当前位置:网站首页>Analysis of the characteristics of page owner
Analysis of the characteristics of page owner
2022-07-03 13:56:00 【kaka__ fifty-five】
This analysis is based on linux kernel 4.19.195.
linux Kernel page owner characteristic , Reference resources file , Mainly for Tracking about who allocated each page, Easy to locate memory leaks 、 Memory usage problem . This article simply analyzes from the perspective of source code page owner Implementation principle of .
page owner The overall design idea of the feature is very simple , It is through extension page Structure , Add member variables to store this page Allocated call stack and flag bit , then hack Memory page allocation and release interface , When memory pages are allocated , Save call stack information , Set flag bit ; When the memory page is released , Clear the call stack information , Clear flag bits . then , Through one debugfs The interface of , Pass the call stack information of all memory pages that have been allocated at the time of reading the interface to the user state , And made a tool in user mode , It is used to count the information of these call stacks .
This article focuses on the analysis of kernel state when pages are allocated ,page owner Characteristic behavior .
We know , Before memory pages are allocated , Will walk in post_alloc_hook function , Do some processing ,post_alloc_hook Function will call set_page_owner function , Finish saving the memory page allocation call stack .
static inline void set_page_owner(struct page *page,
unsigned int order, gfp_t gfp_mask)
{
if (static_branch_unlikely(&page_owner_inited))
__set_page_owner(page, order, gfp_mask);
}
noinline void __set_page_owner(struct page *page, unsigned int order,
gfp_t gfp_mask)
{
struct page_ext *page_ext = lookup_page_ext(page);
depot_stack_handle_t handle;
if (unlikely(!page_ext))
return;
handle = save_stack(gfp_mask);
__set_page_owner_handle(page_ext, handle, order, gfp_mask);
}
First step , Call function lookup_page_ext Get the page Corresponding struct page_ext Structure . The kernel for each page The structure is equipped with a struct page_ext Structure , Equivalent to page Extension of structure , I guess it's because I really don't want to expand page Volume of the structure , Just made such a compromise , Otherwise, it can be directly written into page Inside the structure .
The second step , call save_stack function , Save the call stack when the page is allocated , And return a handle like handle, Use in step 3 . This function is mainly analyzed below .
The third step , The information obtained in the second step handle, Write to the corresponding struct page_ext Structure , And set the flag bit , Indicates that the page has been allocated .
The first and third steps are relatively simple , Next, analyze the second step .
static noinline depot_stack_handle_t save_stack(gfp_t flags)
{
unsigned long entries[PAGE_OWNER_STACK_DEPTH];
struct stack_trace trace = {
.nr_entries = 0,
.entries = entries,
.max_entries = PAGE_OWNER_STACK_DEPTH,
.skip = 2
};
depot_stack_handle_t handle;
save_stack_trace(&trace);
if (trace.nr_entries != 0 &&
trace.entries[trace.nr_entries-1] == ULONG_MAX)
trace.nr_entries--;
/* * We need to check recursion here because our request to stackdepot * could trigger memory allocation to save new entry. New memory * allocation would reach here and call depot_save_stack() again * if we don't catch it. There is still not enough memory in stackdepot * so it would try to allocate memory again and loop forever. */
if (check_recursive_alloc(&trace, _RET_IP_))
return dummy_handle;
handle = depot_save_stack(&trace, flags);
if (!handle)
handle = failure_handle;
return handle;
}
First , Call function save_stack_trace Get call stack information ;
then , Using functions depot_save_stack Store the call stack in memory .
depot_save_stack It's a god horse ?
stay lib/stackdepot.c In the document , We found the implementation of this function . From the comments at the beginning of the file , You can see that , This file is a library that stores the call stack , This library , Only memory will be used to store call stack information , This information will not be deleted . also , A hash table will be used , To store the handle representing these call stacks , in addition , Memory for storing call stack information , It is equivalent to a large array , You only need to add data to this memory each time , And record the first address of the call stack information . Let's take a look at the functions depot_save_stack The specific implementation method of .
static void *stack_slabs[STACK_ALLOC_MAX_SLABS]; // Save a large array of call stacks , among , Each element points to a piece of memory , Used to store call stack information ; The reason for this is to save some memory , Instead of applying for all memory at once
static int depot_index;//stack_slabs Of index
static int next_slab_inited; // Indicate the next index Of stack_slabs Whether memory has been allocated
static size_t depot_offset;//stack_slabs[depot_index] Of depot_offset
/** * depot_save_stack - save stack in a stack depot. * @trace - the stacktrace to save. * @alloc_flags - flags for allocating additional memory if required. * * Returns the handle of the stack struct stored in depot. */
depot_stack_handle_t depot_save_stack(struct stack_trace *trace,
gfp_t alloc_flags)
{
u32 hash;
depot_stack_handle_t retval = 0;
struct stack_record *found = NULL, **bucket;
unsigned long flags;
struct page *page = NULL;
void *prealloc = NULL;
if (unlikely(trace->nr_entries == 0))
goto fast_exit;
hash = hash_stack(trace->entries, trace->nr_entries);
bucket = &stack_table[hash & STACK_HASH_MASK];
/* * Fast path: look the stack trace up without locking. * The smp_load_acquire() here pairs with smp_store_release() to * |bucket| below. */
found = find_stack(smp_load_acquire(bucket), trace->entries,
trace->nr_entries, hash);
if (found)
goto exit;
/* * Check if the current or the next stack slab need to be initialized. * If so, allocate the memory - we won't be able to do that under the * lock. * * The smp_load_acquire() here pairs with smp_store_release() to * |next_slab_inited| in depot_alloc_stack() and init_stack_slab(). */
if (unlikely(!smp_load_acquire(&next_slab_inited))) {
/* * Zero out zone modifiers, as we don't have specific zone * requirements. Keep the flags related to allocation in atomic * contexts and I/O. */
alloc_flags &= ~GFP_ZONEMASK;
alloc_flags &= (GFP_ATOMIC | GFP_KERNEL);
alloc_flags |= __GFP_NOWARN;
page = alloc_pages(alloc_flags, STACK_ALLOC_ORDER);
if (page)
prealloc = page_address(page);
}
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&depot_lock, flags);
found = find_stack(*bucket, trace->entries, trace->nr_entries, hash);
if (!found) {
struct stack_record *new =
depot_alloc_stack(trace->entries, trace->nr_entries,
hash, &prealloc, alloc_flags);
if (new) {
new->next = *bucket;
/* * This smp_store_release() pairs with * smp_load_acquire() from |bucket| above. */
smp_store_release(bucket, new);
found = new;
}
} else if (prealloc) {
/* * We didn't need to store this stack trace, but let's keep * the preallocated memory for the future. */
WARN_ON(!init_stack_slab(&prealloc));
}
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&depot_lock, flags);
exit:
if (prealloc) {
/* Nobody used this memory, ok to free it. */
free_pages((unsigned long)prealloc, STACK_ALLOC_ORDER);
}
if (found)
retval = found->handle.handle;
fast_exit:
return retval;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(depot_save_stack);
First use the function hash_stack Determine which hash bucket the handle information of the call stack is stored in , Used to reduce repeated memory consumption .
then ,find_stack Function to find out whether there is the same call stack in the corresponding hash bucket , Some words , You can go straight back to , After all, the call stack is already stored in memory .
Next, through variables next_slab_inited, To determine whether it is necessary to apply for memory .
Call again find_stack Prevent concurrent problems .
If the call stack has not been stored before , Then use depot_alloc_stack Function stores call stack information .
After storage , Function exit .
Let's continue to see depot_alloc_stack Implementation of function
/* Allocation of a new stack in raw storage */
static struct stack_record *depot_alloc_stack(unsigned long *entries, int size,
u32 hash, void **prealloc, gfp_t alloc_flags)
{
int required_size = offsetof(struct stack_record, entries) +
sizeof(unsigned long) * size;
struct stack_record *stack;
required_size = ALIGN(required_size, 1 << STACK_ALLOC_ALIGN);
if (unlikely(depot_offset + required_size > STACK_ALLOC_SIZE)) {
if (unlikely(depot_index + 1 >= STACK_ALLOC_MAX_SLABS)) {
WARN_ONCE(1, "Stack depot reached limit capacity");
return NULL;
}
depot_index++;
depot_offset = 0;
/* * smp_store_release() here pairs with smp_load_acquire() from * |next_slab_inited| in depot_save_stack() and * init_stack_slab(). */
if (depot_index + 1 < STACK_ALLOC_MAX_SLABS)
smp_store_release(&next_slab_inited, 0);
}
init_stack_slab(prealloc);
if (stack_slabs[depot_index] == NULL)
return NULL;
stack = stack_slabs[depot_index] + depot_offset;
stack->hash = hash;
stack->size = size;
stack->handle.slabindex = depot_index;
stack->handle.offset = depot_offset >> STACK_ALLOC_ALIGN;
stack->handle.valid = 1;
memcpy(stack->entries, entries, size * sizeof(unsigned long));
depot_offset += required_size;
return stack;
}
Um. , Basically is memcpy 了 , Copy the call stack information to " In large array ".
The overall framework is basically like this , Or look at the original author's notes , Can get a lot of information .
边栏推荐
- Go: send the get request and parse the return JSON (go1.16.4)
- Dynamic programming 01 knapsack and complete knapsack
- JS continues to explore...
- Golang — template
- [combinatorics] permutation and combination (examples of combinatorial number of multiple sets | three counting models | selection problem | combinatorial problem of multiple sets | nonnegative intege
- [556. Next larger element III]
- Qt学习19 Qt 中的标准对话框(上)
- Go 1.16.4: manage third-party libraries with Mod
- Ocean CMS vulnerability - search php
- [how to solve FAT32 when the computer is inserted into the U disk or the memory card display cannot be formatted]
猜你喜欢

