当前位置:网站首页>Credit card fraud detection based on machine learning
Credit card fraud detection based on machine learning
2022-07-26 04:18:00 【Mr. Sisi 666】
Credit card fraud detection based on machine learning
One 、 Credit card fraud detection based on machine learning
1.1 Preface
- Data sources :Kaggle Credit card fraud detection data set https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/mlg-ulb/creditcardfraud?resource=download;
- In this paper XGBoost、 Random forests 、KNN、 Logical regression 、SVM And decision tree to solve the problem of credit card fraud detection ;
1.2 case analysis
1.2.1 Import the required modules to python Environmental Science
# 1、 Import the required modules to python Environment
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from termcolor import colored as cl
import itertools
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score, f1_score
1.2.2 Reading data , Delete useless Time Column
- About data : The data we are going to use is Kaggle Credit card fraud detection data set . It contains V1 To V28, yes PCA The main ingredients obtained , And ignore time features that are not useful for building models .
- The remaining features are... Including the total transaction amount " amount of money " Characteristics and information on whether the transaction is a fraud case " Category " features , Category 0 Identification fraud , Category 1 Is normal .
df = pd.read_csv(r'../creditcard.csv')
print("Data's columns contain:\n", df.columns)
print("Data shape:\n", df.shape)
df.drop('Time', axis=1, inplace=True)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', df.shape[1])
print(df.head())
''' Data's columns contain: Index(['Time', 'V1', 'V2', 'V3', 'V4', 'V5', 'V6', 'V7', 'V8', 'V9', 'V10', 'V11', 'V12', 'V13', 'V14', 'V15', 'V16', 'V17', 'V18', 'V19', 'V20', 'V21', 'V22', 'V23', 'V24', 'V25', 'V26', 'V27', 'V28', 'Amount', 'Class'], dtype='object') Data shape: (284807, 31) V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 \ 0 -1.359807 -0.072781 2.536347 1.378155 -0.338321 0.462388 0.239599 1 1.191857 0.266151 0.166480 0.448154 0.060018 -0.082361 -0.078803 2 -1.358354 -1.340163 1.773209 0.379780 -0.503198 1.800499 0.791461 3 -0.966272 -0.185226 1.792993 -0.863291 -0.010309 1.247203 0.237609 4 -1.158233 0.877737 1.548718 0.403034 -0.407193 0.095921 0.592941 V8 V9 V10 V11 V12 V13 V14 \ 0 0.098698 0.363787 0.090794 -0.551600 -0.617801 -0.991390 -0.311169 1 0.085102 -0.255425 -0.166974 1.612727 1.065235 0.489095 -0.143772 2 0.247676 -1.514654 0.207643 0.624501 0.066084 0.717293 -0.165946 3 0.377436 -1.387024 -0.054952 -0.226487 0.178228 0.507757 -0.287924 4 -0.270533 0.817739 0.753074 -0.822843 0.538196 1.345852 -1.119670 V15 V16 V17 V18 V19 V20 V21 \ 0 1.468177 -0.470401 0.207971 0.025791 0.403993 0.251412 -0.018307 1 0.635558 0.463917 -0.114805 -0.183361 -0.145783 -0.069083 -0.225775 2 2.345865 -2.890083 1.109969 -0.121359 -2.261857 0.524980 0.247998 3 -0.631418 -1.059647 -0.684093 1.965775 -1.232622 -0.208038 -0.108300 4 0.175121 -0.451449 -0.237033 -0.038195 0.803487 0.408542 -0.009431 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 \ 0 0.277838 -0.110474 0.066928 0.128539 -0.189115 0.133558 -0.021053 1 -0.638672 0.101288 -0.339846 0.167170 0.125895 -0.008983 0.014724 2 0.771679 0.909412 -0.689281 -0.327642 -0.139097 -0.055353 -0.059752 3 0.005274 -0.190321 -1.175575 0.647376 -0.221929 0.062723 0.061458 4 0.798278 -0.137458 0.141267 -0.206010 0.502292 0.219422 0.215153 Amount Class 0 149.62 0 1 2.69 0 2 378.66 0 3 123.50 0 4 69.99 0 '''
1.2.3 Exploratory data analysis and data preprocessing
cases = len(df)
nonfraud_cases = df[df.Class == 0] # Non fraud
fraud_cases = df[df.Class == 1] # cheat
fraud_percentage = round(len(nonfraud_cases) / cases * 100, 2)
