当前位置:网站首页>C language pointer (special article)
C language pointer (special article)
2022-07-07 09:07:00 【A big cat 1201】
author : A big cat 1201
special column :《C Language learning 》
Maxim : You just try to , Leave the rest to time !
C Language pointer ( Special article )
The article in front of benmew 《C Language ( On 、 in 、 Next )》 In the three articles, the types and usage of pointers are explained in detail from simple to deep , Based on these three articles , Put forward a concept in particular —— Callback function .
Callback function
Concept :
- Callback function is to call a function through function pointer . Put the pointer of the function ( Address ) Pass as argument to another function , When this pointer is used to call the function it points to , Let's just say this is a callback function .
Be careful
- The callback function is not called directly by the function's implementer , That is, it is not used directly through the function name .
- It is called by another party when a specific event or condition occurs , Used to respond to the event or condition .
Library function qsort
There is one int An array of types , We will arrange them in ascending order .
#include <stdio.h>
void bubble_sort(int arr[], int sz)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
int flag = 1;
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = tmp;
flag = 0;// As long as the exchange occurs, the flag bit is written 0
}
}
// Judge whether the exchange is completed
if (flag)
{
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Bubble ascending arrangement
bubble_sort(arr, sz);
// Print elements in an array
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Through bubble sorting , The original descending array is rearranged into an ascending array .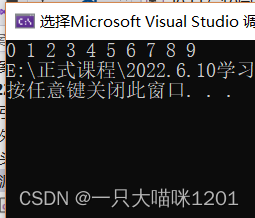
stay C Language library functions , There is a sort function for us to use , That's it qsort function .
Let's take a look at its definition :

This is its function declaration and the header file to be referenced .
That's right qsort Introduction to function parameters .
- qsort The function implements sorting through quick sorting
void qsort(void* base, size_t num, size_t width, int(__cdecl* compare)(const void* elem1, const void* elem2));
- The parameters are
- The starting address of the data to be sorted
- The number of data to be arranged
- To arrange the size of each data in the data
- The way of sorting
The sorting method is defined by the user , Write the comparison method as a function , Then pass the address of the function as an argument to qsort Function can use . So it has a formal parameter of type function pointer variable type , The address used to receive the comparison function .
int(__cdecl* compare)(const void* elem1, const void* elem2)
- The function pointer points to
- The two formal parameters are const void* Pointer variable type of type
- The return type is int type , That is, pointer variables elem1 and emel2 The difference between the two numbers pointed to
If elem1 The number of points is greater than elem2 Number of points , Return a value greater than 0 Number of numbers .
If elem1 The number pointed to is equal to elem2 Number of points , Returns a 0.
If elem1 The number of points is less than elem2 Number of points , Return a value less than 0 Number of numbers .- among elem1 It refers to the previous number in the data to be sorted ,elem2 It refers to the last number in the data to be sorted .
Then among the formal parameters const void* What does the pointer variable of type mean ?
void* Pointer variable of type
const Just for decoration , Modify the pointer variable into a constant variable , bring * emel1 perhaps * emel2 It cannot be used to modify its value by dereference .
void* A pointer of type is a pointer without type
When you need a pointer variable , But I don't know what type of pointer variable it is for the time being , You can write it as a void * Pointer to type .
After knowing the required pointer variable type , You can cast void * The pointer variable of type is converted to what we need .
Such as
(int*)emel1It can be void * Pointer variable of type emel1 Convert into int * Pointer variable of type .
We use qsort Function to sort the array in ascending order .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int int_cmp(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int width = sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, width, int_cmp);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
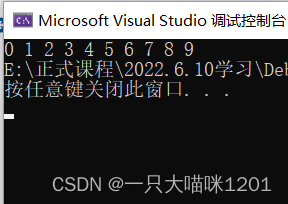
The result is the same as that we used bubble sorting .
Sorting of various types of data
Have you ever thought about it , Why is the pointer of formal parameter type in user-defined comparison function void * What about the type? ?
qsort The author of kuhan certainly didn't know what type of data the user wanted to compare when writing , So set it as a void * Pointer variable of type , When users are writing comparison functions by themselves , take void * Class pointer variables can be converted into their own needs .
qsort Function can sort any type of data
Here are some examples :
- char Sort of type data
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int char_cmp(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*((char*)e2) - *((char*)e1));
}
int main()
{
char arr[] = "abcdef";
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) - 1;// Character end flag '\0' There's no need to sort
int width = sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, width, char_cmp);
printf("%s\n", arr);
return 0;
}
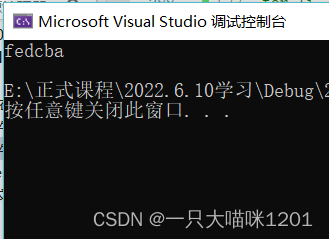
String by ASCII The code values are arranged in descending order .
- Arrangement of structure type data
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
};
int struct_cmp_age(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (((struct stu*)e1)->age - ((struct stu*)e2)->age);// The transformed pointer must be enclosed in parentheses
}
int main()
{
struct stu s[3] = {
{
"zhangsan",18},{
"lisi",25},{
"wangwu",21} };
int sz = sizeof(s) / sizeof(s[0]);
int width = sizeof(s[0]);
qsort(s, sz, width, struct_cmp_age);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%s,%d\n", s[i].name, s[i].age);
}
return 0;
}

