当前位置:网站首页>3.C语言用代数余子式计算行列式
3.C语言用代数余子式计算行列式
2022-07-06 09:19:00 【是王久久阿】
目录
1.代数余子式计算行列式的原理
注意:行列式一定是方阵!
二阶行列式计算
杀戮法:
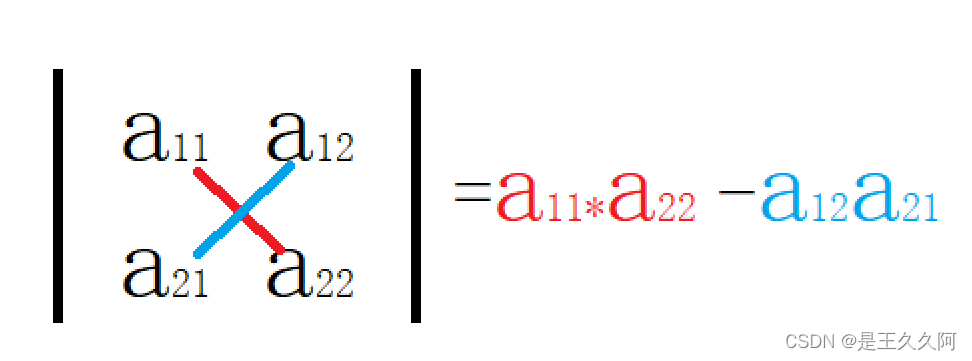
二阶行列式的计算方法非常简单,主对角线元素相乘—副对角线元素相乘,故又称杀戮法。
三阶行列式计算
划线法:
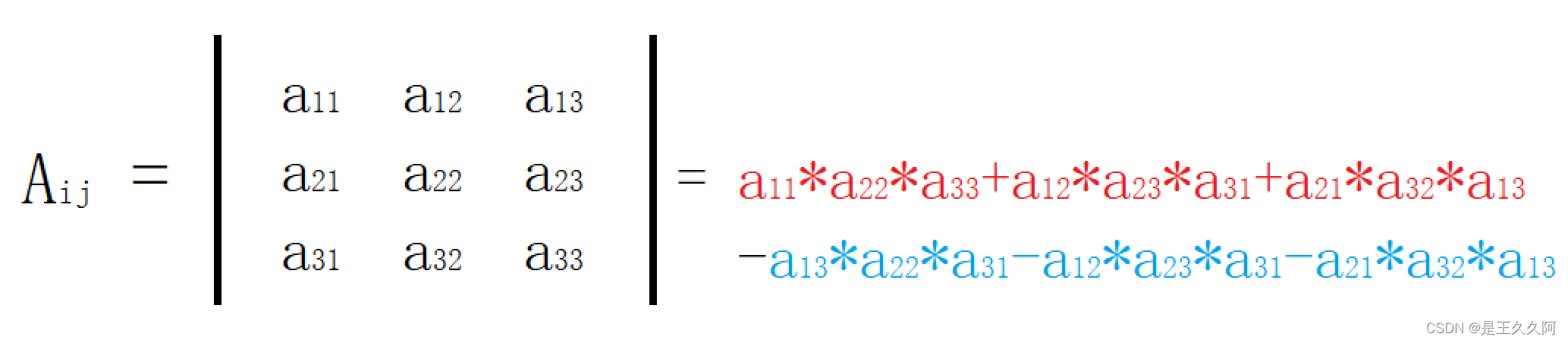
划线法如下图所示
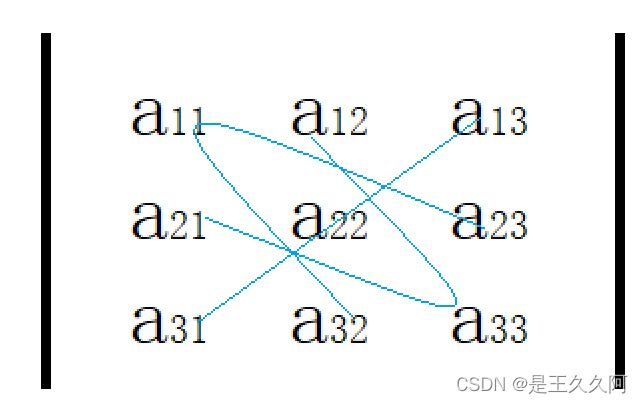
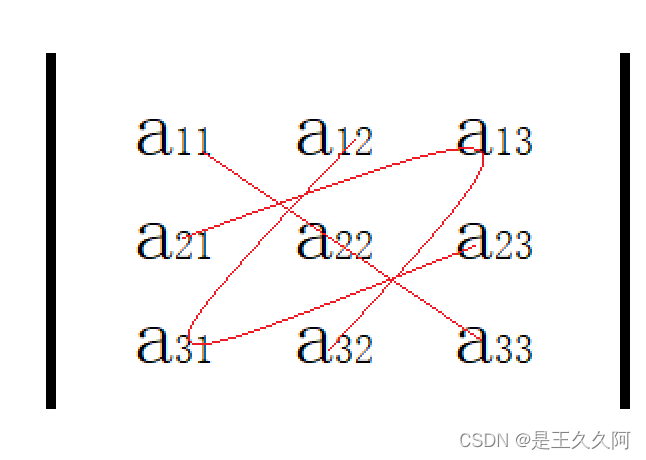
按定义计算
计算行列式时,可以将其按行或列展开进行计算
以三阶行列式为例:

将行列式A按第一行展开:
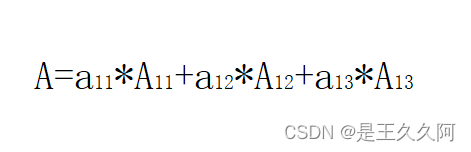
其中,Aij为aij的代数余子式(i为行号,j为列号),例如:A11为a11的代数余子式。
代数余子式的计算方法:
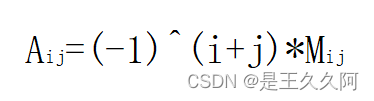
其中,(-1)^(i+j)表示为-1的i+j次方,用来决定代数余子式的正负,Mij为余子式。
余子式:
行列式去其i行j列,剩下的元素组成一个新的行列式,该矩阵为aij的余子式。
例如,a11的余子式为:
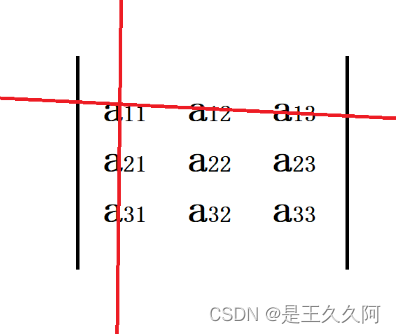
去其第一行第一列,剩下的元素按照现有的排列组合成新的行列式。
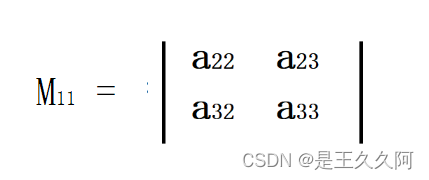
在计算行列式的值时,我们可以选择0多的那一行和那一列进行展开,大大缩减计算量。
2.代码实现
核心思想:
当我们求高阶行列式的值时,可以利用求代数余子式的方式将求高阶行列式逐步转换为求低阶行列式的问题。利用递归的思想可以解决此类问题,将大事化小,小事化了。
输入矩阵main
在C语言中,矩阵可以利用二维数组数组将其存储起来。
当然用数组存放矩阵也有其缺陷:数组的大小是不可以改变的。在没学动态规划之前,可以根据使用的大小开辟足够大的内存空间,以此来应对该问题。
