当前位置:网站首页>图论的扩展
图论的扩展
2022-07-06 04:43:00 【Zqchang】
超级源点
这个题目就是模板题
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010, M = 20010, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, T;
int h[N], e[M], w[M], ne[M], idx;
int dist[N], q[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
void spfa()
{
int scnt;
scanf("%d", &scnt);
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
while (scnt -- )
{
int u;
scanf("%d", &u);
dist[u] = 0;
q[tt ++ ] = u;
st[u] = true;
}
while (hh != tt)
{
int t = q[hh ++ ];
if (hh == N) hh = 0;
st[t] = false;
for (int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
if (!st[j])
{
q[tt ++ ] = j;
if (tt == N) tt = 0;
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
while (scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &T) != -1)
{
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
idx = 0;
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
spfa();
if (dist[T] == INF) dist[T] = -1;
printf("%d\n", dist[T]);
}
return 0;
}
拆点(分层图)
拯救大兵瑞恩
state是状压那个感觉
拆点其实就是多了一维状态,加了一些限制
在最短路中,所有需要拆点或者分层的问题,都可以先用dp的分析方式来考虑,另一种就是,考虑一下当前这个状态,可以用来更新哪些状态。
所有最短路里面的问题,用第二种比较直观,因为第二种和最短路模型更加接近
也就是考虑当前状态可以更新哪些状态
多一把钥匙是肯定不亏的,所以有钥匙就用钥匙
dp中状态计算有两种方式,第一种是算一下当前这个状态,可以由哪些状态变过来
虽然能用dp的思想来想,但是不能用dp的思想来做,因为dp需要有个拓扑序,但是这个题目中可能存在环
dp可以看成拓扑图上的最短路
这样就可以看作在图中只有0和1两种权值,进而可以用双端队列广搜
跑最短路的时候,为了方便,可以把一个两维坐标映射成一维,如图
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <deque>
#include <set>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 11, M = 360, P = 1 << 10;
int n, m, k, p;
int h[N * N], e[M], w[M], ne[M], idx;
int g[N][N], key[N * N];//给点定编号,记录钥匙所在的地方
int dist[N * N][P];//记录一下这个点的这个状态所用的最小步数
bool st[N * N][P];//判断这个点的这个状态有没有用过
set<PII> edges;
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
void build()
{
int dx[4] = {
-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {
0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
for (int u = 0; u < 4; u ++ )
{
int x = i + dx[u], y = j + dy[u];
if (!x || x > n || !y || y > m) continue;
int a = g[i][j], b = g[x][y];
if (!edges.count({
a, b})) add(a, b, 0);//没有门和墙,有一个双向边
}
}
int bfs()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1][0] = 0;
deque<PII> q;
q.push_back({
1, 0});
while (q.size())
{
PII t = q.front();
q.pop_front();
if (st[t.x][t.y]) continue;
st[t.x][t.y] = true;
if (t.x == n * m) return dist[t.x][t.y];
if (key[t.x])
{
int state = t.y | key[t.x];
if (dist[t.x][state] > dist[t.x][t.y])
{
dist[t.x][state] = dist[t.x][t.y];
q.push_front({
t.x, state});
}
}
for (int i = h[t.x]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (w[i] && !(t.y >> w[i] - 1 & 1)) continue; // 有门并且没有钥匙
if (dist[j][t.y] > dist[t.x][t.y] + 1)
{
dist[j][t.y] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1;
