当前位置:网站首页>Kubernetes -- detailed usage of kubectl command line tool
Kubernetes -- detailed usage of kubectl command line tool
2022-07-07 20:07:00 【Wu Shengzi night song】
kubectl As a client CLI Tools , You can use the command line to Kubernetes Cluster operation .
kubectl Usage overview
kubectl The syntax of the command line is as follows :
kubectl [command] [TYPE] [NAME] [flags]
command: Sons command , Used to operate Kubernetes Commands for cluster resource objects , for example create、delete、describe、get、apply etc.TYPE: The type of resource object , Case sensitive , Can be in singular form 、 Plural or abbreviated identificationkubectl get pod pod1kubectl get pods pod1kubectl get po pod1
NAME: The name of the resource object , Case sensitive . If you do not specify a name , The system will return to belong to TYPE A list of all the objects offlags:kubectl Optional parameters to the subcommand , For example, using-sAppoint apiserver Of URL Address without default value
kubectl The types of resource objects that can be operated are shown in the following table :
| The name of the resource object | abbreviation |
| clusters | |
| componentstatuses | cs |
| configmaps | cm |
| daemonsets | ds |
| deployments | deploy |
| endpoiints | ep |
| events | ev |
| horizontalpodautoscalers | hpa |
| ingresses | ing |
| Jobs | |
| limitranges | limits |
| nodes | no |
| namespaces | ns |
| networkpolicies | |
| nodes | no |
| statefulsets | |
| persistentvolumeclaims | pvc |
| persistentvolumes | pv |
| pods | po |
| podsecuritypolicies | psp |
| podtemplates | |
| replicasets | rs |
| replicationcontrollers | rc |
| resourcequotas | quota |
| cronjob | |
| secrets | |
| serviceaccounts | |
| services | svc |
| storageclasses | sc |
| thirdpartyresources |
You can also operate on multiple resource objects at the same time in one command line , With many TYPE and NAME The combination logo of , as follows :
Get multiple Pod Information about :kubectl get pods pod1 pod2
Get information about multiple objects :kubectl get pod/pod1 rc/rc1
Apply more than one at the same time yaml file , With many -f file parameter :kubectl get pod -f pod1.yaml -f pod2.yamlkubectl create -f pod1.yaml -f rc1.yaml -f service1.yaml
kubectl The subcommand explains
| Sons command | grammar | explain |
| annotate | kubectl annotate(-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME ) KEY_1=VAL_1 ... KEY_N=VAL_N [--overwrite][--all] [--resource-version=version][flag] | Add or update the annotation Information |
| api-versions | kubectl api-versions [flags] | List the current system supports API Version list , The format is "group/version" |
| apply | kubectl apply -f FILENAME [flags] | From the configuration file or stdin Update the configuration of resource objects in |
| attach | kubectl attach POD -c CONTAINER [flags] | Attach to a running container |
| autoscale | kubectl autoscale (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) [--min=MINPODS] --max=MAXPODS [--cpu-percent=CPU][flags] | Yes Deployment、ReplicaSet or ReplicationController Set the horizontal automatic expansion and shrinkage |
| cluster_info | kubectl cluster_info [flags] | Show clusters Master And information about the built-in Services |
| completion | kubectl completion SHELL [flags] | Output shell Command execution result code (bash or zsh) |
| config | kubectl config SUBCOMMAND [flags] | modify cubeconfig file |
| convert | kubectl convert -f FILENAME [flags] | Convert configuration files to different API edition |
| cordon | kubectl cordon NODE [flags] | take Node Marked as unschedulable, namely " Isolation " Out of the cluster scheduling range |
| create | kubectl create -f FILENAME [flags] | From the configuration file or stdin Create resource objects in |
| delete | kubectl delete (-f FILENAME | TYPE [NAME | /NAME | -l label | -all])[flags] | According to the configuration file 、ST set 、 Resource name or label selector Delete resource object |
| describe | kubectl describe (-f FILENAME | TYPE [NAME_PREFIX | /NAME | -l label])[flags] | Describe the details of one or more resource objects |
| drain | kubectl drain NODE [flags] | First of all, will Node Set to unschedulable, Then delete the Node All of the Pod, But it won't be deleted piserver Managed Pod |