在输入行列式的时候,还需要确定其阶数n才能进行计算。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include<assert.h>
#define COL 10//为二维数组开辟的最大内存
int main()
{
int arr[COL][COL] = { 0 };
int i = 0, j = 0;
int n = 0;//阶数
printf("行列式阶数:>");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("请输入行列式:>\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i][j]);
}
}
printf("%d", Det(arr, n));
}行列式的计算Det
因为1阶行列式不用计算,就是其本身,而3阶、2阶的行列式又可以根据划线法和杀戮法计算,这里可以将递归的条件设置为n>3,只有四阶及以上的行列式才进行递归,四阶以下的行列式直接计算得出结果。
- 在行列式计算前,为了保证数组的安全性,在接收数组的时候加上const,保证数组在函数内部无法修改。
- 行列式的阶数只有大于等于1时才有意义,在函数开头利用assert断言n是否大于0:条件为真函数运行,条件为假assert则会报警告,assert需包含头文件。
int Cof(const int arr2[COL][COL], int i, int n);//声明:计算行列式
//计算行列式
int Det(const int arr[COL][COL], int n)
{
assert(n > 0);
int sum = 0;
int i = 0;
if (n == 1)//1阶行列式直接得出结果
{
sum = arr[0][0];
}
else if (n == 2)
{
sum = arr[0][0] * arr[1][1] - arr[0][1] * arr[1][0];//杀戮法求解
}
else if (n == 3)
{
sum = arr[0][0] * arr[1][1] * arr[2][2]
+ arr[0][1] * arr[1][2] * arr[2][0]
+ arr[1][0] * arr[2][1] * arr[0][2]
- arr[0][2] * arr[1][1] * arr[2][0]
