当前位置:网站首页>JDBC从手写连接到引用DBCP和C3P0
JDBC从手写连接到引用DBCP和C3P0
2022-08-03 05:27:00 【耳冉鹅】
1、数据库驱动
驱动: 声卡、显卡、数据库
我们的程序会通过数据库驱动,和数据库打交道
2、JDBC
SUN公司为了简化开发人员(对数据库的统一)的操作,提供了一个(Java操作数据库的)规范,俗称JDBC
这些规范的实现由具体的厂商去做
对于开发人员而言,只需要掌握JDBC接口的操作即可
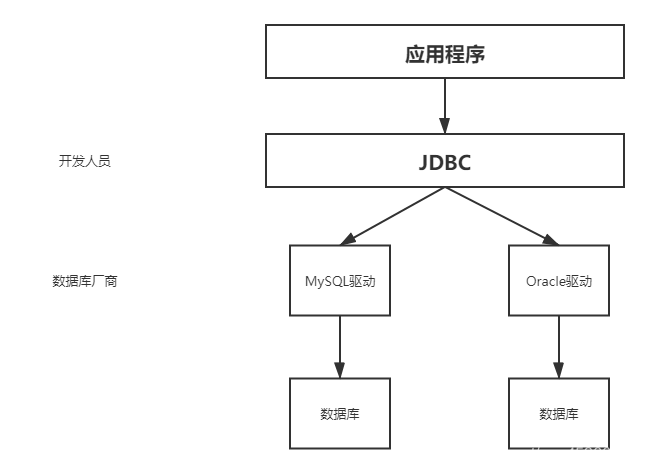
文档尾附上项目的目录结构,大家可参考创建
3、第一个JDBC程序
建表语句
CREATE DATABASE jdbcStudy CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
USE jdbcStudy;
CREATE TABLE `users`(
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR(40),
PASSWORD VARCHAR(40),
email VARCHAR(60),
birthday DATE
);
INSERT INTO `users`(id,NAME,PASSWORD,email,birthday)
VALUES(1,'zhansan','123456','[email protected]','1980-12-04'),
(2,'lisi','123456','[email protected]','1981-12-04'),
(3,'wangwu','123456','[email protected]','1979-12-04')
1、创建一个普通项目
2、导入数据库驱动
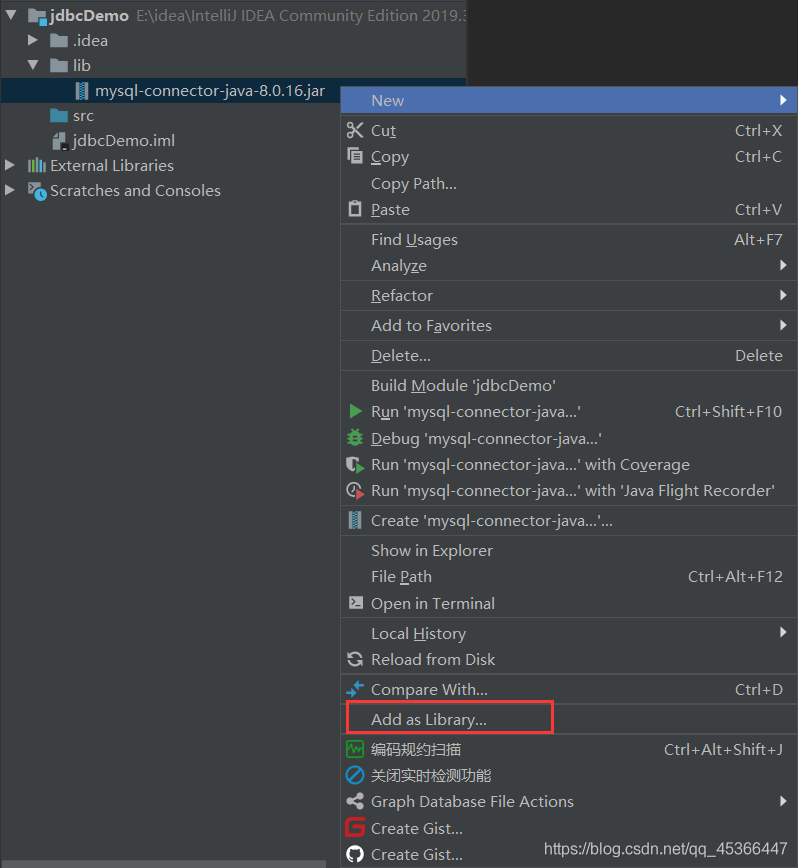
当jar包可展开时,即为成功
3、编写测试代码
import java.sql.*;
public class JdbcDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
// 1.加载驱动 固定写法
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 2.用户信息和url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&userUnicode=true&characaterEncoing=utf8&userSSL=true";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
// 3.连接成功 数据库对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 4.执行SQL的对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 5.执行SQL对象去执行SQL,可能存在结果,查看返回结果
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users";
// 返回的结果集,结果集封装了我们全部查询出来的结果
