当前位置:网站首页>Basic operation of chain binary tree (implemented in C language)
Basic operation of chain binary tree (implemented in C language)
2022-07-07 18:55:00 【Brant_ zero】
Catalog
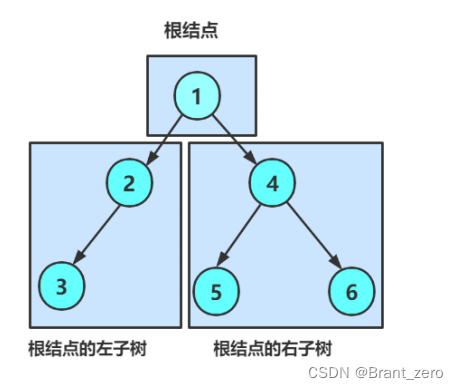
One 、 Creation of chain binary tree
Two 、 Depth traversal of trees
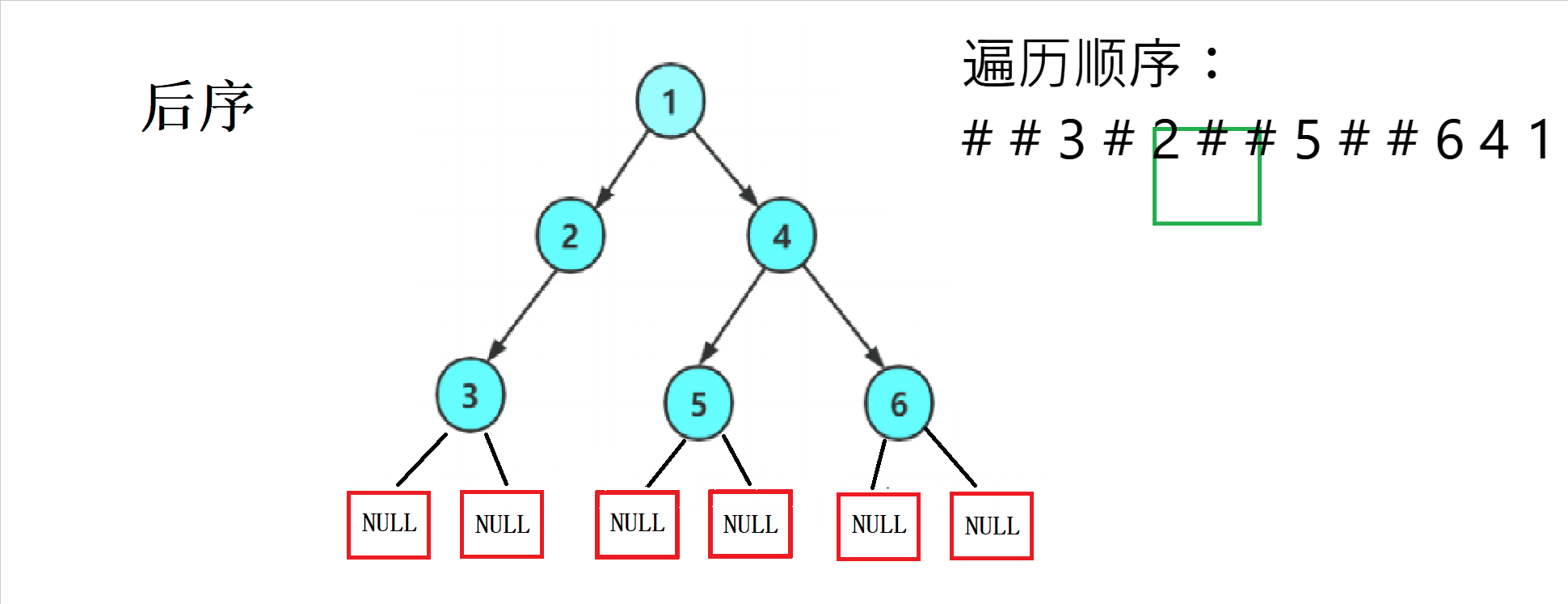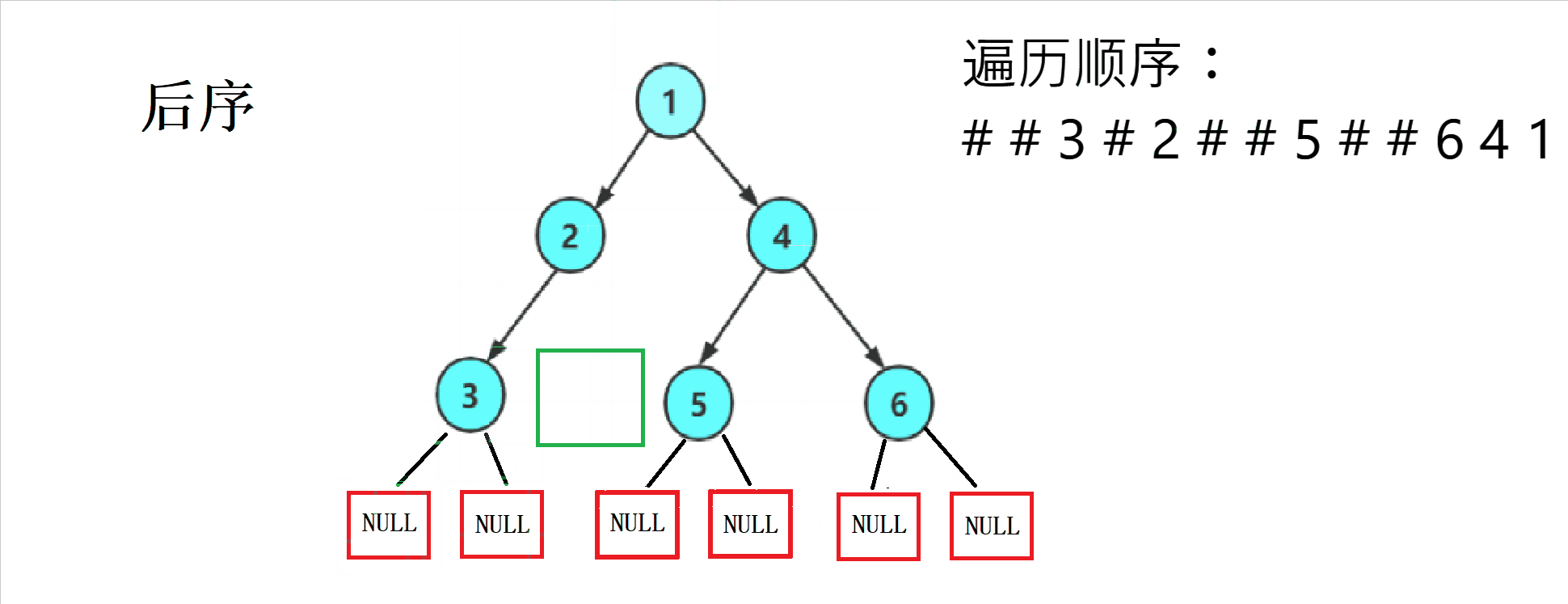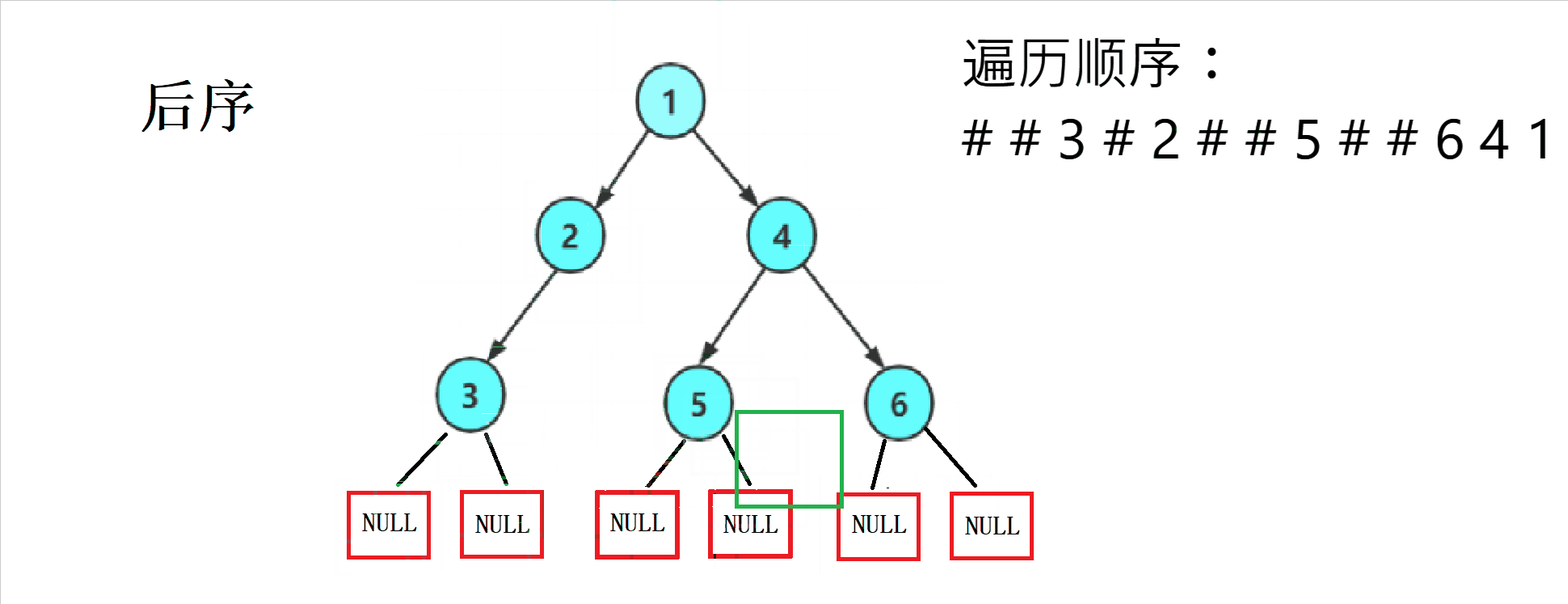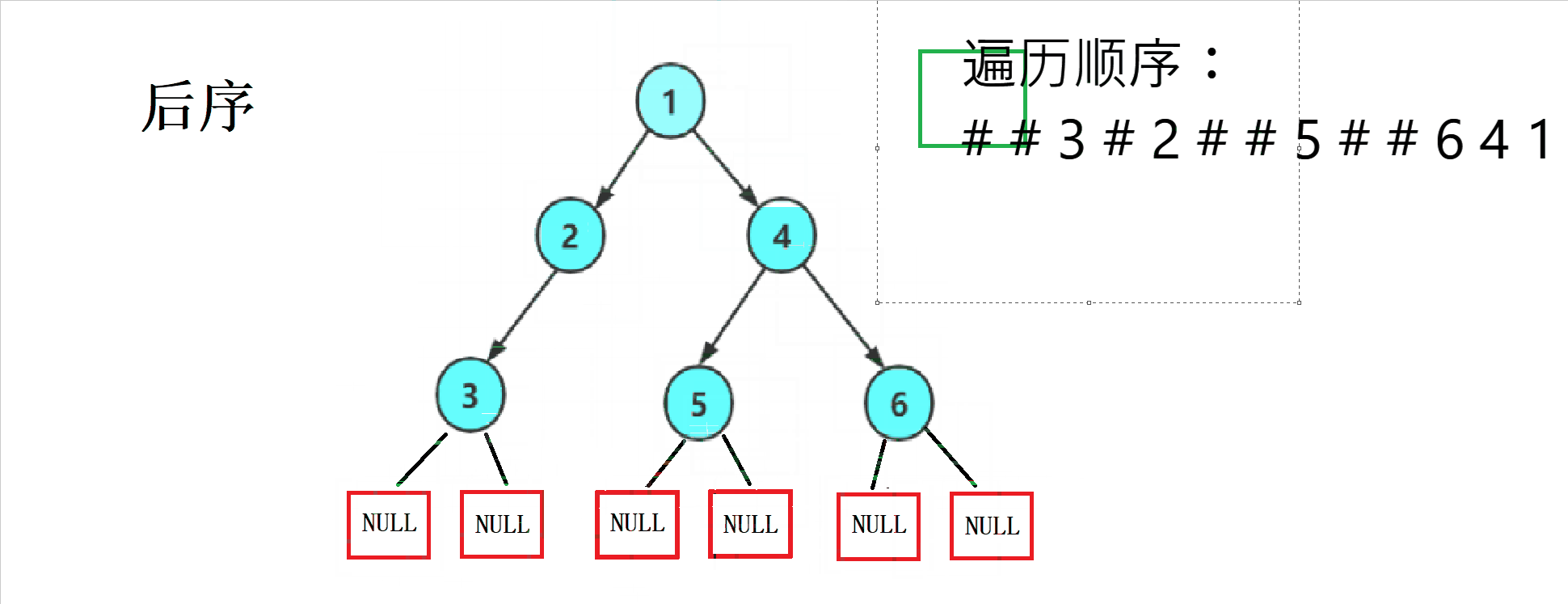
1. Before the order 、 Middle preface 、 After the sequence traversal
1.2 Traversal sequence diagram of three ways
3、 ... and 、 Sequence traversal of trees
3.2 Identification of complete binary tree
Four 、 The basic functions of trees
4.1 The number of nodes in the tree
4.2 The number of leaf nodes in the tree
4.3 The first k Number of layer nodes
This blog is about the most common chain binary tree , The function of this structure in practical application is not great , But we still have to learn this structure . The purpose of learning this structure is to lay a foundation for us to study more complex tree structures in the future . I don't say much nonsense , Just start .
