当前位置:网站首页>Depth first search of graph
Depth first search of graph
2022-07-03 16:55:00 【Wukong doesn't buy vegetables anymore】
That is to say , How to traverse a graph structure , So here is an idea provided by our predecessors , Called depth first search , That is to say DFS(Depth First Search):
Its idea : Suppose our graph here is the structure of a tree
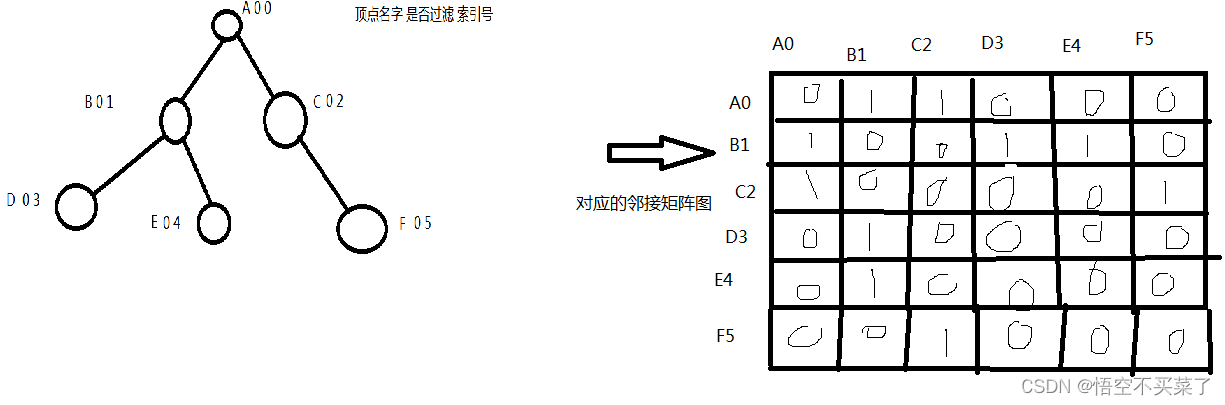
In fact, for the depth traversal of a graph , Or use the idea of recursion :
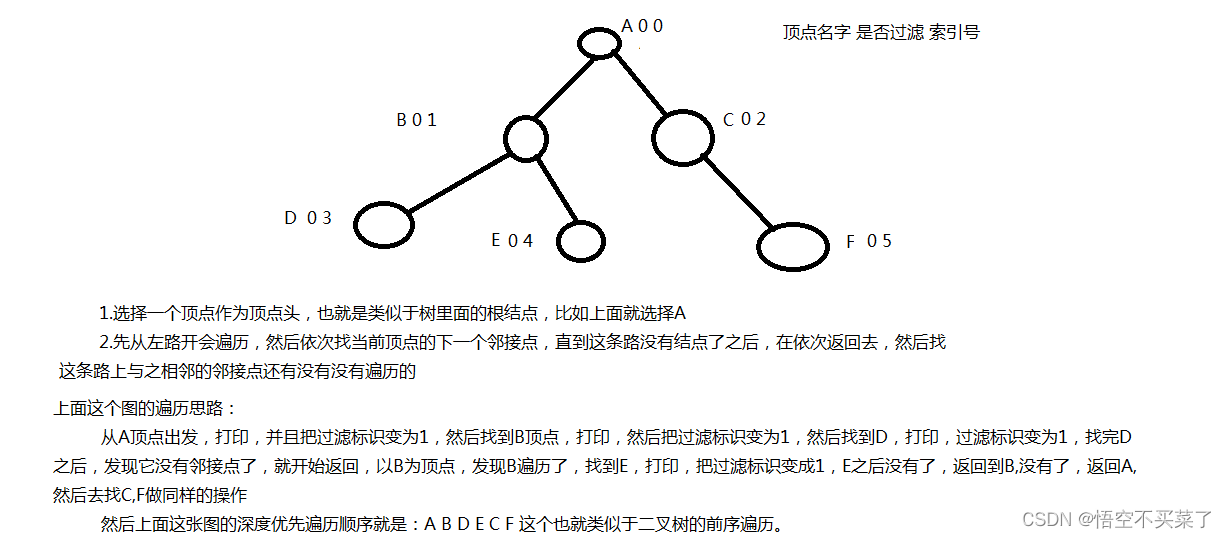
Let's look at the specific recursive analysis process :

Don't talk much , Go straight to the code , The following is the implementation traversal of the adjacency matrix of an undirected graph
undirected_graph.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// Maximum number of vertices
#define MAX_VERTEX 30
// Set an array that identifies whether vertices are accessed
int visit[MAX_VERTEX];
// Define the graph structure
typedef struct _graph
{
// Vertex array , Store vertex names
char **vertex;
// Array of edges
int edge[MAX_VERTEX][MAX_VERTEX];
// Number of vertices
int vertex_num;
// The number of sides
int edge_num;
}graph;
// Calculate the position of the user input vertex in the array
// Here, for example, enter a v1,v2, So for an undirected graph ,(v1,v2) And (v2,v1) All represent the same side
int calc_vertex_pos(graph &g,char* v)
{
// Traverse the vertex array
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
// This is equivalent to string comparison
if(strcmp(v,g.vertex[i]) == 0) {
return i;// Find and return directly to this location
}
}
return -1;
}
// Create a diagram
void create_graph(graph &g)
{
printf(" Please enter the number of vertices and edges of the graph : The vertices edge \n");
scanf("%d %d",&g.vertex_num,&g.edge_num);
printf(" Please enter %d A peak value \n",g.vertex_num);
// Start a loop to assign vertex values to the vertex array
// Before assignment, you need to make room on the heap to store the string
g.vertex = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * g.vertex_num);
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
char str[100] = {0};
scanf("%s",str);
// This array points to an allocated space
g.vertex[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (strlen(str) + 1));
strcpy(g.vertex[i],str);
}
// Initialize the two-dimensional array of edges
// Count by the number of vertices n, To form a n*n Two dimensional array of
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
for(int j = 0;j < g.vertex_num;j++) {
// Initialize all the corresponding edges to 0 Does not exist
