当前位置:网站首页>String class
String class
2022-07-06 13:08:00 【犇犇犇犇犇犇犇】
String type
Catalog :
List of articles
1. Common methods
stay java in , String is a reference type ,String There are many methods in class that are convenient for us to use , Its functions are applicable to various scenarios , Now let's introduce these common methods .
1.1 Construction method
You can enter the official help manual to search String class , We can see String Class in java.lang The package is imported by default , And it was final The modified .
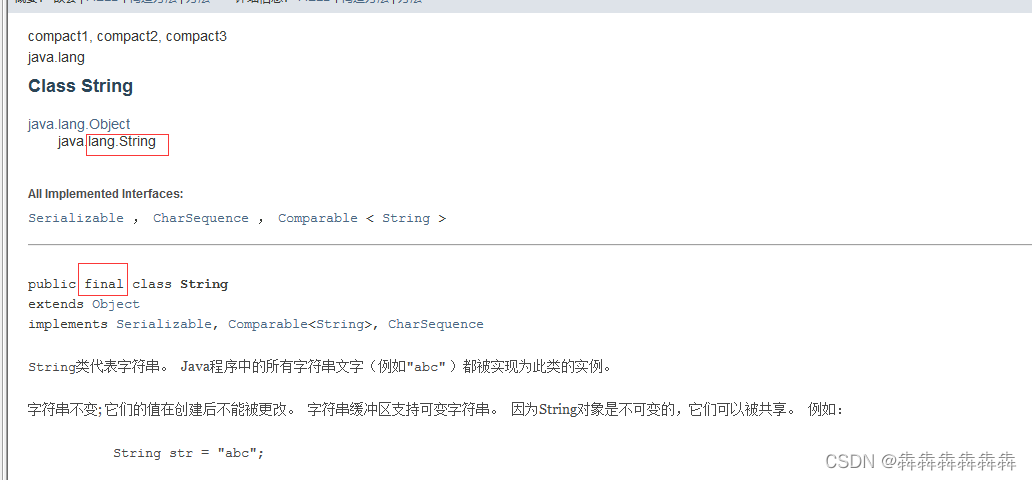
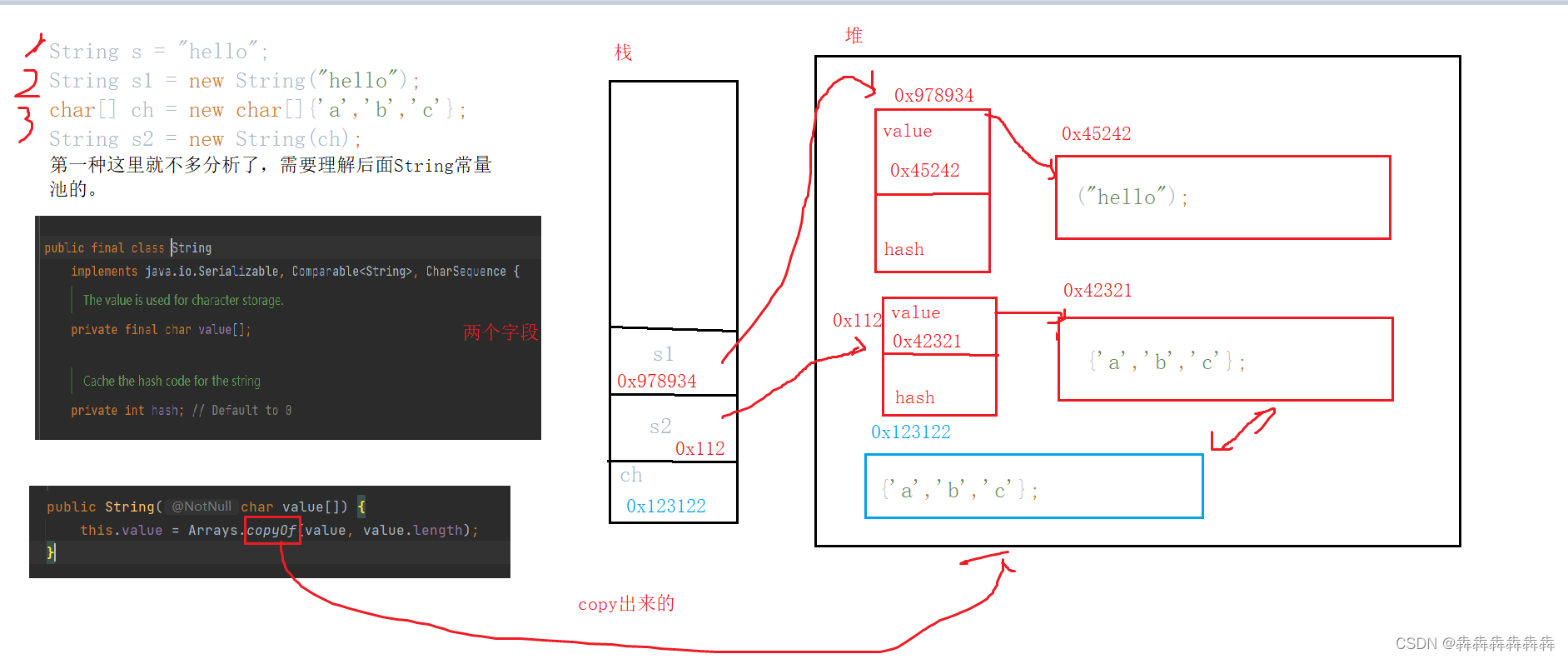
There are many ways to construct strings , There are three common construction methods
String s1 = "hello";// AbbreviationString s1 = new String("hello");char[] ch = new char[]{ 'a','b','c'}; String s1 = new String(ch);
The first method is used most , The most simple .
Let's analyze the memory distribution of these construction methods
1.2 String lookup (indexOf)
| Method | usage |
|---|---|
| string.charAt(index) | It is used to get a character in the string directly through subscript |
| string.indexOf(char ch) | Used to find the first character in the string ch The location of |
| string.lastindexOf(char ch) | Find characters from back to front ch First occurrence |
| string.indexOf(string ch)lastindexof It's fine too | Used to find strings ch First occurrence |
| string.indexOf(char ch ,int fromindex)last It's fine too | The front is the same ,fromindex It means to start looking from this position |
public static void main5(String[] args) {
String s1 = "ababacabcdaseasq";
String s2 ="www.baidu.com";
System.out.println(s2.lastIndexOf('.',4));
System.out.println(s2.lastIndexOf('.'));
System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf('ab'));
}
public static void main4(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(s1.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println("====================");
System.out.println(s1.indexOf('h'));// Find the first character
System.out.println(s1.indexOf('l',3));
System.out.println("====================");
String s2 = "abaabcabcdabsaea";
System.out.println(s2.indexOf("abcd"));
}
1.3 String comparison (equals,compareTo)
Generally, we use == To express , For basic types == The comparison is whether the content is the same , But for reference types == The comparison is whether the same object is referenced , This cannot meet our requirements to compare content .
For reference types, we use equals Compare ,equals The return value of the boolean,java Case insensitive equalsIgnoreCase Method .
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "HELLO";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));//true
equals You can only compare whether two strings are the same , To compare the size, we need to use compareTo Method because String Realized CompareTo Interface ,compareTo The return value type of is int, Again java A comparison that ignores case is also provided in compareToIgnoreCase Method .
