当前位置:网站首页>A complete tutorial for getting started with redis: problem location and optimization
A complete tutorial for getting started with redis: problem location and optimization
2022-07-07 02:49:00 【Gu Ge academic】
Redis Persistence has always been an impact Redis High incidence of performance , In this section, we combine common
Analyze, locate and optimize persistence problems .
5.3.1 fork operation
When Redis do RDB or AOF When rewriting , An essential operation is to perform fork Operational innovation
Build a process , For most operating systems fork It was a big mistake . although fork Created
The child process does not need to copy the physical memory space of the parent process , But the space memory pages of the parent process will be copied
surface . For example, for 10GB Of Redis process , You need to copy about 20MB Memory page table for , therefore fork
The operation time is closely related to the total memory of the process , If you use virtualization technology , especially Xen fictitious
machine ,fork The operation will be more time-consuming .
fork Time consuming problem location : For high flow Redis example OPS Can be up to 5 All the above , If fork
The operation time will slow down at the second level Redis Tens of thousands of orders are executed , The impact on online application delay is very
obvious . Under normal circumstances fork The time should be every GB Consume 20 Millisecond or so . Can be in info stats system
Check in the plan latest_fork_usec Indicator acquisition last fork Operating time , Unit microseconds .
How to improve fork Operation time :
1) Prefer physical machines or efficient support fork Virtualization technology of operation , Avoid using
Xen.
2) control Redis Instance maximum available memory ,fork Time consumption is proportional to the amount of memory , Online suggestions
Every Redis Instance memory control in 10GB within .
3) The reasonable configuration Linux Memory allocation policy , Avoid low physical memory fork Failure , have
See 12.1 section “Linux Configuration optimization ”.
4) Reduce fork Frequency of operation , Such as moderate relaxation AOF Automatic trigger time , Avoid unnecessary
Full replication of .
5.3.2 Subprocess cost monitoring and optimization
The subprocess is responsible for AOF perhaps RDB File rewriting , Its operation process mainly involves CPU、 Inside
save 、 Consumption of three parts of hard disk .
1.CPU
·CPU Overhead analysis . The subprocess is responsible for writing the data in the process to the file in batches , This process
Belong to CPU Intensive operation , Usually subprocesses are single core CPU The utilization rate is close to 90%.
·CPU Consumption optimization .Redis yes CPU Intensive services , Do not bind single core CPU operation .
Because subprocesses are very expensive CPU, It will compete with the parent process for single core resources .
Don't talk to other people CPU Intensive services deployed together , cause CPU Over competition .
If you deploy multiple Redis example , Try to ensure that only one child process performs rewriting at the same time
Work , See... For details 5.4 Section multi instance deployment ”.
2. Memory
· Memory consumption analysis . Child process passed fork Operation produces , The occupied memory size is equal to that of the parent
cheng , In theory, you need twice as much memory to complete the persistence operation , but Linux There is a copy on write mechanism
(copy-on-write). Parent child processes share the same physical memory page , When the parent process handles write requests
Ask time to create a copy of the page to be modified , And the child process is fork The entire parent process is shared during operation
memory dump .
· Memory consumption monitoring .RDB When rewriting ,Redis The log output capacity is as follows :
* Background saving started by pid 7692
* DB saved on disk
* RDB: 5 MB of memory used by copy-on-write
* Background saving terminated with success
If there are memory modification operations during rewriting , The parent process is responsible for creating the secondary of the modified memory page
Ben , It can be seen from the log that this part of memory is consumed 5MB, It can be regarded as RDB Rewrite consumption
了 5MB Of memory .
AOF When rewriting ,Redis The log output capacity is as follows :
* Background append only file rewriting started by pid 8937
* AOF rewrite child asks to stop sending diffs.
* Parent agreed to stop sending diffs. Finalizing AOF...
* Concatenating 0.00 MB of AOF diff received from parent.
* SYNC append only file rewrite performed
* AOF rewrite: 53 MB of memory used by copy-on-write
* Background AOF rewrite terminated with success
* Residual parent diff successfully flushed to the rewritten AOF (1.49 MB)
* Background AOF rewrite finished successfully
The consumption of page copy maintained by the parent process is the same as RDB The rewriting process is similar to , The difference is AOF Rewriting requires
want AOF Rewrite buffer , Therefore, the memory consumption can be estimated as :
53MB+1.49MB, That is to say AOF The amount of memory consumed by child processes when rewriting .