print(cl('CASE COUNT', attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('-' * 40, attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('Total number of cases are {}'.format(cases), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('Number of Non-fraud cases are {}'.format(len(nonfraud_cases)), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('Number of fraud cases are {}'.format(len(fraud_cases)), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('Percentage of fraud cases is {}%'.format(fraud_percentage), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('-' * 40, attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('CASE AMOUNT STATISTICS', attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('-' * 40, attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('NON-FRAUD CASE AMOUNT STATS', attrs=['bold']))
print(nonfraud_cases.Amount.describe())
print(cl('-' * 40, attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('FRAUD CASE AMOUNT STATS', attrs=['bold']))
print(fraud_cases.Amount.describe())
print(cl('-' * 40, attrs=['bold']))
# By looking at ,‘Amount’ The amount changes greatly , It needs to be standardized
sc = StandardScaler()
amount = df.Amount.values
df.Amount = sc.fit_transform(amount.reshape(-1, 1))
print(cl(df.Amount.head(10), attrs=['bold']))
# Feature selection and dataset splitting
x = df.drop('Class', axis=1).values
y = df.Class.values
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
''' CASE COUNT ---------------------------------------- Total number of cases are 284807 Number of Non-fraud cases are 284315 Number of fraud cases are 492 Percentage of fraud cases is 99.83% ---------------------------------------- CASE AMOUNT STATISTICS ---------------------------------------- NON-FRAUD CASE AMOUNT STATS count 284315.000000 mean 88.291022 std 250.105092 min 0.000000 25% 5.650000 50% 22.000000 75% 77.050000 max 25691.160000 Name: Amount, dtype: float64 ---------------------------------------- FRAUD CASE AMOUNT STATS count 492.000000 mean 122.211321 std 256.683288 min 0.000000 25% 1.000000 50% 9.250000 75% 105.890000 max 2125.870000 Name: Amount, dtype: float64 ---------------------------------------- 0 0.244964 1 -0.342475 2 1.160686 3 0.140534 4 -0.073403 5 -0.338556 6 -0.333279 7 -0.190107 8 0.019392 9 -0.338516 Name: Amount, dtype: float64'''
1.2.4 Build six classification models
- Decision Tree
tree_model = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4, criterion='entropy').fit(x_train, y_train)
tree_yhat = tree_model.predict(x_test)
- K-Nearest Neighbors
knn_model = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5).fit(x_train, y_train)
knn_yhat = knn_model.predict(x_test)
- Logistic Regression
lr_model = LogisticRegression().fit(x_train, y_train)
lr_yhat = lr_model.predict(x_test)
- SVM
svm_model = SVC().fit(x_train, y_train)
svm_yhat = svm_model.predict(x_test)
- Random Forest Tree
rf_model = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=4).fit(x_train, y_train)
rf_yhat = rf_model.predict(x_test)
- XGBoost
xgb_model = XGBClassifier(max_depth=4).fit(x_train, y_train)
xgb_yhat = xgb_model.predict(x_test)
1.2.5 Use evaluation indicators to evaluate the classification model created
- Accuracy rate
print(cl('-' * 40, attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('ACCURACY SCORE', attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('Accuracy score of the Decision Tree model is {}'.format(round(accuracy_score(y_test, tree_yhat), 4)),
attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('Accuracy score of the knn model is {}'.format(round(accuracy_score(y_test, knn_yhat), 4)), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('Accuracy score of the Logistic Regression model is {}'.format(round(accuracy_score(y_test, lr_yhat), 4)),
attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('Accuracy score of the SVM model is {}'.format(round(accuracy_score(y_test, svm_yhat), 4)), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('Accuracy score of the Random Forest model is {}'.format(round(accuracy_score(y_test, rf_yhat), 4)),
