当前位置:网站首页>反射注解基础
反射注解基础
2022-08-03 05:09:00 【*super】
一、反射
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
1.字节码文件对象的创建
Class类:
获取class对象的三种方式
方式一:通过Object类中的getOobject()方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p =new Person();
Class c = p.getClass();//获取到Person对应的Class类的对象
System.out.println(c);
}方式二:通过类名.class 获取到字节码文件对象(任意数据类型都具备一个class静态属性,看上去要比第一种方式简单)。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p =new Person();
Class c1 = Person.class;
System.out.println(c1);
}方式三:通过Class类中的方法(将类名作为字符串传递给Class类中的静态方法forName即可)。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Person p =new Person();
Class c3= Class.forName("fan.Person");
System.out.println(c3);
}2.通过反射获取构造方法并使用
在反射机制中,把类中的成员(构造方法、成员方法、成员变量)都封装成了对应的类进行表示。其中,构造方法使用类Constructor表示。可通过class类中提供的方法获取构造方法:
package fan;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/7 5:26
* @Version 1.0
*/
//获取Persor的构造方法
public class demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
//1.获取Person的字节码文件对象
Class c= Class.forName("fan.Person");
// Constructor[] con= c.getConstructors();//获取到Person类的所有public构造方法
Constructor[] con1=c.getDeclaredConstructors();//获取到Person类的所有构造方法
for (Constructor constructor : con1) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
Constructor con2=c.getConstructor(String.class);//获取某一个public构造方法
System.out.println(con2);
Constructor con3=c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,Integer.class);//获取某一个private构造方法
System.out.println(con3);
}
}
3.通过构造方法创建对象
package fan;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/7 5:38
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class c= Class.forName("fan.Person");
//获取到Person的空参构造方法
Constructor con1= c.getConstructor(null);
//执行构造方法创建对象
Object obj= con1.newInstance(null);
System.out.println(obj);
//获取到Person的私有构造方法
Constructor con2=c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,Integer.class);
//取消访问控制
con2.setAccessible(true);
Object obj1=con2.newInstance("张三",22);
System.out.println(obj1);
}
}
4.获取成员变量
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class c= Class.forName("fan.Person");
//获取所有public成员变量
Field[] fs= c.getFields();
for (Field f : fs) {
System.out.println(f);
}
//获取所有成员变量
Field[] fs1 = c.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fs1) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}获取和设詈成员变量
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.获取Person的字节码对象
Class c= Class.forName("fan.Person");
//2.获取构造方法
Constructor con = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, Integer.class);
//3.取消访问限制
con.setAccessible(true);
//4.执行构造方法创建对象
Object obj = con.newInstance("张三", 22);
//5.获取公共成员变量
Field f1 = c.getField("address");
//6.给address赋值
f1.set(obj,"河北");
//7.取出address的值
System.out.println(f1.get(obj));
//8.获取name和age的值
Field f2 = c.getDeclaredField("name");
f2.setAccessible(true);
f2.get(obj);
System.out.println(f2.get(obj));
}5.通过反射获取成员方法并使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class c= Class.forName("fan.Person");
// Method[] methods =c.getMethods();//获取person类里所有public方法
Method[] methods =c.getDeclaredMethods();//获取person类里所有方法
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
Method m1=c.getMethod("method1",null);
System.out.println(m1);
Method m2=c.getMethod("method2",String.class);
System.out.println(m2);
}执行方法:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class c= Class.forName("fan.Person");
Constructor con = c.getConstructor(null);//获取空参的构造方法
Object obj =con. newInstance(null);//创建对象
Method m1 = c.getMethod( "method1",null);
m1. invoke(obj,null);//执行无参数的方法
Method m2 = c.getMethod( "method2",String.class) ;
m2. invoke(obj,"hello");
Method m3 = c.getDeclaredMethod( "method3",null);//获取私有的方法
m3.setAccessible(true);//取消访问限制
m3.invoke(obj,null);
}6.泛型擦除
思考,将已存在的ArrayList<integer>集合中添加一个字符串数据,如何实现呢?
