当前位置:网站首页>OSI model notes
OSI model notes
2022-07-04 11:07:00 【Mountains and rivers far away, fireworks on earth】
ISO— International Organization for Standardization
OSI : Open system interconnection ( Reference model )
OSI: Open Systems Interconnection model (open organization interconnection)
Suggest OSI Model purpose : Make communication between different systems easy , It does not require any changes to the logical structure of its low-level hardware and software .
Be careful :OSI The model is not a protocol , It's a model .( Focus on Theory )
TCP/IP Reference model :TCP/IP It is a layered protocol composed of interacting modules , Each layer provides a specific function , No interdependence .
TCP/IP----TCP/IP Routing technology Volume I Volume two (CCIE)jeff
application layer , The presentation layer , The session layer ----- Control level
Transport layer , The network layer , Data link layer , The physical layer ---- Data level
Layered thinking
application layer (7 layer ): Receive user data , Interface of human-computer interaction , Application oriented .
The presentation layer (6 layer ): Logic language ( Software language ) Convert to machine language ( Binary language ), translate , encryption
The session layer (5 layer ): For each kind of data transmitted ( Traffic ) establish ( management : maintain 、 End ) One
Virtual connection ( In order to prevent different types of data from affecting each other, the control level : The top three
Data level : The next four floors
Transport layer (4 layer ): 1. Distinguish traffic 2. Define the data transmission mode
OSI
Port number : port ID , Range of values 1-65535
Static port : Also known as indicating port range 1-1023( Correspond to the flow one by one , Binding relationship )