- arr[0][1] * arr[1][0] * arr[2][2]
- arr[1][2] * arr[2][1] * arr[0][0];//划线法求解
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)//按第一行展开
{
if (arr[0][i] != 0)//展开项不为0才计算
{
sum += ((int)pow(-1, i + 2)) * arr[0][i] * (Cof(arr, i, n));//2阶以上继续递归
}
else
sum += 0;//展开项为0
}
}
return sum;
}余子式Cof
接收Det函数传过来的二维数组,取其行列,剩下的元素组成新的二维数组再传给Det函数。两个函数相互调用,直到阶数小于4。
int Det(const int arr[COL][COL], int n);//声明:计算代数余子式
//找到余子式
int Cof(const int arr[COL][COL], int i, int n)
{
assert(n > 0);
int k = 0;
int j = 0;
int arr2[COL][COL] = { 0 };
for (k = 0; k < n - 1; k++)//去除0行i列,剩下的组成新的矩阵
{
for (j = 0; j < n - 1; j++)
{
if (j < i)
{
arr2[k][j] = arr[k + 1][j];
}
else
{
arr2[k][j] = arr[k + 1][j + 1];
}
}
}
return Det(arr2, n - 1);
}3.该方法的不足
尽管我们设置了很多方法来避免无用的递归
- 展开项为0则不进行计算
- 3阶以下行列式直接计算
但是如果求高阶的行列式还是有所不足:假如求10阶行列式,则需要递归10!/ 6=604,800次,深度递归最终导致程序运行的非常缓慢。
边栏推荐
- [Topic terminator]
- First acquaintance with C language (Part 2)
- Network layer 7 protocol
- Interview Essentials: talk about the various implementations of distributed locks!
