当前位置:网站首页>[point cloud processing paper crazy reading cutting-edge version 12] - adaptive graph revolution for point cloud analysis
[point cloud processing paper crazy reading cutting-edge version 12] - adaptive graph revolution for point cloud analysis
2022-07-03 09:14:00 【LingbinBu】
Adaptive Graph Convolution for Point Cloud Analysis
Abstract
- problem : The standard convolution operation cannot be performed in 3D The feature correspondence is distinguished between points
- Method : In this paper, Adaptive Graph Convolution(AdaptConv), according to 3D Point to the characteristics of dynamic learning Generate adaptive kernel
- Use and fixing / Isotropic kernel comparison ,AdaptConv Improved point cloud Flexibility of convolution , Effectively and accurately get a variety of relationships between different semantic parts
- Different from the method of using attention weight ,AdaptConv Make convolution operation more adaptive , Not simply for neighboring points Assign different weights
- Code :PyTorch edition
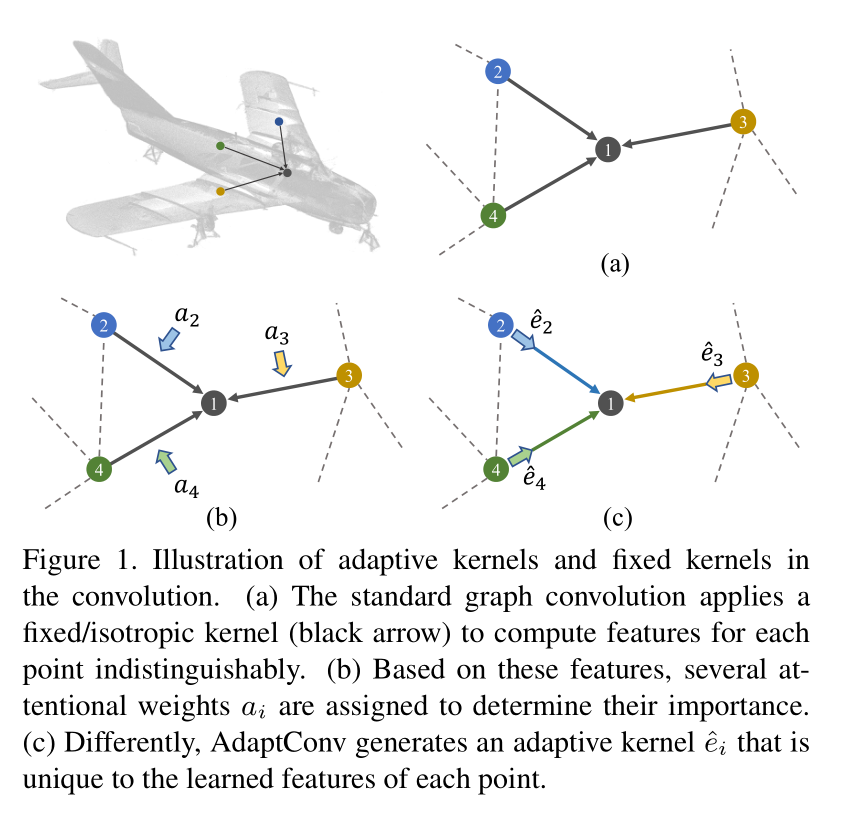
introduction
Graph CNNs According to the space between points / Feature similarity will point cloud Expressed as graph data , And will images Upper 2D Convolution is extended to 3D light .
The standard Graph CNNs Usually, the shared weight function is used to extract the corresponding edge features of each pair of points , This will lead to a fixed / Convolution in the same direction kernel, When applied to all point pairs , Will ignore the corresponding relationship between different characteristics .
The key contribution of this work is AdaptConv In the graph Use in convolution , Instead of a weight function based on the characteristics of the results .
Besides , Some feature convolution designs have also been developed , It can carry out adaptive convolution more flexibly .
Method
Adaptive graph convolution
remember X = { x i ∣ i = \mathcal{X}=\left\{x_{i} \mid i=\right. X={ xi∣i= 1 , 2 , … , N } ∈ R N × 3 1,2, \ldots, N\} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times 3} 1,2,…,N}∈RN×3 Enter a point cloud for , F = { f i ∣ i = 1 , 2 , … , N } ∈ R N × D \mathcal{F}=\left\{f_{i} \mid i=1,2, \ldots, N\right\} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D} F={ fi∣i=1,2,…,N}∈RN×D Is the corresponding feature , among x i x_{i} xi Means the... Th i i i Point ( x , y , z ) (\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{y}, \mathbf{z}) (x,y,z) coordinate , In other cases , It can also be combined with other features .