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("id: "+resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.print("name: "+resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.print("password: "+resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.print("email: "+resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println("birthday: "+resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
}
// 6.释放连接
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
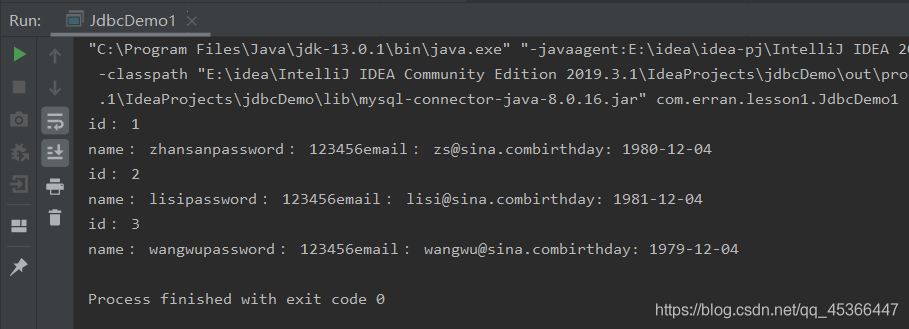
步骤总结
- 加载驱动
- 连接数据库 DriverManager
- 获得执行SQL的对象 Statement
- 获得返回的结果集 resultSet
- 释放连接
DriverManager
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver());
// 查看源码可知该操作执行了两次新创建连接的操作,duck不必
URL
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&userUnicode=true&characaterEncoing=utf8&userSSL=true";
// userUnicode=true
// characaterEncoing=utf8
// userSSL=true
// 若不加serverTimezone=GMT%2B8,则会报错:Exception in thread "main" java.sql.SQLException: The server time zone value '�й���ʱ��' is unrecognized or represents more than one time zone. You must configure either the server or JDBC driver (via the serverTimezone configuration property) to use a more specifc time zone value if you want to utilize time zone support.(该错误为是系统时间错误)
Statement 执行SQL的对象 PrepareStatement执行SQL的对象
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users"; // 编写SQL
statement.executeQuery(); // 查询操作返回 ResultSet
statement.execute(); // 执行任何SQL
statement.executeUpdate(); // 更新、插入、删除 -- 返回一个受影响的行数
ResultSet 查询的结果集: 封装了所有的查询结果
// 不知道SQL列类型时使用
resultSet.getObject();
// 已知SQL列类型时使用
resultSet.getString();
resultSet.getInt();
resultSet.getDate();
......