Catalog
One 、 Creation of chain binary tree
Two 、 Depth traversal of trees
2.1 Before the order 、 Middle preface 、 After the sequence traversal
2.1.1 Traversal sequence diagram of three ways
3、 ... and 、 The basic functions of trees
3.1 The number of nodes in the tree
3.2 The number of leaf nodes in the tree
3.3 The first k Number of layer nodes
Four 、 Sequence traversal of trees
4.2 Identification of complete binary tree
One 、 Creation of chain binary tree
First, let's create a tree , There are three steps to create a tree :① Define the structure of nodes in the tree ② Create a new node ③ Link nodes ; In this way, a tree can be built .
1.1 Define node structure
// Node creation
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDataType data;
}BTNode;1.2 Node creation
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
assert(node);
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}1.3 Links to nodes
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
// link
node1->left = node2; // 1
node1->right = node4;// 2 4
node2->left = node3;// 3 # 5 6
node4->left = node5;// # # # # # #
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}Two 、 Depth traversal of trees
We have created the tree , Next, let's take a look at the links of our tree , At this point, we need to traverse the tree . But the structure of trees is special , Different from the array we learned before , Traversal is very convenient . Therefore, the following traversal methods are extended .
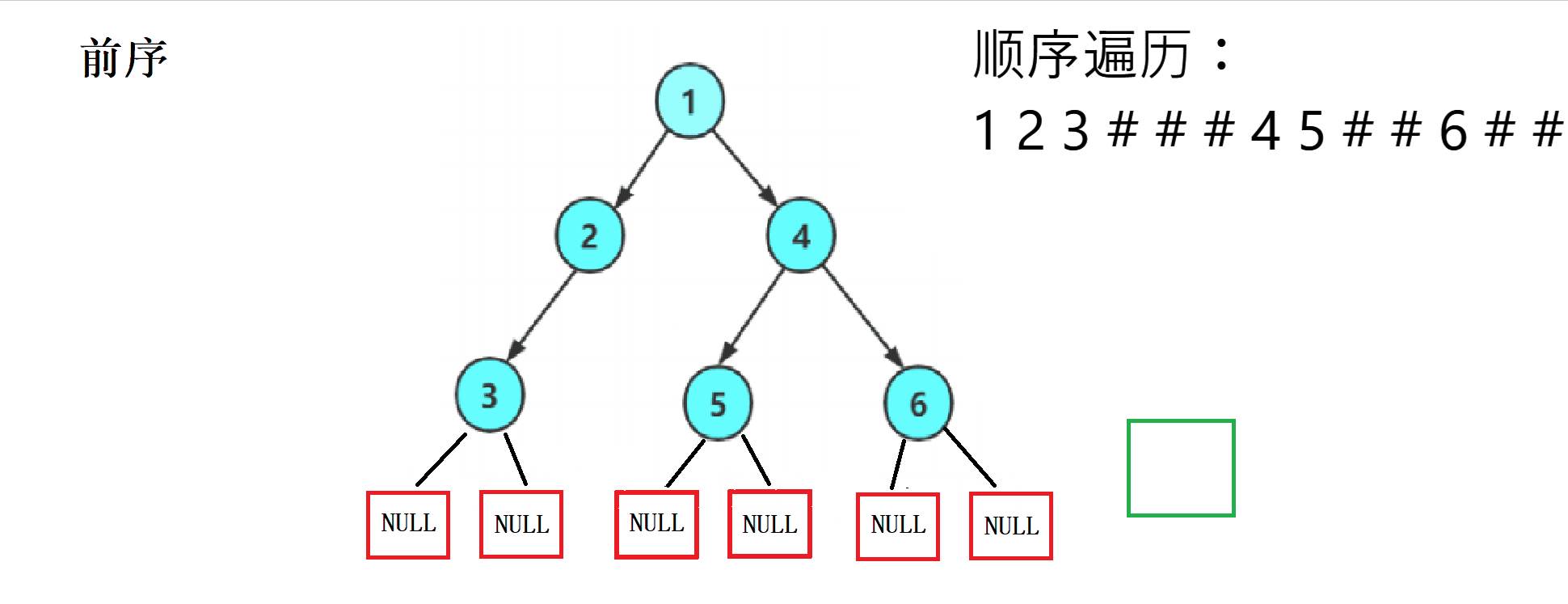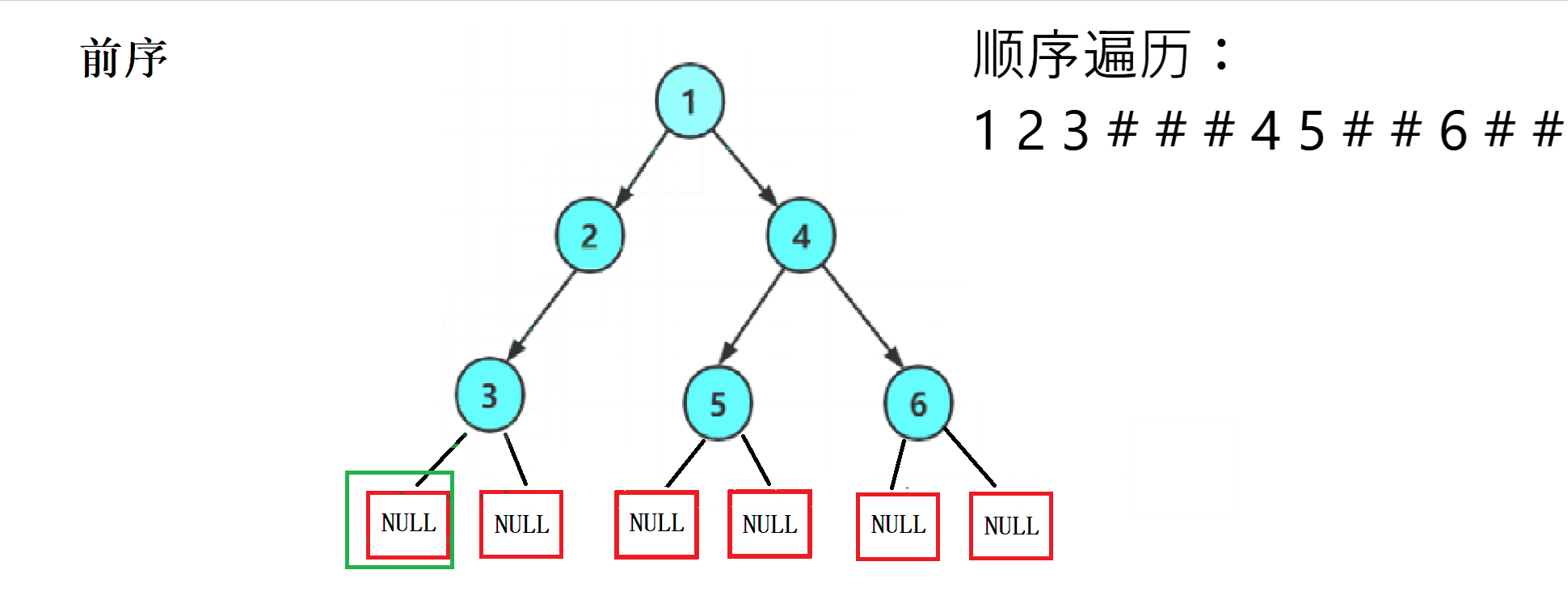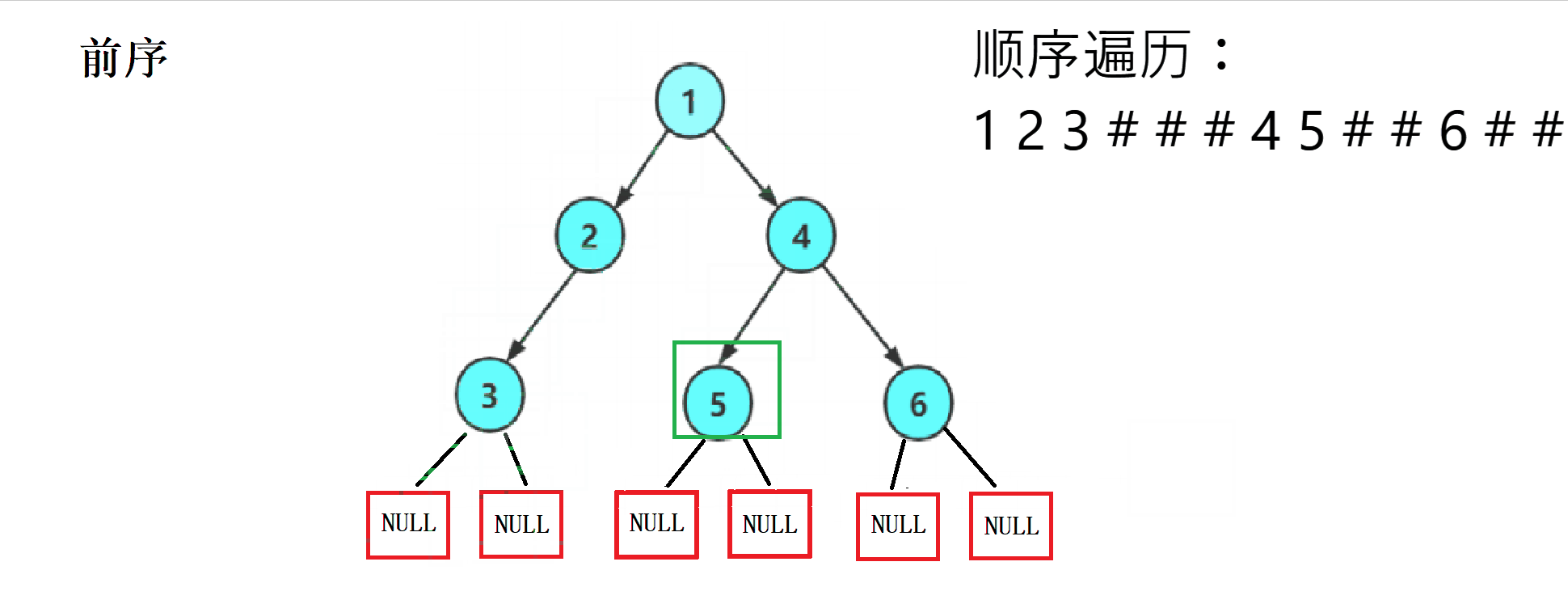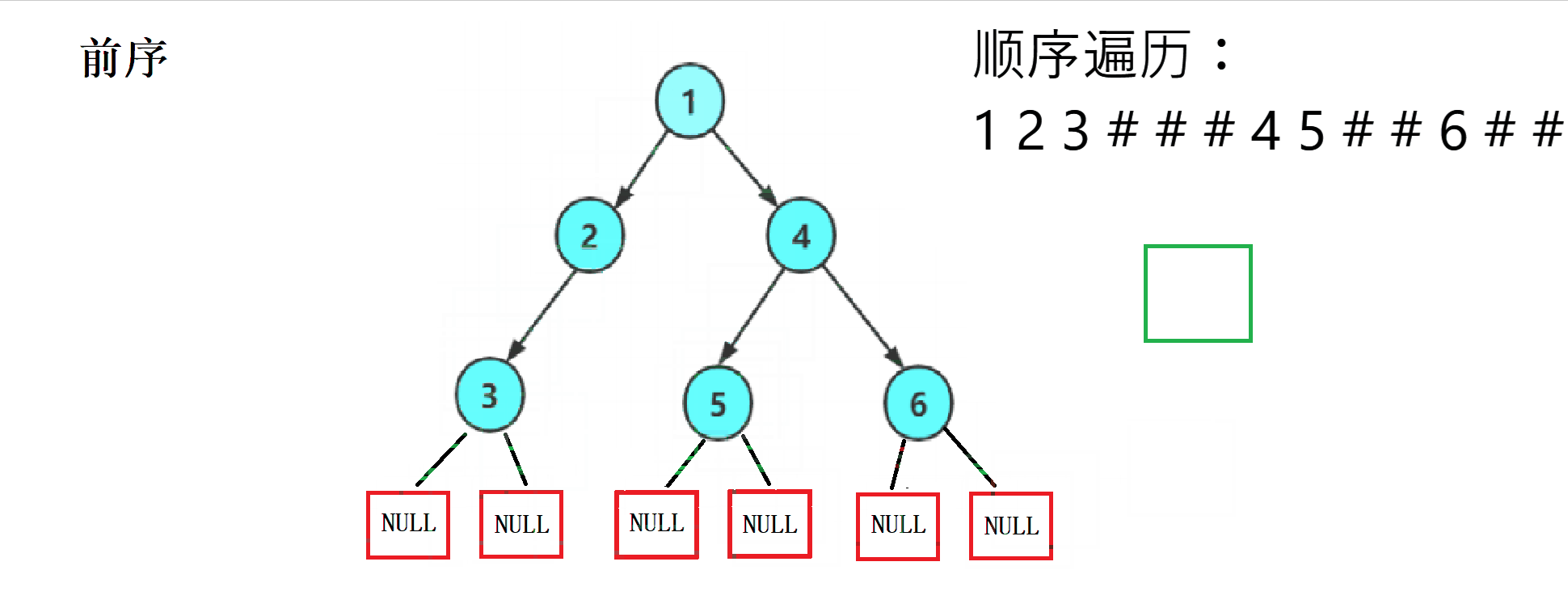
1. Before the order 、 Middle preface 、 After the sequence traversal
The access order of the three ways
Before the order ——( root --> The left subtree --> Right subtree )
Middle preface ——( The left subtree --> root --> Right subtree )
In the following order ——( The left subtree --> Right subtree --> root )
1.2 Traversal sequence diagram of three ways

2. Code implementation
This ergodic regularity is strong , We can easily write it using recursion , And divide each into NULL Print a # As a substitute for .
The former sequence traversal
// The former sequence traversal
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}In the sequence traversal