其实程序编译后产生的.class文件中是没有泛型约束的,这种现象我们称为泛型的擦除。那么,我们可以通过反射技术,来完成向有泛型约束的集合中,添加任意类型的元素。
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<Integer>();
arr.add(3);
arr.add(5);
// arr.add("hello"");
Class c = Class.forName("java.util.ArrayList");
Method m = c.getMethod("add", Object.class);
m.invoke(arr,"he11o");
System.out.println(arr);
}7.反射配置文件
(1)people.txt
className=fan.Person methodName=method1
(2)psvm
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties properties =new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("people.txt"));
String className = properties.getProperty("className");
String methodName=properties.getProperty("methodName");
Class c= Class.forName("className");
Constructor con =c.getConstructor(null);
Object obj=con.newInstance(null);
Method m=c.getMethod(methodName,null);
m.invoke(obj,null);
}二、注解
注解(Annotation)是一种标记性的接口,注解本质上是一个接口,它维承了Annotation接口,注解相当于一种标记,在程序中加了注解就等于为程序打上了某种标记,没加,则等于没有某种标记,它可以声明在包、类、字段、方法、局部变量、方法参数等的前面,用来对这些元素进行说明,注释。
1.预置注解@Deprecated
public class Hero {
@Deprecated
public void say(){
System.out.println("say");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("run");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hero{}";
}
}public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero h=new Hero();
h.say();//已经过时
h.run();
}2.元注解
元注解是可以注解到注解上的注解,或者说元注解是一种基本注解,但是它能够应用到其它的注解上面。
public @interface TestAnnoation {
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
Retention 的英文意为保留期的意思。当@Retention应用到一个注解上的时候,它解释说明了这个注解的的存活时间。
它的取值如下:
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE注解只在源码阶段保留,在编译器进行编译时它将被丢弃忽视。
RetentionPolicy.CLASS 注解只被保留到编译进行的时候,它并不会被加载到JVM中。 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME注解可以保留到程序运行的时候,它会被加载进入到JVM中,所以在程序运行时可以获取到它。
@Documented;
顾名思义,这个元注解肯定是和文档有关。它的作用是能够将注解中的元素包含到Javadoc 中去。
@Target
Target是目标的意思,@Target指定了注解运用的地方。
当一个注解被@Target注解时,这个注解就被限定了运用的场景。类比到标签,原本标签是你想张贴到哪个地方就到哪个地方,但是因为@Target 的存在,它张贴的地方就非常具体了,比如只台张贴到方法上、类上、方法参数上等等。
@Target有下面的取值:
ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE可以给一个注解进行注解。
ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR 可以给构造方法进行注解。
ElementType.FIELD可以给属性进行注解。
ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE可以给局部变量进行注解。
ElementType.METHOD可以给方法进行注解。
ElementType.PACKAGE可以给一个包进行注解.