释放资源
// 6.释放连接
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close(); // 耗资源,一定要关闭
4、statement对象
Jdbc中的statement对象用于向数据库发送SQL语句。若想完成对数据库的增删改查,只需要通过这个对象向数据库发送增删改查语句即可
Statement对象的executeUpdate方法用于向数据库发送增、删、改的SQL语句,executeUpdate执行后,将会返回一个整数(即操作导致数据库数据改变的行数)
Statement.executeQuery方法用于向数据库发送查询语句,返回值代表查询结果的ResultSet对象
CRUD----create
使用executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据添加操作
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "insert into user() values()";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("插入成功!!");
}
CRUD----delete
使用executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据删除操作
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "delete from user where id =1";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("删除成功!!");
}
CRUD----update
使用executeQuery(String sql)方法完成数据查询操作
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from user where id =2";
ResultSet rs = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(rs.next()){
// 根据获取列的数据类型,分别调用rs的相应方法映射到java对象中
}
代码实现
1、提取工具类
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String driver =null;
private static String url =null;
private static String username =null;
private static String password =null;
static{
try {
InputStream resourceAsStream = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
// 驱动只需加载一次
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
// 释放资源
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2、编写增删改的方法
Insert
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestInsert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "INSERT INTO users (`id`,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`) VALUES(4,'a','123','[email protected]','2021-03-06')";
int i=statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("插入成功!!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
Delete
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "DELETE FROM users WHERE `id` =5";
int i=statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("删除成功!!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
Update
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TextUpdate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "UPDATE users SET `NAME` ='no1' WHERE `id` =1";
int i=statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("更新成功!!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
Select
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestSelect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from users where id =1";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("NAME"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
}
}
SQL注入的问题
sql存在漏洞,会被攻击而导致数据泄露 SQL会被拼接 ‘or’
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 正常登录
// login("no1","123456");
login(" 'or '1=1","123456");
}
public static void login(String username, String password) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME` ='"+username+"' AND `PASSWORD` ='"+password+"'";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("=================");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
5、PrepareStatement对象
PrepareStatement可以防止SQL注入且效率更高
Insert
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.*;
public class TestInsert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 使用“?”占位符 来代替参数