Then calculate the directed graph according to the given point cloud G ( V , E ) \mathcal{G}(\mathcal{V}, \mathcal{E}) G(V,E), among V = { 1 , … , N } \mathcal{V}=\{1, \ldots, N\} V={ 1,…,N} and E ⊆ V × V \mathcal{E} \subseteq \mathcal{V} \times \mathcal{V} E⊆V×V Represents a collection of vertices and edges . By including self-loop Of k k k-nearest neighbors (KNN) structure graph.
In the given input D D D After Witt's sign ,AdaptConv layer A new set of M M M Whitman's sign , The number of points is the same as the input . And previous graph convolution Layer by layer , It can more accurately reflect the local structural characteristics .
remember x i x_{i} xi yes graph convolution The center of , N ( i ) = { j : ( i , j ) ∈ E } \mathcal{N}(i)=\{j:(i, j) \in \mathcal{E}\} N(i)={ j:(i,j)∈E} Is the index of adjacent points . Due to the irregularity of the point cloud , The previous method is usually in x i x_{i} xi All of the neighbored points Apply fixed kernel function , Used to capture patch The geometric information of . however , Different neighbored points May get corresponding x i x_{i} xi Different characteristics , Especially when x i x_{i} xi Located in a prominent area , Such as corners or edges . under these circumstances , fixed kernel It may not be possible to graph convolution Get the geometric representation information for classification or segmentation .
In the method of this paper , Designed an adaptive kernel, Used to calculate the significant relationship between each pair of points . about M M M Every channel of dimensional output features ,AdaptConv Will dynamically generate a kernel, It is applied in points features ( f i , f j ) \left(f_{i}, f_{j}\right) (fi,fj) The function on :
e ^ i j m = g m ( Δ f i j ) , j ∈ N ( i ) . \hat{e}_{i j m}=g_{m}\left(\Delta f_{i j}\right), j \in \mathcal{N}(i) . e^ijm=gm(Δfij),j∈N(i).
among m = 1 , 2 , … , M m=1,2, \ldots, M m=1,2,…,M Express M M M One of the output dimensions , Corresponds to a separate filter. Δ f i j = [ f i , f j − f i ] \Delta f_{i j}=\left[f_{i}, f_{j}-f_{i}\right] Δfij=[fi,fj−fi] Used to capture global structure and local domain features , [ ⋅ , ⋅ ] [\cdot, \cdot] [⋅,⋅] The splicing operation is , g ( ⋅ ) g(\cdot) g(⋅) Is the feature mapping function , namely M L P MLP MLP.
And 2D The calculation in convolution is the same , take D D D Dimension input and corresponding filter The weight is convoluted to get M M M One dimension in dimensional output , This article will adaptive kernel And the corresponding point ( x i , x j ) \left(x_{i}, x_{j}\right) (xi,xj) Convolution :