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "HELLO";
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));//0
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3));//0
1.4 transformation
- toggle case
| Method | function |
|---|---|
| toUpperCase() | Change all lowercase strings to uppercase ( Letter ) |
| toLowerCase() | Change all uppercase strings to lowercase ( Letter ) |
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "HELLO";
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());//HELLO
System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());//hello
System.out.println(s1);//hello
System.out.println(s2);//HELLO
Chinese regardless
- String to array (toCharArray)
String s1 = "hello";
char[] ch = s1.toCharArray();
for (char x : ch) {
System.out.println(x);
}
- Numeric conversion string (valueOf)
| Method | function |
|---|---|
| string.valueOf( Basic types i) | Put the basic type i Convert to string type |
| Basic types .valueOf(String s) | take string Convert type to base type |
| Basic types .parse***(String s)( This conversion is generally used ) | take string Convert type to base type |
| Basic types .valueOf(String s radix x) radix Express x Base number (parse*** Also have ) | take String The value of type is pressed x Conversion from decimal to decimal |
String s1 = String.valueOf(123);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.5);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
String s3 = String.valueOf(new Student(12));// It can also be an object
System.out.println(s3);
int a = Integer.valueOf("0101",2);//5
System.out.println(a);
int b = Integer.parseInt("1000");//1000
System.out.println(b);
1.5 String replacement (replace)
| Method | function |
|---|---|
| String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) | Replace all specified contents |
| String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | Replace the first content |
String s1 = "ababcabcdeaaweqggh";
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s1.replace('a', 'k'));//kbkbckbcdekkweqggh
System.out.println(s1.replace("ab", "wt"));//wtwtcwtcdeaaweqggh
System.out.println(s1.replaceAll("ab","zc"));//zczcczccdeaaweqggh
System.out.println(s1.replaceFirst("ab","1122"));//1122abcabcdeaaweqggh
1.6 String splitting (split)
Divide the string into several strings according to the specified separator
| Method | function |
|---|---|
| String[] split(String regex) | Split all strings |
| String[] split(String regex, int limit) | The string in the specified format , Split into limit Group |
String s1 = "ni hao ma zui jin";
String[] s2 = s1.split(" ",3);
for (String x : s2) {
System.out.println(x);
//ni
//hao
//ma zui jin
}
Escape the specified special separator, such as :,.
String s1 = "255\\255\\255\\255";
// Special characters need to be escaped
String[] s2 = s1.split("\\\\");// Because the string also needs escape , So there are two escape
for (String x : s2) {
System.out.println(x);
}
String s1 = "255.255.255.255";
// Special characters need to be escaped
String[] s2 = s1.split("\\.");
for (String x : s2) {
System.out.println(x);
}
You can also give multiple delimiters to split multiple times
String s1 = "zaiganma nihao&=nibuhao";
String[] s2 = s1.split(" |&");
for(Stiring x : s2){
System.out.println(x);
}
// Split multiple times
s2 = s1.split(" ");
for (String x : s2) {
String[] s3 = x.split("=");
for (String x1 : s3) {
System.out.println(x1);
}
}
1.7 String interception (substring)
This is nothing to say simple
String s1 = "liuyuhao";
System.out.println(s1.substring(3));
System.out.println(s1.substring(2, 5));//[2,5) Left closed right away
1.8 Other operating
trim() Delete the space on the left and right sides of the string , Tabulation , Line break, etc
String s1 = " liu yu ";
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s1.trim());
intern() Manually enter the pool , The following is about constant pool
char[] ch = {
'a','b','c'};
String s1 = new String(ch);
s1.intern();// Manually enter the pool
String s2 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
String Class method , If the return is basically new String object . because String The content in cannot be modified after it is created ,String Is an unchangeable object , So try to avoid direct modification of the string
String s1 = "hello";
s1 += " word";
System.out.println(s1);
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("hello");
stringBuilder.append(" word");
Because its bottom layer actually relies on StringBuilder class , Many temporary variables will be created in the middle , So for string modification, we directly use StringBuilder and StringBuffer.String The reason why the content of cannot be changed is String Fields in the class value By final modification , indicate value Cannot reference other character arrays , But you can modify the contents of the reference array .
