当前位置:网站首页>It's hard to hear C language? Why don't you take a look at this (V) pointer
It's hard to hear C language? Why don't you take a look at this (V) pointer
2022-07-04 12:22:00 【The Great Gatsby.】
1. Write it at the front
All the programs and variables we write in the computer are found through the corresponding addresses , When you know the address and length of this thing , Then you can read this thing . This thing can be a function , It can be variables and so on . So you can know how important the address is ! that C Is there anything in a language that stores addresses , I'm glad to tell you , Yes , It's the pointer , A pointer is a variable that holds the address of a variable .
2. Pointer and address
First of all, we need to know how computer storage is divided . We can think of allocating memory according to a series of numbers , So the address we know can be understood as number , But with the number, you only know the address of this variable , But to read this variable , You need to know the length of this variable , Suppose the length of this variable is 1 Bytes , You read the two bytes after this address , Then the content read out is wrong .
No matter what variables are, there are two elements , One element is the name of the variable ( Similar address ), Another element is the variable type ( The length occupied ) With these pre knowledge , We can talk about C Pointers and addresses in languages .
Since each variable is the address and the corresponding length , Then can we save the address and length into a variable , Of course , This is the pointer .
So much has been said , So how does the pointer declare ? The details are as follows :
int x = 1,y = 2;
int *z = &x;
y = *z; // y = 1
Address operators & Can only be applied to objects in memory , Variables and array elements .( Take the corresponding address )
Unary operator * Is an indirect addressing or indirect reference operator . When it acts on a pointer , Will access the object pointed to by the pointer .
So the pointer variables still don't escape the above two rules , One is the address , One is length . So it also has a name and type , However, this type stores the type of variable in this address .
A pointer can only point to a specific type of object , in other words , Each pointer must point to a specific data type ( An exception is to point to void A pointer to a type can hold a pointer to any type , But it cannot indirectly refer to itself )
& Is to take the address of this variable ,* Is to take the content of the variable pointed to by this pointer , The operation of pointer variable is actually the operation of the address stored in pointer variable , But if you add * The contents of the variable pointed to by the address in the pointer variable are calculated accordingly , The details are as follows :
int a = 1;
int *p = &a;
*p += 1; // a It becomes 2
p += 1; // This time is a Add 4 Bytes
3. Pointers and function parameters
because C Language passes parameter values to the called function by passing values . therefore , The called function cannot directly modify the value of the calling function . Let's look at a commutative function , The details are as follows :
void swap(int x, int y) {
int temp;
temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
This does not change the exchange value , Because it's value transfer , So it's a copy . We can use pointer to exchange data , Because with the address, you can modify the original variable . The specific code is as follows :
void swap(int *px, int *py){
int temp;
temp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = temp;
}
Let's take another look at the program , The details are as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int getch(void);
void ungetch(int);
/* getint: get next integer from input into *pn */
int getint(int *pn) {
int c, sign;
while (isspace(c = getch())) /* skip white space */
;
if (!isdigit(c) && c != EOF && c != '+' && c != '-') {
ungetch(c); /* it is not a number */
return 0;
}
sign = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1;
if (c == '+' || c == '-')
c = getch();
for (*pn = 0;isdigit(c);c = getch())
*pn = 10 * *pn + (c - '0');
*pn *= sign;
if (c != EOF)
ungetch(c);
return c;
}
The version getint The function returns... When it reaches the end of the file EOF, Returns when the next input is not a number 0, Returns a positive value when the input contains a meaningful number .
4. Pointers and arrays
First look at the following procedure , The specific code is as follows :
int strlen(char *s)
{
int n;
for (n = 0; *s != '\0'; s++)
n++;
return n;
}
int strlen(char s[])
{
int n;
for (n = 0; s[n] != '\0'; n++);
return n;
}
The above code is to find the length of the array , One is achieved by pointer , One is implemented by array . We all know that an array is a continuous space , When the first function is passed in, the first address of the array , Then add... To this initial address every time 1, Then calculate the corresponding length , When the content in the address is ’\0’ When , It means the end of the array , At this time, the length of the array is calculated . There is also one that is calculated directly from the subscript of the array .
Always remember that a pointer is a variable , The corresponding calculation can be carried out , And the array name is just an array name , He cannot calculate it accordingly .
When passing an array name to a function , What is actually passed is the address of the first element of the array .
