当前位置:网站首页>AtCoder Grand Contest 013 E - Placing Squares
AtCoder Grand Contest 013 E - Placing Squares
2022-07-05 05:31:00 【solemntee】
Portal :E - Placing Squares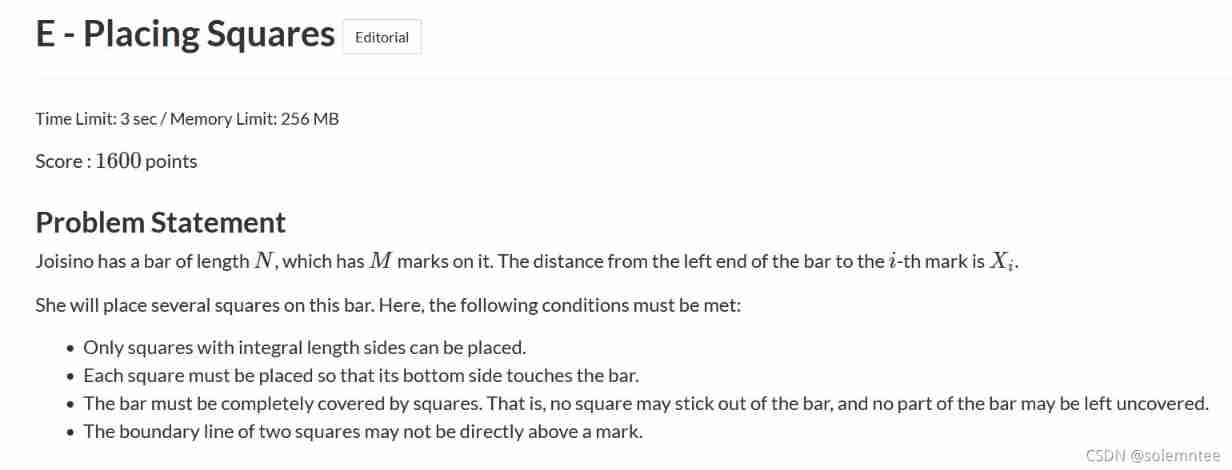
 The question : Now there is one with a length of n The stick
The question : Now there is one with a length of n The stick
On the stick m m m A sign , The first i The distance between the marks and the left endpoint is x i x_i xi
You need to put some squares on this stick , Satisfy :
The side length of each square is a positive integer
Each square must have a side close to the stick
The stick must be completely covered , The boundary of the square cannot exceed the stick
The junction of two adjacent squares cannot be marked
Define the beauty degree of each scheme as the product of all square areas
Seek the sum of the beauty of all legal schemes , The answer is right 1 0 9 + 7 10^9+7 109+7 modulus
First of all, let's enjoy the official explanation 
First of all, the contribution and can be transformed into the number of schemes through a clever transformation . Modify the model of the original problem slightly : Now there is n n n Consecutive spaces , Partition plates must be placed on the left and right boundaries , You can place partitions in two adjacent spaces , You can put red and blue balls in the space . Contribution and the number of solutions equivalent to the converted problem , This becomes a count d p dp dp.
consider d p [ i ] [ j ] dp[i][j] dp[i][j] Before considering i i i position , After the last partition j j j The number of ball schemes .
Consider the transfer of violence enumerated in section i i i There's a place for ( 0 , 1 , 2 ) (0,1,2) (0,1,2) Ball and whether it is in the i i i Place the baffle in two places , The specific derivation process will not be repeated
d p [ i ] [ 0 ] = d p [ i − 1 ] [ 0 ] ∗ 2 + d p [ i − 1 ] [ 1 ] ∗ 2 + d p [ i − 1 ] [ 2 ] ∗ 1 d p [ i ] [ 1 ] = d p [ i − 1 ] [ 0 ] ∗ 1 + d p [ i − 1 ] [ 1 ] ∗ 1 + d p [ i − 1 ] [ 2 ] ∗ 0 d p [ i ] [ 0 ] = d p [ i − 1 ] [ 0 ] ∗ 1 + d p [ i − 1 ] [ 1 ] ∗ 2 + d p [ i − 1 ] [ 2 ] ∗ 1... dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0]*2+dp[i-1][1]*2+dp[i-1][2]*1\\ dp[i][1]=dp[i-1][0]*1+dp[i-1][1]*1+dp[i-1][2]*0\\ dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0]*1+dp[i-1][1]*2+dp[i-1][2]*1 ... dp[i][0]=dp[i−1][0]∗2+dp[i−1][1]∗2+dp[i−1][2]∗1dp[i][1]=dp[i−1][0]∗1+dp[i−1][1]∗1+dp[i−1][2]∗0dp[i][0]=dp[i−1][0]∗1+dp[i−1][1]∗2+dp[i−1][2]∗1...