Operation and maintenance tips
To write shell The script is based on Redis Logs can quickly locate excessive memory consumption during child process rewriting
situation .
Memory consumption optimization :
1) Same as CPU Optimization is the same. , If you deploy multiple Redis example , Try to ensure that there are only
A subprocess is working .
2) Avoid child process rewriting in case of a large number of writes , This will cause the parent process to maintain a large number of
Page copy , Cause memory consumption .
Linux kernel stay 2.6.38 The kernel has added Transparent Huge Pages(THP), Support
huge page(2MB) Page allocation , Default on . When turned on, it can reduce fork Create child process
The speed of , But enforcement fork after , If open THP, Copy page units from the original 4KB Turn into
2MB, It will greatly increase the memory consumption of the parent process during rewriting . It is recommended to set “sudo echo
never>/sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled” close THP. more THP details
See 12.1 section Linux Configuration optimization ”.
3. Hard disk
· Hard disk overhead analysis . The main responsibility of the subprocess is to AOF perhaps RDB Files written to the hard disk are persistent
turn . It is bound to cause hard disk write pressure . according to Redis rewrite AOF/RDB The amount of data , Combined with the system
Tools such as sar、iostat、iotop etc. , The hard disk load during rewriting can be analyzed .
· Hard disk overhead optimization . The optimization method is as follows :
a) Don't deploy with other services with high hard disk load . Such as : Storage service 、 Information team
Column services, etc .
b)AOF Rewriting consumes a lot of hard disk IO, Configuration can be turned on no-appendfsync-on-
rewrite, Off by default . It means that AOF Don't do it during rewriting fsync operation .
c) When open AOF Functional Redis Used when writing scenes with high traffic , If ordinary machinery is used
disk , Write throughput is generally in 100MB/s about , At this time Redis The bottleneck of the instance mainly lies in AOF Sync
On hard disk .
343
d) For a stand-alone configuration, there are multiple configurations Redis Examples , Different instances can be configured for disk storage
AOF file , Allocate the hard disk write pressure .
Operation and maintenance tips
To configure no-appendfsync-on-rewrite=yes when , In extreme cases, the whole... May be lost AOF
Data during rewriting , You need to decide whether to configure according to data security .
5.3.3 AOF Add blocking
When open AOF Persistence , The common strategy of synchronizing the hard disk is everysec, For balance
And data security . For this way ,Redis Use another thread to execute... Per second fsync Sync
Hard disk . When the system hard disk resources are busy , Can cause Redis Main thread blocking , Pictured 5-5 Shown .
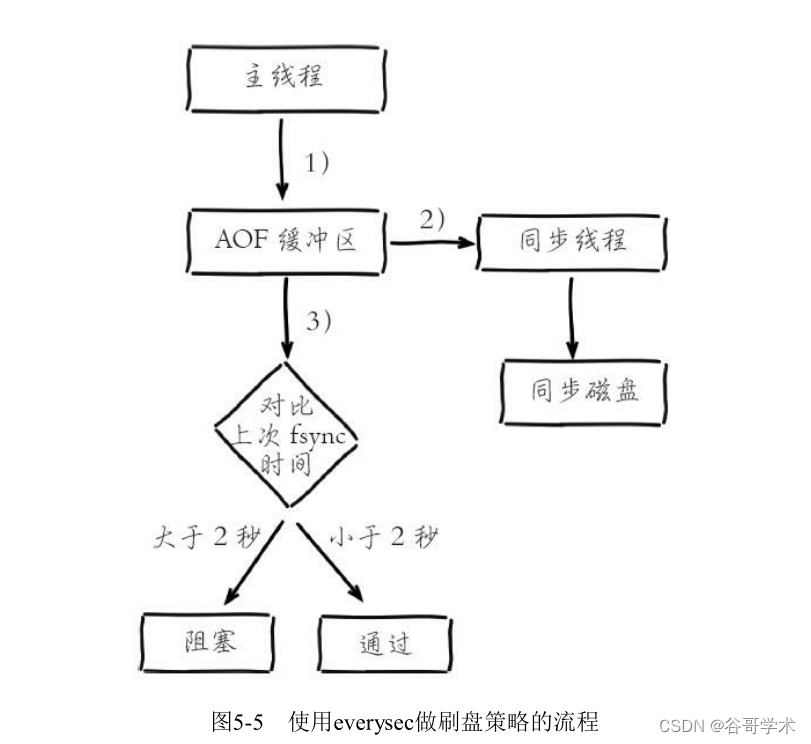
Blocking process analysis :
1) The main thread is responsible for writing AOF buffer .