| edit | kubectl edit (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME)[flags] | Edit the properties of the resource object , Online updating |
| exec | kubectl exec POD [-c CONTAINER] [-i] [-t] [flags] [--COMMAND [args...]] | Execute a command in a container |
| explain | kubectl explain [--include-extended-apis=true] [--recursive=false] [flags] | A detailed description of resource object properties |
| expose | kubectl expose (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME)[--port=port][--protocol=TCP|UDP][--target-port=number-or-name][--name=name][----extenal-ip=external-ip-of-service][--type=type] | There will be one that already exists RC、Service、Deployment or Pod Exposed as a new Service |
| get | kubectl get (-f FILENAME | TYPE [NAME | /NAME | -l label])[--watch][--sort-by=FIELD][[-o | --output] =OUTPUT_FORMAT][flags] | Displays a summary of one or more resource objects |
| label | kubectl label (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) KEY_1=VAL_1 ...KEY_N=VAL_N [--overwrite][--all][--resource-version=version][flags] | Set or update the resource object labels |
| logs | kubectl logs POD [-c CONTAINER] [--follow][flags] | Print a container log on the screen |
| Patch | kubectl patch (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) --patch PATCH [flags] kubectl patch (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) --patch PATCH [flags] | With merge Form to modify the values of some fields of the resource object |
| port-forward | kubectl port-forward POD [LOCAL_PORT:] REMOTE_PORT [...[LOCAL_PORT_N:]REMOTE_PORT_N][flags] | Map a port number of this machine to Pod Port number , Usually used for testing |
| proxy | kubectl proxy [--port=PORT][--www=static-dir][--www-prefix][--api-prefix=prefix][flags] | Map a port number of this machine to apiserver |
| replace | kubectl replace -f FILENAME [flags] | From the configuration file or stdin Replace resource objects |
| rolling-update | kubectl rolling-update OLD_CONTROLLER_NAME ([NEW_CONTROLLER_NAME] --image=NEW_CONTAINER_IMAGE | -f NEW_CONTROLLER_SPEC)[flags] | Yes RC Rolling upgrade |
| run | kubectl run NAME --image=image [--env="key=value"][--port=port][--replicas=replicas][--dry=run=bool][--overrides=inline-json][flags] | Based on a mirror image in Kubenetes Start one on the cluster Deployment |
| scale | kubectl scale (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) --replicas=COUNT [--resource-version=version][--current-replicas=count][flags] | Capacity expansion 、 Let's shrink to one Deployment、ReplicaSet、RC or Job in Pod The number of |
| set | kubectl set SUBCOMMAND [flags] | Set a specific information of the resource object , At present, only support to modify the image of the container |
| taint | kubectl taint NODE NAME KEY_1=VAL_1:TAINT_EFFECT_1 ... KEY_N=VAL_N:TAINT_EFFECT_N [flags] | Set up Node Of taint Information , Used to put specific Pod Schedule to a specific Node The operation of , by Alpha Features of the version |
| uncordon | kubectl uncordon NODE [flags] | take Node Set to schedulable |
| version | kubectl version [--client][flags] |
kubectl parameter list
kubectl The common startup parameters of the command line are as follows :
| Parameter name and value example | explain |
| –alsologtostderr=false | Set to true Identify that the log is output to the file at the same time as stderr |
| –as=‘’ | Set the user name for this operation |
| –certificate-authority=‘’ | be used for CA Authorized by the cert File path |
| –client-certificate=‘’ | be used for TLS The client certificate file path of |
| –client-key=‘’ | be used for TLS The client of key File path |
| –cluster=‘’ | Set the... To use kubeconfig Medium cluster name |
| –context=‘’ | Set the... To use kubeconfig Medium context name |
| –insecure-skip-tls-verify=false | Set to true Identity skip TLS Security authentication mode , Will be HTTPS Unsafe connection |
| –kubeconfig=‘’ | kubeconfig Profile path , Include in the configuration file Master Address information and necessary authentication information |
| –log-backtrace-at=:0 | Record the log every time "file: Line number " Print once stack trace |
| –log-dir=‘’ | Log file path |
| –log-flush-frequency=5s | Set up flush Log file interval |