Dynamic port : Range 1024-65535 ( Correspond to the flow one by one , No binding )
Common port numbers :
HTTP—80 TCP
HTTPS —443 TCP
RIP----520 UDP
Telnet— Remote login service 23 TCP
SSH ---- Remote login ( High security encryption authentication ),22 TCP
DNS---- Domain name resolution ,53 TCP and UDP
Unreliable transmission mode and flow characteristics :1. Large flow 2. High real-time performance 3. Insensitive to data loss
reliable : How to ensure reliability ? 1. Acknowledgement mechanism 2. Retransmission mechanism
TCP: Transmission control protocol , Is a reliable connection oriented transport protocol
UDP: User datagram protocol , It is a non connection oriented unreliable transmission protocol
TCP data structure :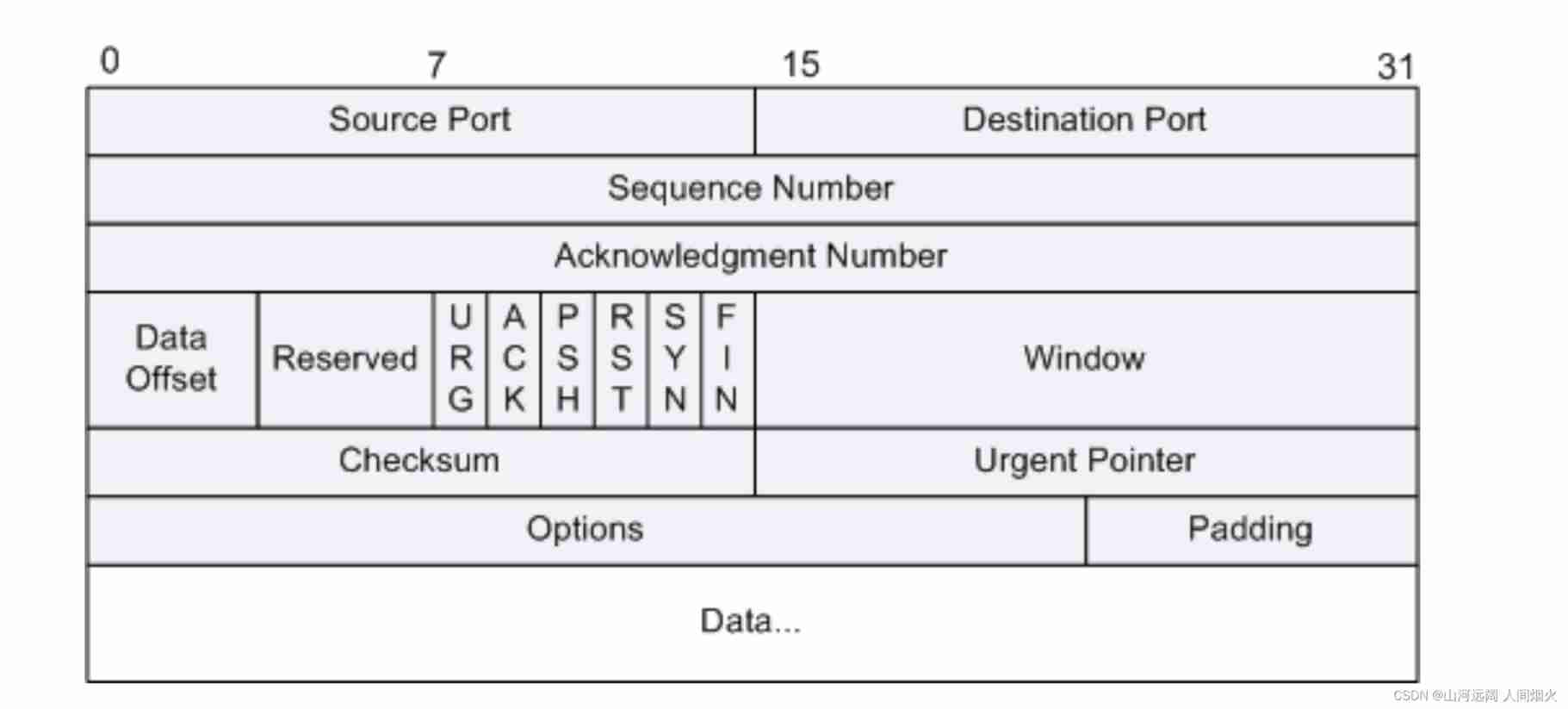
UDP data structure :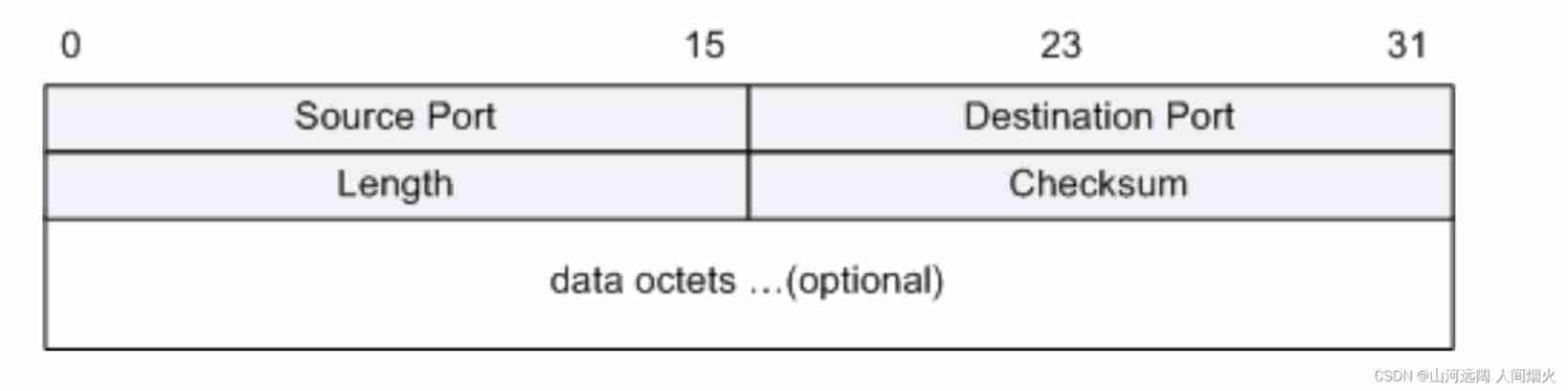
Connection oriented : Before transmitting data , Both parties negotiate to ensure that the data can be transmitted .
How to ensure connection oriented ?( Three times mobile phone system )
Three times mobile phone system : Ensure connection oriented , Also known as TCP Three handshakes of
Three times handshake between host and server
Synchronization request :syn req confirm :Ack
like : The first handshake . Host synchronization request server port
The second handshake . The server port responds to the confirmation and synchronizes the request host
The third handshake . The host confirms the server port
Acknowledgement mechanism : Explicit confirmation Implicit confirmation
Optimization mechanism : Flow control mechanism ( Sliding window mechanism ); Reorder
Segmented transmission of data : When transmitting large data, follow MTU Value for segmented transmission .