amount to
A N S [ i ] = { 2 2 1 1 1 0 1 2 1 } ∗ A N S [ i − 1 ] ANS[i]= \left\{ \begin{matrix} 2 & 2 &1 \\ 1 & 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 2 & 1 \end{matrix} \right\} *ANS[i-1] ANS[i]=⎩⎨⎧211212101⎭⎬⎫∗ANS[i−1]
Obviously, the matrix can be used for fast power optimization .
Of course, the transfer at the diaphragm is slightly different , No more details here .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int N=3;
struct Matrix{
int a[N][N];
Matrix(){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));}
Matrix operator *(const Matrix &B)
{
Matrix c;
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
c.a[i][j]=(c.a[i][j]+1LL*a[i][k]*B.a[k][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
return c;
}
}A,B,C,D;
Matrix fpow(Matrix A,long long b)///A^b
{
Matrix ret,B=A;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)ret.a[i][i]=1;
while(b)
{
if(b&1)ret=ret*B;
B=B*B;
b>>=1;
}
return ret;
}
void init()
{
A.a[0][0]=2,A.a[0][1]=2,A.a[0][2]=1;
A.a[1][0]=1,A.a[1][1]=1,A.a[1][2]=0;
A.a[2][0]=1,A.a[2][1]=2,A.a[2][2]=1;
B.a[0][0]=1,B.a[0][1]=0,B.a[0][2]=0;
B.a[1][0]=1,B.a[1][1]=1,B.a[1][2]=0;
B.a[2][0]=1,B.a[2][1]=2,B.a[2][2]=1;
C.a[0][0]=1,C.a[0][1]=2,C.a[0][2]=1;
C.a[1][0]=0,C.a[1][1]=0,C.a[1][2]=0;
C.a[2][0]=0,C.a[2][1]=0,C.a[2][2]=0;
}
int a[1000005];
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
init();
Matrix ans;
ans.a[0][0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
ans=fpow(A,a[i]-a[i-1]-1)*ans;
ans=B*ans;
}
ans=fpow(A,n-a[m]-1)*ans;
ans=C*ans;
// for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
// {
// for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
// {
// printf("%d%c",ans.a[i][j],(j==N-1)?'\n':' ');
// }
// }
printf("%d\n",(ans.a[0][0]%mod+mod)%mod);
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- SSH password free login settings and use scripts to SSH login and execute instructions
- 剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
- [turn to] MySQL operation practice (I): Keywords & functions
- Haut OJ 1347: addition of choice -- high progress addition
- 剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
- 对象的序列化
- Alu logic operation unit
- Sword finger offer 53 - ii Missing numbers from 0 to n-1
- Solon Logging 插件的添加器级别控制和日志器的级别控制
- Zheng Qing 21 ACM is fun. (3) part of the problem solution and summary
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
常见的最优化方法
剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
[speed pointer] 142 circular linked list II
远程升级怕截胡?详解FOTA安全升级
Haut OJ 1316: sister choice buys candy III
What is the agile proportion of PMP Exam? Dispel doubts
On-off and on-off of quality system construction
object serialization
[turn]: OSGi specification in simple terms
剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
Little known skills of Task Manager
Sword finger offer 06 Print linked list from beginning to end
Haut OJ 1352: string of choice
TF-A中的工具介绍
游戏商城毕业设计
MySQL数据库(一)
一个新的微型ORM开源框架
Double pointer Foundation
Remote upgrade afraid of cutting beard? Explain FOTA safety upgrade in detail
Haut OJ 1401: praise energy
![[to be continued] [UE4 notes] L3 import resources and project migration](/img/81/6f75f8fbe60e037b45db2037d87bcf.jpg)