当前位置:网站首页>STM32LL library use - SPI communication
STM32LL library use - SPI communication
2022-08-02 15:28:00 【Tianshan no longevity tea】
STM32使用前的准备
对于要使用的每个STM32芯片,首先我们手上必备的两本手册(ST官网有pdf版):
- 参考手册(Reference manual)
- 数据手册(Datasheet)
其中参考手册包括各个功能模块的具体信息、原理、各种工作模式介绍、配置方法以及寄存器相关信息;数据手册包括芯片的基本参数、引脚数量与各自功能、电气特性、封装信息等内容.一般在选型与硬件设计阶段,参考数据手册多一些,而到了程序设计阶段,参考手册就是必须的了.
以下是STM32G4系列的参考手册的“自我介绍”:
This reference manual targets application developers. It provides complete information on how to use the STM32G4 Series microcontroller memory and peripherals.
本参考手册的目标是应用程序开发人员. 它提供了关于的完整信息如何使用STM32G4系列单片机的内存和外设.
SPI相关设置
我们以STM32G系列为例,直接翻到SPI章节,SPI结构示意图如下:
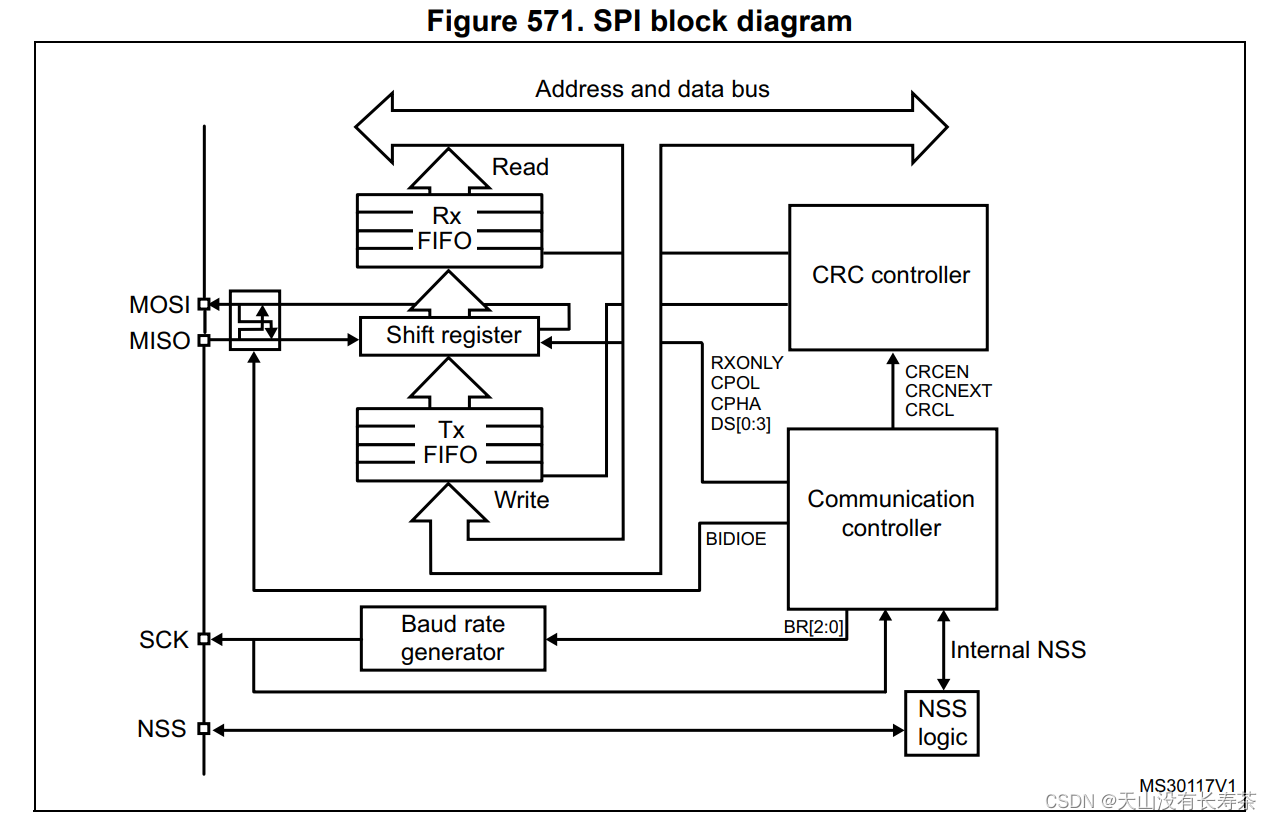
一共4pins can be connected to peripherals:
- MISO(Master In / Slave Out data):该引脚在从模式下发送数据,在主模式下接收数据
- MOSI(Master Out / Slave In data):该引脚在主模式下发送数据,在从模式下接收数据
- SCK(Serial Clock):The clock signal transmitted from the master device to the slave device
- NSS(Slave select):Used by the master to select the slave
The schematic diagram of the full-duplex communication mode between a single master device and a single slave device is as follows:
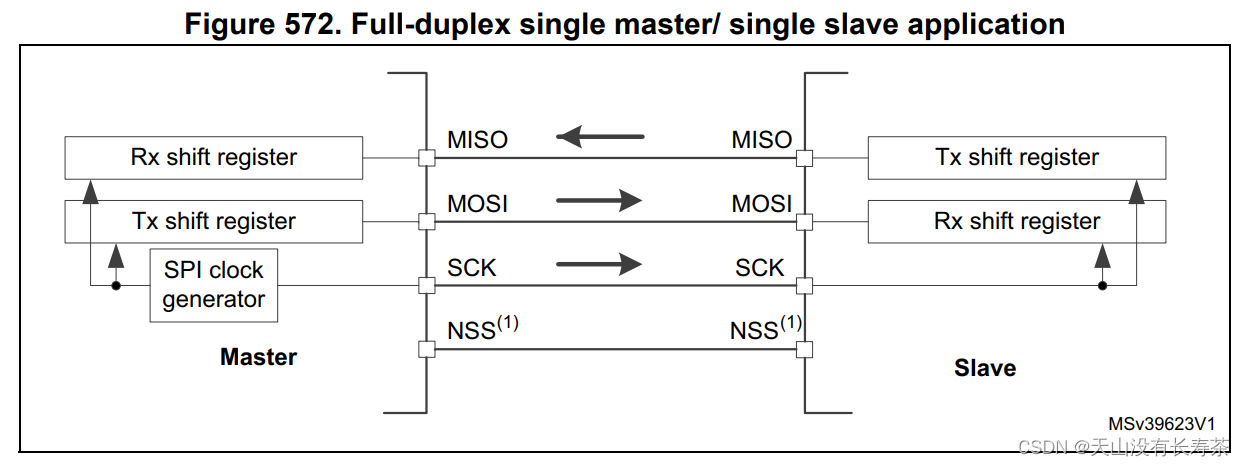
我们采用STM32CubeMXBasic configuration can be easily completed,Actually, you only need to write the code required for actual communication as follows
Basic communication code
Tx:发送缓冲区;Rx:接收缓冲区;DR:数据寄存器
Status indicator:
- Tx buffer empty flag (TXE):发送缓冲区为空
- Rx buffer not empty (RXNE):接收缓冲区非空
- Busy flag (BSY):SPIData is being transferred
基本工作原理:The master sends a value to the slave(指令),The slave then returns a value according to the received command
We use it in common casesSTM32作为主机
- 等待TXE标志置1(Tx空),Indicates that the buffer is sent at this timeTxThere are no values to send in
- 将数据写入SPIx_DR寄存器,对DRThe write operation will write the dataTx末尾
- 等待BSY标志置0(即busy,置1表明TxThe data in is being transferred).During the data passMOSI发送给从机,The information returned by the slave is passedMISOBack to the host receive bufferRx
- 等待RXNE标志置1(Rx非空),表明此时RxThe received value exists
- 读取SPIx_DR寄存器,对DR的读操作将返回RxThe earliest value in
// data_in:待发送的值
// data_out:接收到的值
static int spi_transmit_receive(uint16_t data_in, uint16_t *data_out){
int state = 0;
*data_out = 0;
uint32_t timeout_cnt;
static const uint32_t timeout_cnt_num = 10000;
// Wait until TXE flag is set to send data
timeout_cnt = 0;
while(!LL_SPI_IsActiveFlag_TXE(SPI1)){
timeout_cnt ++;
if(timeout_cnt > timeout_cnt_num){