g.edge[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// The contents of the above two arrays are initialized
// Let's set the relationship between edges , Is whether there is an edge
printf(" Please enter %d Edges and their corresponding vertices 1, The vertices 2\n",g.edge_num);
// Set the relationship between two vertices with edges
char v1[10];
char v2[10];
// How many sides are there , It corresponds to how many vertices there are
for(int i = 0;i < g.edge_num;i++) {
scanf("%s %s",v1,v2);
// Then we calculate the position of the vertex in the array
// yes 0 ah ,1 ah , still 2 Ah, wait, such a relationship
int m = calc_vertex_pos(g,v1);// such as v1=0
int n = calc_vertex_pos(g,v2);//v2 = 1 (0,1) It means there is an edge , Set the position value to 1
// meanwhile (1,0) This position should also be set to 1, After all, it is an undirected graph
g.edge[m][n] = 1;
g.edge[n][m] = 1;
}
}
// Print a picture
void print_graph(graph& g)
{
// To print a graph is to print this two-dimensional array
printf("\t");
// Loop horizontal vertex header
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
printf("%s\t",g.vertex[i]);
}
// Loop through the contents of a two-dimensional array
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
// Print horizontal vertex header
printf("\n");// Change one line at a time
printf("%s\t",g.vertex[i]);
// Then output a line of content
for(int j = 0;j < g.vertex_num;j++) {
printf("%d\t",g.edge[i][j]);
}
}
printf("\t");
}
// Depth first search on a map
void DFS(graph &g,int index)
{
// Change the access mark of this point to 1
visit[index] = 1;
// Then print this point
printf("%s ",g.vertex[index]);
// Then traverse the adjacent nodes all the way down
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
if(g.edge[index][i] == 1 && visit[i] != 1) {
DFS(g,i);// It shows that this point can also be printed
}
}
}
void DFSTraverse(graph &g)
{
// Initialize the filtered identifier of the vertex array
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
visit[i] = 0;// None of them were visited
}
// Traverse each vertex at once
for(int j = 0;j < g.vertex_num;j++) {
// Judge the mark of this point
if(visit[j] != 1) {
DFS(g,j);
}
}
}
// Build a diagram
void test01()
{
graph g;
create_graph(g);
print_graph(g);
printf("\n---------\n");
DFSTraverse(g);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
Running results :
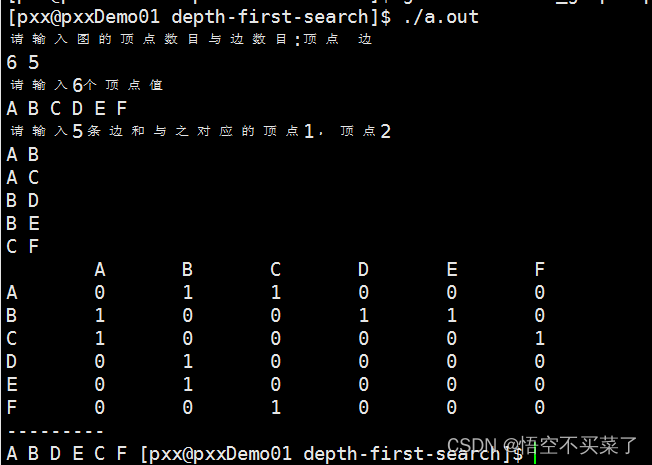
Okay , This is the depth first search of adjacency matrix undirected graph , The same is true for directed graphs , Is this similar to the preorder traversal of a binary tree , But this is only for the adjacency matrix , Let's see how to traverse a graph represented by adjacency table .
