当前位置:网站首页>[C language] data type storage, original code, inverse code and complement code
[C language] data type storage, original code, inverse code and complement code
2022-06-11 23:22:00 【InfoQ】
The meaning of type :
- It is this type that determines the size of its memory space once it is determined , It also determines how big its scope is . For example, it's like : When you put a variable a The value of is assigned to int plastic , So its storage size is 4 The range of bytes is -32768~32767.
- Be careful , Various types of storage sizes are related to the number of system bits , But the current 64 Bit system is the main .
C The types of languages are divided into
- Memory is a major component of a computer , It is used to save the program and data when the process is running , Also called executable memory . In the computer , Memory space generally refers to the main memory space ( Physical address space ) Or the system allocates memory space for a user program . Methods to expand memory space generally include increasing memory size and virtual memory .
Construction type
- An array type :Why is an array type a construction type ? Because of the assumptionint arr[20], So it's an array type, isn't it . that int [20] It's the type , Then I'll make another change int [10] This type is changing So what if you're a different type? Character type , Floating point type like this , Therefore, array is also a custom type and a construction type .
- Type of structure :struct,Member types are changing , Then its structure is also changing . If you don't know the structure, you can see the content of this structure in my article .
- Enumeration type :enum,This is C A key word of language , At that time, I will take out and write an article to focus on the enumeration type in C What role does language play .
- Consortium type :union, This is also called a community , We won't talk about this now .
Pointer types
- The purpose of a pointer is actually to store an address assigned to a variable in it , And the bytes of the pointer are 4 Bytes .
- In this way, we use a piece of code to let you intuitively see if the pointer is 4 Bytes , Because the blogger told you about the content of the wild pointer, but the content of the pointer has not been told you yet ,At that time, bloggers will also write an article about pointers ,Thus, pointer type is a special type . Pay attention to the , The pointer is defined with *
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int a = 10;
int* p = &a; // Shaping pointer variables p receive a The address of
// Here, all data types are defined as pointers -- 32 position 4byte 64 position 8byte
printf("%d\n", sizeof(int*));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(short*));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(double*));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(char*));
}- Running results :