h i j m = σ * e ^ i j m , Δ x i j * , h_{i j m}=\sigma\left\langle\hat{e}_{i j m}, \Delta x_{i j}\right\rangle, hijm=σ*e^ijm,Δxij*,
among Δ x i j \Delta x_{i j} Δxij Is defined as [ x i , x j − x i ] \left[x_{i}, x_{j}-x_{i}\right] [xi,xj−xi] similarity , * ⋅ , ⋅ * \langle\cdot, \cdot\rangle *⋅,⋅* Represents the inner product of two vectors , Output is h i j m ∈ R h_{i j m} \in \mathbb{R} hijm∈R, σ \sigma σ It's a nonlinear activation function .
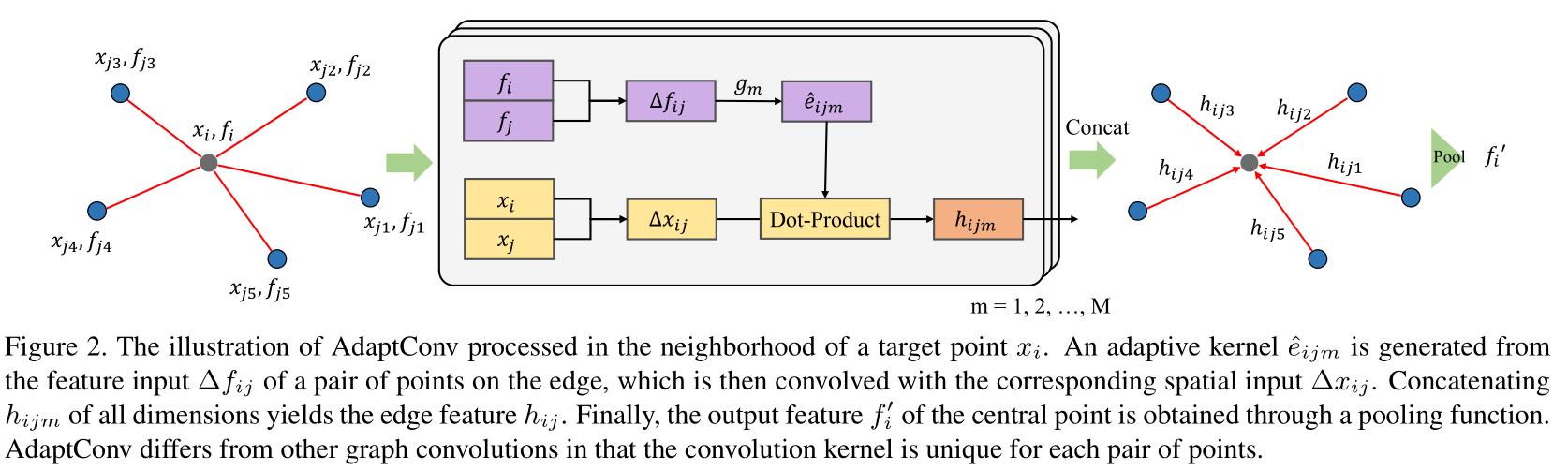
Pictured 2 Shown , The first m m m individual adaptive kernel e ^ i j m \hat{e}_{i j m} e^ijm And corresponding points x j ∈ R 3 x_{j} \in \mathbb{R}^{3} xj∈R3 Of spatial relations Δ x i j \Delta x_{i j} Δxij combination , Express kernel The size of should match the inner product , Feature mapping g m : R 2 D → R 6 g_{m}: \mathbb{R}^{2 D} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{6} gm:R2D→R6. Store for each channel h i j m h_{i j m} hijm, Get the connection point ( x i , x j ) \left(x_{i}, x_{j}\right) (xi,xj) Edge features between h i j = h_{i j}= hij= [ h i j 1 , h i j 2 , … , h i j M ] ∈ R M \left[h_{i j 1}, h_{i j 2}, \ldots, h_{i j M}\right] \in \mathbb{R}^{M} [hij1,hij2,…,hijM]∈RM.
Last , By using the aggregation function of all edge features in the neighborhood central point x i x_{i} xi The output characteristics of :
f i ′ = max j ∈ N ( i ) h i j , f_{i}^{\prime}=\max _{j \in \mathcal{N}(i)} h_{i j}, fi′=j∈N(i)maxhij,
among max It is in the unit of channel max-pooling function . All in all ,AdaptConv Of convolution weights Is defined as defined as Θ = ( g 1 , g 2 , … , g M ) \Theta=\left(g_{1}, g_{2}, \ldots, g_{M}\right) Θ=(g1,g2,…,gM).
Feature decisions
Is to use features to find spatial relationships .
If input x i ∈ R E x_i \in \mathbb{R}^E xi∈RE Contains more information , That's another option , In the experiment, we will consider .
Space information Δ x i j \Delta x_{i j} Δxij Replace with characteristic information Δ f i j \Delta f_{i j} Δfij, You'll get different e ^ i j m \hat{e}_{i j m} e^ijm, This is also an option to consider .
This article chooses to use Δ x i j \Delta x_{i j} Δxij As a transform domain, we have the following considerations :
- Point features have been used to generate adaptive kernel 了 , Convolution using features will lead to redundancy of feature information
- The dimension of features is high ,MLP It's difficult to learn in high-dimensional space
- Large memory consumption , High computational complexity
Network architecture