String sql = "INSERT INTO users (`id`,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?)";
// 预编译sql,
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 手动给参数赋值
preparedStatement.setInt(1,4);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"no4");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "123456");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "[email protected]");
// sql.Date 数据库 java.sql.Date()
// util.Date Java new Date().getTime() ----> System.currentTimeMillis()
preparedStatement.setDate(5, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// 执行
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Delete
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.*;
public class TestDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 使用“?”占位符 来代替参数
String sql = "delete from users where id=?";
// 预编译sql,
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 手动给参数赋值
preparedStatement.setInt(1,4);
// 执行
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Update
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.*;
public class TextUpdate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 使用“?”占位符 来代替参数
String sql = "update users set `NAME`=? where `id`=?";
// 预编译sql,
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 手动给参数赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1,"update4");
preparedStatement.setInt(2,4);
// 执行
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("更新成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Select
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import static com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils.getConnection;
public class TextSelect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection=JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from users where `id`=?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 4);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("NAME"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, preparedStatement, resultSet);
}
}
}
防止SQL注入
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 正常登录
login("no1","123456");
// login(" 'or '1=1","123456");
}
public static void login(String username, String password) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME` =? AND `PASSWORD` =?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// PreparedStatement 防止SQL注入的本质: 把传递进来的参数当做字符
// 假设其中存在转义字符,则直接忽略 ''会被直接转义
statement.setString(1,username);
statement.setString(2,password);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("=================");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
6、使用IDEA连接数据库
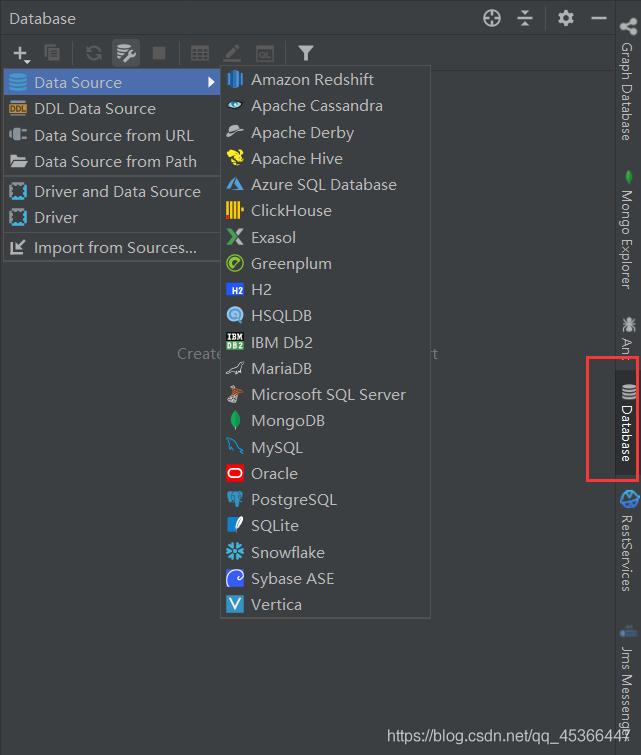
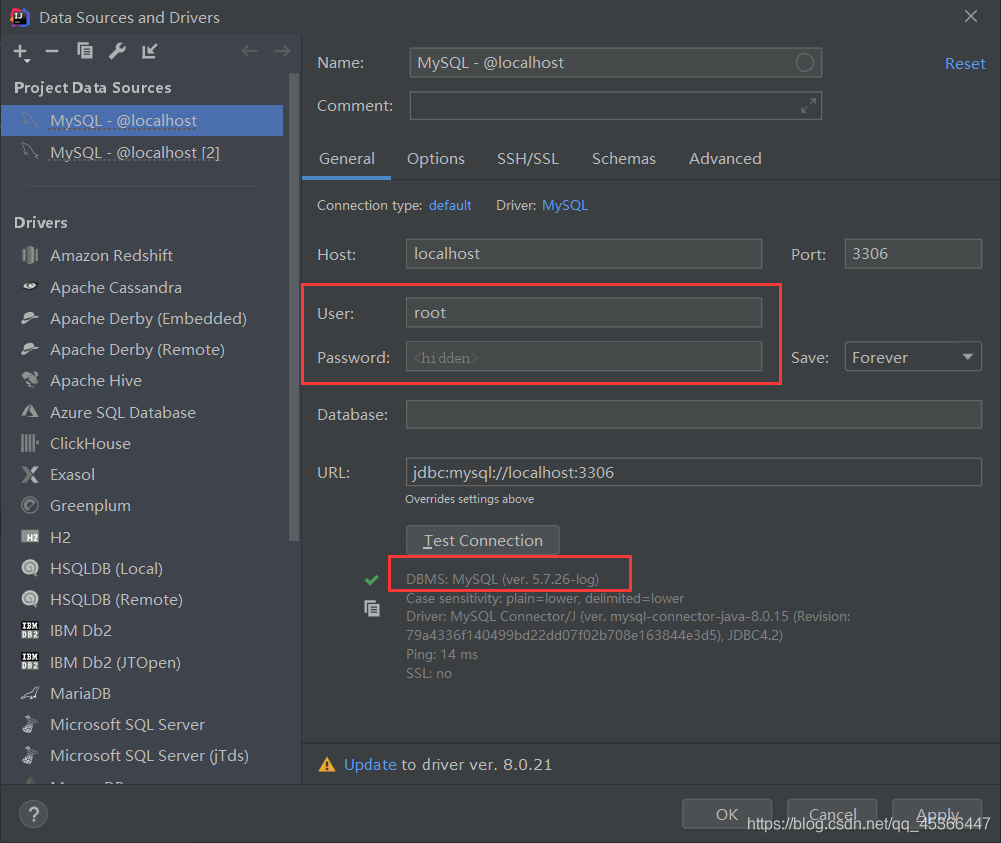
连接不上MySQL的话可参考博主的问题处理中的文章
7、事务
要么都成功,要么都失败
ACID原则
原子性:要么全完成,要么都不完成
一致性:总数不变
隔离性:多个进程互不干扰
持久性:一旦提交 不可逆,持久化到数据库
隔离性的问题:
脏读:一个事务读取了另一个没有提交的事务
不可重复读:在同一事务内,重复读取表中的数据,表数据发生了改变
虚读(幻读):在一个事务内,读取到了别人插入的数据,导致前后读出来的结果不一致
代码实现
1、开启事务 conn.setAutoCommit(false);
2、一组事务执行完毕,提交事务
3、可以在catch语句中显示的定义回滚语句,但默认失败就会回滚
import com.erran.lesson2.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestTransaction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 关闭数据库的自动提交 自动会开启事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql1 = "update account set balance = balance -100 where name = 'A'";
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