Rank three people according to their age .
Change the comparison method to compare by name
int struct_cmp_name(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct stu*)e1)->name, ((struct stu*)e2)->name);
}
The rest of the program remains unchanged .
According to the initials ASCII Code value ascending order will sort three people .
Simulation Implementation qsort function
We wrote a bubble sort program on it , Next, we use the idea of bubble sorting to realize a qsort Functions of library functions my_qsort function .
Refer to the library function qsort Function declaration of
void qsort(void* base, size_t num, size_t width, int(__cdecl* compare)(const void* elem1, const void* elem2));
Take the ascending arrangement of integer arrays as an example :
#include <stdio.h>
// Because I don't know what the data type is , So write it first void* Pointer variable of type
void Swap(char* buf1,char* buf2,int width)
{
int i = 0;
// Exchange by pair
for (i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
char tmp = *buf1;
*buf1 = *buf2;
*buf2 = tmp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
}
void my_qsort(void* base, int sz, int width, int (*pf)(const void*, const void*))
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
int flag = 1;
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
//char* The pointer variable of type plus the data width will get the starting address of each data
if (pf((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0)
{
// Pass the starting address of the two data to the exchange function
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
flag = 0;
}
}
if (flag)
{
break;
}
}
}
int int_cmp(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int width = sizeof(arr[0]);
my_qsort(arr, sz, width, int_cmp);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
The main difficulty is my_qsort Implementation of function .
- Because I don't know what kind of data to sort , So write it as void * type
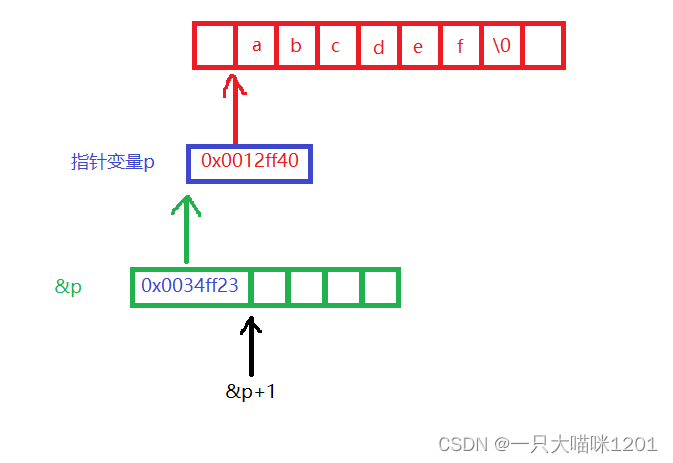
- Inside the function , because void * Pointer variables of type cannot be dereferenced and used , So convert it into the pointer variable of the smallest unit char * Type of .
When you know that the array to be sorted is int After the type , Add a field width to the minimum unit to get the first address of the next data .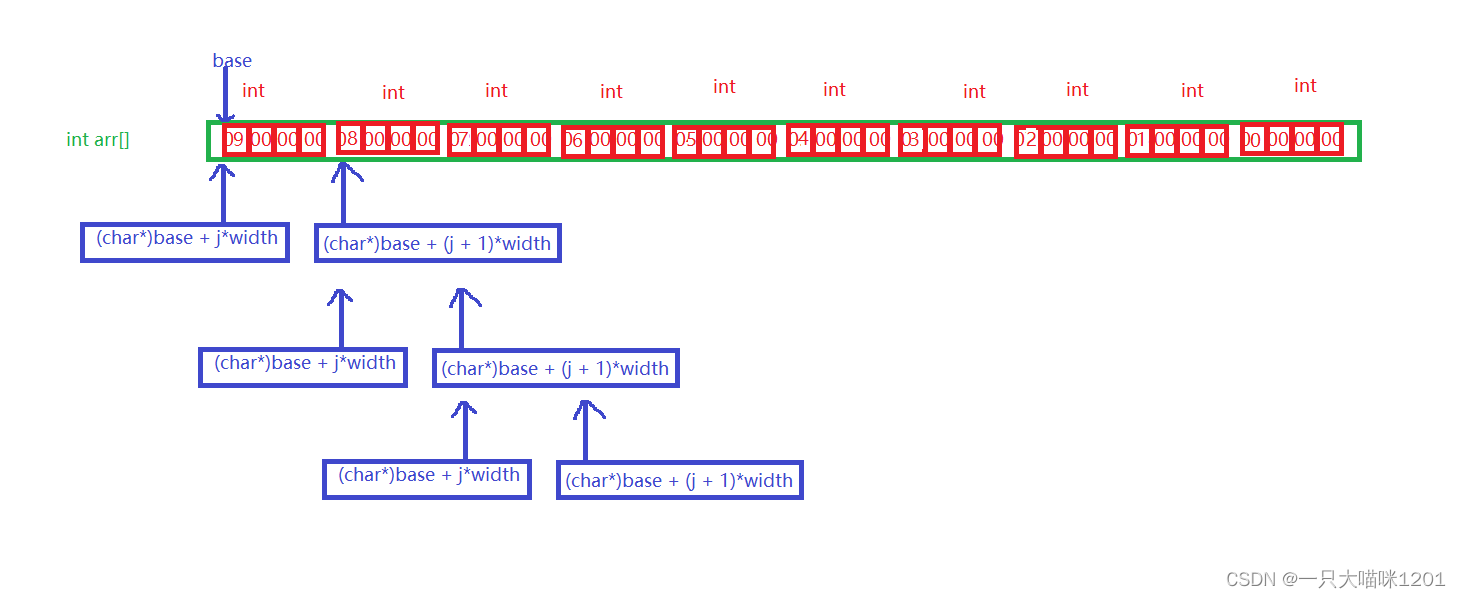
The elements in the array are stored in memory as shown in the figure above .
- Pass the array name as an argument my_qsort After the function , Start bubble sorting
- When calling the comparison function
- Put two in the array int First address of type data , In the picture (char*)base + j * width and (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) Two addresses are passed to the comparison function , This function is called through a function pointer .
- Judge the results after comparison , If you need to exchange , take (char*)base + j * width and (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) Two addresses are passed to Swap Exchange function .
- stay Swap Function , Through domain width width, That is to say int The size of the data type controls the progress of the loop .
- In the loop, two sets of data are exchanged in pairs , Until two int Exchange of type data .
- Until the exchange of all data is realized .
In this way, we have achieved qsort Function of function , And it uses the idea of bubble sorting , Instead of the idea of a quick row .