Let's talk about :

Go straight to the code :
undirect_graph1.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// The maximum number of vertices that can be stored
#define MAX_VERTEX 100
int visit[MAX_VERTEX];
struct edge_node {
int position;// The said vertex Which node index in the array
edge_node *next;// Store the pointer of the next adjacent contact
// The weight here can be written or not
};
struct vertex {
char *name;// Store vertex names , The first level pointer points to the space allocated on a heap
// There is also the storage of each adjacent first adjacent contact , In fact, here it is equivalent to the head node
edge_node *first_node;
};
// Finally, you need the structure of the whole graph
// To store the information of the corresponding diagram
struct graph {
// Store all the information of the vertex
vertex head[MAX_VERTEX];
// Number of vertices and edges
int vertex_num;
int edge_num;
};
// Let's determine the vertex position
int find_pos(graph &g,char *v)// here v If there is a point, you can print , I mean scanf It's impossible to assign values directly
{
for (int i = 0; i < g.vertex_num; i++) {
// Loop the space where the vertex names are stored
if (strcmp(g.head[i].name, v) == 0) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Let's create a diagram first
void create_graph(graph &g)
{
printf(" Please enter the number of vertices and edges :\n");
scanf("%d %d", &g.vertex_num, &g.edge_num);
// Cycle through the values of the vertices
printf(" Please enter %d A peak value :\n", g.vertex_num);
// Loop to assign values to vertices
for (int i = 0; i < g.vertex_num; i++){
char str[30] = { 0 };
scanf("%s", str);
// pure scanf("%s",&g.head[i].name) Definitely not , This name It's a two-level pointer
g.head[i].name = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (strlen(str) + 1));
strcpy(g.head[i].name, str);// In which index position to store the vertex
// In addition to the assignment string , You also need to initialize the address of an adjacent node
g.head[i].first_node = NULL;// Similar to every overhead point next Is full of NULL
}
// Let's start by entering edges , That is, two vertices
printf(" Please enter %d side , The vertices 1, The vertices 2", g.edge_num);
char v1[10];
char v2[10];
// Loop to assign values to edges
for (int i = 0; i < g.edge_num; i++) {
scanf("%s %s", v1,v2);
int m = find_pos(g, v1);
int n = find_pos(g, v2);
// Number of each vertex found in memory
// And then for example m Is it the head representing a vertex , Here you can.