String sql2 = "update account set balance = balance +100 where name = 'B'";
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
// 业务完毕 提交事务
conn.commit();
System.out.println("操作成功!!");
} catch (SQLException e) {
try {
conn.rollback(); // 若失败 则回滚事务
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn, preparedStatement, resultSet);
}
}
}
8、数据库连接池
数据库连接—执行完毕—释放
连接、释放 非常浪费系统资源
池化技术: 准备一些预先的资源,直接连接预先准备好的
最小连接数:10
最大连接数:100 业务最高承载上限
等待超时:100ms
编写连接池,实现一个借口 DataSource
开源数据源实现
DBCP
C3P0
Druid:阿里
使用了这些数据库连接池后,在项目开发中就不需要编写连接数据库的代码了
DBCP
需要的jar包:
commons-dbcp2-2.8.0.jar 下载链接:http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-dbcp/download_dbcp.cgi
commons-pool2-2.9.0.jar 下载链接:http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-pool/download_pool.cgi
若出现错误 “Could not initialize class” 则需要commons-logging-1.2.jar 下载链接:http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-logging/download_logging.cgi
#连接设置
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true
username=root
password=123456
#<!-- 初始化连接 -->
initialSize=10
#最大连接数量
maxActive=50
#<!-- 最大空闲连接 -->
maxIdle=20
#<!-- 最小空闲连接 -->
minIdle=5
#<!-- 超时等待时间以毫秒为单位 6000毫秒/1000等于60秒 -->
maxWait=60000
#JDBC驱动建立连接时附带的连接属性属性的格式必须为这样:【属性名=property;】
#注意:"user" 与 "password" 两个属性会被明确地传递,因此这里不需要包含他们。
connectionProperties=useUnicode=true;characterEncoding=UTF8
#指定由连接池所创建的连接的自动提交(auto-commit)状态。
defaultAutoCommit=true
#driver default 指定由连接池所创建的连接的只读(read-only)状态。
#如果没有设置该值,则“setReadOnly”方法将不被调用。(某些驱动并不支持只读模式,如:Informix)
defaultReadOnly=
#driver default 指定由连接池所创建的连接的事务级别(TransactionIsolation)。
#可用值为下列之一:(详情可见javadoc。)NONE,READ_UNCOMMITTED, READ_COMMITTED, REPEATABLE_READ, SERIALIZABLE
defaultTransactionIsolation=READ_UNCOMMITTED
JdbcUtils_DBCP
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils_DBCP {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
static{
try {
InputStream resourceAsStream = JdbcUtils_DBCP.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbcpconfig.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
// 创建数据源 工厂模式 ----> 创建
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 从数据源中获取连接
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
// 释放资源
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
TestDBCP
import com.erran.lesson5.utils.JdbcUtils_DBCP;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestDBCP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils_DBCP.getConnection();
// 使用“?”占位符 来代替参数
String sql = "INSERT INTO users (`id`,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?)";
// 预编译sql,
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 手动给参数赋值
preparedStatement.setInt(1,4);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"no4");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "123456");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "[email protected]");
// sql.Date 数据库 java.sql.Date()
// util.Date Java new Date().getTime() ----> System.currentTimeMillis()
preparedStatement.setDate(5, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// 执行
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils_DBCP.release(conn, preparedStatement, null);
}
}
}
C3P0
需要的jar包:
- c3p0-0.9.2-pre5.jar
- mchange-commons-java-0.2.3.jar
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<c3p0-config>
<!--
c3p0的缺省(默认)配置
如果在代码中"ComboPooledDataSource ds=new ComboPooledDataSource();"这样写就表示使用的是c3p0的缺省(默认)