attrs=['bold']))
print(
cl('Accuracy score of the XGBoost model is {}'.format(round(accuracy_score(y_test, xgb_yhat), 4)), attrs=['bold']))
''' ACCURACY SCORE Accuracy score of the Decision Tree model is 0.9994 Accuracy score of the knn model is 0.9995 Accuracy score of the Logistic Regression model is 0.9992 Accuracy score of the SVM model is 0.9993 Accuracy score of the Random Forest model is 0.9993 Accuracy score of the XGBoost model is 0.9995 '''
- F1 value
print(cl('-' * 40, attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('F1 SCORE', attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('F1 score of the Decision Tree model is {}'.format(round(f1_score(y_test, tree_yhat), 4)), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('F1 score of the knn model is {}'.format(round(f1_score(y_test, knn_yhat), 4)), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('F1 score of the Logistic Regression model is {}'.format(round(f1_score(y_test, lr_yhat), 4)), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('F1 score of the SVM model is {}'.format(round(f1_score(y_test, svm_yhat), 4)), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('F1 score of the Random Forest model is {}'.format(round(f1_score(y_test, rf_yhat), 4)), attrs=['bold']))
print(cl('F1 score of the XGBoost model is {}'.format(round(f1_score(y_test, xgb_yhat), 4)), attrs=['bold']))
''' F1 SCORE F1 score of the Decision Tree model is 0.8105 F1 score of the knn model is 0.8571 F1 score of the Logistic Regression model is 0.7356 F1 score of the SVM model is 0.7771 F1 score of the Random Forest model is 0.7657 F1 score of the XGBoost model is 0.8449 '''
- Confusion matrix
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes, title, cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
title = 'Confusion Matrix of {}'.format(title)
plt.imshow(cm, cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(marks, classes)
thresh = cm.max() / 2
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])): # The cartesian product
plt.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], 'd'), horizontalalignment='center',
color='white' if cm[i, j] > thresh else 'black')
""" Set text description plt.text(x,y,string,fontsize=15,verticalalignment="top",horizontalalignment="right") Parameters : x,y: Represents the value on the coordinate value string: To indicate caption fontsize: Represents the font size verticalalignment: Vertical alignment , Parameters :[ ‘center’ | ‘top’ | ‘bottom’ | ‘baseline’ ] horizontalalignment: Horizontal alignment , Parameters :[ ‘center’ | ‘right’ | ‘left’ ] """
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predict label')
# Calculating the confusion matrix
tree_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, tree_yhat, labels=[0, 1])
knn_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, knn_yhat, labels=[0, 1])
lr_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, lr_yhat, labels=[0, 1])
svm_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, svm_yhat, labels=[0, 1])
rf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, rf_yhat, labels=[0, 1])
xgb_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, xgb_yhat, labels=[0, 1])
# adopt rc The configuration file is used to define various default properties of the graph
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6, 6)
classes = ['Non-fraud(0)', 'Fraud(1)']
tree_cm_plot = plot_confusion_matrix(tree_matrix,classes =classes, title='Decision Tree')
plt.savefig('tree_cm_plot.png')
plt.show()
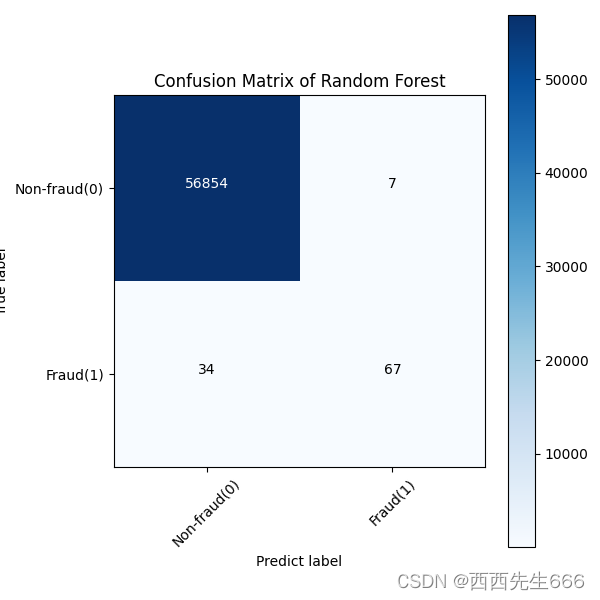
The abscissa in the figure is predict label, The ordinate is true label;
knn_cm_plot = plot_confusion_matrix(knn_matrix,classes =classes, title='KNN')
plt.savefig('knn_cm_plot.png')
plt.show()