// In the sequence traversal
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}After the sequence traversal
// After the sequence traversal
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}3. Traversal detection
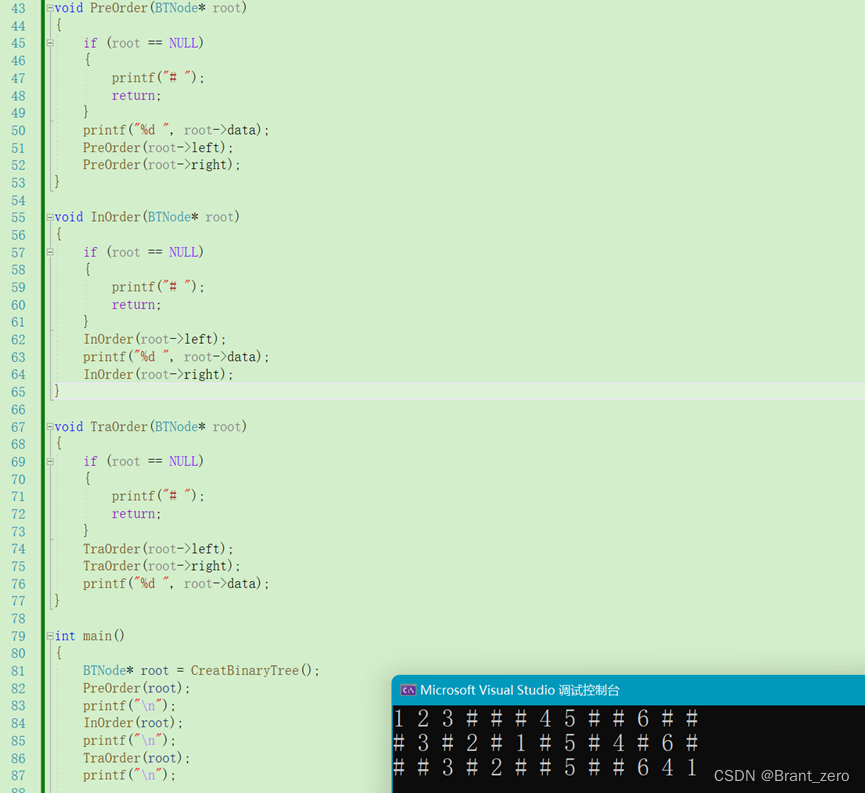
3、 ... and 、 Sequence traversal of trees
After completing the above three depth traversals , Someone must want to ask , If I want to traverse layer by layer, how can I achieve it ?
The implementation of sequence traversal can only be realized with the help of queues , How to realize it? Let's look down .
3.1 Sequence traversal
thought :
① Put the root node in the queue .
② Pop up the header element and print , Then put the left node and the right node of the queue header element into the queue in turn
③ Repeat until the queue is empty , You can traverse the entire tree layer by layer .
because , If the left subtree or right subtree is empty , You won't put it in the queue , In this way, the front nodes will be out of the queue in turn according to the law of forward first out , It can achieve the purpose of our sequence traversal .
