not
^ // Exclusive or
^~ // Same as or
~& // And non
~| // Or not
Bit operation is to operate on each bit of the variable . If the length of two operands is not equal , The higher order of the shorter number will be filled with zero , Then perform the corresponding bit operation , The length of the output result is consistent with the length of the operand with a longer bit width .
2.2.8 Shift Operators
The shift operator is used to shift the operand to the left of the operator to the left or right , The number of shifts depends on the number of bits on the right side of the operator .
<< // Logic shift left
>> // Logical shift right
<<< // Move arithmetic left
>>> // Count right
The syntax is as follows :< Operands >< Shift Operators >< Shift digit >
data<<n
Hint:
The logical shift operator has no shift process and does not involve sign bits , The sign bit is not specially processed .
Arithmetic shift operators , Left shift process , The sign bits remain the same . Shift right , The sign bit is constantly copied on the left and shifted to the right .
2.2.9 Splicing operator
Splicing operator {} It is used for splicing two or more wire mesh variables or register type variables , To form a whole .
2.2.10 Reduction operators
The bitwise contraction operator operates on all bits of a single operand , The result returns a single digit .
reg [3:0] d;
reg y1,y2;
y1=&d;// Contraction and ,y1=d[3]&d[2]&d[1]&d[0]
y2=&d;// Contraction and ,y2=d[3]|d[2]|d[1]|d[0]
2.3 modular (module) Definition
2.3.1 Module definition
The module definition part includes the module name and IO Port definition part , With the key words module Start , With the key words endmodule end . The syntax is as follows :
module Module name ( port 1, port 2, port 3,…, port n);
// Between ports ,. The statement ends with ;
endmodule
In design , It is recommended that one file be used for each module , And the file name is the same as the module name .
2.3.2 Port definition
Verilog Support input,output,inout Three port types .input Represents the input port ;output Represents the output port ;inout Represents two-way port ;
2.4 Assignment statement
2.4.1 assign assignment
utilize assgin Statement is a continuous assignment , It is similar to connecting ports in a circuit , The excitation signal value changes , The structure will change . This statement is used in always Out of statement block . Only use assgin Sentence to wire Type variable assignment .
2.4.2 Block assignment
Blocking assignment uses = Assign a value .
2.4.3 Nonblocking assignment
Non blocking assignment uses <= Assign a value .Hint:
Both blocking assignment and non blocking assignment can be called process assignment . Can only be used with registers (reg) Variable assignment . The meaning of blocking assignment is before the end of the previous blocking assignment statement , The latter statement cannot be executed and is blocked . Non blocking assignment means that non blocking statements are executed at the same time , Mutual indifference .
2.5 initial/always sentence
initial Statements are not comprehensive statements , Related codes cannot be integrated into hardware circuits . It is generally used in simulation scenes , Start running once at zero time of the simulation time .always A statement block is a periodic statement block . The code will be executed in sequence .
The most general statement block structure is as follows :
always @( Sensitive signal list )
begin
......
end
@ The expression in the following brackets is the list of sensitive signals , Used to mark appropriate always When should the code in the statement block be executed . If there is no sensitive signal list, any of the input signals in the statement block changes , The statement in the statement block begins to execute .
When there is a list of sensitive signals , It can be further divided into level sensitive and clock edge sensitive . As shown in the following code :
always @(a or b)
begin
......
end
a、b Any signal change in , Will execute the statements in the statement block .
always @ (posdege clk)
begin
......
end
always @ (negedge clk)
begin
......
end
The above two pieces of code are clk When the rising or falling edge of comes , The statement block starts executing .
2.6 Conditional statements
2.6.1 if sentence
if-else The syntax of the statement is as follows :
if ( Conditional expression 1) Block statement 1;
else if ( Conditional expression 2) Block statement 2;
...
else if ( Conditional expression n) Block statement n;
else Block statement n+1;
2.6.2 case sentence
case The syntax of the statement is as follows :
case( expression )
List the values 1: Sentence block 1;
List the values 2: Sentence block 2;
......
List the values n: Sentence block n;
default: Sentence block n+1;
endcase
2.6.3 casez and casex sentence
except case-endcase Beyond the sentence , There's something similar casez-endcase and casex-endcase.casez List values and expressions in z Considered irrelevant , Judgment for "1".casex List values and expressions in x and z Are considered irrelevant , Judgment for "1".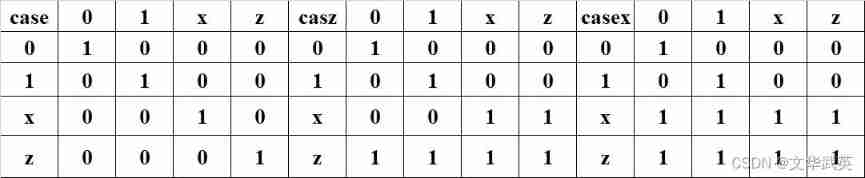
2.7 Loop statement
2.7.1 for sentence
Verilog in for Statement and C The same usage in language .
2.7.1 while sentence
Verilog in while Statements and C The same usage in language .
2.7.3 repeat sentence
repeat It is expected that the loop will be repeated as many times as specified in the loop control condition expression , The number of cycles is determined before executing the statement . If the cycle control condition is x or z, Execution times are 0 Time .
The grammatical structure is
repeat( Loop control condition expression ) Block statement ;
2.8 Hierarchical design
Verilog The designed logic module can refer to the previously designed logic module . Its grammatical structure is as follows :
bottom1 u1(.a(q), .b(p), .c(intsig));
bottom2 u2(.l(intsig), .m(r), .n(out));
边栏推荐
- Go project operation method
- 一文掌握基于深度学习的人脸表情识别开发(基于PaddlePaddle)
- Pandora IOT development board learning (HAL Library) - Experiment 4 serial port communication experiment (learning notes)
- Submit code process
- 富滇银行完成数字化升级|OceanBase数据库助力布局分布式架构中台
- All things work together, and I will review oceanbase's practice in government and enterprise industry
- @How to use bindsinstance in dagger2
- Integration of revolution and batch normalization
- Warning: implicitly declaring library function 'printf' with type 'int (const char *,...)‘
- BBR encounters cubic
猜你喜欢