graph The structure of is dynamically updated at every level
experiment
Classifcation

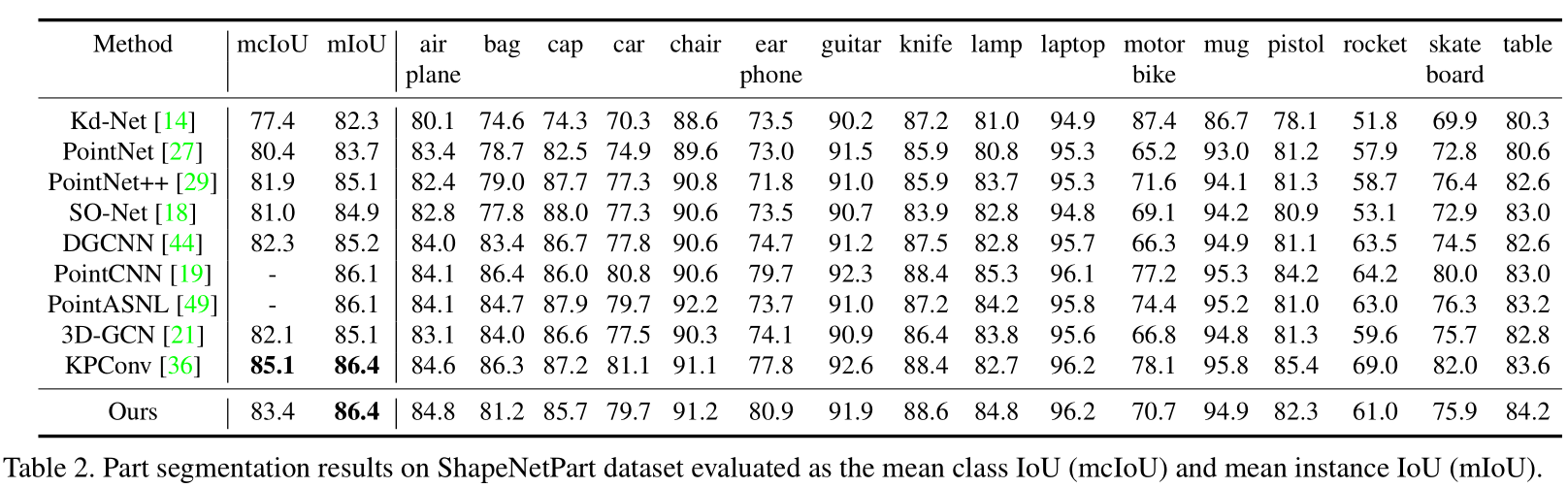
Part segmentation
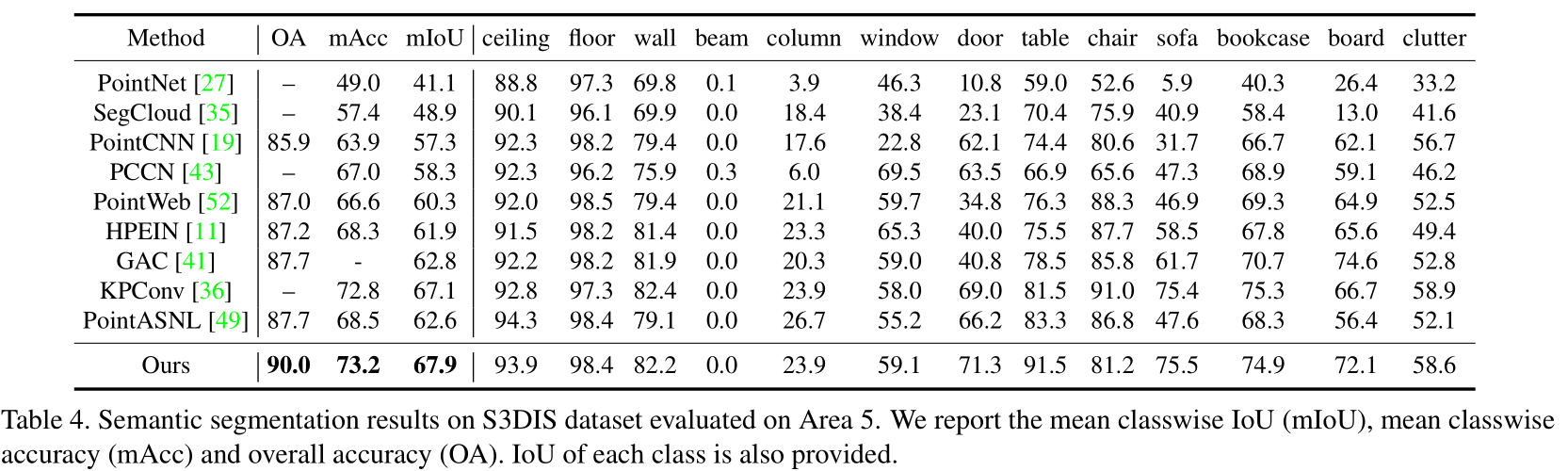
Indoor scene segmentation