state = -1;
break;
}
}
// Transmit data in 16 Bit mode
LL_SPI_TransmitData16(SPI1, data_in);
// Check BSY flag
timeout_cnt = 0;
while(LL_SPI_IsActiveFlag_BSY(SPI1)){
timeout_cnt ++;
if(timeout_cnt > timeout_cnt_num){
state = -1;
break;
}
}
// Check RXNE flag
timeout_cnt = 0;
while(!LL_SPI_IsActiveFlag_RXNE(SPI1)){
timeout_cnt ++;
if(timeout_cnt > timeout_cnt_num){
state = -1;
break;
}
}
// Read 16-Bits in the data register
*data_out = LL_SPI_ReceiveData16(SPI1);
return state;
}所涉及的LL库相关函数:
/** * @brief Write 16-Bits in the data register * @rmtoll DR DR LL_SPI_TransmitData16 * @param SPIx SPI Instance * @param TxData Value between Min_Data=0x00 and Max_Data=0xFFFF * @retval None */ __STATIC_INLINE void LL_SPI_TransmitData16(SPI_TypeDef *SPIx, uint16_t TxData) { #if defined (__GNUC__) __IO uint16_t *spidr = ((__IO uint16_t *)&SPIx->DR); *spidr = TxData; #else SPIx->DR = TxData; #endif /* __GNUC__ */ } /** * @brief Read 16-Bits in the data register * @rmtoll DR DR LL_SPI_ReceiveData16 * @param SPIx SPI Instance * @retval RxData Value between Min_Data=0x00 and Max_Data=0xFFFF */ __STATIC_INLINE uint16_t LL_SPI_ReceiveData16(SPI_TypeDef *SPIx) { return (uint16_t)(READ_REG(SPIx->DR)); } /** * @brief Check if Tx buffer is empty * @rmtoll SR TXE LL_SPI_IsActiveFlag_TXE * @param SPIx SPI Instance * @retval State of bit (1 or 0). */ __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t LL_SPI_IsActiveFlag_TXE(SPI_TypeDef *SPIx) { return ((READ_BIT(SPIx->SR, SPI_SR_TXE) == (SPI_SR_TXE)) ? 1UL : 0UL); } /** * @brief Get busy flag * @note The BSY flag is cleared under any one of the following conditions: * -When the SPI is correctly disabled * -When a fault is detected in Master mode (MODF bit set to 1) * -In Master mode, when it finishes a data transmission and no new data is ready to be * sent * -In Slave mode, when the BSY flag is set to '0' for at least one SPI clock cycle between * each data transfer. * @rmtoll SR BSY LL_SPI_IsActiveFlag_BSY * @param SPIx SPI Instance * @retval State of bit (1 or 0). */ __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t LL_SPI_IsActiveFlag_BSY(SPI_TypeDef *SPIx) { return ((READ_BIT(SPIx->SR, SPI_SR_BSY) == (SPI_SR_BSY)) ? 1UL : 0UL); } /** * @brief Check if Rx buffer is not empty * @rmtoll SR RXNE LL_SPI_IsActiveFlag_RXNE * @param SPIx SPI Instance * @retval State of bit (1 or 0). */ __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t LL_SPI_IsActiveFlag_RXNE(SPI_TypeDef *SPIx) { return ((READ_BIT(SPIx->SR, SPI_SR_RXNE) == (SPI_SR_RXNE)) ? 1UL : 0UL); }