5. Arithmetic address
As we mentioned earlier, pointers are also variables , So the calculation of pointer is allowed , But what about the operation of pointers ? The operation of pointer is based on the type of pointer , If your type is int The type of words , Then you'll add 4 Bytes , If it is char Type words , Then you'll add 1 Bytes . If you grasp this content , Let's take a look at an example first .
Let's first look at an imperfect storage allocation program . It consists of two functions . The first function alloc(n) Return a point n Pointer to consecutive character storage locations ,alloc The caller of the function can use this pointer to store the character sequence . The second function afree(p) Free the allocated storage space , So that it can be reused later . But why are these two functions imperfect ? Because the calls of these two functions must be called in the way of stack .
Let's take a look at these two functions, specifically as follows :
#define ALLOCSIZE 10000 /* size of available space */
static char allocbuf[ALLOCSIZE]; /* storage for alloc */
static char *allocp = allocbuf; /* next free position */
char *alloc(int n) /* return pointer to n characters */
{
if (allocbuf + ALLOCSIZE - allocp >= n) {
/* it fits */
allocp += n;
return allocp - n; /* old p */
} else /* not enough room */
return 0;
}
void afree(char *p) /* free storage pointed to by p */
{
if (p >= allocbuf && p < allocbuf + ALLOCSIZE)
allocp = p;
}
From the above example, we can know that pointers can perform comparison operations , But comparing operations makes sense , Only two pointers point to members of the same array , Such comparison is meaningful . Suppose we have two pointers , They're pointers p And a pointer q, These two pointers point to an array at the same time , This time the pointer p The address pointed to is in the pointer q Before the address pointed to , that p<q It was established .
We also saw that the pointer has a method of addition and subtraction , They are also effective , For example, pointer p+1, At this time, if the pointer p yes int Type of , that p+1 Is in the p Add... To the original address 4 Bytes . So we can reverse the subtraction . I won't go into too much detail here .
summary : Valid pointer operations include assignment operations between the same types ; Addition or subtraction between pointer and integer ; Subtraction or comparison between two pointers pointing to elements in the same array ; Assign the pointer to 0 Or pointer and 0 The comparison between .
6. Character pointers and functions
We all know that a string constant is an array of characters . At the same time, there is a at the end of the character array ’\0’.
Let's first look at the following two definitions , The details are as follows :
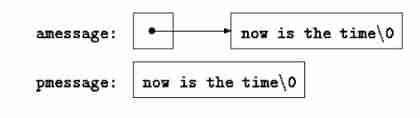
char amessage[] = "nw is the time"; /* Define an array */
char *pmessage = "now is the time"; /* Define a pointer */
In the above statement ,amessage Is just enough to store initialization strings and empty characters ‘\0’ One dimensional array of . A single character in the array can be modified , but amessage Always point to the same storage location . On the other hand ,pmessage It's a pointer , Its initial value points to a string constant , It can then be modified to point to other addresses , But if you try to modify the contents of the string , The result is undefined
Now let's look at the different implementations of the following two functions , The details are as follows :
// Copy in a non pointer way
void strcpy(char *s, char *t)
{
int i;
i = 0;
while ((s[i] = t[i]) != '\0')
i++;
}
// Copying by pointer
void strcpy(char *s, char *t)
{
int i;
i = 0;
while ((*s = *t) != '\0') {
s++;
t++;
}
}
void strcpy(char *s, char *t)
{
while ((*s++ = *t++) != '\0')
;
}
void strcpy(char *s, char *t)
{
while (*s++ = *t++)
;
}
The first version is implemented by array , The second version is implemented through pointers , It mainly reads the content of the address pointed by the pointer and copies it accordingly . Then the second version was upgraded constantly , Finally, I wrote the most refined and final version .
Let's look at another function , The details are as follows :
// Compare the size of two characters , Non pointer implementation
int strcmp(char *s, char *t)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; s[i] == t[i]; i++)
if (s[i] == '\0')
return 0;
return s[i] - t[i];
}
// Compare the size of two characters , Pointer implementation
int strcmp(char *s, char *t)
{
for ( ; *s == *t; s++, t++)
if (*s == '\0')
return 0;
return *s - *t;
}
7. Pointer array and pointer to pointer
Since we saved the address of the variable , This is the pointer variable . But what if the stored variable is a pointer variable ? Then it's the pointer to the pointer . It can be understood as a secondary pointer .