| –logtostderr=true | Set to true Output log to stderr, No output to log file |
| –match-server-version=false | Set to true Indicates that the version number of the client must be consistent with that of the server |
| –namespace=‘’ | Set the location of this operation namespace |
| –password=‘’ | Set up apiserver Of basic authentication Password |
| -s, --server=‘’ | Set up apiserver Of URL Address , The default value is localhost:8080 |
| –stderrthreshold=2 | In the threshold Logs above level are output to stderr |
| –token=‘’ | Set access apiserver The safety of the token |
| –user=‘’ | Appoint kubeconfig user name |
| –username=‘’ | Set up apiserver Of basic authentication Username |
| –v=0 | glog The level of logging |
| –vmodule= | glog Detailed log level based on Module |
kubectl Output format
kubectl The command can display the results in a variety of formats , The output is formatted by -o Parameter assignment :kubectl [command] [TYPE] [NAME] -o=<output_format>
| Output format | explain |
-o=custom-columns=<spec> | Output according to the custom column name , Comma separated |
-o=custom-columns-file=<filename> | Get the custom column name from the file and output |
-o=json | With JSON Format display results |
-o=jsonpath=<template> | Output jsonpath Field information defined by an expression |
-o=jsonpath-file=<filename> | Output jsonpath Field information defined by an expression , From the file |
-o=name | Output only the name of the resource object |
-o=wide | Output extra information . about Pod, Will output Pod Where Node name |
-o=yaml | With yaml Format display results |
Common output formats are as follows
Show Pod For more information :kubectl get pod <pod-name> -o wide
With yaml Format display Pod Details of :kubectl get pod <pod-name> -o yaml
Display with custom column names Pod Information about :kubectl get pod <pod-name> -o=custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,RSRC:.metadata.resourceVersion
Custom column name output based on file :kubectl get pods <pod-name> -o=custom-columns-file=template.txt
template.txt The contents of the file are :
NAME RSRC
metadata.name metadata.resourceVersion
The output is :
NAME RSRC
pod-name 52305
in addition , You can also sort the output results by a certain field , adopt –sort-by Parameter with jsonpath Expression :kubectl [command] [TYPE] [NAME] --sort-by=<jsonpath_exp>
for example , Sort by name :kubectl get pods --sort-by=.metadata.name
kubectl The operation sample
1. Create resource object
according to yaml Configuration file created at one time service and rc:kubectl create -f my_service.yaml -f my-rc.yaml
according to directory All under directory .yaml、.yml、.json Create the file definition :kubectl create -f directory
2. View resource objects
View all Pod list :kubectl get pods
see rc and service list :kubectl get rc, service
3. Describe resource objects
Show Node Details of :kubectl describe nodes <node-name>
Show Pod Details of :kubectl describe pods/<pod-name>
Show by RC Managed Pod Information about :kubectl describe pods <rc-name>
4. Delete resource object
be based on pod.yaml Defined name delete Pod:kubectl delete -f pod.yaml
Delete all containing a label Of Pod and service:kubectl delete pods, services -l name=<label-name>
Delete all Pod:kubectl delete pods --all
5. Execute the command of the container
perform Pod Of date command , By default Pod The first container in executes :kubectl exec <pod-name> date
Appoint Pod A container in the executes date command :kubectl exec <pod-name> -c <container-name> date
adopt bash get Pod Of a container in TTY, Equivalent to login container :kubectl exec -ti <pod-name> -c <container-name> /bin/bash
6. View the container's log
See the container output to stdout Log :kubectl logs <pod-name>
Track and view container logs , amount to tail -f Results of command :kubectl logs -f <pod-name> -c <container-name>
边栏推荐
- LeetCode力扣(剑指offer 36-39)36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表37. 序列化二叉树38. 字符串的排列39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
- 力扣 989. 数组形式的整数加法
- LeetCode_7_5
- c语言如何判定是32位系统还是64位系统
- equals 方法
- Le PGR est - il utile au travail? Comment choisir une plate - forme fiable pour économiser le cœur et la main - d'œuvre lors de la préparation de l'examen!!!