ElementType.PARAMETER 可以给一个方法内的参数进行注解。
ElementType.TYPE 可以给一个类型进行注解,比如类、接口、枚举。
@lnherited
Inherited是继承的意思,但是它并不是说注解本身可以继承,而是说如果一个超类被@Inherited注解过的注解进行注解的话,那么如果它的子类没有被任何注解应用的话,那么这个子类就继承了超类的注解。
3.注解的属性
注解既然本质上是接口,那么注解里面自然就是抽象方法,也被叫做属性。
public @interface TestAnnoation {
int id() default -1;
String message();
}@TestAnnoation(id=1,message = "hello")//一个属性可以直接写值
4.类上注解的提取
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Inherited
public @interface TestAnnoation {
int id() default -1;
String message() default "hello";
}@TestAnnoation
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean isHas = Test.class.isAnnotationPresent(TestAnnoation.class);//判断Test类上是否有@TestAnnoation注解
if (isHas){
TestAnnoation ann = Test.class.getAnnotation(TestAnnoation.class);//获取到TestAnnoationi注解
System.out.println(ann.id());
System.out.println(ann.message());
}
}
}5.属性上注解的提取
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Check {
String value();
}public class Test2 {
@Check(value="hi")
int a;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Field f = Test2.class.getDeclaredField("a");//获取到属性a
f.setAccessible(true);
Check c = f.getAnnotation(Check.class);
System.out.println(c.value());
}
}6.方法上注解的提取
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface PerForm {
}public class Test2 {
@Check(value="hi")
int a;
@PerForm
public void test1(){
System.out.println("test1");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Method m = Test2.class.getDeclaredMethod("test1");
m.setAccessible(true);
Annotation[] anns = m.getAnnotations();
for (int i=0;i<anns.length;i++) {
System.out.println(anns[i].annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
}
}7.注解案例
我要写一个测试框架,测试程序员的代码有无异常。
程序员A:我写了一个类,它的名字叫做NoBug,因为它所有的方法都没有错误。
我:自信是好事,不过为了防止意外,让我测试一下如何?
程序员A:怎么测试?
我:把你写的代码的方法都加上 @Check这个注解就好了。
程序员A:好的。
package zhu.anli;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/7 7:27
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Check {
}package zhu.anli;
import zhu.Check;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/7 7:26
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Calculater {
@Check
public void add(){
System.out.println("add");
}
@Check
public void sub(){
int i= 1/0;
System.out.println("sub");
}
@Check
public void times(){
System.out.println("times");
}
}
package zhu.anli;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/7 7:30
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculater cal =new Calculater();
Class c = cal.getClass();//获取到Calculater的字节码对象
Method[] m = c.getMethods();//获取Calculater中的所有方法
int errNum=0;//记录出错次数
StringBuilder builder=new StringBuilder();//记录出错的信息
for (Method method : m) {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Check.class)){
try {
method.invoke(cal,null);
} catch (Exception e) {
errNum++;
builder.append("出错的方法是:"+method.getName()+"错误是:"+e.getCause().getMessage());
}
}
}
System.out.println("出错了"+errNum+"次");
System.out.println(builder.toString());
}
}
8.注解应用junit
Junit测试框架
测试分类:
黑盒测试:不需要写代码,给输入值,看程序是否能够输出期望的值。
白盒测试:需要写代码的,关注程序具体的执行流程。
package zhu.jisuan;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/7 7:47
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class ji {
public int add(int num1,int num2){
return num1+num2;
}
public int sub(int num1,int num2){
return num1-num2;
}
public int mul(int num1,int num2){
return num1*num2;
}
}
package zhu.jisuan;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/7 7:49
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Testji {
@Test//需要引入junit的jar包
public void testadd(){
ji ji=new ji();
System.out.println(ji.add(1,1));
Assert.assertEquals(2,c.add(1,1));//断点值比较 期望值与实际值
}
@Before//先执行
public void init(){
System.out.println("初始化");
}
@After//最后执行
public void finish(){
System.out.println("结束");
}
}
边栏推荐
- Fluorescent marker peptides FITC/AMC/FAM/Rhodamine TAMRA/Cy3 / Cy5 / Cy7 - Peptide
- Super handy drawing tool is recommended
- IO process thread -> thread -> day5
- Alienware上线首个数字时装AR试穿体验
- Odps temporary query can write SQL, turned out to a named?
