What is? Scrapy
- be based on Twisted The asynchronous processing framework of
- pure python Implementation of the crawler framework
- The basic structure :5+2 frame ,5 A component ,2 Middleware
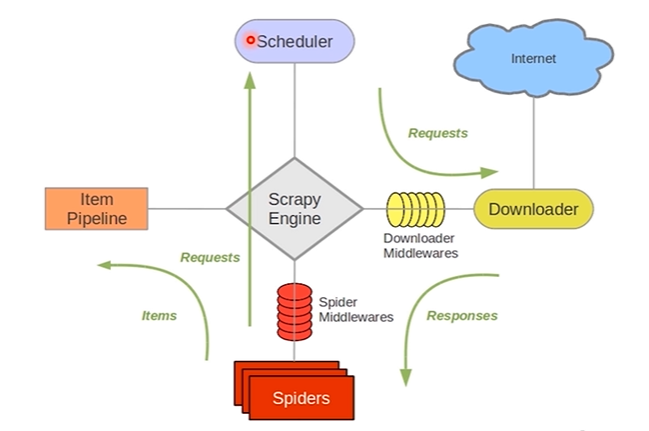
5 A component :
- Scrapy Engine: engine , Responsible for the communication of other components Carry out signal and data transmission ; be responsible for Scheduler、Downloader、Spiders、Item Pipeline The transmission of intermediate communication signals and data , This component is equivalent to a crawler “ The brain ”, It's the dispatch center of the whole reptile
- Scheduler: Scheduler , take request Request to queue up , When the engine needs to be returned to the engine , Pass the request through the engine to Downloader; Simply put, it's a queue , Be responsible for receiving the information sent by the engine request request , Then queue the request , When the engine needs to request data , Give the data in the request queue to the engine . Initial crawling URL And the information to be crawled obtained later in the page URL Put into the scheduler , Waiting for crawling , At the same time, the scheduler will automatically remove the duplicate URL( If specific URL It does not need to be de duplicated, but can also be realized by setting , Such as post Requested URL)
- Downloader: Downloader , Put the engine engine Sent request Receive , And will response The result is returned to the engine engine, Then the engine passes it to Spiders Handle
- Spiders: Parser , It handles everything responses, Analyze and extract data from it , obtain Item The data required for the field , And will need to follow up URL Submit to engine , Once again into the Scheduler( Scheduler ); It is also the entrance URL The place of
- Item Pipeline: Data pipeline , That is, we encapsulate de duplication 、 Where classes are stored , Responsible for handling Spiders Data obtained in and post-processing , Filter or store, etc . When the page is parsed by the crawler, the data required is stored in Item after , Will be sent to project pipeline (Pipeline), And process the data in several specific order , Finally, it is stored in local file or database
2 Middleware :
- Downloader Middlewares: Download Middleware , It can be regarded as a component that can customize and extend the download function , It is a specific hook between the engine and the downloader (specific hook), Handle Downloader To the engine response. The crawler can be automatically replaced by setting the downloader middleware user-agent、IP And so on .
- Spider Middlewares: Crawler middleware ,Spider Middleware is in the engine and Spider Specific hooks between (specific hook), Handle spider The input of (response) And the output (items And requests). Custom extension 、 The engine and Spider Components of communication function between , Extend by inserting custom code Scrapy function .