-->
<default-config>
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">root</property>
<property name="acquiredIncrement">5</property>
<property name="initialPoolSize">10</property>
<property name="minPoolSize">5</property>
<property name="maxPoolSize">20</property>
</default-config>
<!--
c3p0的命名配置
如果在代码中"ComboPooledDataSource ds=new ComboPooledDataSource("MySQL");"这样写就表示使用的是mysql的缺省(默认)
-->
<named-config name="MySQL">
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">123456</property>
<property name="acquiredIncrement">5</property>
<property name="initialPoolSize">10</property>
<property name="minPoolSize">5</property>
<property name="maxPoolSize">20</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
JdbcUtils_C3P0
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils_C3P0 {
private static ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = null;
static{
try {
// 代码配置
// dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
// dataSource.setDriverClass();
// dataSource.setUser();
// dataSource.setPassword();
// dataSource.setJdbcUrl();
//
// dataSource.setMaxPoolSize();
// dataSource.setMinPoolSize();
dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("MySQL");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 从数据源中获取连接
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
// 释放资源
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
TestC3P0
import com.erran.lesson5.utils.JdbcUtils_C3P0;
import com.erran.lesson5.utils.JdbcUtils_DBCP;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestC3P0 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils_C3P0.getConnection();
// 使用“?”占位符 来代替参数
String sql = "INSERT INTO users (`id`,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?)";
// 预编译sql,
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 手动给参数赋值
preparedStatement.setInt(1,5);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"no4");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "123456");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "[email protected]");
// sql.Date 数据库 java.sql.Date()
// util.Date Java new Date().getTime() ----> System.currentTimeMillis()
preparedStatement.setDate(5, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// 执行
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils_C3P0.release(conn, preparedStatement, null);
}
}
}
结论
无论使用说明数据源,本质都是一样的,DataSource接口不会变,方法就不会变
项目目录结构
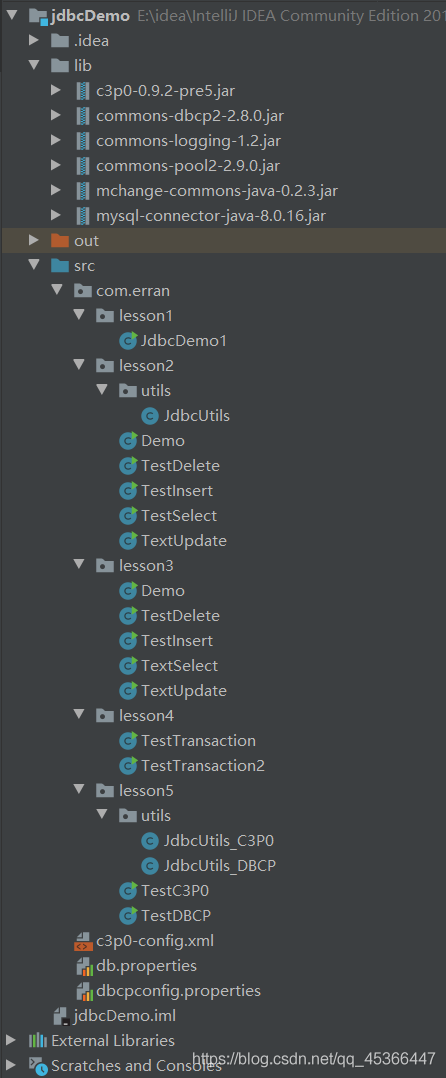
项目资源可在博主的资源中免费下载奥,欢迎交流以及批评指正~
边栏推荐
- Oracle 数据库集群常用巡检命令
- JS--正则表达式
- go test执行多个文件夹下相同目录的用例
- 二层交换机,三层交换机,路由器内容总结记录
- 2-php学习笔记之控制语句,函数
- 6. What is the difference between Vector, ArrayList and LinkedList?(design, performance, safety)
- Dynamic adjustment of web theme (2) Extraction
- ORM框架:Dapper的使用
- 使用ZBrush制作恶魔模型
- Difference between @JsonProperty and JSONField?
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Podman一篇就学会
VI和VIM编辑指令
二层交换机,三层交换机,路由器内容总结记录
JS--正则表达式
Dynamic adjustment of web theme (2) Extraction
802.1AS的BMCA(最佳主时钟选举)理解
【随笔】平常心
二分查找2 - x的平方根
二分查找5 - 第一个错误的版本
Oracle 11g静默安装
【C语言】斐波那契数列
【七夕特效】 -- 满屏爱心
一文看懂常见域名后缀的含义
【C语言】关于数组传参问题/首地址
5. What is the difference between int and Integer?
【3D建模制作技巧分享】ZBrush快捷键如何设置
2-php学习笔记之控制语句,函数
cobalt strike 的基础使用
6. What is the difference between Vector, ArrayList and LinkedList?(design, performance, safety)
ESXI中损坏虚拟机数据如何找回