2)AOF The thread is responsible for performing synchronous disk operations once a second , And record the last synchronization
between .
3) The main thread is responsible for comparing the last time AOF Synchronization time :
· If the last synchronization success time is in 2 Seconds , The main thread directly returns .
· If the time from the last successful synchronization exceeds 2 second , The main thread will block , Until the synchronization operation is completed
become .
Through to AOF Two problems can be found in blocking processes :
1)everysec Configuration can be lost at most 2 Second data , No 1 second .
2) If the system fsync slow , Will lead to Redis Main thread blocking affects efficiency .
AOF Blocking problem location :
1) happen AOF Blocking time ,Redis Output the following log , Used to record AOF fsync Blocking causes
Slow down Redis The act of serving :
Asynchronous AOF fsync is taking too long (disk is busy). Writing the AOF buffer
without waiting for fsync to complete, this may slow down Redis
2) Whenever it happens AOF When an additional blocking event occurs , stay info Persistence In statistical work, ,
aof_delayed_fsync The indicators will add up , Check this indicator to facilitate positioning AOF Blocking problem .
3)AOF Synchronization allows up to 2 Second delay , When the delay occurs, it indicates that the hard disk is under high load
topic , You can use monitoring tools such as iotop, Positioning consumes hard disk IO Process of resources .
Optimize AOF The additional blocking problem is mainly to optimize the system hard disk load , See the previous section for optimization methods .
5.4 Multi instance deployment
Redis Single threaded architecture makes it impossible to make full use of CPU Multicore properties , The usual practice is to
More than one... Deployed on machines Redis example . When multiple instances are enabled AOF After rewriting , Will produce between each other
Pair up CPU and IO competition . This section mainly introduces the analysis and optimization of this scenario .
The previous section introduced the subprocess overhead related to persistence . For single machines Redis Deploy , If
Run multiple sub processes at the same time , The impact on the current system will be very obvious , Therefore, a
measures , Isolate subprocess work .Redis stay info Persistence Provides us with monitoring
Metrics for the health of child processes , As shown in the table 5-2 Shown .
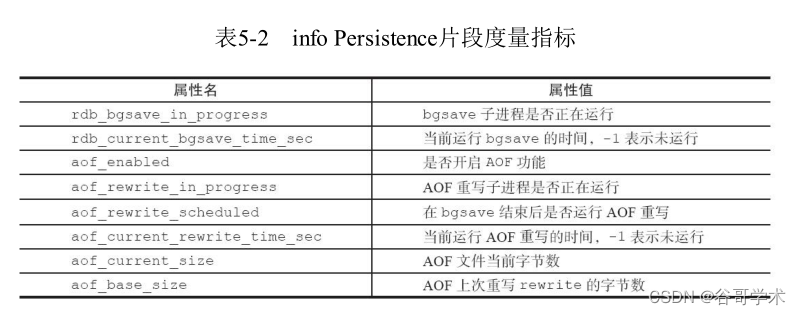
Based on the above indicators , It can be controlled by external program polling AOF Execution of rewrite operation ,
The whole process is as shown in the figure 5-6 Shown .

Process description :
1) External programs regularly poll and monitor the machine (machine) On all the Redis example .
2) For opening AOF Example , see (aof_current_size-
aof_base_size)/aof_base_size Confirm the growth rate .
3) When the growth rate exceeds a certain threshold ( Such as 100%), perform bgrewriteaof Command manual trigger
Of the current instance AOF rewrite .
4) Cycle check during operation aof_rewrite_in_progress and
aof_current_rewrite_time_sec indicators , until AOF Rewrite end .
5) Confirm instance AOF After rewriting , Check other instances and repeat 2)~4) Step by step .
So as to ensure that every Redis example AOF Rewrite serialization execution .