We need to write a sort , For different string lengths , Sort . At this time, we need to introduce pointer array to deal with this problem . If the text lines to be sorted are stored end to end in a long character array , Then each text line can be accessed by a pointer to its first character . such , Pass a pointer to two lines of text to the function strcmp You can compare these two text lines . When exchanging two lines of text in reverse order , In fact, what is exchanged is the pointer corresponding to these two text lines in the correction array , Instead of the two lines of text themselves .

Then it can be divided into the following three steps :
- Read all input lines
- Sort lines of text
- Print text lines in order
The specific code is as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXLINES 5000 /* max #lines to be sorted */
// Express lineptr Is a person with MAXLINES One dimensional array of elements , Each element of the array is a pointer to a character type object .
char *lineptr[MAXLINES]; /* pointers to text lines */
int readlines(char *lineptr[], int nlines);
void writelines(char *lineptr[], int nlines);
void qsort(char *lineptr[], int left, int right);
/* sort input lines */
main() {
int nlines; /* number of input lines read */
if ((nlines = readlines(lineptr, MAXLINES)) >= 0) {
qsort(lineptr, 0, nlines - 1);
writelines(lineptr, nlines);
return 0;
} else {
printf("error: input too big to sort\n");
return 1;
}
}
#define MAXLEN 1000 /* max length of any input line */
int getline(char *, int);
char *alloc(int);
/* readlines: read input lines */
int readlines(char *lineptr[], int maxlines) {
int len, nlines;
char *p, line[MAXLEN];
nlines = 0;
while ((len = getline(line, MAXLEN)) > 0)
if (nlines >= maxlines || (p = alloc(len)) == NULL)
return -1;
else {
line[len - 1] = '\0'; /* delete newline */
strcpy(p, line);
lineptr[nlines++] = p;
}
return nlines;
}
/* writelines: write output lines */
void writelines(char *lineptr[], int nlines) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < nlines; i++)
printf("%s\n", lineptr[i]);
}
Then let's look at the sorting algorithm , The details are as follows :
/* qsort: sort v[left]...v[right] into increasing order */
void qsort(char *v[], int left, int right)
{
int i, last;
void swap(char *v[], int i, int j);
if (left >= right) /* do nothing if array contains */
return; /* fewer than two elements */
swap(v, left, (left + right)/2);
last = left;
for (i = left+1; i <= right; i++)
if (strcmp(v[i], v[left]) < 0)
swap(v, ++last, i);
swap(v, left, last);
qsort(v, left, last-1);
qsort(v, last+1, right);
}
Let's do one last thing swap function
void swap(char *v[], int i, int j)
{
char *temp;
temp = v[i];
v[i] = v[j];
v[j] = temp;
}
8. Multidimensional arrays
A multidimensional array is an array in an array , We can first look at the following example , A problem of date conversion , Convert the date representation of a month and a day into the representation of the day of a year . Because the date of February in leap year is different from that in normal year , So we use a one-dimensional array to represent the days of each month, which we cannot express , Here we need a two-dimensional array , In this way, the number of days of each month in normal and leap years can be saved at the same time . The specific code is as follows :
static char daytab[2][13] = {
{
0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31},
{
0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}
};
/* day_of_year: set day of year from month & day */
int day_of_year(int year, int month, int day) {
int i, leap;
leap = year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0;
for (i = 1; i < month; i++)
day += daytab[leap][i];
return day;
}
/* month_day: set month, day from day of year */
void month_day(int year, int yearday, int *pmonth, int *pday) {
int i, leap;
leap = year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0;
for (i = 1; yearday > daytab[leap][i]; i++)
yearday -= daytab[leap][i];
*pmonth = i;
*pday = yearday;
}
If you pass a two-dimensional array as an argument to a function , Then the number of columns of the array must be specified in the parameter declaration of the function . There are three ways to write :
f(int daytab[2][13]);
f(int daytab[][13]);
f(int (*daytab)[13])
The last form of declaration is that the parameter is a pointer , It points to having 13 A one-dimensional array of integer elements . Because square brackets [] Has a higher priority than * The priority of the , Therefore, parentheses must be used in the above statement .
