当前位置:网站首页>Dichotomy, discretization, etc
Dichotomy, discretization, etc
2022-07-05 05:36:00 【Falling spring is only inadvertently】
Two points answer , Discretization, etc
Two points answer
The best cattle fence
Code :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const double eps = 1e-5;
double a[N],b[N],sum[N];
int n,f;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&f);
for(int i = 1 ;i<=n;++ i)scanf("%lf",&a[i]);
double L = -1e6 , r = 1e6;
// Two point average
while(L + eps < r ){
double mid = (L + r)/2;
// Is the average of this length greater than mid , All minus mid Then it becomes Is the sum of this paragraph greater than 0
for(int i = 1;i<= n ;++i) b[i] = a[i] - mid;
// Find the prefix and
for(int i = 1;i<=n;++i) sum[i] = sum[i-1] + b[i];
double ans = -1e10;
double min_val = 1e10;
for(int i = f;i<=n;++i){
min_val = min(min_val,sum[i-f]);
ans = max(ans,sum[i] - min_val);
}
if(ans >=0) L = mid; else r = mid;
}
cout<<int(r*1000)<<endl;
return 0;
}
discretization
The movie
Their thinking :
This topic is a good discrete problem , Because the language here , Is very scattered , So we can bring them together , That is to redefine these languages , Rebranding 1,2,3,…,n1,2,3,…,n.
This topic is about statistics , Because the time limit is very strict , So I used C++11 Hash level of map,
Code :
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n,m;
map<int,int>lg;
int a[N] ,b[N] ,ans[N];
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i= 1;i<= n ;++i){
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
lg[x]++;
}
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
int maxx = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)
maxx = max(maxx,lg[a[i]]); // Get the number of people who can speak the most
int k = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)
if(lg[a[i]] == maxx) // Go through this number Find the number of the movie inside and save it in the array
ans[k++] = i;
if(k == 1) // If there is only one , Direct output
printf("%d\n",ans[0]);
else{
int res = 0,pos = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<k;++i) // Otherwise, in these films , Find the movie number that makes you happy , If the same, choose the latter
if(lg[b[ans[i]]] >= res){
res = lg[b[ans[i]]];
pos = ans[i];
}
printf("%d\n",pos);
}
return 0;
}
Median
Warehouse location
Their thinking ;
Sort + Median
The median has very excellent properties , For example, in this topic , The distance from each point to the median , Are the most desirable to meet the overall situation , Not local optimality .
Specifically , We are located at all points on the left of the warehouse , The sum of the distance to the warehouse is pp, The sum of the distances on the right is qq, Then we must let p+qp+q As small as possible .
When the warehouse moves to the left ,pp Will be reduced xx, however qq Will increase n−xn−x, So when it is the median of the warehouse ,p+qp+q Minimum .
The same sentence , Drawing comprehension is very important .
First, let's look at two points 
And so on n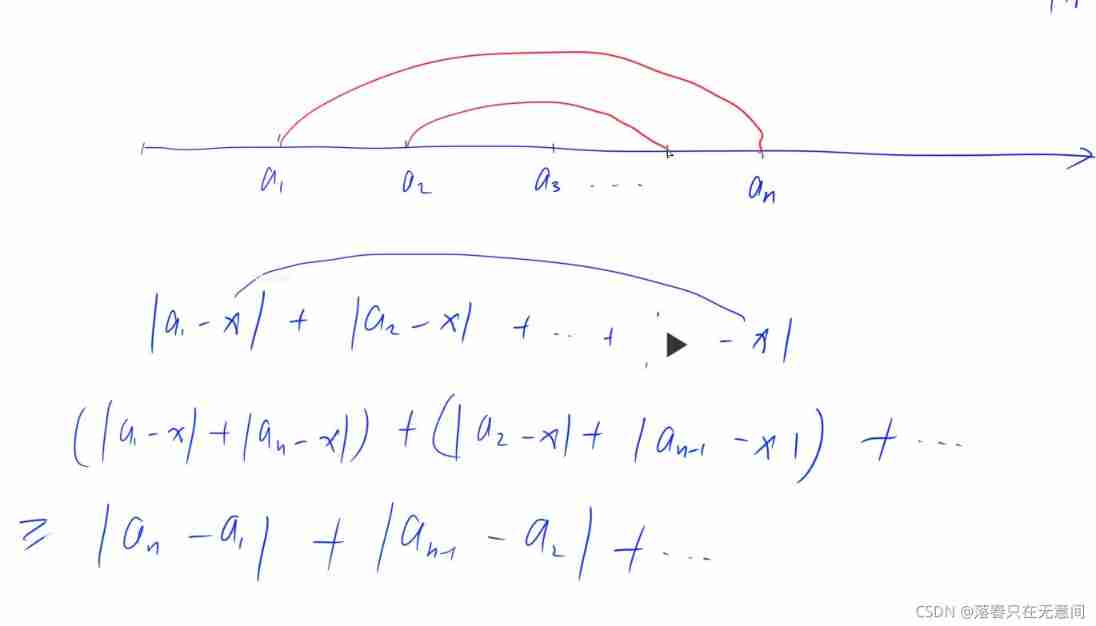
Code :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n,a[N];
long long ans;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n;++i)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sort(a+1,a+1+n);
int pos ;
if(n&1)
pos = (n+1)>>1;
else
pos = n >>1;
ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<= n;++i)
ans += abs(a[i] - a[pos]);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}
Dynamic median
Their thinking :
skill :
- Big root pile and small root pile
priority_queue<int> down; // Big root pile
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> up; // Heap
- n The number with odd position in the number and the middle position .