GoLand 2021.1.1: configure the multi line display of the tab of the open file
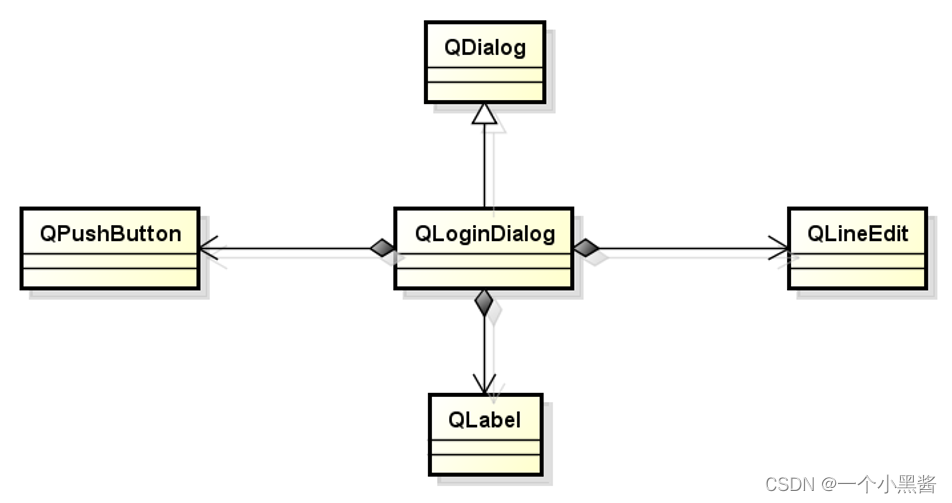
Qt学习18 登录对话框实例分析