- Visual Studio 插件之CodeMaid自动整理代码
- 开源OA开发平台:合同管理使用手册
- 力扣 88.合并两个有序数组
- 使用高斯Redis实现二级索引
猜你喜欢
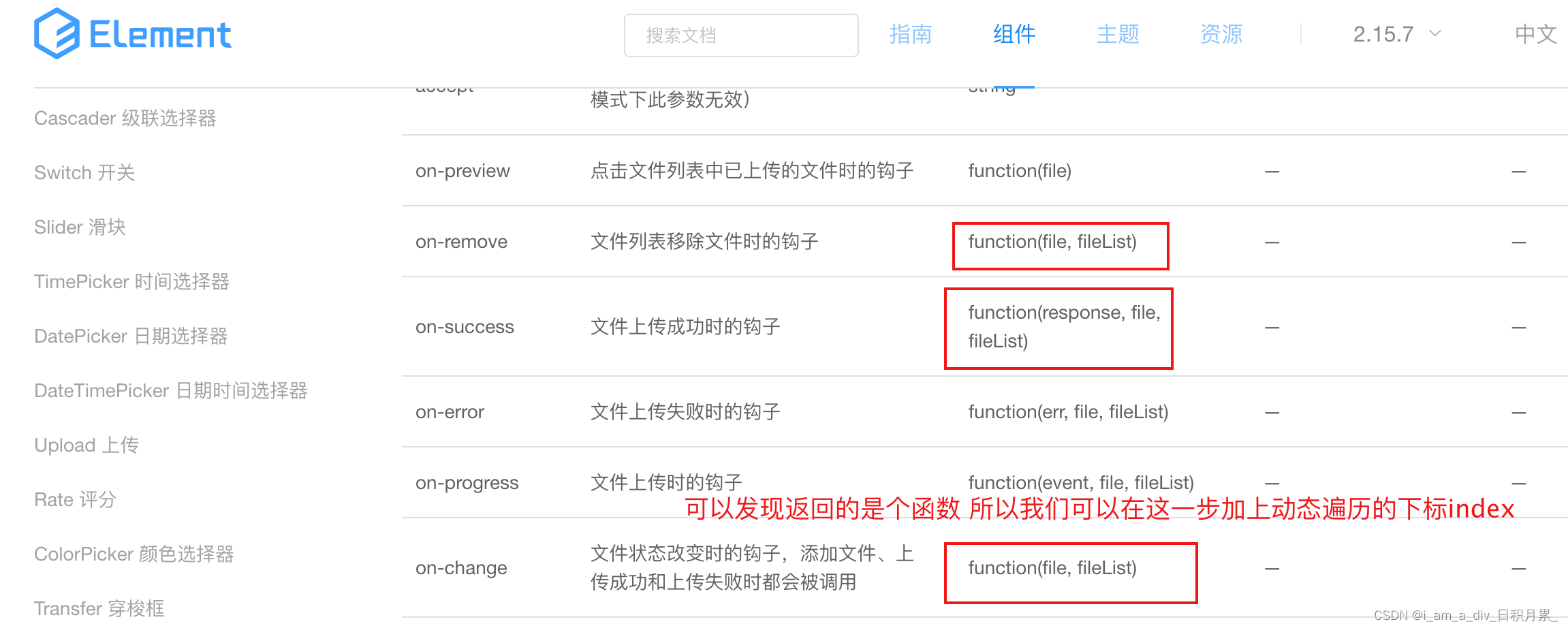
Dynamic addition of El upload upload component; El upload dynamically uploads files; El upload distinguishes which component uploads the file.