lr_cm_plot = plot_confusion_matrix(lr_matrix,classes =classes, title='Logistic Regression')
plt.savefig('lr_cm_plot.png')
plt.show()

svm_cm_plot = plot_confusion_matrix(svm_matrix,classes =classes, title='SVM')
plt.savefig('svm_cm_plot.png')
plt.show()

rf_cm_plot = plot_confusion_matrix(rf_matrix,classes =classes, title='Random Forest')
plt.savefig('rf_cm_plot.png')
plt.show()
xgb_cm_plot = plot_confusion_matrix(xgb_matrix,classes =classes, title='XGBoost')
plt.savefig('xgb_cm_plot.png')
plt.show()

边栏推荐
- p-范数(2-范数 即 欧几里得范数)
- 2022 Hangzhou Electric Multi school bowcraft
- 图互译模型
- Retail chain store cashier system source code management commodity classification function logic sharing
- Matlab drawing
- How to write the abbreviation of the thesis?
- Pits encountered by sdl2 OpenGL
- Web测试方法大全
- 零售连锁门店收银系统源码管理商品分类的功能逻辑分享
- (翻译)按钮位置约定能强化用户使用习惯
猜你喜欢

Inventory the concept, classification and characteristics of cloud computing

吴恩达机器学习课后习题——逻辑回归

VM virtual machine has no un bridged host network adapter, unable to restore the default configuration

Comprehensive evaluation and decision-making method

Soft simulation rasterization renderer

When you try to delete all bad code in the program | daily anecdotes

荐书|《DBT技巧训练手册》:宝贝,你就是你活着的原因

Dijango learning

Can literature | relationship research draw causal conclusions

Working ideas of stability and high availability guarantee
随机推荐
吴恩达机器学习课后习题——逻辑回归
【二叉树】二叉树中的最长交错路径
VM虚拟机 没有未桥接的主机网络适配器 无法还原默认配置
Seat / safety configuration upgrade is the administrative experience of the new Volvo S90 in place
解决:RuntimeError: Expected object of scalar type Int but got scalar type Double
Luoda development - audio stream processing - AAC / loopbacktest as an example
firewall 命令简单操作
华为高层谈 35 岁危机,程序员如何破年龄之忧?
Retail chain store cashier system source code management commodity classification function logic sharing
How to build an enterprise level OLAP data engine for massive data and high real-time requirements?
Can literature | relationship research draw causal conclusions
【SVN】一直出现 Please execute the ‘Cleanup‘ command,cleanup以后没有反应的解决办法
2021 CIKM |GF-VAE: A Flow-based Variational Autoencoder for Molecule Generation
Makefile knowledge rearrangement (super detailed)
[cloud native] talk about the understanding of the old message middleware ActiveMQ
2022 Hangzhou Electric Multi school bowcraft
Recommendation | DBT skills training manual: baby, you are the reason why you live
测试用例设计方法之——招式组合,因果判定
综合评价与决策方法
Use of rule engine drools