Empty type
- A special return type , Represents an empty function , That is, a function without a return value . Empty type ( No type ) void Used to show that a function does not return any value . It can also point to void Pointer to type , After explanation , This pointer can point to various types of data objects
- void There is no reference , When you add no parameters when defining a program , Although the program will run . But there will be a waring Hints are unnecessary parameters
The return type of the function
#include<stdio.h>
void print()
{
printf("hello word\n");
}
int main(void)
{
print();
}The parameters of the function
#include<stdio.h>
void print()// It is also possible to transfer parameters without parameters , But not here, so we C Language does not receive
{
printf("hello word\n");
}
int main(void)
{
print(10);// stay print Give arguments to the function 10
}Shaping the storage space in memory
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int a = 5;
int b = -3;
}
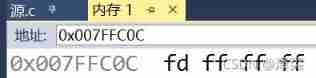
- Did you find out , The storage results of these two are different , Next, I'll tell you how plastic is stored in memory .
- In fact, it is necessary to understand the original code first , Inverse code , And the concept of complement .
- In the computerSigned number ( plastic )There are three ways to express it, namely : Original code , Inverse and complement . The three representations have two parts: sign bit and numeric bit ,The sign bit is used 0 Representation bit " just ", use 1 Expressed as " negative ",The three representations of numerical bits are different . notes : Unsigned source code, inverse code and complement code are the same .
- There are two kinds of signed numbers. One is called positive number , The other is called a negative number . It's the same in positive numbers , However, in negative numbers, these three expressions are different
- Above are three cases of negative numbers ,........... This is omitted if it's a plastic front 32 Digit number , Note that the highest position here is 1, So there are three forms of negative numbers .
Original code
- Directly convert the number into binary according to the positive or negative form
int a = 5;//4 Bytes —— 32bit position
//0( The highest positive number )0000000000000000000000000000101
int b = -3;
//1( The highest negative number )1111111111111111111111111111101
Inverse code
Complement code
Why is the complement stored in the computer ?
Introduction to big end and small end :
- Big end : Storage mode meansMemoryThe low order in is saved inMemoryIn the middle ofHigh addressamong , And the high end of the data , Save inMemoryOfLow addressamong .
- The small end : Storage mode meansdataThe low order in is saved inMemoryMiddle low address , And the high end of the data , Save inMemoryOfLow addressamong .
- Memory spaces are numbered , We all call the low bit of memory low address , If the number is large, it is called high address , Data can be stored in any way , But when you go back to your program, how must you store it? For example, what you shape and store is 11 22 44 33 ( Binary conversion hex 1 Bytes =4 individual bit position ), Then you also need to shape and store it in this way 11 22 44 33 ! But we don't usually store memory like this . There are usually two storage methods. One is calledBig endAnother storage mode isThe small endThe storage mode of .
- The assumption is :0x11223344, This 44 It's low , and 11 It's the high position , Then the number of high addresses to be saved to memory , The high bit of the data is stored at the low address —— Big end
- Suppose again :0x44332211, This 44 It's low , and 11 It's the high address , Low byte data is stored at a low address in memory , The high byte data is stored at the high address —— The small end
Judge the big end and the small end
- int a = 1;
- The small end :0x01 00 00 00
- Big end :0x00 00 00 01
Code demonstration
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int a = 1;
char *p = (char*)&a;
if (*p == 1)
{
printf(" The small end \n");
}
else
{
printf(" Big end \n");
}
return 0;
}Custom function code
#include<stdio.h>
int Testing()
{
int a = 1;
char * pb = (char*)&a;
if (*pb == 1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
int ret = Testing();
// return 1 Represents the small end , return 0 It represents big end
if (ret == 1)
{
printf(" The small end \n");
}
else
{
printf(" Big end \n");
}
return 0;
}- The pointer type determines how many bytes the pointer dereference accesses , such as :charp; So herep Only one byte can be accessed , According to the data type you define
- The pointer type determines the pointer +1,-1 It's a few bytes , such as :char * p + 1; So what is skipped is a byte Judge according to the data type int Namely 4 byte
- Be careful : The integer lifting complement is the highest sign bit ,'0' Being positive ,'1' Negative
The storage of floating point in memory
- 3.14 、1E10( This is actually 1.010 Of 10 Power —E)
- C Floating point types in languages are float、double and long double type .
- The first 1 Columns are general notation ;
- The first 2 Column is scientific notation ;
- The first 3 The column is exponential notation ( Also known as e Notation );
- This is how scientific notation is written in computers ,e The following numbers represent 10 The index of ;
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int n = 9;
float *pFloat = (float *)&n;
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%d\n",n);
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%lf\n", *pFloat);
*pFloat = 9.0;
printf("num Value :%d\n", n);
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%lf\n",*pFloat);
return 0;
}- Running results :
- As can be seen from the above code : Floating point and integer memory are stored in different forms !
- Some friends may have some questions , Why does the second line run the result *pFloat The answer is :0.000000, And the third line num The result of the operation is :1091567616, I think it should be 9.000000 and 9 ah . good , Don't worry. Now let's talk about why !
- Print :0.000000 Because : If you take it back in the form of a floating point number when you put it in the form of a plastic number , Not getting the result we expected , Is it possible to explain how to store the result of integer and floating-point typeIt's different, If it's the same, it'sThe same result
- Print :1091567616 Because :*pFloat We put it in the form of floating point numbers , And then to n The positive form of is taken as an integer ,Took out a wrong value
- This explains the difference between the storage method of shaping and the storage method of floating-point type
- Floating point binary complement
- for example :7.0 — 0111 — 0111.0( Give... After the decimal point 0 That's all right. ) This is it. 7.0 Binary representation of
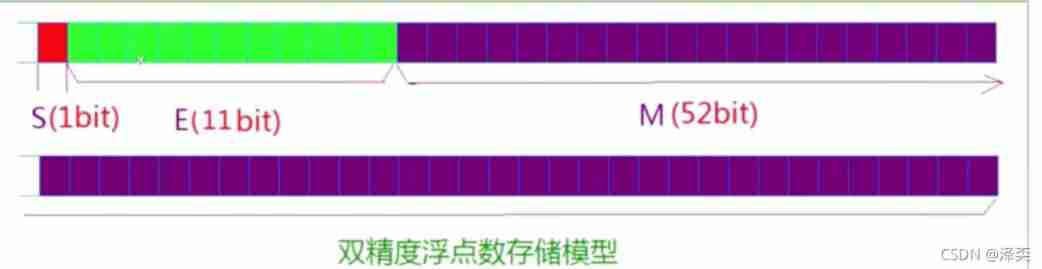
- Any binary floating point number V It can be expressed in the following form :
- (-1)^ M * 2 ^ E
- (-1)^ s The sign bit , Whens = 0 When ,V = Positive numbers(except 0 outside , Any number of 0 The second power equals 1) Whens=1 When ,V = negative
- M It represents a significant number , Greater than or equal to 1, Less than 2
- 2 ^ E Indicates the index bit
Storage mode diagram :