// As the head of the linked list
// Then we implement header insertion , To express a connection
// Finally, we implement an interaction of the relationship , This is for an undirected graph v1 And v2 and v2 And v1 Same relationship
// Create a new adjacency point
edge_node *p_new = (edge_node*)malloc(sizeof(edge_node));
// Then start inserting... In the head , This head is m spot
p_new->position = n;
// here p_new Must first refer to
p_new->next = g.head[m].first_node;
g.head[m].first_node = p_new;
// Then implement v0 And v1 An alternation of , It means
edge_node *p_new1 = (edge_node*)malloc(sizeof(edge_node));
// In fact, it is to achieve a m And n Alternation of
p_new1->position = m;
p_new1->next = g.head[n].first_node;
g.head[n].first_node = p_new1;
}
}
// Print this picture
void print_graph(graph &g)
{
for (int i = 0; i < g.vertex_num; i++) {
printf("%s: ", g.head[i].name);
// Get the head node to traverse a single linked list
edge_node *p_node = g.head[i].first_node;
while (p_node != NULL) {
// Get is n, Looking for it m
int index = p_node->position;
printf("%s ", g.head[index].name);
p_node = p_node->next;
}
// Line break
printf("\n");
}
}
// Depth first traversal of adjacency table
void DFS(graph &g,int index)
{
// Change this logo into 1
visit[index] = 1;
printf("%s ",g.head[index].name);// Print vertex
edge_node *p_node = g.head[index].first_node;
// There is a cycle inside
while(p_node != NULL) {
int index = p_node->position;
// Judge whether this point has been traversed
if(!visit[index]) {
DFS(g,index);
}
p_node = p_node->next;
}
}
void DFSTraverse(graph &g)
{
// Initialize all vertex traversal identifiers to 0
for(int i = 0;i < g.vertex_num;i++) {
visit[i] = 0;
}
// Then start traversing each vertex
for(int j = 0;j < g.vertex_num;j++) {
// Vertices that have not been traversed will come in
if(!visit[j]) {
DFS(g,j);
}
}
}
int main()
{
graph g;
create_graph(g);
print_graph(g);
printf("\n---------------\n");
DFSTraverse(g);
return 0;
}
Running results :

Why don't you want to traverse the preorder , Because when we insert data with adjacency table , Is to choose the head plug , such as A B After the deposit ,A C Come in again , Then memory means death A C B , So you want to traverse the preamble , Input The edge can be changed into A B C That's all right. .
Next, let's analyze the large of adjacency matrix and adjacency table O, For adjacency matrices , He is looking for all the corresponding edges from the two-dimensional array , So its time complexity is O(n^2), For adjacency tables , Lies in the number of vertices and edges , More time-consuming , So its time complexity is O(n), Relatively speaking, it's ok , Especially for many points , Sparse graph with few edges , Time efficiency is very high .
边栏推荐
- What material is sa537cl2? Analysis of mechanical properties of American standard container plate
- 比亚迪、长城混动市场再“聚首”
- Analysis of variance summary
- Necessary ability of data analysis
- Leetcode: lucky number in matrix
- 关于学习Qt编程的好书精品推荐
- PyTorch 1.12发布,正式支持苹果M1芯片GPU加速,修复众多Bug
- 匯編實例解析--實模式下屏幕顯示
- LeetCode 1657. Determine whether the two strings are close
- What is the pledge pool and how to pledge?