q.push_back({
j, t.y});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> p >> k;
for (int i = 1, t = 1; i <= n; i ++ )//初始化节点编号
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
g[i][j] = t ++ ;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (k -- )
{
int x1, y1, x2, y2, c;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> c;
int a = g[x1][y1], b = g[x2][y2];//找到两点对应的编号
edges.insert({
a, b}), edges.insert({
b, a});//表示这里有一个墙或者门了
if (c) add(a, b, c), add(b, a, c);//建门,墙的话是不能通过的,所以只标记一下,并不建边
}
build();//建立剩余的边
int s;
cin >> s;
while (s -- )
{
int x, y, c;
cin >> x >> y >> c;
key[g[x][y]] |= 1 << c - 1;//记录钥匙
}
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
}
使用dp的思想计数类
dp可以粗略看成是最短路在拓扑图上进行跑
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 400010, mod = 100003;
int n, m;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int dist[N], cnt[N];
int q[N];
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
void bfs()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
cnt[1] = 1;
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
q[0] = 1;
while (hh <= tt)
{
int t = q[hh ++ ];
for (int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + 1)
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + 1;
cnt[j] = cnt[t];
q[ ++ tt] = j;
}
else if (dist[j] == dist[t] + 1)//这里可以看成状态转移方程式
{
cnt[j] = (cnt[j] + cnt[t]) % mod;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
add(a, b), add(b, a);
}
bfs();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) printf("%d\n", cnt[i]);
return 0;
}
这个题目题意大概是,给你起点和终点,问你最多有多少条最短路,如果次短路就比最短路多1,那么还要加上次短路的条数
多开了一维存储次短路,然后像dp一样在dij里面进行更新
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010, M = 20010;
struct Ver
{
int id, type, dist;
bool operator> (const Ver &W) const
{
return dist > W.dist;
}
};
int n, m, S, T;
int h[N], e[M], w[M], ne[M], idx;
int dist[N][2], cnt[N][2];
bool st[N][2];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int dijkstra()
{
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt);
dist[S][0] = 0, cnt[S][0] = 1;
priority_queue<Ver, vector<Ver>, greater<Ver>> heap;
heap.push({
S, 0, 0});
while (heap.size())
{
Ver t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ver = t.id, type = t.type, distance = t.dist, count = cnt[ver][type];
if (st[ver][type]) continue;
st[ver][type] = true;
for (int i = h[ver]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j][0] > distance + w[i])
{
dist[j][1] = dist[j][0], cnt[j][1] = cnt[j][0];
heap.push({
j, 1, dist[j][1]});
dist[j][0] = distance + w[i], cnt[j][0] = count;
heap.push({
j, 0, dist[j][0]});
}
else if (dist[j][0] == distance + w[i]) cnt[j][0] += count;
else if (dist[j][1] > distance + w[i])
{
dist[j][1] = distance + w[i], cnt[j][1] = count;