边栏推荐
- Niuke programming problem -- double pointer of 101 must be brushed
- [Mori city] random talk on GIS data (II)
- Wireshark installation
- Argo workflows source code analysis
- unity中跟随鼠标浮动的面板,并可以自适应文字内容的大小
- Huitong programming introductory course - 2A breakthrough
- Compress JS code with terser
- HAVE FUN | “飞船计划”活动最新进展
- Fundamentals of process management
- 哈希表及完整注释
猜你喜欢
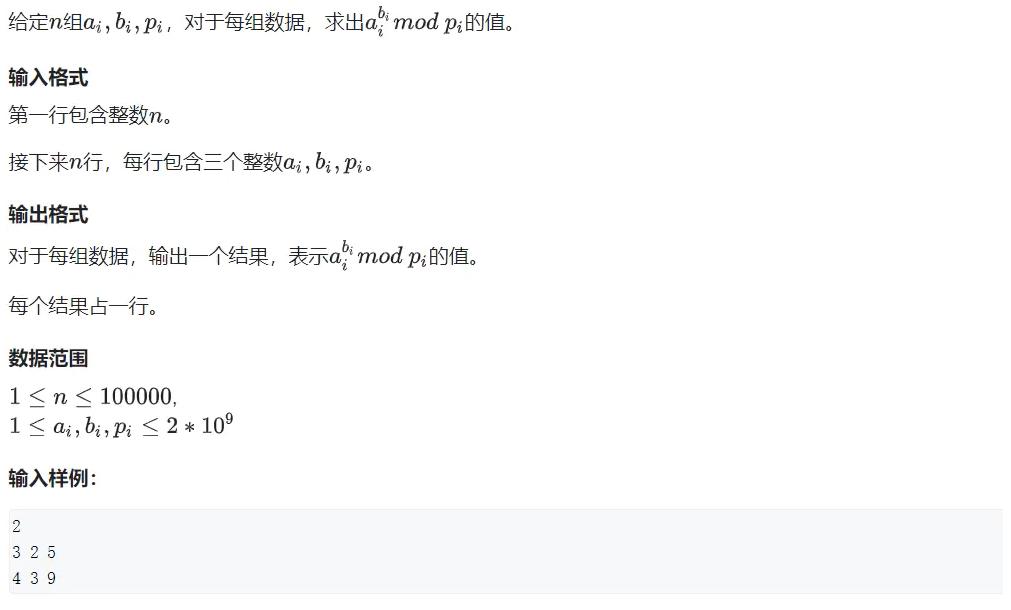
Number theory --- fast power, fast power inverse element
Django database (SQLite) basic introductory tutorial
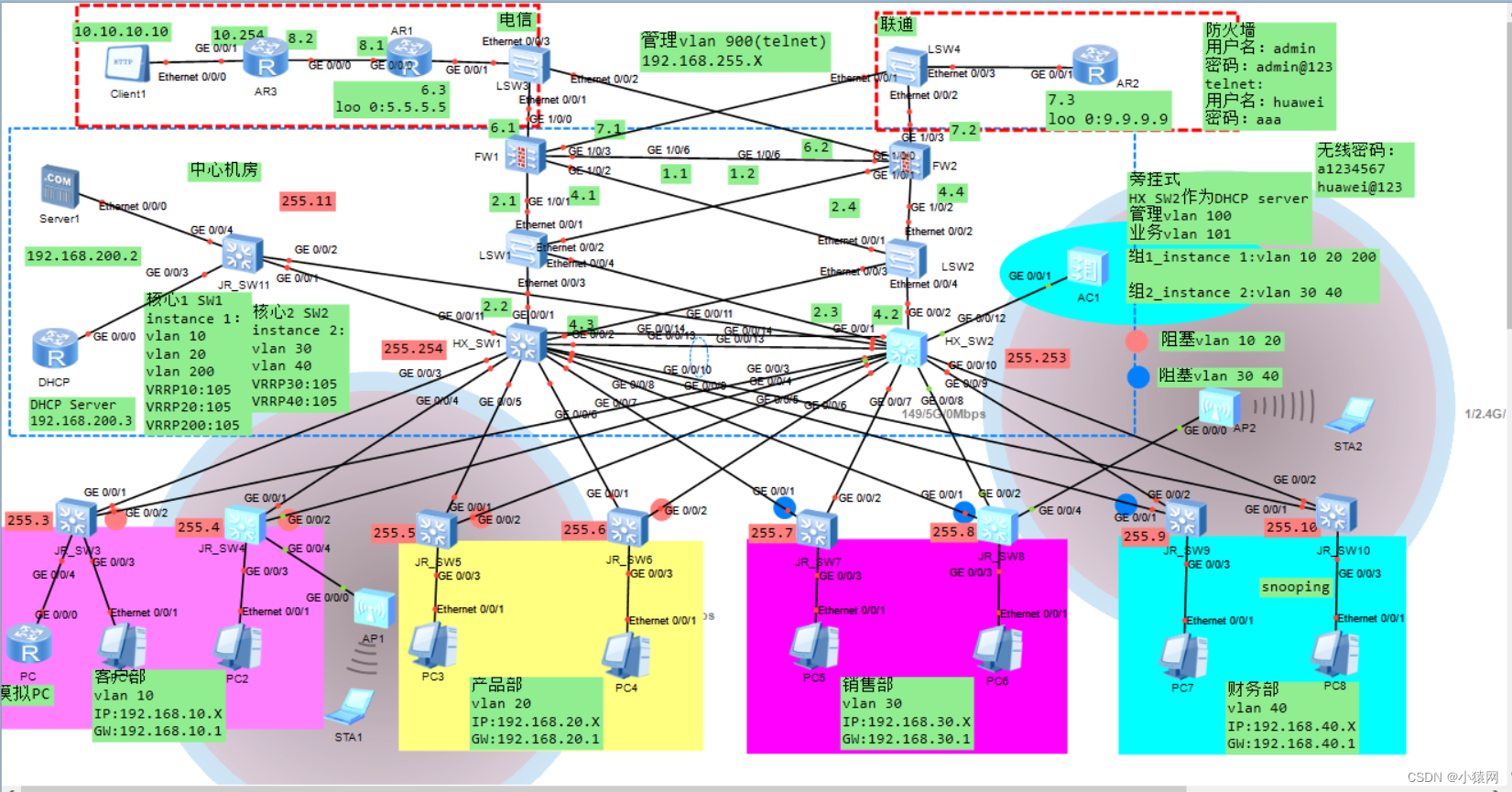
Planning and design of double click hot standby layer 2 network based on ENSP firewall
6-6漏洞利用-SSH安全防御
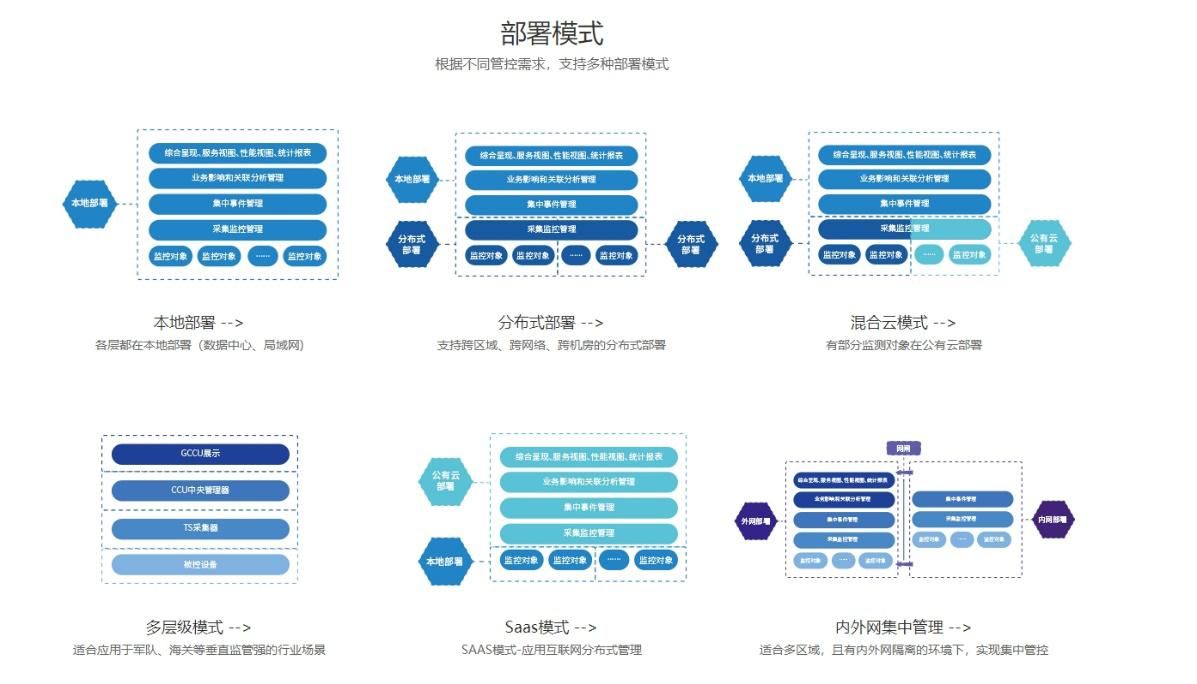