MTU: Maximum transmission unit , The default is 1500 byte , You can modify ( But not recommended ) expand :
Bit ---- The bit ( The smallest unit of the Internet ) A binary 【0 1】
1000bit=1kb
1000kb=1Mb
1000Mb=1Gb
1000Gb=1Tb
1000Tb=1Pb
file system (NTFS) of use 210=1024
Byte: byte , A byte is 8 individual bit
1000B=1KB
1000KB=1MB
1000MB=1GB
1000GB=1TB
Rate unit :
100Mbps=100 mega The bit Per second 12.5MBPS=12.5 mega byte Per second
PDU: Protocol data unit
PDU The representation of data in different layers
4 layer PDU( Proper noun ):segment piecewise Fragmentation
The network layer (3 layer ): Addressing Addressing
Address :
Addressing protocol : IP (IPV4 IPV6) IPX apple talk novell NSAP
IPv4: use 32 Binary addressing .
A binary be called 1 position bit .
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
IP Address ( Generally refer to ipv4):32 It's binary ,0 and 1 constitute For addressing
Network mask :32 It's binary , Successive 1+ Successive 0 constitute , Successive 1 Represents the network bit , Successive 0 Represents the host bit .
Network bit Host bit
1101 1000.0001 0001.0000 0001.0000 0001
216.17.1.1
Simple algorithm :0000 0001=1
0000 0010=2
0000 0100=4
0000 1000=8
0001 0000=16
0010 0000=32
0100 0000=64
1000 0000=128
255.255.0.0
1111 1111.1111 1111.0000 0000.0000 0000
Write a complete IP Address time :IP Address + Network mask
Address classification :
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
A Class address : The first is fixed as 0
( front 8 Bit is network bit , after 24 Bit host bit )2 To the seventh power of ,2 Of 24 Power IP
0XXX XXXX —0-127(1-126), The netmask defaults to 255.0.0.0
B Class address : The first two are fixed as 10
( front 16 Bit is network bit , after 16 Host location )2 Of 14 Power network segment ,2 Of 16 Power host bits
10XX XXXX—r, The netmask defaults to 255.255.0.0
C Class address : The first three are fixed 110
110X XXXX—192-223, The netmask defaults to 255.255.255.0
( front 24 Bit is network bit , after 8 Bit is host bit )
(A,B,C Class address is unicast address , Identify only one user )
D Class address : The first four are fixed as 1110
1110 XXXX—224-239, Multicast address , No mask
E Class address : The first four are fixed as 1111
1111 XXXX—240-255, Scientific research address .
Special address :
1.0.X.X.X Invalid address ( Reserved address ),0.0.0.0 Invalid address placeholder
2.127.0.0.1 Local testing (127.X.X.X Address of the test )
3. network number , The network bit remains unchanged All hosts are 0 The address of ( Used to describe a network segment )
162.1.1.1------------------162.1.0.0 255.255.0.0
255.255.0.0
4. Restricted broadcast address ,255.255.255.255
5. directional ( direct ) Broadcast address , The network bit remains unchanged , All hosts are 1
200.1.1.1 —> 200.1.1.255
255.255.255.0
6. Local link address :link-local { 169.254.0.0 255.255.0.0 }
Public address : Globally unique identification address
Private address : Address without unique identification
10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
172.{16-31}.0.0 255.255.0.0
192.168.X(0-255).0 255.255.255.0
Three layers PDU:packet package
A B C Class addresses are called unicast addresses
unicast : One to one transmission
Multicast : One to many transmission
radio broadcast : One to all transmission modes
Data link layer (2 layer ): LAN ( Ethernet Ethernet) Wide area network (PPP HDLC ATM FR )
Second floor address :Mac Address ( Media access control )— Physical address Hardware address Burn address
LLC layer : Logical link control sublayer
MAC layer : Media access control sublayer
Mac Address structure : 48 It's binary Writing uses 12 Hexadecimal ( A hex requires
Use 4 A binary representation ) The way of writing : Subtractive hexadecimal or dotted hexadecimal
60-F2-62-3C-E3-53 Minus hexadecimal )----- terminal host The server mobile phone
60F2.623C.E353 Point sixteen mechanism )---- Connect to the device Router A firewall ASA
front 24 position : manufacturer ID ----OUI( Uniform resource identifiers )
after 24 position : product ID ----interface ID ( Interface identifier )
On the second floor ( data )PDU :frame frame
The physical layer (1 layer ): Focus on Mechanical characteristics of network hardware Optical properties Electrical characteristics
First floor PDU:bit Bit stream
Transmission medium : Optical fiber 、 Twisted pair (RJ45)
Ethernet cable :8 strip ----4 paragraph ---- Twisted in two
Wired media : Coaxial cable , Twisted pair , Optical fiber
Wireless media :WiFi, bluetooth ,wimax
Coaxial cable : Thick cable (10mbps transmission distance 500m) Thin cable
Optical fiber : Single mode fiber ( Single light source , Linear transmission )
Multimode fiber ( It can transmit many kinds of light )
Twisted pair :
568A Linear sequence : Green and white 、 green 、 Orange white 、 blue 、 Bluish white 、 orange 、 Brown and white 、 Brown
568B Linear sequence : Orange white 、 orange 、 Green and white 、 blue 、 Bluish white 、 green 、 Brown and white 、 Brown
Divide by line sequence :
Parallel lines : Also known as the through line , Same line sequence . Parallel lines are used for different layers of equipment .
