当前位置:网站首页>Krypton Factor purple book chapter 7 violent solution
Krypton Factor purple book chapter 7 violent solution
2022-07-05 23:07:00 【Porter hunter of the program】
Catalog
Title Description
Background
You have been employed by the organisers of a Super Krypton Factor Contest in which contestants have very high mental and physical abilities. In one section of the contest the contestants are tested on their ability to recall a sequenace of characters which has been read to them by the Quiz Master. Many of the contestants are very good at recognising patterns. Therefore, in order to add some difficulty to this test, the organisers have decided that sequences containing certain types of repeated subsequences should not be used. However, they do not wish to remove all subsequences that are repeated, since in that case no single character could be repeated. This in itself would make the problem too easy for the contestants. Instead it is decided to eliminate all sequences containing an occurrence of two adjoining identical subsequences. Sequences containing such an occurrence will be called “easy”. Other sequences will be called “hard”.
For example, the sequence ABACBCBAD is easy, since it contains an adjoining repetition of the subsequence CB. Other examples of easy sequences are:
- BB
- ABCDACABCAB
- ABCDABCD
Some examples of hard sequences are:
- D
- DC
- ABDAB
- CBABCBA
In order to provide the Quiz Master with a potentially unlimited source of questions you are asked to write a program that will read input lines from standard input and will write to standard output.
Input description
Each input line contains integers nn and LL (in that order), where n>0n>0 and LL is in the range 1≤L≤261≤L≤26. Input is terminated by a line containing two zeroes.
Output description
For each input line prints out the nn-th hard sequence (composed of letters drawn from the first LL letters in the alphabet), in increasing alphabetical order (Alphabetical ordering here corresponds to the normal ordering encountered in a dictionary), followed (on the next line) by the length of that sequence. The first sequence in this ordering is ‘A’. You may assume that for given nn and LL there do exist at least nn hard sequences.
As such a sequence is potentially very long, split it into groups of four (4) characters separated by a space. If there are more than 16 such groups, please start a new line for the 17th group.
Your program may assume a maximum sequence length of 80.
For example, with L=3L=3, the first 7 hard sequences are:
A
AB
ABA
ABAC
ABACA
ABACAB
ABACABA
The sample input
7 3
30 3
0 0
Sample output
ABAC ABA
7
ABAC ABCA CBAB CABA CABC ACBA CABA
28
The main idea of the topic
Enter a n and L, From before L A difficult string of letters ( Adjacent ones do not have the same string ), Sort in dictionary order , Output No n A difficult string .
Ideas
Recursive deep search , Add judgment , Judge the time, just judge the suffix , The previous part has determined that the conditions are met , Just judge the later .
AC Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N = 1e5+10;
int n,l,cnt;
int a[N];
int dfs(int t)
{
if(cnt++ == n){// Already found No n individual
for(int i = 0;i < t;i++)// Output time pay attention to the format required by the topic
{
if(i%4 == 0 && i != 0 && i%64 != 0)
cout << " ";
else if(i != 0 && i%64 == 0)
cout << endl;
printf("%c", 'A'+a[i]);
}
if(t%64 != 0)
cout << endl;
cout << t << endl;
return 0;
}
for(int i = 0;i < l;i++){// Deep search traversal
a[t] = i;
int flag = 1;
for(int j = 1;j*2 <= t+1;j++){// Judge whether the conditions of difficult string are met
int flag1 = 1;
for(int k = 0;k <j;k++){
if(a[t-k] != a[t-j-k]){
flag1 = 0;
break;
}
}
if(flag1)
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
/*
Judgment method : From the end , If the last one is not equal to the one adjacent to the front, the first one is satisfied ,
Secondly, make two judgments at intervals , In turn , Judge whether there is dissatisfaction .
Because it has been judged before , So each one only needs to be sentenced once .
*/
if(flag){
if(!dfs(t+1))//!dfs The representative found it and returned 0
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main()
{
while(cin >> n >> l){
cnt = 0;
if(n == 0 && l == 0){
return 0;
}
dfs(0);
}
}
Be careful
Particular attention : Format problem , The title clearly states , Every time 4 One for a group , One line at a time 16 Group , Output length time , If there happens to be one last 16 There is no need to wrap a group , If not , Need to output a newline .