Unity can be written as :
(n+1)>>1
Code :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int t,T,id,n;
// Take the top of the big root pile as the median
int main(){
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%d%d",&id,&n);
printf("%d %d\n",id,(n+1)>>1);
int cnt = 0;
priority_queue<int> down; // Big root pile
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> up; // Heap
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
// The big root heap is empty , Or the current value is less than or equal to the median , Insert big root heap
if(down.empty() || x<= down.top()) down.push(x);
else up.push(x);// Otherwise, insert the small root pile
// Because it's the big root pile, and the top of the pile is the median , Under normal circumstances The number of large root piles should be Number of small root piles + 1
// therefore If Greater than up.size() + 1 , Put the top on the small root pile
if(down.size() > up.size() + 1){
up.push(down.top()),down.pop() ;}
// And the small heel pile is smaller than 1 individual , So If equal to, it's even more
if(up.size() > down.size()) {
down.push(up.top()) , up.pop(); }
if(i&1){
printf("%d ",down.top());
if(++cnt % 10 == 0)putchar('\n');
}
}
if(cnt %10)
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
Reverse alignment
Definition
For a sequence a, if
i < j a n d a [ i ] > a [ j ] , be call a [ i ] And a [ j ] structure become The inverse order Yes i<j\ and \ a[i] > a[j] , said a[i] And a[j] Form an inverse pair of i<j and a[i]>a[j], be call a[i] And a[j] structure become The inverse order Yes
Using merge sort to find
Code :
// left = 1, right = n;
void msort(int left , int right){
if(left == right)return ;
int mid = (left + right) >>1,i,j,k;
msort(left,mid),msort(mid+1,right);
k = left;
for( i = left,j = mid+1;i<=mid && j<=right;){
if(a[i]<=a[j])
b[k++] = a[i++];
else
b[k++] = a[j++] , ans += mid - i + 1; // It shows that the second half is smaller than the first half
// Number of them Namely i For the first half of the comparison , That is, it is larger than the second half
// The number is it Distance to the middle position .
}
while(i<=mid)b[k++] = a[i++];
while(j<=right) b[k++] = a[j++],ans += mid-i+1;
// printf("ans %d \n",ans);
for( i = left;i<=right;++i)
a[i] = b[i];
}
Odd digital problem
This kind of topic has a conclusion :
When n It's an odd number
If and only if the numbers in the grid are written in one line in turn in two situations n*n-1 After the sequence of elements , Regardless of spaces , If the parity of the reverse order pair is the same .
When n When it's even
If and only if the numbers in the grid are written in one line in turn in two situations n*n-1 After the sequence of elements , Regardless of spaces ,“ The difference of reverse logarithm ” and " The difference between the number of lines with spaces in the two situations " The same parity can .
Code :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
const int N = 3e5 + 10;
int n,a[N],b[N];
long long cnt1 , cnt , ans;
void msort(int left , int right){
if(left == right)return ;
int mid = (left + right) >>1,i,j,k;
msort(left,mid),msort(mid+1,right);
k = left;
for( i = left,j = mid+1;i<=mid && j<=right;){
if(a[i]<=a[j])
b[k++] = a[i++];
else
b[k++] = a[j++] , ans += mid - i + 1; // It shows that the second half is smaller than the first half
// Number of them Namely i For the first half of the comparison , That is, it is larger than the second half
// The number is it Distance to the middle position .
