当前位置:网站首页>How many checks does kubedm series-01-preflight have
How many checks does kubedm series-01-preflight have
2022-07-05 08:46:00 【runzhliu】
We know kubeadm init There will be a lot of preflight The inspection of , These mainly refer to kernel parameters 、 modular 、CRI Etc , If there are any configurations that do not conform Kubernetes The requirements of , Will throw Warning perhaps Error Information about , The following is preflight Main logic of
// Checker validates the state of the system to ensure kubeadm will be
// successful as often as possible.
type Checker interface {
Check() (warnings, errorList []error)
Name() string
} If there is diy Of check demand , You can inherit this interface in your code Expand , The following is an example. check Example , Obviously ContainerRuntimeCheck It's right CRI That is, the inspection carried out when the container is running
// ContainerRuntimeCheck verifies the container runtime.
type ContainerRuntimeCheck struct {
runtime utilruntime.ContainerRuntime
}
// Name returns label for RuntimeCheck.
func (ContainerRuntimeCheck) Name() string {
return "CRI"
}
// Check validates the container runtime
func (crc ContainerRuntimeCheck) Check() (warnings, errorList []error) {
klog.V(1).Infoln("validating the container runtime")
if err := crc.runtime.IsRunning(); err != nil {
errorList = append(errorList, err)
}
return warnings, errorList
} The real function of checking is the following function , In fact, it is the host computer that executes crictl info, And receive its return , Old irons might as well run it directly on the host to see the results
// IsRunning checks if runtime is running
func (runtime *CRIRuntime) IsRunning() error {
if out, err := runtime.crictl("info").CombinedOutput(); err != nil {
return errors.Wrapf(err, "container runtime is not running: output: %s, error", string(out))
}
return nil
}be-all Check There will be small staggered parts inside , For example, check the firewall , First of all Firewall This service does service check, Then the specific port will be checked
Here's all check The statistics of
- CRI: Check whether the container is running
- Service: Check whether the enable and active
- Firewall: Check whether the firewall is closed
- Port: Check whether some ports are released
- Privileged: Check some permissions
- Dir Available: Check whether the directory is valid
- File Available: Check whether the document is valid
- File Existing: Check if the file exists
- File Content: Check whether there is specified content in the file
- In Path: Check whether some executable files are in the specified directory
- Hostname: Check the format of the hostname
- HTTP Proxy: Check if the machine has Proxy Set up
- HTTP Proxy CIDR: Check which addresses of this machine will go Proxy
- System Verification: Check the system version
- Kubernetes Version: Check Kubernetes Version of
- Kubelet Version: Check Kubelet Version of
- SwapCheck: Check Swap Whether to shut down
- External Etcd Version: Check external etcd Version of
- Image Pull: Check whether the image warehouse is connected
- Num CPU: Check the machine CPU Is the quantity in line with kubeadm Minimum requirements for
- Mem: Check whether the local memory conforms to kubeadm Minimum requirements for
When really doing the examination , It will also distinguish between controlplane Or ordinary worker node , The specific checks to be done by different roles are different
Let's see In Path This check , That is to check whether some necessary binary files or commands have been installed , In addition, we have to see mandatory If it is true Words , That is what must be met , Otherwise, it is dispensable , But if not, it will prompt , Users will be advised to install
InPathCheck{executable: "crictl", mandatory: true, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "conntrack", mandatory: true, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "ip", mandatory: true, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "iptables", mandatory: true, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "mount", mandatory: true, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "nsenter", mandatory: true, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "ebtables", mandatory: false, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "ethtool", mandatory: false, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "socat", mandatory: false, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "tc", mandatory: false, exec: execer},
InPathCheck{executable: "touch", mandatory: false, exec: execer})Finally, let's take a look System Verification, Mainly for the host system to carry out some module detection , Let's mainly take a look at Linux Inspection under , Many modules of the kernel have and do not , There is still a big difference , So don't underestimate this part of the inspection , I think the main thing is Linux There is nothing wrong with the system , Sometimes it is precisely this part of the content that is more difficult to check
// DefaultSysSpec is the default SysSpec for Linux
var DefaultSysSpec = SysSpec{
OS: "Linux",
KernelSpec: KernelSpec{
Versions: []string{`^3\.[1-9][0-9].*$`, `^([4-9]|[1-9][0-9]+)\.([0-9]+)\.([0-9]+).*$`}, // Requires 3.10+, or newer
// TODO(random-liu): Add more config
// TODO(random-liu): Add description for each kernel configuration:
Required: []KernelConfig{
{Name: "NAMESPACES"},
{Name: "NET_NS"},
{Name: "PID_NS"},
{Name: "IPC_NS"},
{Name: "UTS_NS"},
{Name: "CGROUPS"},
{Name: "CGROUP_CPUACCT"},
{Name: "CGROUP_DEVICE"},
{Name: "CGROUP_FREEZER"},
{Name: "CGROUP_PIDS"},
{Name: "CGROUP_SCHED"},
{Name: "CPUSETS"},
{Name: "MEMCG"},
{Name: "INET"},
{Name: "EXT4_FS"},
{Name: "PROC_FS"},
{Name: "NETFILTER_XT_TARGET_REDIRECT", Aliases: []string{"IP_NF_TARGET_REDIRECT"}},
{Name: "NETFILTER_XT_MATCH_COMMENT"},
{Name: "FAIR_GROUP_SCHED"},
},
Optional: []KernelConfig{
{Name: "OVERLAY_FS", Aliases: []string{"OVERLAYFS_FS"}, Description: "Required for overlayfs."},
{Name: "AUFS_FS", Description: "Required for aufs."},
{Name: "BLK_DEV_DM", Description: "Required for devicemapper."},
{Name: "CFS_BANDWIDTH", Description: "Required for CPU quota."},
{Name: "CGROUP_HUGETLB", Description: "Required for hugetlb cgroup."},
{Name: "SECCOMP", Description: "Required for seccomp."},
{Name: "SECCOMP_FILTER", Description: "Required for seccomp mode 2."},
},
Forbidden: []KernelConfig{},
},
Cgroups: []string{"cpu", "cpuacct", "cpuset", "devices", "freezer", "memory", "pids"},
CgroupsOptional: []string{
// The hugetlb cgroup is optional since some kernels are compiled without support for huge pages
// and therefore lacks corresponding hugetlb cgroup
"hugetlb",
// The blkio cgroup is optional since some kernels are compiled without support for block I/O throttling.
// Containerd and cri-o will use blkio to track disk I/O and throttling in both cgroup v1 and v2.
"blkio",
},
CgroupsV2: []string{"cpu", "cpuset", "devices", "freezer", "memory", "pids"},
CgroupsV2Optional: []string{"hugetlb", "blkio"},
RuntimeSpec: RuntimeSpec{
DockerSpec: &DockerSpec{
Version: []string{`1\.1[1-3]\..*`, `17\.0[3,6,9]\..*`, `18\.0[6,9]\..*`, `19\.03\..*`, `20\.10\..*`},
GraphDriver: []string{"aufs", "btrfs", "overlay", "overlay2", "devicemapper", "zfs"},
},
},
}边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Programming implementation of subscriber node of ROS learning 3 subscriber