猜你喜欢
A survey of state of the art on visual slam
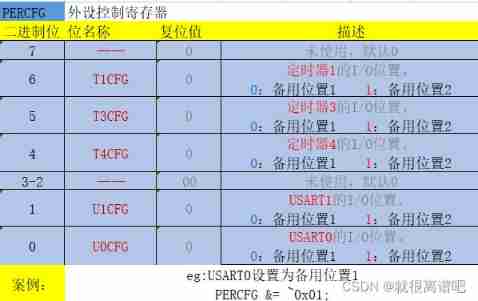
CC2530 common registers for serial communication
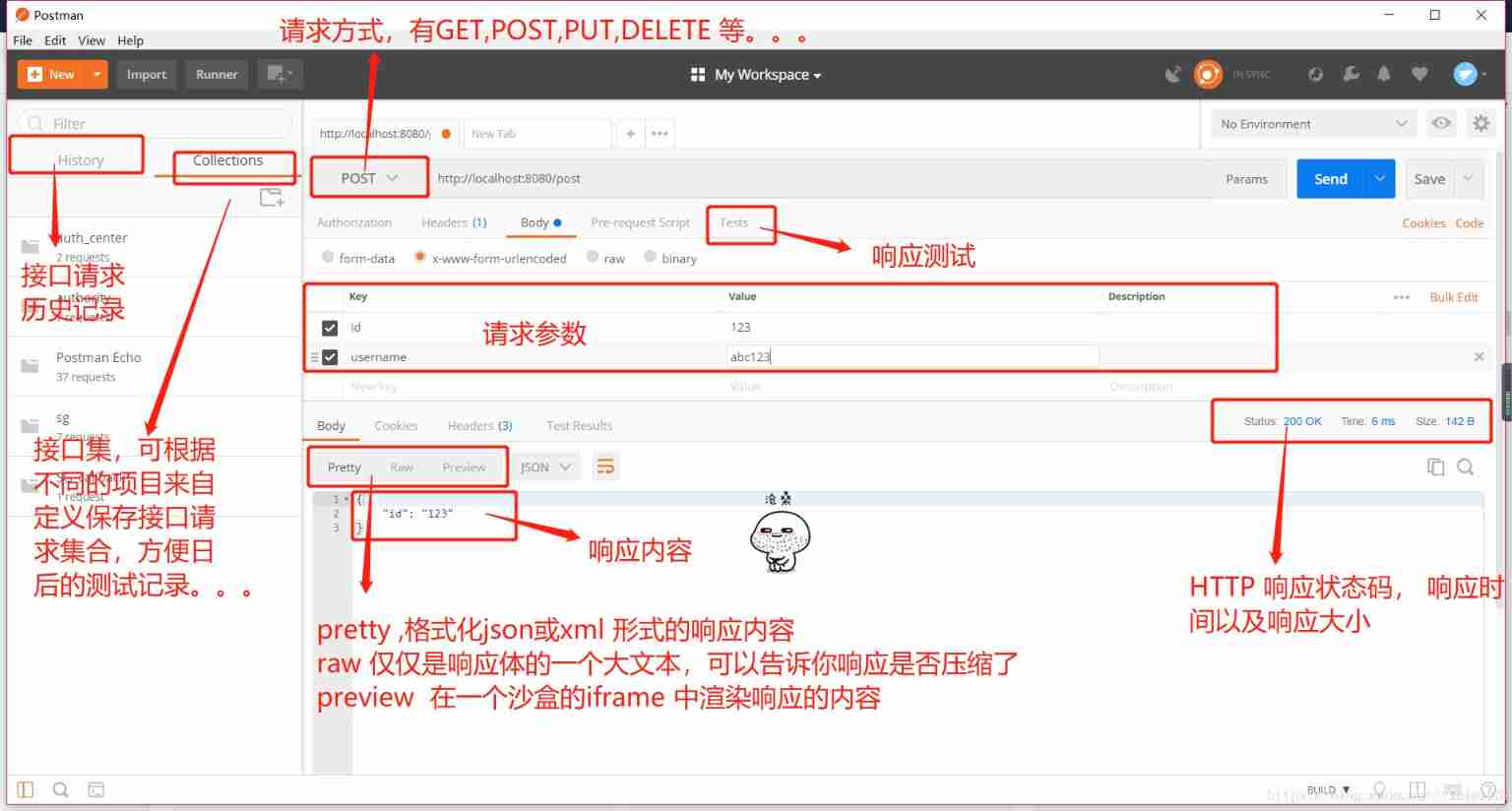
The most complete postman interface test tutorial in the whole network, API interface test

Thread pool executes scheduled tasks
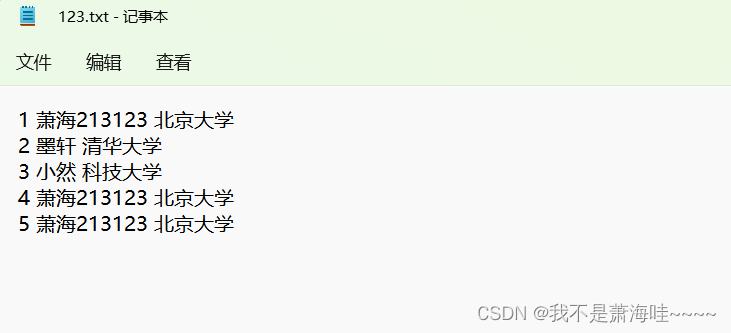
C语言按行修改文件

Static program analysis (I) -- Outline mind map and content introduction

线程池:业务代码最常用也最容易犯错的组件
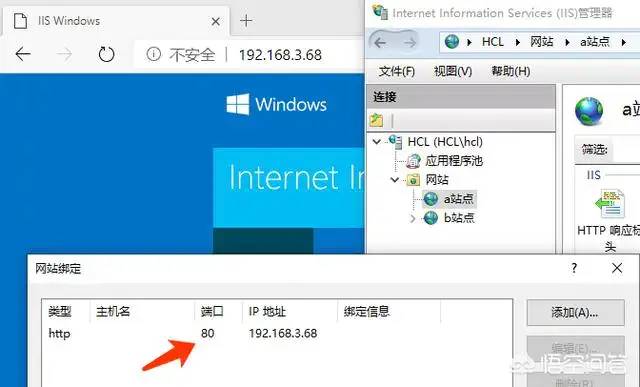
一台服务器最大并发 tcp 连接数多少?65535?
爱可可AI前沿推介(7.3)

于文文、胡夏等明星带你玩转派对 皮皮APP点燃你的夏日
随机推荐
What is the maximum number of concurrent TCP connections for a server? 65535?
Data driving of appium framework for mobile terminal automated testing
美团一面:为什么线程崩溃崩溃不会导致 JVM 崩溃
Necessary ability of data analysis
Central South University | through exploration and understanding: find interpretable features with deep reinforcement learning
消息队列消息丢失和消息重复发送的处理策略
Yu Wenwen, Hu Xia and other stars take you to play with the party. Pipi app ignites your summer
Kotlin learning quick start (7) -- wonderful use of expansion
匯編實例解析--實模式下屏幕顯示
网络安全web渗透技术
PHP production website active push (website)
[combinatorics] recursive equation (characteristic equation and characteristic root | example of characteristic equation | root formula of monadic quadratic equation)
于文文、胡夏等明星带你玩转派对 皮皮APP点燃你的夏日
[combinatorics] polynomial theorem (polynomial coefficients | full arrangement of multiple sets | number of schemes corresponding to the ball sub model | polynomial coefficient correlation identity)
[Jianzhi offer] 58 - ii Rotate string left
ucore概述
关于学习Qt编程的好书精品推荐
Shentong express expects an annual loss of nearly 1billion
2022爱分析· 国央企数字化厂商全景报告
Overview of satellite navigation system