}
while(i<=mid)b[k++] = a[i++];
while(j<=right) b[k++] = a[j++],ans += mid-i+1;
// printf("ans %d \n",ans);
for( i = left;i<=right;++i)
a[i] = b[i];
}
int main(){
while(~scanf("%d",&n)){
int ok = 0,x; // Not put 0 add
for(int i=1;i<=n*n;++i)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
if(!x)
ok = 1;
else
a[i-ok] = x;
}
ans = 0 , memset(b,0,sizeof b);
msort(1,n*n);
cnt = ans , memset(b,0,sizeof b),ok = 0;
memset(a,0,sizeof a); // because 0 The location may be different, so empty
for(int i=1;i<=n*n;++i)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
if(!x)
ok = 1;
else
a[i-ok] = x;
}
ans = 0,msort(1,n*n);
//printf("%d %d\n",cnt,ans);
if((cnt & 1) == (ans & 1) ) // Remember to put parentheses , & operation Than == All small
printf("TAK\n");
else
printf("NIE\n");
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Yolov5 adds attention mechanism
- High precision subtraction
- Haut OJ 1243: simple mathematical problems
- Configuration and startup of kubedm series-02-kubelet
- Pointnet++学习
- On-off and on-off of quality system construction
- 2022 极术通讯-Arm 虚拟硬件加速物联网软件开发
- Control unit
- 网络工程师考核的一些常见的问题:WLAN、BGP、交换机
- [es practice] use the native realm security mode on es
猜你喜欢

2017 USP Try-outs C. Coprimes

CF1634E Fair Share
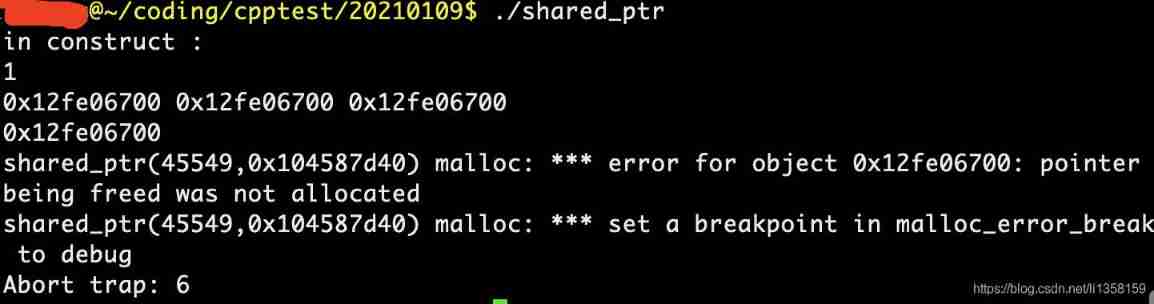
shared_ Repeated release heap object of PTR hidden danger
![[jailhouse article] performance measurements for hypervisors on embedded ARM processors](/img/c0/4843f887f77b80e3b2329e12d28987.png)
[jailhouse article] performance measurements for hypervisors on embedded ARM processors
Support multi-mode polymorphic gbase 8C database continuous innovation and heavy upgrade

CCPC Weihai 2021m eight hundred and ten thousand nine hundred and seventy-five

Educational Codeforces Round 116 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Arena
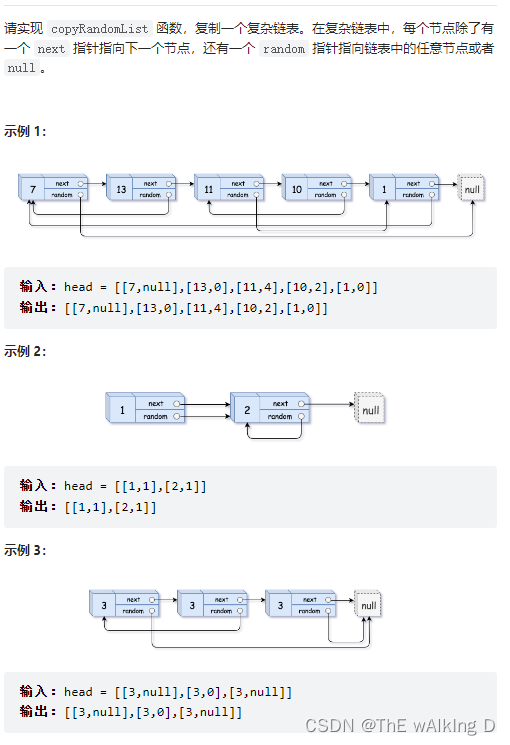
Sword finger offer 35 Replication of complex linked list
Pointnet++ learning
Palindrome (csp-s-2021-palin) solution
随机推荐
Chapter 6 data flow modeling - after class exercises
Analysis of backdoor vulnerability in remote code execution penetration test / / phpstudy of national game title of national secondary vocational network security B module
Educational Codeforces Round 116 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Arena
游戏商城毕业设计
26、 File system API (device sharing between applications; directory and file API)
Over fitting and regularization
Educational codeforces round 109 (rated for Div. 2) C. robot collisions D. armchairs
Zzulioj 1673: b: clever characters???
Sword finger offer 06 Print linked list from beginning to end
剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
Add level control and logger level control of Solon logging plug-in
Sword finger offer 35 Replication of complex linked list
Reader writer model
每日一题-无重复字符的最长子串
Personal developed penetration testing tool Satania v1.2 update
[jailhouse article] performance measurements for hypervisors on embedded ARM processors
kubeadm系列-02-kubelet的配置和启动
Sword finger offer 09 Implementing queues with two stacks
High precision subtraction
To be continued] [UE4 notes] L4 object editing