Ablation studies
Adaptive convolution vs Fixed kernels & Feature decisions

Robustness test
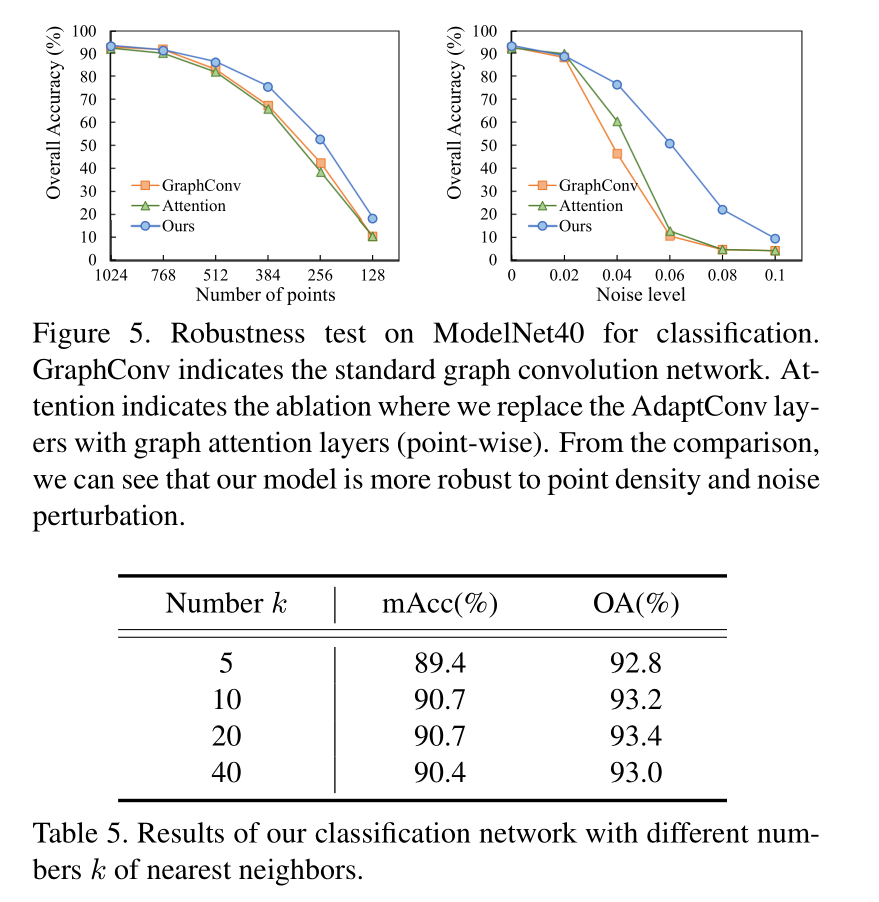
Efficiency

Visualization and learned features
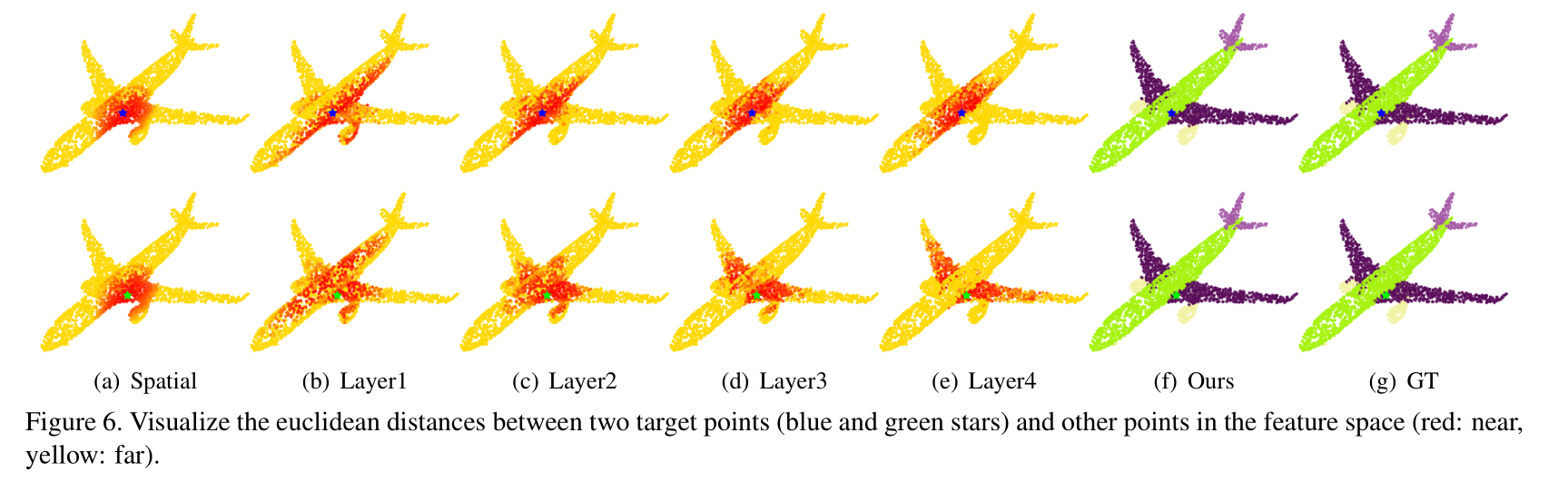
边栏推荐
- AcWing 787. 归并排序(模板)
- Vscode connect to remote server
- 【毕业季|进击的技术er】又到一年毕业季,一毕业就转行,从动物科学到程序员,10年程序员有话说
- Introduction to the basic application and skills of QT
- Too many open files solution
- 低代码前景可期,JNPF灵活易用,用智能定义新型办公模式
- C language file reading and writing
- LeetCode 324. Swing sort II
- Tag paste operator (#)
- Vs2019 configuration opencv3 detailed graphic tutorial and implementation of test code
猜你喜欢

Find the combination number acwing 885 Find the combination number I

精彩回顾|I/O Extended 2022 活动干货分享

AcWing 785. 快速排序(模板)
We have a common name, XX Gong

Character pyramid

数字化管理中台+低代码,JNPF开启企业数字化转型的新引擎

How to check whether the disk is in guid format (GPT) or MBR format? Judge whether UEFI mode starts or legacy mode starts?
Binary tree traversal (first order traversal. Output results according to first order, middle order, and last order)

【点云处理之论文狂读前沿版9】—Advanced Feature Learning on Point Clouds using Multi-resolution Features and Learni

With low code prospect, jnpf is flexible and easy to use, and uses intelligence to define a new office mode
随机推荐
数字化管理中台+低代码,JNPF开启企业数字化转型的新引擎
Using variables in sed command
Vs2019 configuration opencv3 detailed graphic tutorial and implementation of test code
【点云处理之论文狂读经典版12】—— FoldingNet: Point Cloud Auto-encoder via Deep Grid Deformation
AcWing 785. Quick sort (template)
PIC16F648A-E/SS PIC16 8位 微控制器,7KB(4Kx14)
C language file reading and writing
Gaussian elimination acwing 883 Gauss elimination for solving linear equations
Use of sort command in shell
Common penetration test range
Tag paste operator (#)
State compression DP acwing 291 Mondrian's dream
What is an excellent fast development framework like?
We have a common name, XX Gong
Introduction to the usage of getopts in shell
Just graduate student reading thesis
Vscode connect to remote server
AcWing 788. 逆序对的数量
数位统计DP AcWing 338. 计数问题
Recommend a low code open source project of yyds