Sorting of various types of data
Like library functions qsort like that , We wrote it ourselves my_qosrt Functions can also implement different data types , Write on it my_qsort Function has been arranged int Data of type , Next, I will sort other data types .
- char Sort of type data
int char_cmp(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*(char*)e2 - *(char*)e1);
}
int main()
{
char arr[] = "abcdef";
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int width = sizeof(arr[0]);
my_qsort(arr, sz, width, char_cmp);
printf("%s\n", arr);
return 0;
}
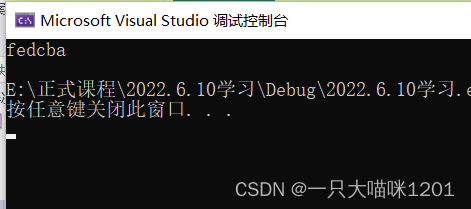
And using library functions qsort The result is the same .
- Structure type data sorting
struct stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
};
int struct_cmp_age(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (((struct stu*)e1)->age - ((struct stu*)e2)->age);// The transformed pointer must be enclosed in parentheses
}
int main()
{
struct stu s[3] = {
{
"zhangsan",18},{
"lisi",25},{
"wangwu",21} };
int sz = sizeof(s) / sizeof(s[0]);
int width = sizeof(s[0]);
my_qsort(s, sz, width, struct_cmp_age);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%s,%d\n", s[i].name, s[i].age);
}
return 0;
}
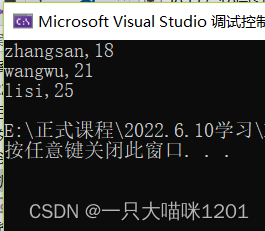
And library functions qsort The result is the same , It also arranges three people according to their ages .
Change the comparison function to sort by name
int struct_cmp_name(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct stu*)e1)->name, ((struct stu*)e2)->name);
}
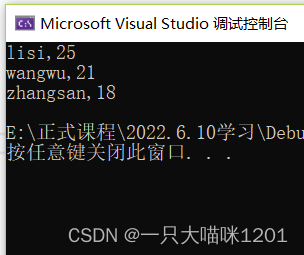
Same as library function qsort The result is the same , According to the initials of the name ASCII The code values are arranged from small to large .
In the sorting of the above two data types ,my_qsort Functions and Swap The function is not written , Their specific contents are written with reference my_qsort Function procedure is ok .
Writing my_qsort In the process of function , Make full use of callback functions , The main application is in comparison function , Whether we simulate it ourselves my_qsort Or library functions qsort, After the user defines the comparison function , This function is called by using the callback function .
C Language pointer conclusion
C The characteristics of language mainly lie in the flexible use of pointers , Through 《C Language pointer ( Part 1 、 medium-length 、 The next part 、 Special article )》 Introduction of four articles , Turn the pointer from shallow to deep , It is described in detail in the table , The various pointer types involved and their usage can cope with most of the scenarios we encounter in the programming process .
边栏推荐
- Port occupation troubleshooting
- How can I apply for a PMP certificate?
- How long does the PMP usually need to prepare for the exam in advance?
- How does the project manager write the weekly summary and weekly plan?
- channel. Detailed explanation of queuedeclare parameters
- Tronapi wave field interface - source code without encryption - can be opened twice - interface document attached - package based on thinkphp5 - detailed guidance of the author - July 6, 2022 - Novice
- Analysis of Hessian serialization principle
- Speaking of a software entrepreneurship project, is there anyone willing to invest?
- 数据在内存中的存储
- 串口实验——简单数据收发
猜你喜欢
2021 year end summary
LED模拟与数字调光