// Sequence traversal
// thought Put a root node Pop up a root node Connect and store the left node and the right node ,
// When the queue is empty, it will not be put
void LevelOrder (BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
// If the queue is not empty, continue the above operation
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
// The right data
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestroy (&q);
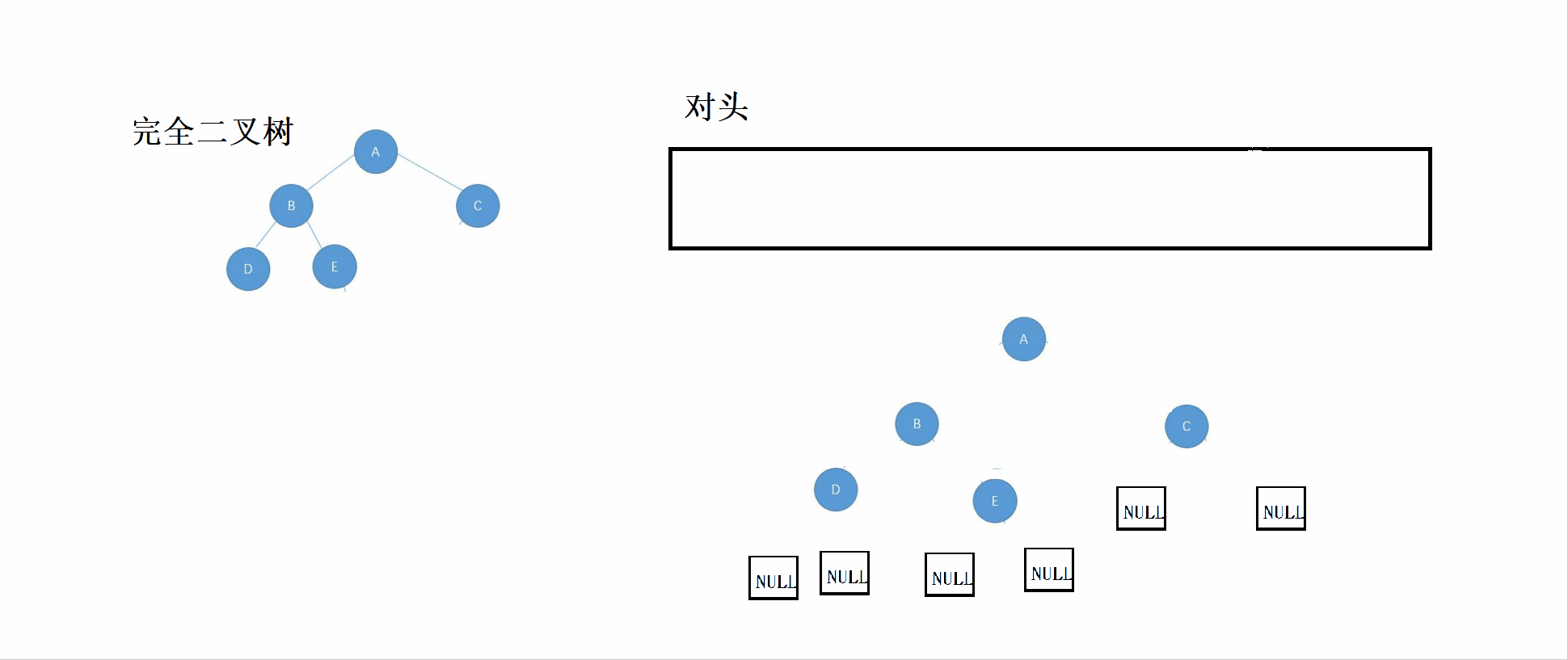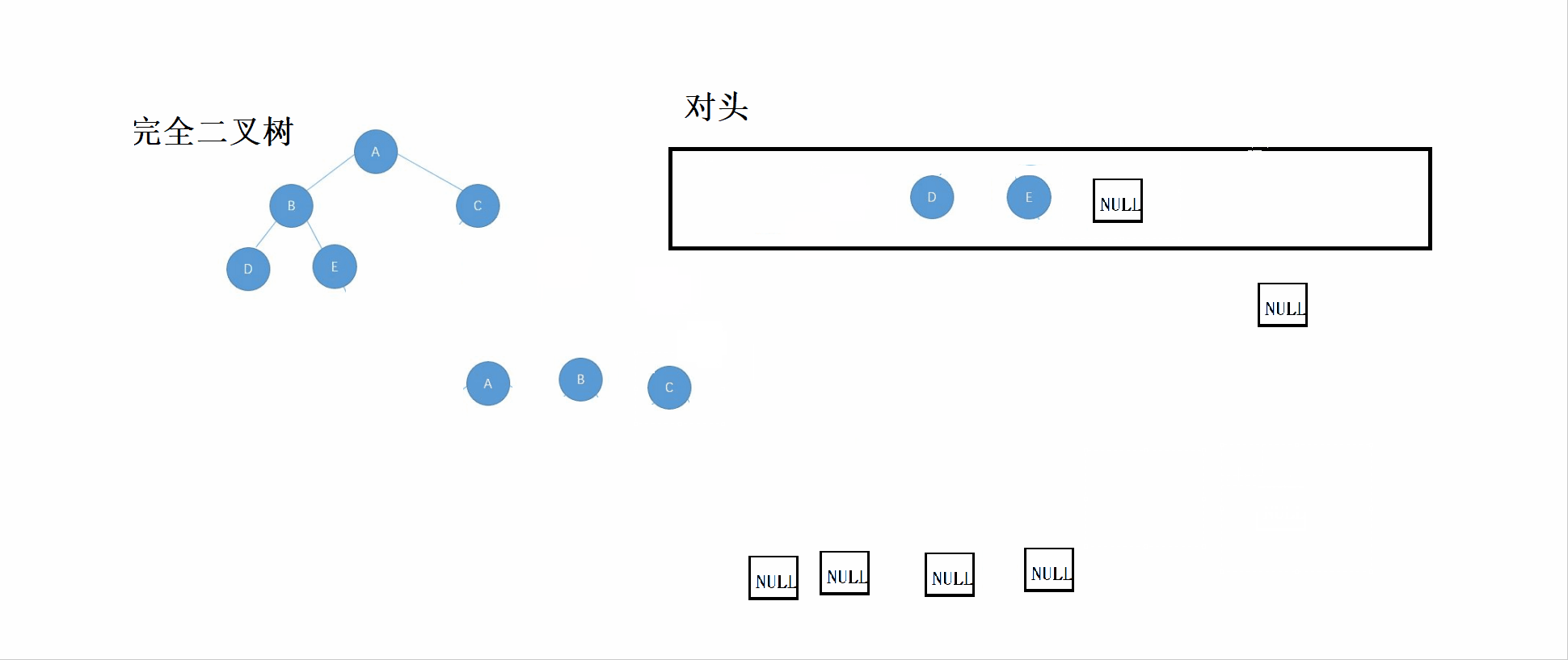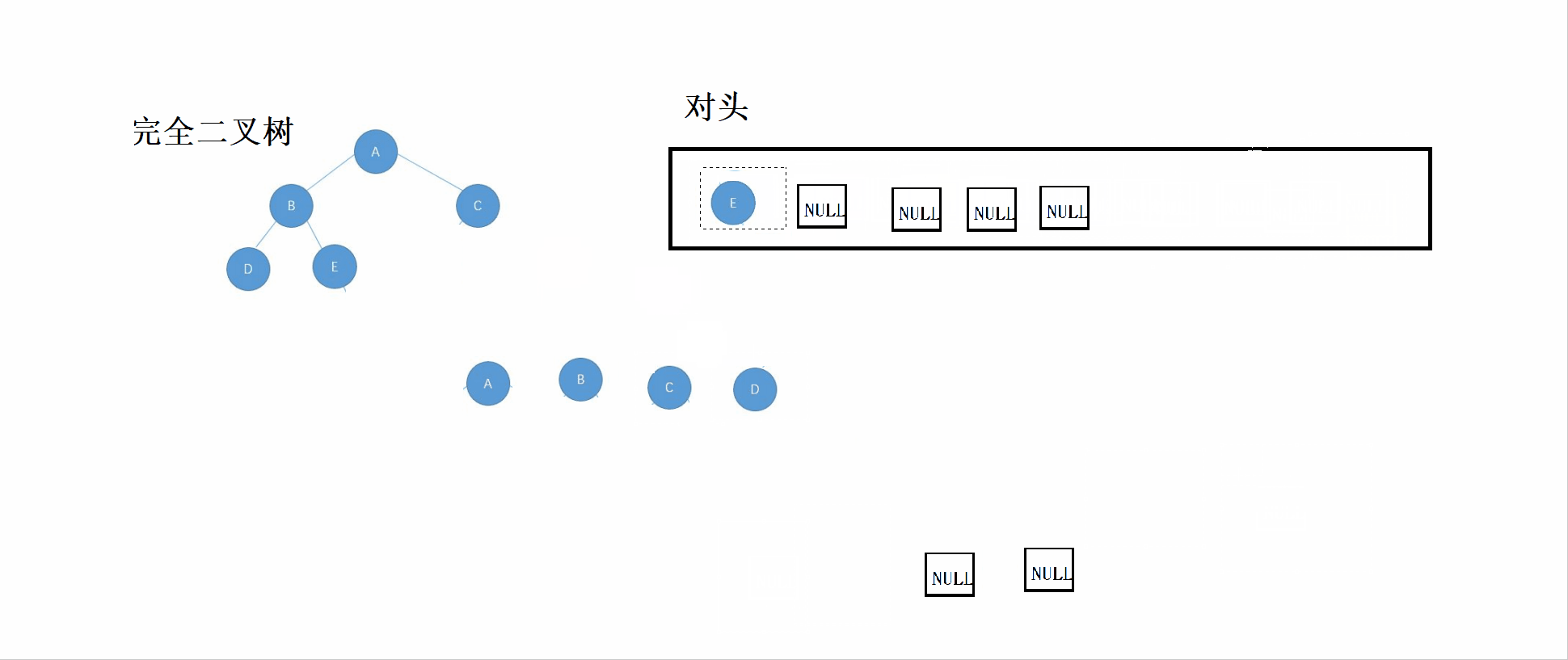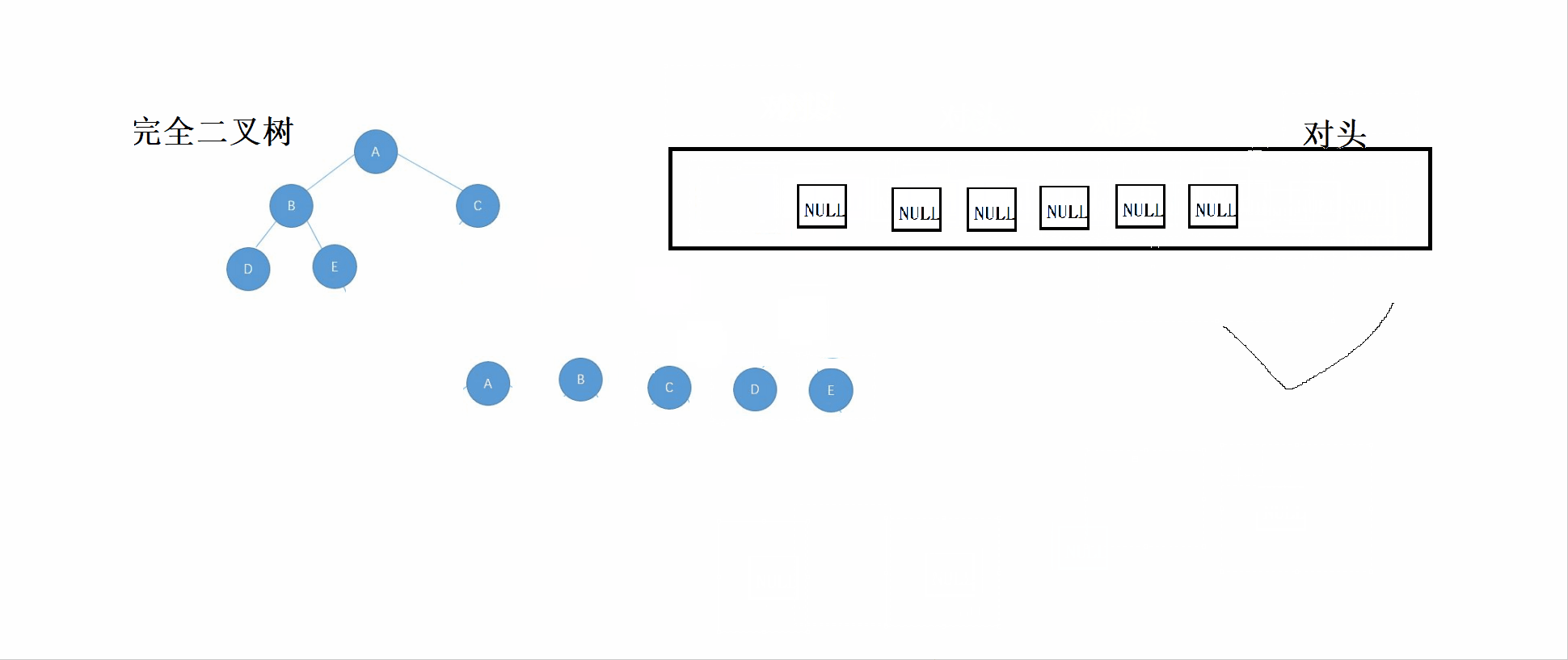
}3.2 Identification of complete binary tree
Perfect binary tree :n-1 Layer is full , The last layer of discontent , Full binary tree is a special kind of complete binary tree .