What are the characteristics of the operation and maintenance management system
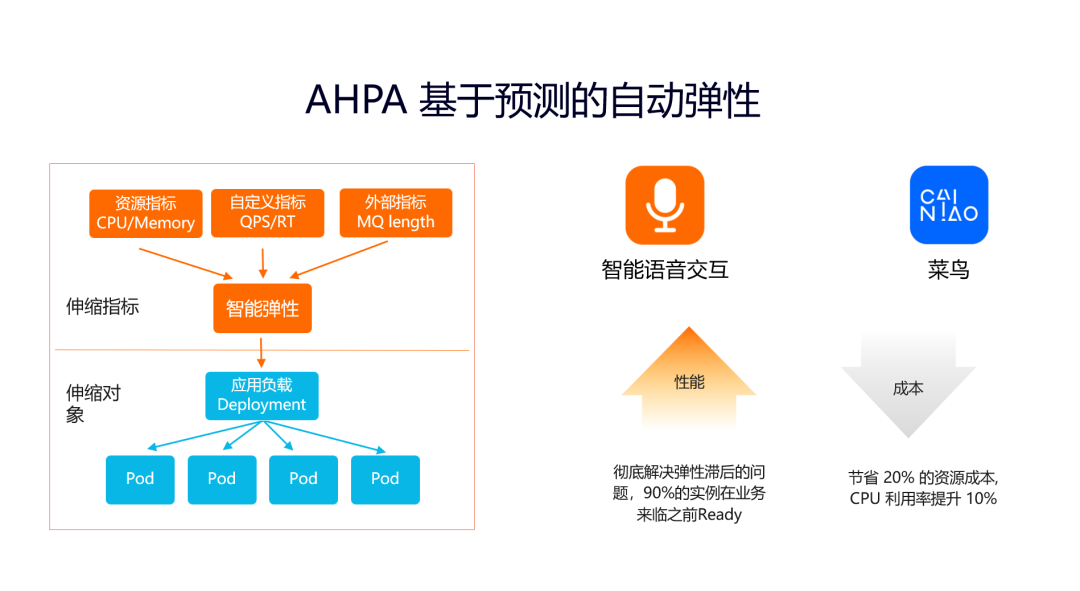
Ali yunyili: how does yunyuansheng solve the problem of reducing costs and improving efficiency?
Summer Challenge database Xueba notes (Part 2)~
Huitong programming introductory course - 2A breakthrough
The annual salary of general test is 15W, and the annual salary of test and development is 30w+. What is the difference between the two?
The annual salary of general test is 15W, and the annual salary of test and development is 30w+. What is the difference between the two?
随机推荐
MySQL - common functions - string functions
wzoi 1~200
从零安装Redis
ODBC database connection of MFC windows programming [147] (with source code)
[leetcode]Search for a Range
Have fun | latest progress of "spacecraft program" activities
CDB PDB 用户权限管理
PCL 常用拟合模型及使用方法
Electrical engineering and automation
The third season of ape table school is about to launch, opening a new vision for developers under the wave of going to sea
Here comes a white paper to uncover the technology behind Clickhouse, a node with 10000 bytes!
Summer Challenge database Xueba notes (Part 2)~
运维管理系统有哪些特色
AWS学习笔记(一)
Common fitting models and application methods of PCL
[leetcode]Search for a Range
安全交付工程师
MES管理系统的应用和好处有哪些
你不可不知道的Selenium 8种元素定位方法,简单且实用
The panel floating with the mouse in unity can adapt to the size of text content