解决:exceptiole ‘xxxxx.QRTZ_LOCKS‘ doesn‘t exist以及mysql的my.cnf文件追加lower_case_table_names后启动报错

为什么RTOS系统要使用MPU?
Detailed explanation and application of merging and sorting
数字图像处理实验目录

ADC of stm32

Detailed explanation of 'viewpager' in compose | developer said · dtalk
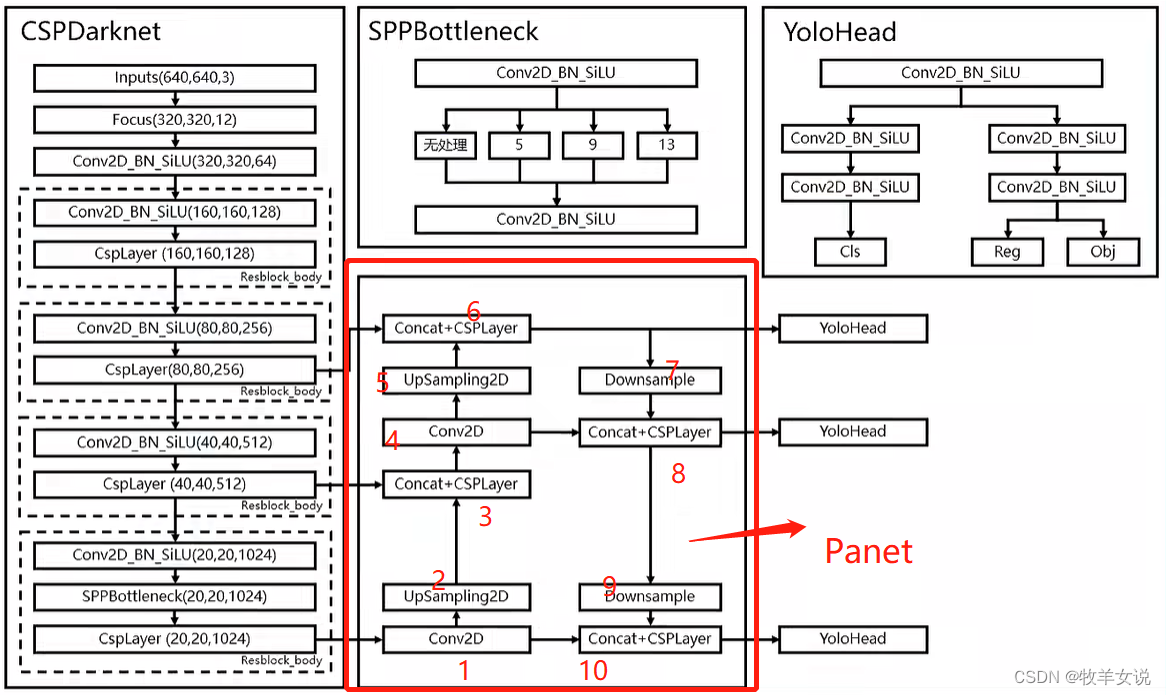
YOLOX加强特征提取网络Panet分析
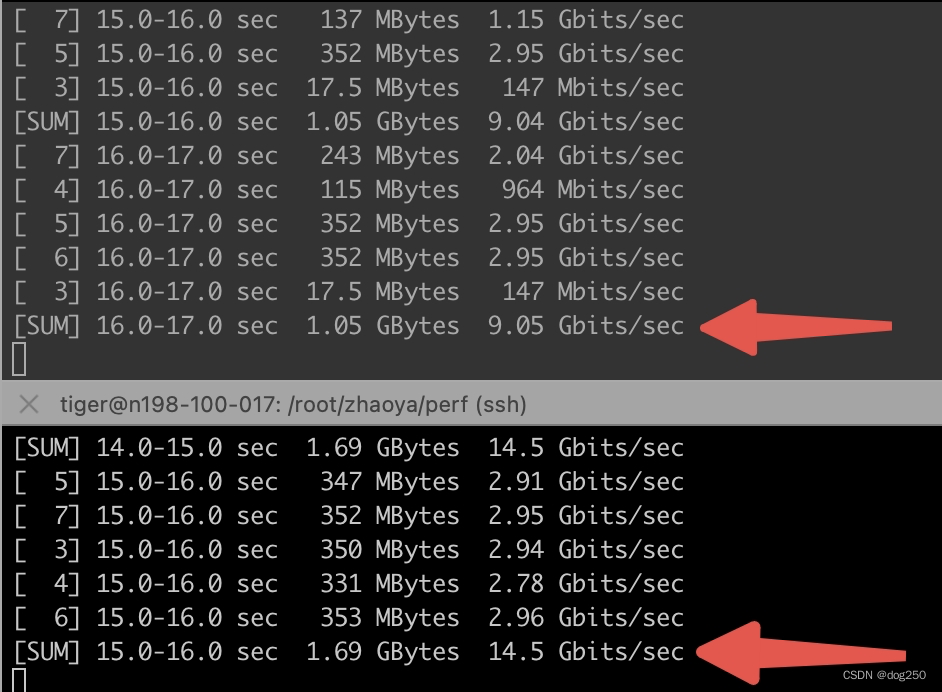
BBR 遭遇 CUBIC
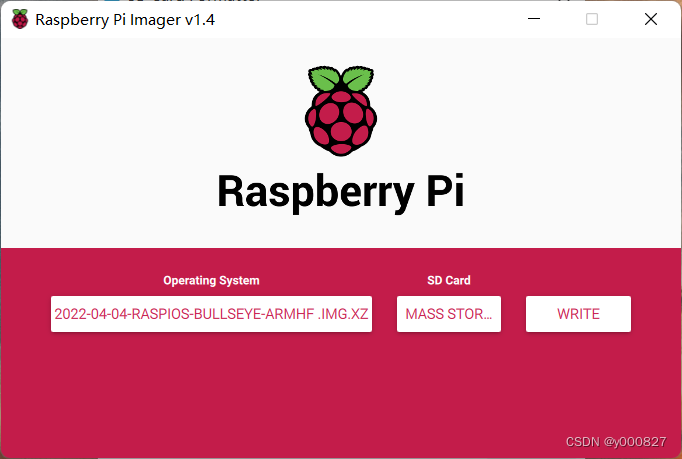
Connexion à distance de la tarte aux framboises en mode visionneur VNC

程序员版本的八荣八耻~
随机推荐
Three solutions to frequent sticking and no response of explorer in win11 system
Troubleshooting the cause of the crash when STM32 serial port dam receives 253 bytes
非路由组件之头部组件和底部组件书写
SharedPreferences 保存List<Bean> 到本地并解决com.google.gson.internal.LinkedTreeMap cannot be cast to异常
购买完域名之后能干什么事儿?
Detailed explanation of 'viewpager' in compose | developer said · dtalk
4 special cases! Schools in area a adopt the re examination score line in area B!
Tronapi wave field interface - source code without encryption - can be opened twice - interface document attached - packaging based on thinkphp5 - detailed guidance of the author - July 1, 2022 08:43:
Sword finger offer II 099 Sum of minimum paths - double hundred code
Doorplate making C language
Third party payment function test point [Hangzhou multi tester _ Wang Sir] [Hangzhou multi tester]
golang入门:for...range修改切片中元素的值的另类方法
SQL advanced syntax
简述中台的常识
Fudian bank completes the digital upgrade | oceanbase database helps to layout the distributed architecture of the middle office
内网渗透 | 手把手教你如何进行内网渗透
PotPlayer设置最小化的快捷键
Strictly abide by the construction period and ensure the quality, this AI data annotation company has done it!
Brief introduction to common sense of Zhongtai
[live broadcast appointment] database obcp certification comprehensive upgrade open class