thought :
① According to the rules of sequence traversal , Set the root node 、 The left subtree 、 Put the right subtree into the queue
② If the header data is NULL, Then stop inserting into the queue .
③ Check the queue , If NULL There are non NULL node , Then it means that the tree is not a complete binary tree , Until the queue is empty ( That is, after the last node of the complete binary tree, it is all NULL node ).
Look at this first GIF chart , Then you can combine the code to see and understand .

// Judge whether the current tree is a complete binary tree
// If there is non empty after empty , It's not a complete binary tree
bool TreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
else
{
// If it is empty, it will jump out of sequence traversal
break;
}
//1. If there are all complete binary trees behind
//2. If there is non empty after empty , Is not a complete binary tree
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
return false;
}
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}Four 、 The basic functions of trees
It's not enough to traverse the tree , Let's implement more common functions .
4.1 The number of nodes in the tree
// Find the number of nodes
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}4.2 The number of leaf nodes in the tree
// Two ways to find the number of leaf nodes
int TreeLeafSize1(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return ((root->left == NULL) && (root->right == NULL)) ? 1 :
TreeLeafSize1(root->left) + TreeLeafSize1(root->right) ;
}4.3 The first k Number of layer nodes
// Please k Number of layer nodes
//1. Transform to find the left subtree k-1 layer , Right subtree k-1 layer
int KLeveSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return KLeveSize(root->left, k - 1) + KLeveSize(root->right, k - 1);
}4.4 Find the node of the tree
// Find the node of the tree
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
/*if (TreeFind(root->left, x) )
return TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (TreeFind(root->right, x))
return TreeFind(root->right, x);*/
// The above method will traverse deep twice Not recommended
BTNode* LeftNode = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (LeftNode)
return LeftNode;
BTNode* RightNode = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (RightNode)
return RightNode;
return NULL;
}4.5 Depth of tree
// Find the depth of the binary tree
int TreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int left = TreeDepth(root->left);
int right = TreeDepth(root->right);
return left > right ? left+1 : right+1;
}4.6 Destruction of trees
// Destruction of binary tree
// Post order traversal destruction
void TreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
TreeDestory(root->left);
TreeDestory(root->right);
// Should not be in Check the use of
//free Print the release before
printf("\n%p : %d ", root,root->data);
free(root);
}Compared with the previous stack and queue, the binary tree is more difficult , Be familiar with recursion , You can slowly digest it in combination with drawing . The code of recursive classes is not easy to debug , You can observe by printing in combination with depth traversal , Or read the code on the computer drawing board to understand .
This blog is over , Binary tree is still very difficult , Next, I'll do some exercises and start learning pile , I hope you will continue to pay attention .
边栏推荐
- Recommend free online SMS receiving platform in 2022 (domestic and foreign)
- Standard ACL and extended ACL
- 简单几步教你如何看k线图图解
- Three forms of multimedia technology commonly used in enterprise exhibition hall design
- 能同时做三个分割任务的模型,性能和效率优于MaskFormer!Meta&UIUC提出通用分割模型,性能优于任务特定模型!开源!...
- go语言的字符串类型、常量类型和容器类型
- 我感觉被骗了,微信内测 “大小号” 功能,同一手机号可注册两个微信
- PIP related commands
- 静态路由配置
- socket编程之常用api介绍与socket、select、poll、epoll高并发服务器模型代码实现
猜你喜欢
持续测试(CT)实战经验分享
GSAP animation library

RIP和OSPF的区别和配置命令
Redis
Static routing configuration
Reinforcement learning - learning notes 8 | Q-learning
Idea completely uninstalls installation and configuration notes

Three forms of multimedia technology commonly used in enterprise exhibition hall design
String type, constant type and container type of go language
Learn to make dynamic line chart in 3 minutes!
随机推荐
C语言中匿名的最高境界
嵌入式C语言程序调试和宏使用的技巧
RIP和OSPF的区别和配置命令
线程池和单例模式以及文件操作
单臂路由和三层交换的简单配置
Redis cluster and expansion
嵌入式面试题(算法部分)
App capture of charles+drony
debian10编译安装mysql
Datasimba launched wechat applet, and datanuza accepted the test of the whole scene| StartDT Hackathon
持续测试(CT)实战经验分享
【塔望方法论】塔望3W消费战略 - U&A研究法
Calculation of torque target value (ftorque) in servo torque control mode
App capture of charles+postern
Standard ACL and extended ACL
高考填志愿规则
[demo] circular queue and conditional lock realize the communication between goroutines
PHP面试题 foreach($arr as &$value)与foreach($arr as $value)的用法
回归问题的评价指标和重要知识点总结
DeSci:去中心化科学是Web3.0的新趋势?