边栏推荐
- Evolution of APK reinforcement technology, APK reinforcement technology and shortcomings
- Multi view 3D reconstruction
- Three.js-01 入门
- Common model making instructions
- d3dx9_ What if 29.dll is missing? System missing d3dx9_ Solution of 29.dll file
- Metasploit (MSF) uses MS17_ 010 (eternal blue) encoding:: undefined conversionerror problem
- February 13, 2022 -5- maximum depth of binary tree
- 并查集实践
- Thoroughly understand JVM class loading subsystem
- Non rigid / flexible point cloud ICP registration
猜你喜欢

February 13, 2022-4-symmetric binary tree
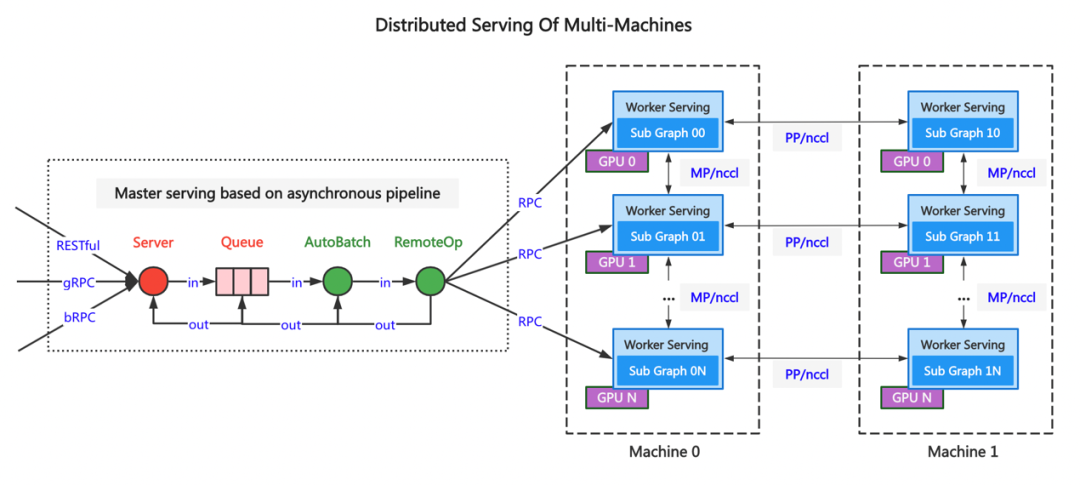
Paddle Serving v0.9.0 重磅发布多机多卡分布式推理框架
Common model making instructions
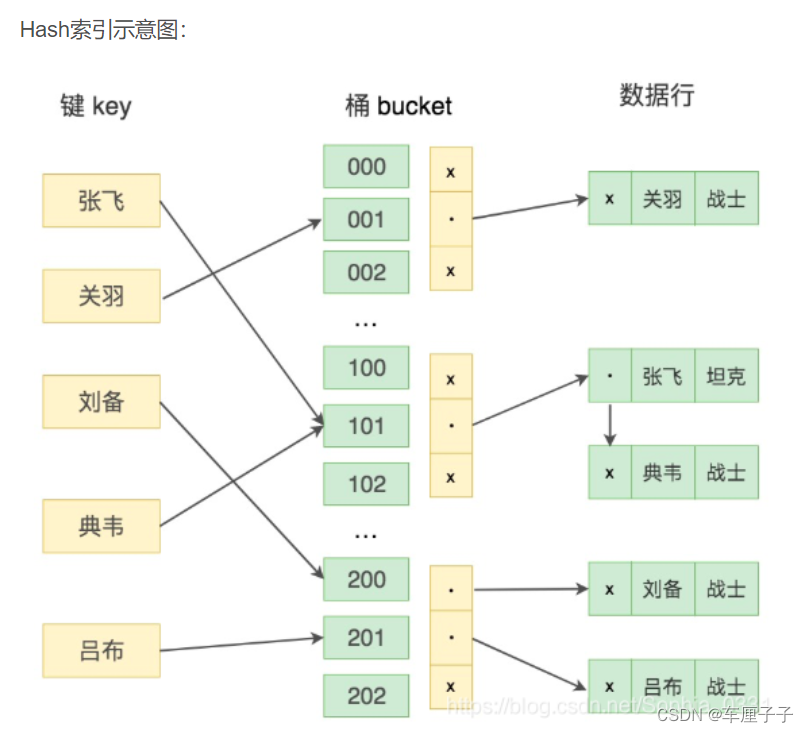
Basic knowledge of database (interview)
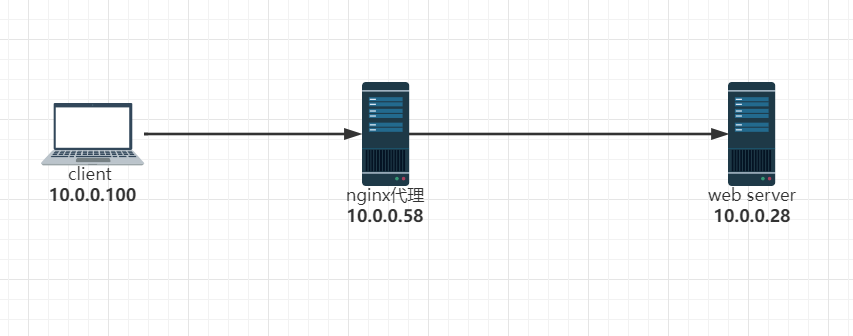
实现反向代理客户端IP透传

2:第一章:认识JVM规范1:JVM简介;
2022 G3 boiler water treatment simulation examination and G3 boiler water treatment simulation examination question bank
d3dx9_ How to repair 31.dll_ d3dx9_ 31. Solution to missing DLL
Getting started stm32--gpio (running lantern) (nanny level)
TypeError: this. getOptions is not a function
随机推荐
3 find the greatest common divisor and the least common multiple
Global and Chinese market of networked refrigerators 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Global and Chinese market of water treatment technology 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
openresty ngx_lua正则表达式
Yiwen gets rid of the garbage collector
Global and Chinese markets of tantalum heat exchangers 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Nail error code Encyclopedia
Metasploit(msf)利用ms17_010(永恒之蓝)出现Encoding::UndefinedConversionError问题
[digital signal denoising] improved wavelet modulus maxima digital signal denoising based on MATLAB [including Matlab source code 1710]
Methods modified by static
Evolution of APK reinforcement technology, APK reinforcement technology and shortcomings
Common model making instructions
Element positioning of Web Automation
Alibaba Tianchi SQL training camp task4 learning notes
[speech processing] speech signal denoising and denoising based on Matlab GUI low-pass filter [including Matlab source code 1708]
Distributed solution selection
Selenium+Pytest自动化测试框架实战
TOPSIS code part of good and bad solution distance method
利用LNMP实现wordpress站点搭建
Krypton Factor-紫书第七章暴力求解