1.9String Constant pool
String constant pool, also known as StringTable In fact, it is an efficient query data structure .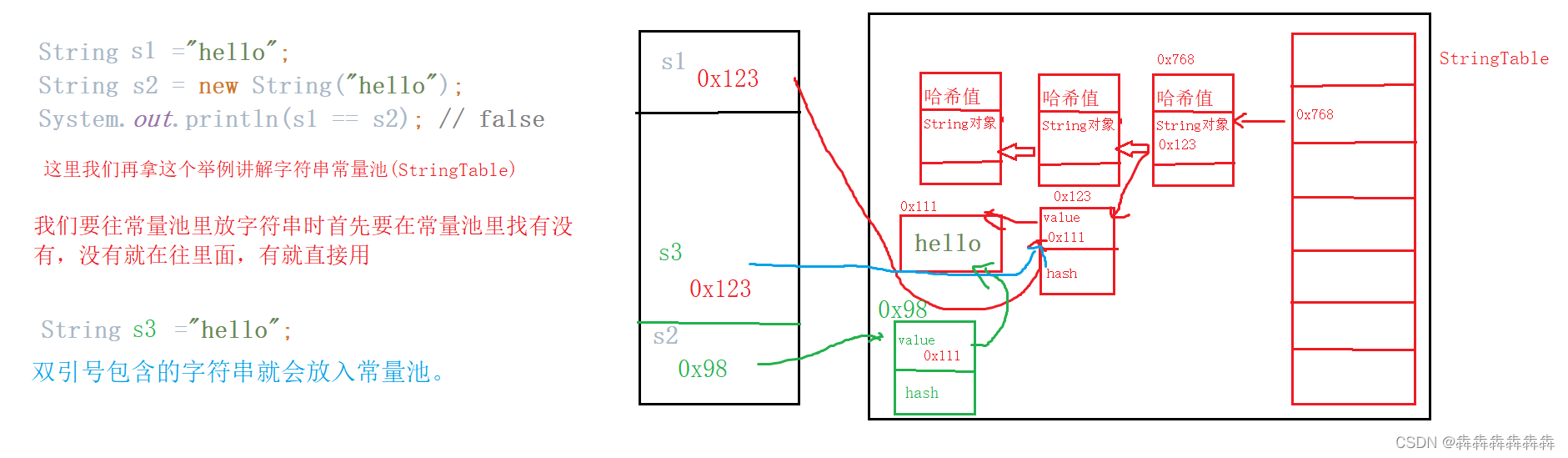
inter() Manually enter the pool 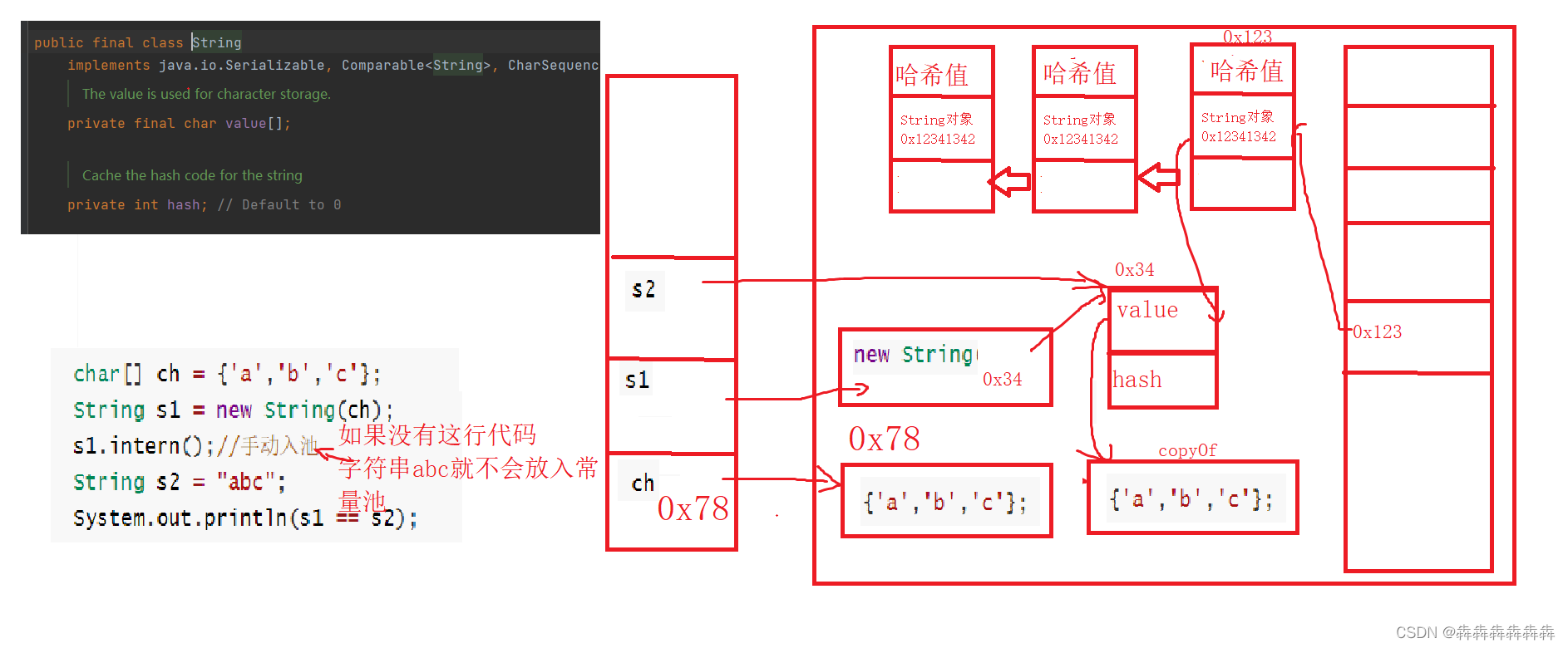
2.StringBuilder and StringBuffer
Be careful String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder Differences among the three
- String The content of cannot be modified ,StringBuffer and StringBuilder The content of can be modified
- StringBuffer and StringBuilder Both methods are roughly the same
- StringBuffer Synchronous processing , Multithreading is very safe ,StringBuilder If not, do you handle , Unsafe when multithreading .
Here are some key points String There is no way ,StringBuffer The same way
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
String s1 = "hello";
stringBuilder.append(s1);// Convert the string to StringBuilder
stringBuilder.insert(0,"lyh ");// stay 0 The subscript position starts inserting ,lyh
stringBuilder.insert(1,1);// stay 1 Insert at subscript position ,1
stringBuilder.deleteCharAt(1);// Delete 1 Of subscript position 1
stringBuilder.setCharAt(0,'z');// take 0 The character in the subscript position is changed to z
stringBuilder.codePointAt(1);// return 1 Of subscript characters ASCII Code value
stringBuilder.reverse();// String reversal
String str = stringBuilder.toString();//StringBuilder turn String