Cross line : The line sequence is different . Cross lines are used for equipment on the same floor .
All negative : Also known as console Line , Configuration line , The line sequence is opposite , Network equipment for user control .
Shielded twisted pair (STP);( Plus metal cover , Shielding interference )
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
weak current
Strong electricity
Classify according to the degree of twist :3 class 4 class —(10Mbps) 5 class super 5 class —(100Mbps) 6 class super 6 class (1000Mbps– stay 6 Class line 8 Roots are used at the same time )
TCP/IP Model :
application layer ( application layer The presentation layer The session layer )
Host to host layer ( Transport layer )
The Internet layer ( The network layer )
Network interface layer ( Data link layer The physical layer )
Data encapsulation : The process of generating data
Data unpacking : The process of receiving data for reading

边栏推荐
- Local MySQL forget password modification method (Windows) [easy to understand]
- Climb Phoenix Mountain on December 19, 2021
- Canoe the second simulation engineering xvehicle 3 CAPL programming (operation)
- Some tips on learning database
- Summary of collection: (to be updated)
- TS type gymnastics: illustrating a complex advanced type
- Simple understanding of generics
- Jemeter plug-in technology
- Heartbeat启动后无反应
- QQ one click cookie acquisition
猜你喜欢
Canoe the second simulation engineering xvehicle 3 CAPL programming (operation)
Canoe - the third simulation project - bus simulation-1 overview
Network connection (II) three handshakes, four waves, socket essence, packaging of network packets, TCP header, IP header, ACK confirmation, sliding window, results of network packets, working mode of
XMIND installation
Climb Phoenix Mountain on December 19, 2021
![[test theory] test process management](/img/d2/65865dffacf38d9a8be720868b75f0.jpg)
[test theory] test process management
F12 clear the cookies of the corresponding web address
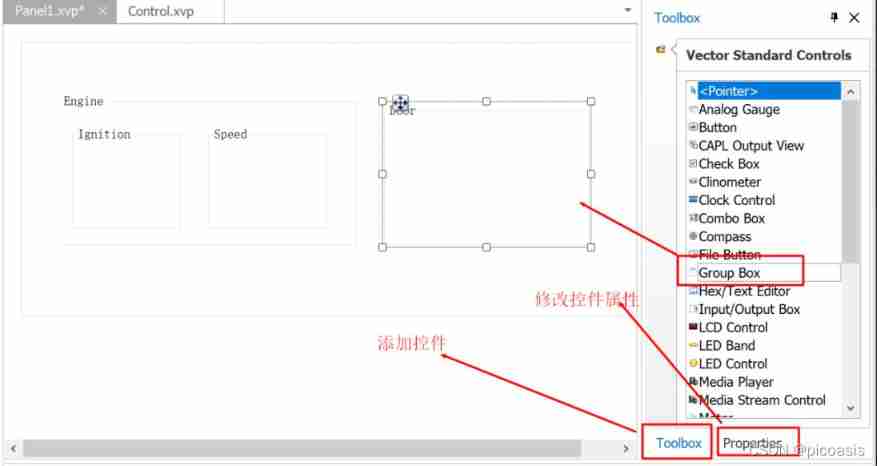
Canoe - the second simulation engineering - xvehicle - 2 panel design (operation)
Personal thoughts on the development of game automation protocol testing tool
Introduction to Lichuang EDA
随机推荐
Elevator dispatching (pairing project) ①
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop and server] FRP intranet penetration
20 kinds of hardware engineers must be aware of basic components | the latest update to 8.13
[test theory] test phase analysis (unit, integration, system test)
Strings and characters
Dictionaries and collections
Performance test overview
Local MySQL forgot the password modification method (Windows)
Basic function exercises
Replace() function
Capl: timer event
array_ The contains() function uses
Solaris 10 network services
Take advantage of the world's sleeping gap to improve and surpass yourself -- get up early
QQ get group information
Performance test process
shell awk
Heartbeat报错 attempted replay attack
Open the neural network "black box"! Unveil the mystery of machine learning system with natural language
Canoe - description of common database attributes