当前位置:网站首页>50. Pow(x, n). O(logN) Sol
50. Pow(x, n). O(logN) Sol
2022-07-05 22:17:00 【isee_ nh】
Move the dichotomy of the official solution , The time complexity is O(log )
)
Implement pow(x, n), which calculates x raised to the power n (i.e., xn).
class Solution {
public:
double fastPow(double x, long long n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 1.0;
}
double half = fastPow(x, n / 2);
if (n % 2 == 0) {
return half * half;
} else {
return half * half * x;
}
}
double myPow(double x, int n) {
long long N = n;
if (N < 0) {
x = 1 / x;
N = -N;
}
return fastPow(x, N);
}
};Example 1:
Input: x = 2.00000, n = 10 Output: 1024.00000
Example 2:
Input: x = 2.10000, n = 3 Output: 9.26100
Example 3:
Input: x = 2.00000, n = -2 Output: 0.25000 Explanation: 2-2 = 1/22 = 1/4 = 0.25
Constraints:
-100.0 < x < 100.0-231 <= n <= 231-1-104 <= xn <= 104
Approach 2: Fast Power Algorithm Recursive
Intuition
Assuming we have got the result of  , how can we get
, how can we get  ? Obviously we do not need to multiply
? Obviously we do not need to multiply  for another
for another  times. Using the formula
times. Using the formula  , we can get
, we can get  at the cost of only one computation. Using this optimization, we can reduce the time complexity of our algorithm.
at the cost of only one computation. Using this optimization, we can reduce the time complexity of our algorithm.
Algorithm
Assume we have got the result of  , and now we want to get the result of
, and now we want to get the result of  . Let
. Let A be result of  , we can talk about
, we can talk about  based on the parity of
based on the parity of n respectively. If n is even, we can use the formula  to get
to get  . If
. If n is odd, then  . Intuitively, We need to multiply another xx to the result, so
. Intuitively, We need to multiply another xx to the result, so  . This approach can be easily implemented using recursion. We call this method "Fast Power", because we only need at most O(logn) computations to get
. This approach can be easily implemented using recursion. We call this method "Fast Power", because we only need at most O(logn) computations to get  .
.
边栏推荐
- boundary IoU 的计算方式
- Damn, window in ie open()
- Win11运行cmd提示“请求的操作需要提升”的解决方法
- Reptile practice
- DataGrid directly edits and saves "design defects"
- A number of ventilator giants' products have been recalled recently, and the ventilator market is still in incremental competition
- Form artifact
- Text组件新增内容通过tag_config设置前景色、背景色
- Daily question brushing record (XIV)
- CA certificate trampled pit
猜你喜欢
How can Bluetooth in notebook computer be used to connect headphones

Official clarification statement of Jihu company
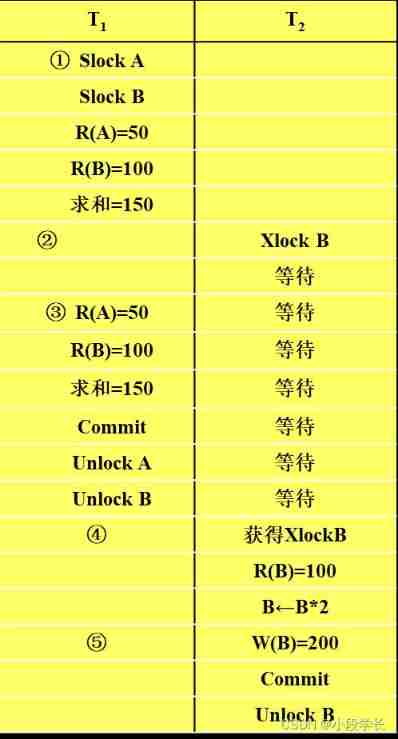
Blocking protocol for concurrency control
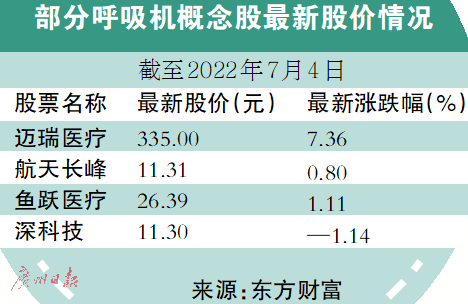
多家呼吸机巨头产品近期被一级召回 呼吸机市场仍在增量竞争

Web3为互联网带来了哪些改变?

The real situation of programmers

Storage optimization of performance tuning methodology

IIC bus realizes client device
Daily question brushing record (XIV)
Interview questions for famous enterprises: Coins represent a given value
随机推荐
Sentinel production environment practice (I)
Evolution of large website architecture and knowledge system
微服务链路风险分析
极狐公司官方澄清声明
Practice: fabric user certificate revocation operation process
阿龙的感悟
Three "factions" in the metauniverse
Leetcode simple question check whether all characters appear the same number of times
IIC bus realizes client device
Web3为互联网带来了哪些改变?
Text组件新增内容通过tag_config设置前景色、背景色
微服务入门(RestTemplate、Eureka、Nacos、Feign、Gateway)
装饰器学习01
Learning of mall permission module
Database tuning solution
Database recovery strategy
Promql demo service
Reptile practice
等到产业互联网时代真正发展成熟,我们将会看待一系列的新产业巨头的出现
Talking about MySQL index