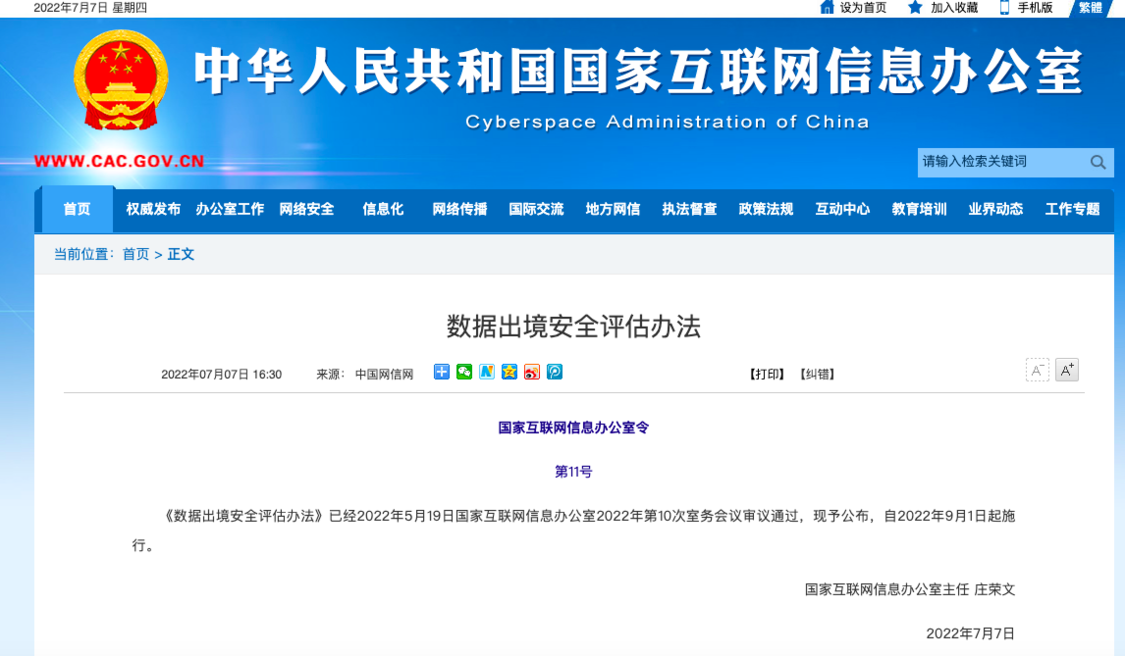
The state cyberspace Office released the measures for data exit security assessment: 100000 information provided overseas needs to be declared

Openeuler prize catching activities, to participate in?
ASP. Net kindergarten chain management system source code

mysql 的一些重要知识
openEuler 资源利用率提升之道 01:概论
vulnhub之school 1

【哲思与实战】程序设计之道
Sword finger offer II 013 Sum of two-dimensional submatrix
Navicat连接2002 - Can‘t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock‘解决
随机推荐
BI的边界:BI不适合做什么?主数据、MarTech?该如何扩展?
Le PGR est - il utile au travail? Comment choisir une plate - forme fiable pour économiser le cœur et la main - d'œuvre lors de la préparation de l'examen!!!
JVM 类加载机制
浅尝不辄止系列之试试腾讯云的TUIRoom(晚上有约,未完待续...)
干货分享|DevExpress v22.1原版帮助文档下载集合
CSDN syntax description
有了ST7008, 蓝牙测试完全拿捏住了
多个线程之间如何协同
Ucloud is a basic cloud computing service provider
Classification automatique des cellules de modules photovoltaïques par défaut dans les images de lecture électronique - notes de lecture de thèse
Mysql, sqlserver Oracle database connection mode
【哲思与实战】程序设计之道
SQL common optimization
Boot 和 Cloud 的版本选型
TS快速入门-泛型
sql 常用优化
Notes...
CSDN语法说明
毕业季|遗憾而又幸运的毕业季
Cloud 组件发展升级