Ocean CMS vulnerability - search php
Installation impression notes

Mastering the cypress command line options is the basis for truly mastering cypress
Students who do not understand the code can also send their own token, which is easy to learn BSC
Dlopen() implements dynamic loading of third-party libraries
Qt学习21 Qt 中的标准对话框(下)

“又土又穷”的草根高校,凭什么被称为“东北小清华”?

从零开始的基于百度大脑EasyData的多人协同数据标注
随机推荐
Qt学习21 Qt 中的标准对话框(下)
Dynamic programming 01 knapsack and complete knapsack
There is nothing new under the sun. Can the meta universe go higher?
消息订阅与发布
[how to earn a million passive income]
顺序表(C语言实现)
Go language unit test 4: go language uses gomonkey to test functions or methods
Using registered classes to realize specific type matching function template
The shadow of the object at the edge of the untiy world flickers, and the shadow of the object near the far point is normal
Qt学习20 Qt 中的标准对话框(中)
Thrift threadmanager and three monitors
金属有机骨架MOFs装载非甾体类抗炎药物|ZIF-8包裹普鲁士蓝负载槲皮素(制备方法)
Resource Cost Optimization Practice of R & D team
[556. Next larger element III]
IBEM mathematical formula detection data set
Implementation of Muduo accept connection, disconnection and sending data
Disruptor -- a high concurrency and high performance queue framework for processing tens of millions of levels
GoLand 2021.1.1: configure the multi line display of the tab of the open file
Several common optimization methods matlab principle and depth analysis
Qt学习18 登录对话框实例分析