Digital triangle model acwing 275 Pass a note

Esp32-ulp coprocessor low power mode RTC GPIO interrupt wake up

C语言指针(下篇)
On December 8th, 2020, the memory of marketing MRC application suddenly increased, resulting in system oom
C语言指针(习题篇)

Interview question: general layout and wiring principles of high-speed PCB

PMP Exam Preparation experience systematically improve project management knowledge through learning

Common short chain design methods
随机推荐
5A summary: seven stages of PMP learning
LeetCode 715. Range 模块
Full link voltage test of the e-commerce campaign Guide
Digital triangle model acwing 275 Pass a note
Cmake command line use
Led analog and digital dimming
Three updates to build applications for different types of devices | 2022 i/o key review
Interview question: general layout and wiring principles of high-speed PCB
LeetCode 736. LISP syntax parsing
PMP Exam details after the release of the new exam outline
【Istio Network CRD VirtualService、Envoyfilter】
How long does the PMP usually need to prepare for the exam in advance?
Unityshader introduction essentials personal summary -- Basic chapter (I)
模拟卷Leetcode【普通】1609. 奇偶树
PMP Exam Preparation experience systematically improve project management knowledge through learning
What is the use of PMP certificate?
串口实验——简单数据收发
Simulation volume leetcode [general] 1706 Where does the ball meet
硬件大熊原创合集(2022/05更新)
9c09730c0eea36d495c3ff6efe3708d8