stringBuilder.append("how are you");//String turn StringBuilder
int num = stringBuilder.capacity();
System.out.println(num);// Get the total size of the underlying saved string space
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
Add :
- String format output
String s1 = String.format("%d-%d-%d",2002,06,24);
System.out.println(s1);
- The length of the string is different from that of the array , String length is a method called , Array calls a field
String s1 = "hello";
System.out.println(s1.length());
int[] array = {
1,2,3,4};
System.out.println(array.length);
- Three algorithms for string matching ,BF,BM,KMP, Here is a brief introduction to ,BF The algorithm is a simple two-level cycle of violent matching ,BM The algorithm uses the idea of a good number pair and a bad number pair to process the substring ,KMP The algorithm cites a next Arrays handle substrings and next Optimization of arrays ,nextval Array , You can learn the specific related content .
Learning results of this section
- I understand String class
- Get the hang of String Various methods in the class
- I understand String Constant pool
- Get to know StringBuilder and StringBuffer Also mastered their various methods
- master String,StringBuffer and StringBuilder The difference between
边栏推荐
- 闇の連鎖(LCA+树上差分)
- 阿里云微服务(一)服务注册中心Nacos以及REST Template和Feign Client
- [dry goods] cycle slip detection of suggestions to improve the fixed rate of RTK ambiguity
- 架构师怎样绘制系统架构蓝图?