heap.push({
j, 1, dist[j][1]});
}
else if (dist[j][1] == distance + w[i]) cnt[j][1] += count;
}
}
int res = cnt[T][0];
if (dist[T][0] + 1 == dist[T][1]) res += cnt[T][1];
return res;
}
int main()
{
int cases;
scanf("%d", &cases);
while (cases -- )
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
idx = 0;
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
scanf("%d%d", &S, &T);
printf("%d\n", dijkstra());
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- After learning classes and objects, I wrote a date class
- The most detailed and comprehensive update content and all functions of guitar pro 8.0
- RTP GB28181 文件测试工具
- 饼干(考试版)
- JVM garbage collector concept
- [FreeRTOS interrupt experiment]
- The web project imported the MySQL driver jar package but failed to load it into the driver
- SharedPreferences 源码分析
- The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
- Luogu deep foundation part 1 Introduction to language Chapter 2 sequential structure programming
猜你喜欢
Fedora/rehl installation semanage
How to realize automatic playback of H5 video
Postman前置脚本-全局变量和环境变量
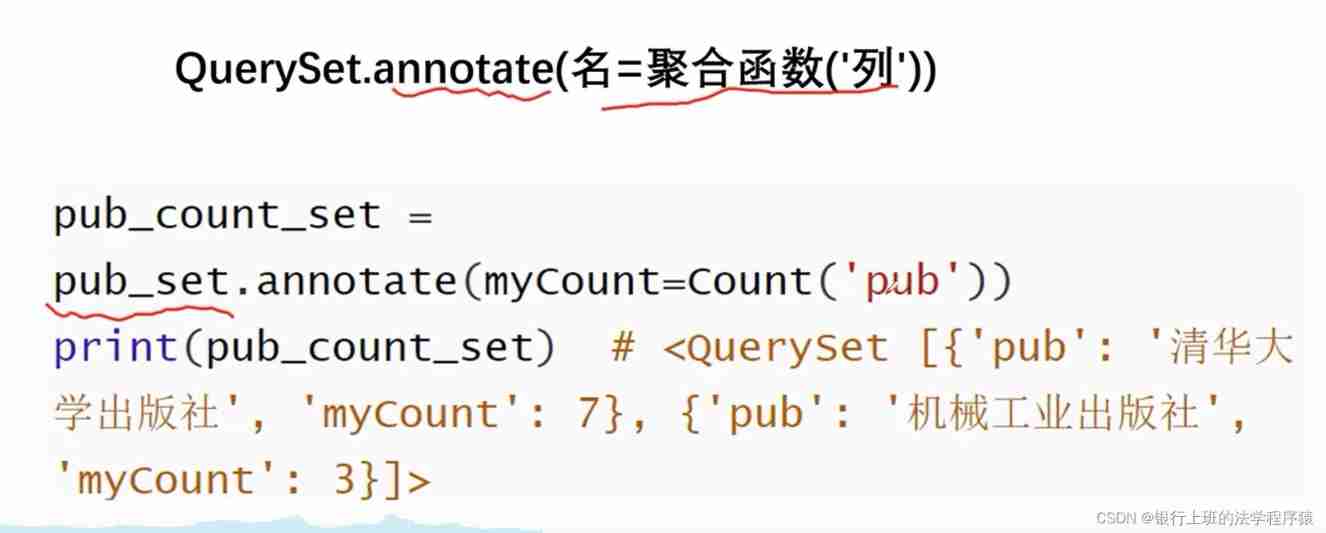
ORM aggregate query and native database operation
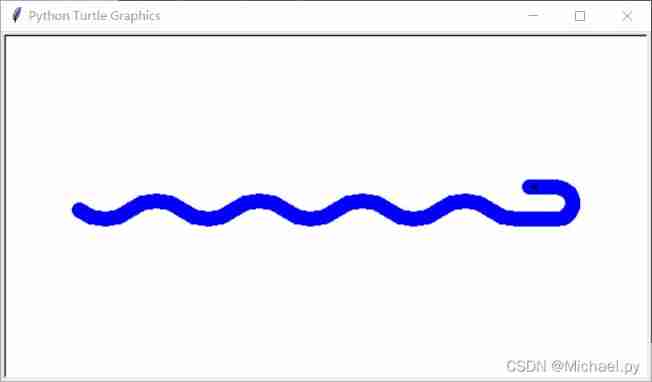
Basic explanation of turtle module - draw curve
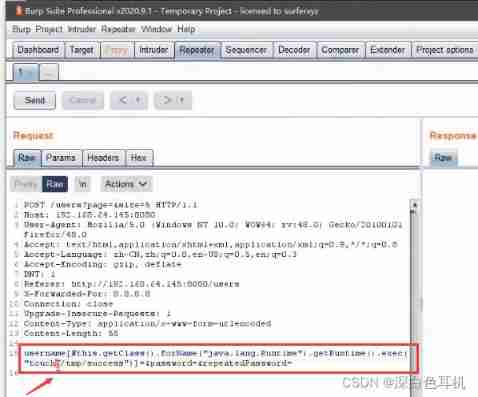
Vulnerability discovery - vulnerability probe type utilization and repair of web applications

程序员在互联网行业的地位 | 每日趣闻

Easyrecovery reliable and toll free data recovery computer software
![[mathematical modeling] differential equation -- sustainable development of fishing industry](/img/7c/2ab6f2a34bc2c97318537ec8e0b0c5.png)
[mathematical modeling] differential equation -- sustainable development of fishing industry
11. Intranet penetration and automatic refresh
随机推荐
Chip debugging of es8316 of imx8mp
也算是学习中的小总结
Redis —— Redis In Action —— Redis 实战—— 实战篇一 —— 基于 Redis 的短信登录功能 —— Redis + Token 的共享 session 应用— 有代码
Lagrange polynomial
View workflow
8. Static file
Dry goods collection | Vulkan game engine video tutorial
win10电脑系统里的视频不显示缩略图
Etcd database source code analysis -- etcdserver bootstrap initialization storage
Excellent PM must experience these three levels of transformation!
Delete subsequence < daily question >
Redis - redis in action - redis actual combat - actual combat Chapter 1 - SMS login function based on redis - redis + token shared session application - with code
tengine 内核参数
Yyds dry inventory automatic lighting system based on CC2530 (ZigBee)
也算是學習中的小總結
[Zhao Yuqiang] deploy kubernetes cluster with binary package
Can CDC pull the Oracle table in full
Selection of slow motion function
Postman测试报告
Jd.com 2: how to prevent oversold in the deduction process of commodity inventory?