实际使用spi_transmit_receive函数时,Generally, the following chip selects need to be set before and after the functionNSS输出,Select the current slave before communication,Communication and then close,Prevent conflicts in multi-master or multi-slave mode.
// NSSChip select pin setting0,Open the current master-slave relationship
LL_GPIO_ResetOutputPin(GPIOx, LL_GPIO_PIN_x);
spi_transmit_receive(controlword, &recbuff);
// NSS置1,Close the current master-slave relationship
LL_GPIO_SetOutputPin(GPIOx, LL_GPIO_PIN_x);边栏推荐
- cmake configure libtorch error Failed to compute shorthash for libnvrtc.so
- KiCad Common Shortcuts
- Cmd Markdown 公式指导手册
- Actual combat Meituan Nuxt +Vue family bucket, server-side rendering, mailbox verification, passport authentication service, map API reference, mongodb, redis and other technical points
- Open the door to electricity "Circuit" (3): Talk about different resistance and conductance
- How to reinstall Win7 system with U disk?How to reinstall win7 using u disk?
- Use libcurl to upload the image of Opencv Mat to the file server, based on two methods of post request and ftp protocol
- pygame draw arc
- 为android系统添加产品的过程
- FP5207电池升压 5V9V12V24V36V42V大功率方案
猜你喜欢
FP7122降压恒流内置MOS耐压100V共正极阳极PWM调光方案原理图
FP7195转模拟恒流调光芯片在机器视觉光源的应用优势
Lightweight AlphaPose
Mysql的锁
Win10 cannot directly use photo viewer to open the picture
flink+sklearn——使用jpmml实现flink上的机器学习模型部署
win10任务栏不合并图标如何设置

FP5207电池升压 5V9V12V24V36V42V大功率方案
SQL的通用语法和使用说明(图文)
What should I do if Windows 10 cannot connect to the printer?Solutions for not using the printer
随机推荐
总结计算机网络超全面试题
Impressions of Embrace Jetpack
Win7怎么干净启动?如何只加载基本服务启动Win7系统
Win11声卡驱动如何更新?Win11声卡驱动更新方法
FP7126降压恒流65536级高辉无频闪调光共阳极舞台灯RGB驱动方案
How to reinstall Win7 system with U disk?How to reinstall win7 using u disk?
刷卡芯片CI520可直接PIN对PIN替换CV520支持SPI通讯接口
Configure clangd for vscode
FP7195转模拟恒流调光芯片在机器视觉光源的应用优势
Binder ServiceManager解析
推开机电的大门《电路》(三):说说不一样的电阻与电导
win10无法直接用照片查看器打开图片怎么办
MATLAB制作简易小动画入门详解
DP4344兼容CS4344-DA转换器
Open the door to electricity "Circuit" (3): Talk about different resistance and conductance
Yolov5 official code reading - prior to transmission
5. Use RecyclerView to elegantly achieve waterfall effect
背包问题-动态规划-理论篇
Publish module to NPM should be how to operate?Solutions to problems and mistake
DP1332E刷卡芯片支持NFC内置mcu智能楼宇/终端poss机/智能门锁