- 使用rtknavi进行RT-PPP测试
- Ten minutes to thoroughly master cache breakdown, cache penetration, cache avalanche
- [算法] 剑指offer2 golang 面试题12:左右两边子数组的和相等
- 阿里云微服务(四) Service Mesh综述以及实例Istio
- All in one 1405: sum and product of prime numbers
- TYUT太原理工大学2022数据库大题之概念模型设计
猜你喜欢
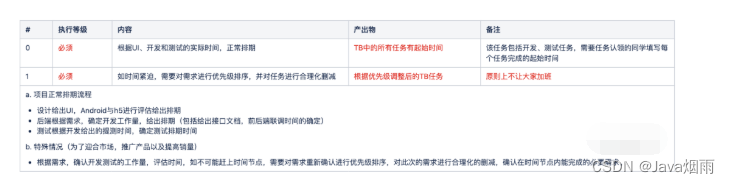
2年经验总结,告诉你如何做好项目管理
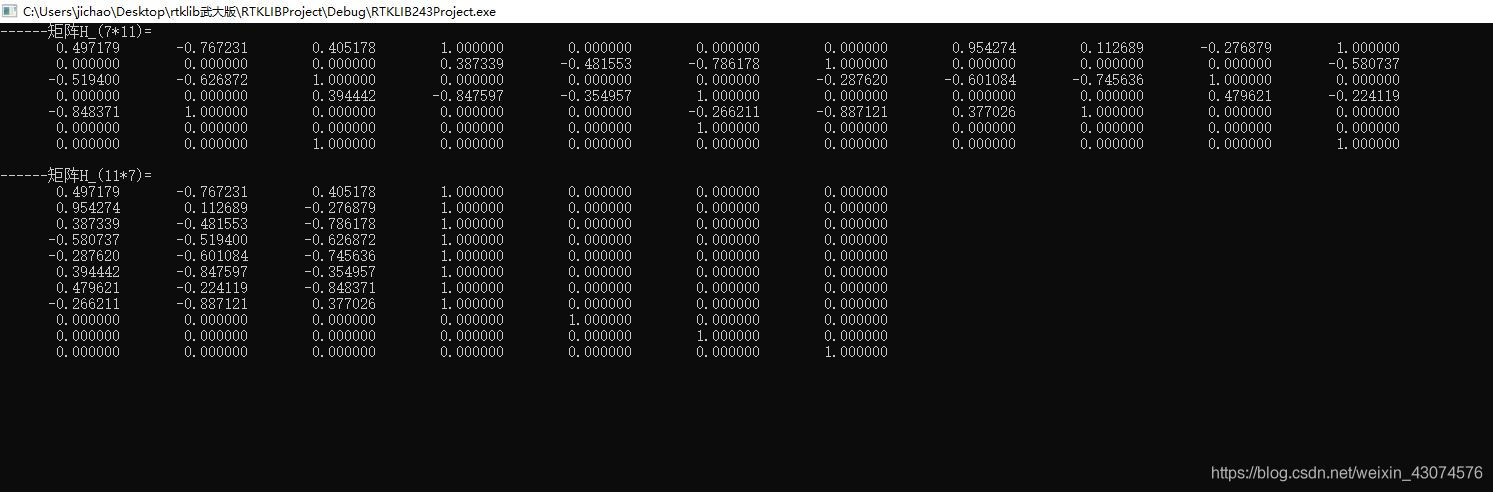
rtklib单点定位spp使用抗差估计遇到的问题及解决
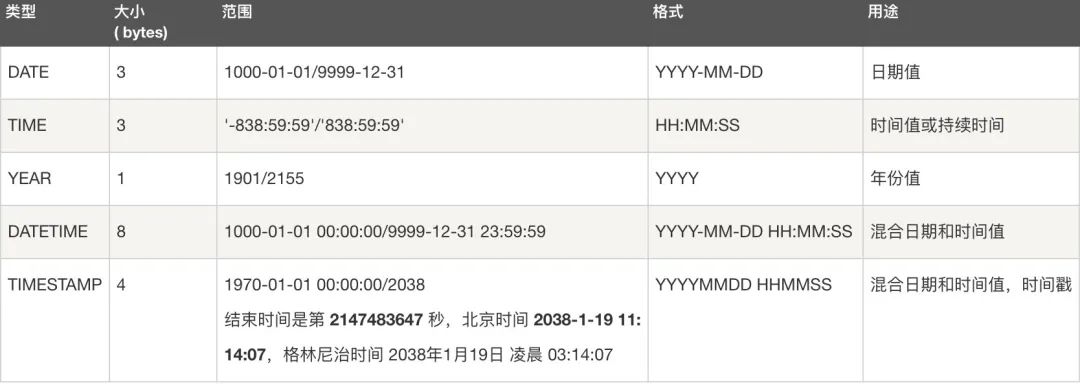
MySQL 三万字精华总结 + 面试100 问,吊打面试官绰绰有余(收藏系列

RTKLIB: demo5 b34f. 1 vs b33
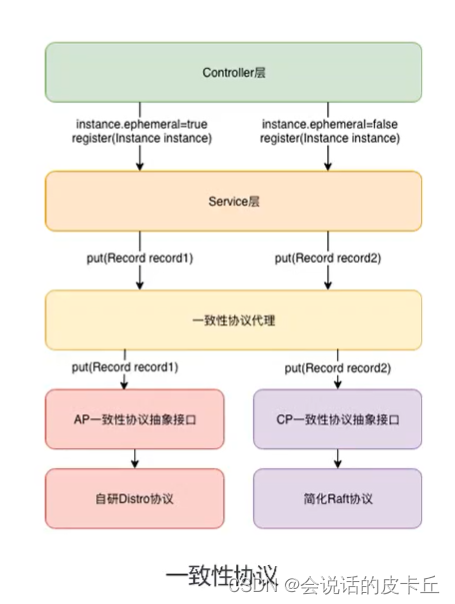
阿里云微服务(二) 分布式服务配置中心以及Nacos的使用场景及实现介绍
Code example of MATLAB reading GNSS observation value o file
![[algorithme] swordfinger offer2 golang question d'entrevue 2: addition binaire](/img/c2/6f6c3bd4d70252ba73addad6a3a9c1.png)
[algorithme] swordfinger offer2 golang question d'entrevue 2: addition binaire
2022 National Games RE1 baby_ tree
TYUT太原理工大学2022软工导论大题汇总
![[algorithm] sword finger offer2 golang interview question 3: the number of 1 in the binary form of the first n numbers](/img/64/0f352232359c7d44f12b20a64c7bb4.png)
[algorithm] sword finger offer2 golang interview question 3: the number of 1 in the binary form of the first n numbers
随机推荐
Detailed explanation of balanced binary tree is easy to understand
Rt-ppp test using rtknavi
[algorithm] sword finger offer2 golang interview question 10: subarray with sum K
记录:newInstance()过时的代替方法
使用rtknavi进行RT-PPP测试
Alibaba cloud side: underlying details in concurrent scenarios - pseudo sharing
[dry goods] cycle slip detection of suggestions to improve the fixed rate of RTK ambiguity
图书管理系统小练习
面渣逆袭:Redis连环五十二问,三万字+八十图详解。
Error: sorting and subscript out of bounds
系统设计学习(一)Design Pastebin.com (or Bit.ly)
MYSQL索引钟B-TREE ,B+TREE ,HASH索引之间的区别和应用场景
记录:初次cmd启动MySQL拒接访问之解决
MySQL 30000 word essence summary + 100 interview questions, hanging the interviewer is more than enough (Collection Series
错误: 找不到符号
4.30 dynamic memory allocation notes
Error: symbol not found
GPS高程拟合抗差中误差的求取代码实现
TYUT太原理工大学2022“mao gai”必背
堆排序【手写小根堆】