9. Initialization of pointer array
The specific code is as follows :
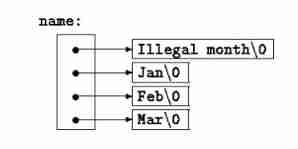
char *month_name(int n)
{
static char *name[] = {
"Illegal month",
"January", "February", "March",
"April", "May", "June",
"July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"
};
10. Pointers and multidimensional arrays
Let's first look at the following definitions , The details are as follows :
int a[10][20];
int *b[10];
From a grammatical point of view ,a[3][4] and b[3][4] It's all for one int Legal reference of object . however a Is a real two-dimensional array , It's assigned 200 individual int Length of storage space . But for b Come on , This definition only assigns 10 A pointer to the , And they are not initialized , Their initialization must be done in a realistic way , Such as static initialization or initialization through code . We can take a look at the following two statements .
char *name[]={
"Illegal manth", "Jan", "Feb", "Mar"};
Let's look at the declaration of a two-dimensional array , The details are as follows :
char aname[][15] = {
"Illegal month", "Jan", "Feb", "Mar" };

11. Pointer to function
stay C In language , The function itself is not a variable , But you can define a pointer to a function , Let's start with the following sorting code , The details are as follows :
/* qsort: sort v[left]...v[right] into increasing order */
void qsort(void *v[], int left, int right,
int (*comp)(void *, void *))
{
int i, last;
void swap(void *v[], int, int);
if (left >= right) /* do nothing if array contains */
return; /* fewer than two elements */
swap(v, left, (left + right)/2);
last = left;
for (i = left+1; i <= right; i++)
if ((*comp)(v[i], v[left]) < 0)
swap(v, ++last, i);
swap(v, left, last);
qsort(v, left, last-1, comp);
qsort(v, last+1, right, comp);
}
Let's look at the declaration of the fourth parameter of the sorting function as follows :
int (*comp)(void *, void *)
It shows that comp Is a pointer to a function , This function has two void* Parameters of type , The return value type is int
In the following statement
if((*comp)(v[i], v[left]) < 0)
comp The use of is consistent with its declaration ,comp Is a pointer to a function ,*comp Represents a function . The following statement is a call to this function :
(*comp)(v[i],v[left])
12. At the end
This blog mainly introduces the following C The pointer to language . We'll continue later C The rest of the language
边栏推荐
- 2021 annual summary - it seems that I have done everything except studying hard
- [solve the error of this pointing in the applet] SetData of undefined
- SAP ui5 date type sap ui. model. type. Analysis of the display format of date
- C language memory layout
- [Android reverse] function interception instance (③ refresh CPU cache | ④ process interception function | ⑤ return specific results)
- Using terminal connection in different modes of virtual machine
- Reptile learning 3 (winter vacation learning)
- 'using an alias column in the where clause in PostgreSQL' - using an alias column in the where clause in PostgreSQL
- Solaris 10 network services
- Summary of Shanghai Jiaotong University postgraduate entrance examination module firewall technology
猜你喜欢
SAP ui5 date type sap ui. model. type. Analysis of the display format of date
Tableau makes data summary after linking the database, and summary exceptions occasionally occur.
2018 meisai modeling summary +latex standard meisai template sharing
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 22](/img/e0/21367eeaeca10c0a2f2aab3a4fa1fb.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 22

Lecture 9
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 16](/img/c3/f3746b161012acc3751b2bd0b8f663.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 16
Automatic translation between Chinese and English
How to create a new virtual machine

JD home programmers delete databases and run away. Talk about binlog, the killer of MySQL data backup
(2021-08-20) web crawler learning 2
随机推荐
QQ get group information
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 8
Method of setting default items in C # ComboBox control code
Data communication and network: ch13 Ethernet
How to use the mongodb ID array to get multiple documents- How to get multiple document using array of MongoDb id?
Test question bank management system - database design [easy to understand]
[ES6] template string: `string`, a new symbol in es2015
Serialization oriented - pickle library, JSON Library
2021-10-20
01. Basics - MySQL overview
C language compilation process
Star leap plan | new projects are continuously being recruited! MSR Asia MSR Redmond joint research program invites you to apply!
CSDN documentation specification
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 15
Exness: positive I win, negative you lose
Definition and method of string
What if the chat record is gone? How to restore wechat chat records on Apple Mobile
QQ get group settings
Ultimate bug finding method - two points
Practical dry goods: deploy mini version message queue based on redis6.0