- 记录:初次cmd启动MySQL拒接访问之解决
- 系统设计学习(二)Design a key-value cache to save the results of the most recent web server queries
- MySQL backup -- common errors in xtrabackup backup
- 阿里云微服务(三)Sentinel开源流控熔断降级组件
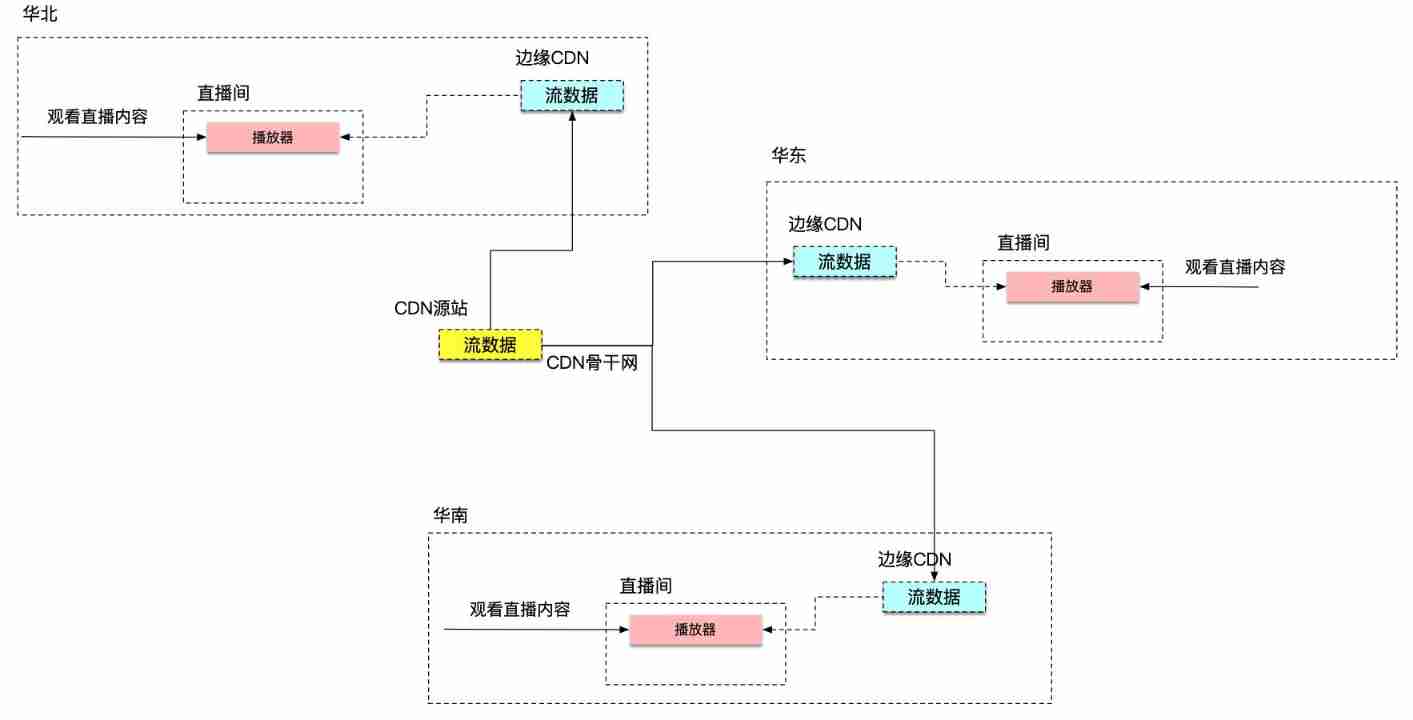
- Application architecture of large live broadcast platform
- TYUT太原理工大学2022软工导论简答题
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
All in one 1405: sum and product of prime numbers
阿里云微服务(三)Sentinel开源流控熔断降级组件
Error: symbol not found
Alibaba cloud microservices (I) service registry Nacos, rest template and feign client
Implement queue with stack
Small exercise of library management system
Database operation of tyut Taiyuan University of technology 2022 database
Alibaba cloud microservices (III) sentinel open source flow control fuse degradation component
Interview Essentials: talk about the various implementations of distributed locks!
Answer to "software testing" exercise: Chapter 1
KF UD decomposition pseudo code implementation advanced [2]
Alibaba cloud side: underlying details in concurrent scenarios - pseudo sharing
Record: I accidentally wrote a recursion next time
TYUT太原理工大学2022数据库大题之数据库操作
13 power map
FileInputStream和BufferedInputStream的比较
【快趁你舍友打游戏,来看道题吧】
A brief introduction to the database of tyut Taiyuan University of technology in previous years
Relational algebra of tyut Taiyuan University of technology 2022 database
The earth revolves around the sun