- The following example : Floating point numbers 9.0
- 1001
- 1001.0
- 1.001 * 2 ^ 3 —— Be careful : This is binary
- (-1) ^0*1.001* 2 ^3 = (-1)^ M * 2 ^ E
- 0 10000010 00100000000000000000000 —— E = 3 + 127 = 130
- The numbers we mentioned above are printed directly as the original code1091567616
- In this way, we can be sure that — s = 0 ,M = 1.001 ,E = 3 , Be careful M = 1.001 It's actually :0001
- The following example : Floating point numbers 0.5
- 0.5
- 0.1 — Be careful : This is one of the binary -1 The first digit after the decimal point , yes 2 The negative power of is 0.5
- 1.0 * 2 ^ -1 —— Convert to scientific counting
- (-1 ^0) *1.0* 2 ^-1—— Be careful : Index E Viewed as an unsigned number
- s = 0,M = 1.0,E = -1
- For eight E It is , The middle number is :127, For eleven E It is , The middle number is 1023,In fact, if your E If it's negative, take -1 Let's give you an example Eight is :-1+127 = 126,11 It's about :-1+1023 = 1022
- ****E Incomplete 0 Not all 1
- Floating point numbers 5.5
- 101.1 // The front is 101 according to 8421 Code to , The back is 2 Negative power of be equal to 0.5
- (-1) ^ 0 * 1.001 * 2 ^ 2
- s = 0 ,M = 1.011 ,E = 2 (E+127=129)
- 0100 0000 1011 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 —— here E The storage of is 129,E The value of the or 129-127=2, If you are double So here we have to subtract 1023 To the real E Value
- 0x40B00000 —— Converted binary hexadecimal digits
- The result of debugging memory :
-
- E All for 0 ( Understanding can )
- E All for 1 ( Understanding can )
边栏推荐
- 【Day3 文献精读】Asymmetrical time and space interference in Tau and Kappa effects
- Cloudcompare source code analysis: read ply file
- Solr之基礎講解入門
- 小程序启动性能优化实践
- Live broadcast preview | featurestore meetup V3 is coming!
- Is the product stronger or weaker, and is the price unchanged or reduced? Talk about domestic BMW X5
- Fonctionnement de la plate - forme d'examen de simulation pour les agents de sécurité - Questions d'examen de certificat a en 2022
- 机器学习之数据处理与可视化【鸢尾花数据分类|特征属性比较】
- 帝国理工等最新《胶囊网络综述》论文,29页pdf阐述胶囊的概念、方法与应用
- Altium designer工程下多个原理图和PCB图的一一对应
猜你喜欢
![[Day8 literature extensive reading] space and time in the child's mind: evidence for a cross dimensional symmetry](/img/c2/e70e7c32c5dc5554dea29cb4627644.png)
[Day8 literature extensive reading] space and time in the child's mind: evidence for a cross dimensional symmetry

Solve the problem of slow downloading plug-ins for idea

Software installation and use, etc
![[technology sharing] after 16 years, how to successfully implement the dual active traffic architecture of zhubajie.com](/img/9f/380dc1a2c1277a216b8c1cd41045bc.jpg)
[technology sharing] after 16 years, how to successfully implement the dual active traffic architecture of zhubajie.com

04 automatic learning rate - learning notes - lihongyi's in-depth learning 2021

Unity3d C#开发微信小游戏音频/音效播放问题解决过程分享

A method of relay for ultra long distance wireless transmission of low power wireless module
![[day4 literature intensive reading] space – time interdependence: evidence against Asymmetric mapping between time and space](/img/ce/f3817690a024cfebcf58a5ccc3cfdc.png)
[day4 literature intensive reading] space – time interdependence: evidence against Asymmetric mapping between time and space

【Day10 文献泛读】Temporal Cognition Can Affect Spatial Cognition More Than Vice Versa: The Effect of ...

2022 safety officer-a certificate test question simulation test platform operation
随机推荐
2022年安全员-A证考题模拟考试平台操作
A new product with advanced product power, the new third generation Roewe rx5 blind subscription is opened
我的创作纪念日
【Day8 文献泛读】Space and Time in the Child‘s Mind: Evidence for a Cross-Dimensional Asymmetry
Google搜索为什么不能无限分页?
Queue (C language)
Games-101 Yan Lingqi 5-6 lecture on raster processing (notes sorting)
IEEE floating point mantissa even round - round to double
Lake Shore—SuperTran 连续流低温恒温器系统
Data processing and visualization of machine learning [iris data classification | feature attribute comparison]
Solve the problem of slow downloading plug-ins for idea
移印工艺流程及应用注意事项
CVPR 2022 | meta learning performance in image regression task
直播预告|FeatureStore Meetup V3 重磅来袭!
Jetpack架构组件学习(3)——Activity Results API使用
Research Report on development trend and competitive strategy of global wafer recycling and OEM service industry
Two way leading circular linked list (C language)
双向带头循环链表(C语言)
【Day15 文献泛读】Numerical magnitude affects temporal memories but not time encoding
Research Report on development trend and competitive strategy of global seabed leakage detection system industry