My university
Matlab tips (28) fuzzy comprehensive evaluation

Beautiful soup parsing and extracting data

Low code platform | apaas platform construction analysis
How to manage the performance of R & D team?

猜谜语啦(7)

猜谜语啦(4)
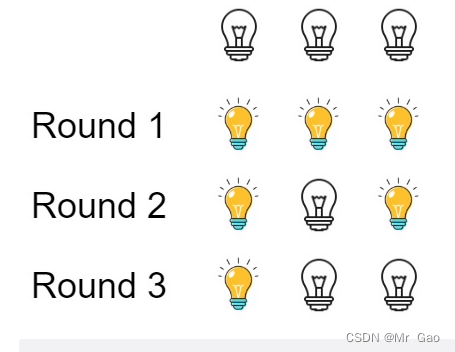
319. Bulb switch

Halcon color recognition_ fuses. hdev:classify fuses by color
随机推荐
Guess riddles (7)
asp.net(c#)的货币格式化
图解八道经典指针笔试题
Redis implements a high-performance full-text search engine -- redisearch
leetcode - 445. Add two numbers II
L298N module use
Business modeling of software model | overview
Affected tree (tree DP)
location search 属性获取登录用户名
Run菜单解析
猜谜语啦(6)
Wheel 1:qcustomplot initialization template
Several problems to be considered and solved in the design of multi tenant architecture
皮尔森相关系数
ROS learning 1- create workspaces and function packs
319. Bulb switch
猜谜语啦(3)
Beautiful soup parsing and extracting data
Guess riddles (2)
Warning: retrying occurs during PIP installation