- Install IIS services (Internet Information Services (Internet Information Services, abbreviated IIS, Internet Information Services)
- 接口和抽象
- GIS数据漫谈(六)— 投影坐标系统
- [Fine talk] Using native js to implement todolist
- 常见荧光染料修饰多种基团及其激发和发射波长数据一览数据
猜你喜欢

How to prepare for the test interface test data
c语言结构体中的冒泡排序
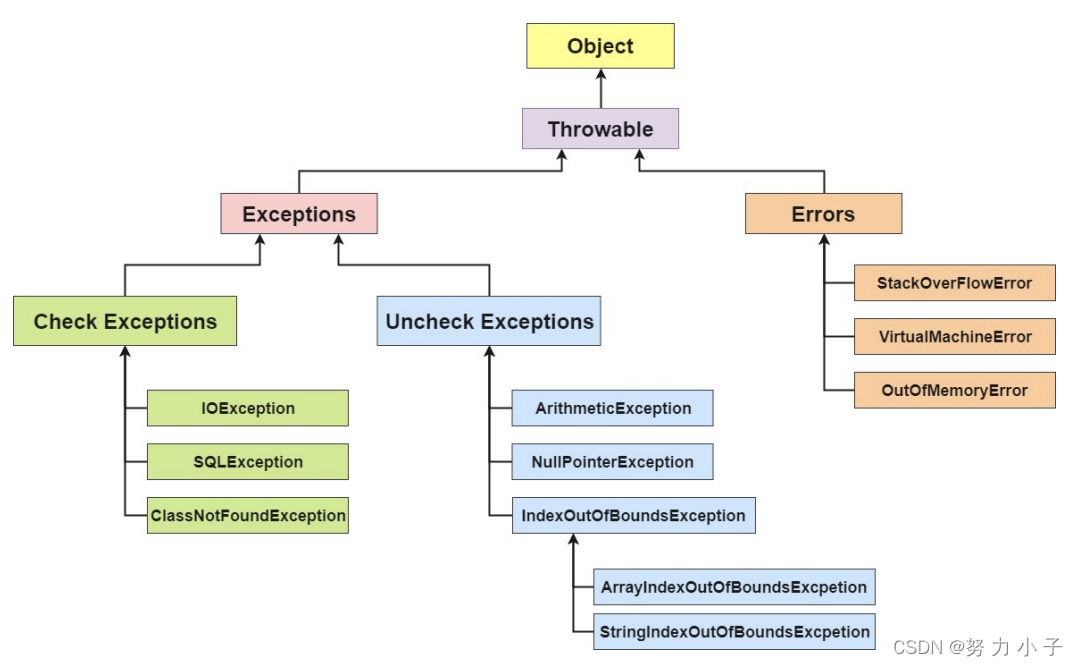
Exception (abnormal) and Error (error) difference analysis
Ali cloud object storage oss private barrels to generate links
Power button 561. An array of split
CobalStrike(CS)基础超级详细版

typescript43-类型兼容性说明
CAD有生僻字如何打出来、如何提交软件相关问题或建议?
Common lipophilic cell membrane dyes DiO, Dil, DiR, Did spectrograms and experimental procedures
Install PostgreSQL on Windows
随机推荐
Kotlin-Flow common encapsulation class: the use of StateFlow
设计模式——组合模式、享元模式(Integer缓存)(结构型模式)
IO process thread -> thread -> day5
js实现一个 bind 函数
【 Harmony OS 】 【 ano UI 】 lightweight data storage
typescript42-readonly修饰符
安装IIS服务(Internet信息服务(Internet Information Services,简写IIS,互联网信息服务)
Exception (abnormal) and Error (error) difference analysis
业务表解析-余额系统
【软件工程之美 - 专栏笔记】35 | 版本发布:软件上线只是新的开始
GIS数据漫谈(五)— 地理坐标系统
数字孪生园区场景中的坐标知识
接口测试框架实战(三)| JSON 请求与响应断言
User password encryption tool
Interface testing framework of actual combat (2) | interface request assertion
UV 裂解的生物素-PEG2-叠氮|CAS:1192802-98-4生物素接头
探索性测试的概念及方法
【开发者必看】【push kit】推送服务服务典型问题合集2
用户密码加密工具
Peptides mediated PEG DSPE of phospholipids, targeted functional materials - PEG - RGD/TAT/NGR/APRPG