Scrapy Operation document ( Chinese ):https://www.osgeo.cn/scrapy/topics/spider-middleware.html
Scrapy Installation of frame
cmd window ,pip Installation
pip install scrapy
Scrapy Common problems during frame installation
Can't find win32api modular ----windows Common in the system
pip install pypiwin32
establish Scrapy Reptile project
New projects
scrapy startproject xxx Project name
example :
scrapy startproject tubatu_scrapy_project
Project directory
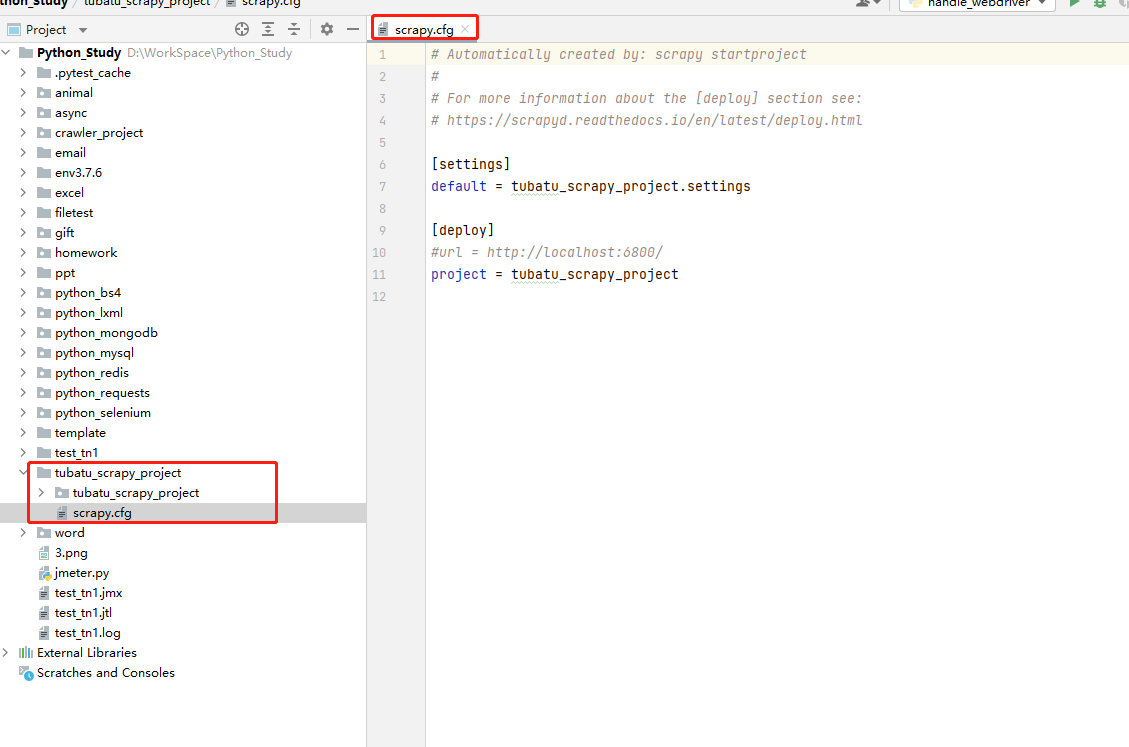
scrapy.cfg: The configuration file for the project , Defines the path of the project configuration file and other configuration information
- 【settings】: Defines the path of the project's configuration file , namely ./tubatu_scrapy_project/settings file
- 【deploy】: Deployment information

- items.py: That's what we define item Where data structures ; That is, which fields we want to grab , be-all item Definitions can be put into this file
- pipelines.py: Pipeline files for the project , It is what we call data processing pipeline file ; Used to write data storage , Cleaning and other logic , For example, store data in json file , You can write logic here
- settings.py: The setup file for the project , You can define the global settings of the project , For example, set the crawler USER_AGENT , You can set... Here ; Common configuration items are as follows :
- ROBOTSTXT_OBEY : Is it followed ROBTS agreement , Generally set as False
- CONCURRENT_REQUESTS : Concurrency , The default is 32 concurrent
- COOKIES_ENABLED : Is it enabled? cookies, The default is False
- DOWNLOAD_DELAY : Download delay
- DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS : Default request header
- SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES : Is it enabled? spider middleware
- DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES : Is it enabled? downloader middleware
- For others, see link
- spiders Catalog : Include the implementation of each crawler , Our parsing rules are written in this directory , That is, the crawler parser is written in this directory
- middlewares.py: Defined SpiderMiddleware and DownloaderMiddleware The rules of middleware ; Custom request 、 Customize other data processing methods 、 Proxy access, etc
Automatic generation spiders Template file
cd To spiders Under the table of contents , Output the following command , Generate crawler files :
scrapy genspider file name Crawling address
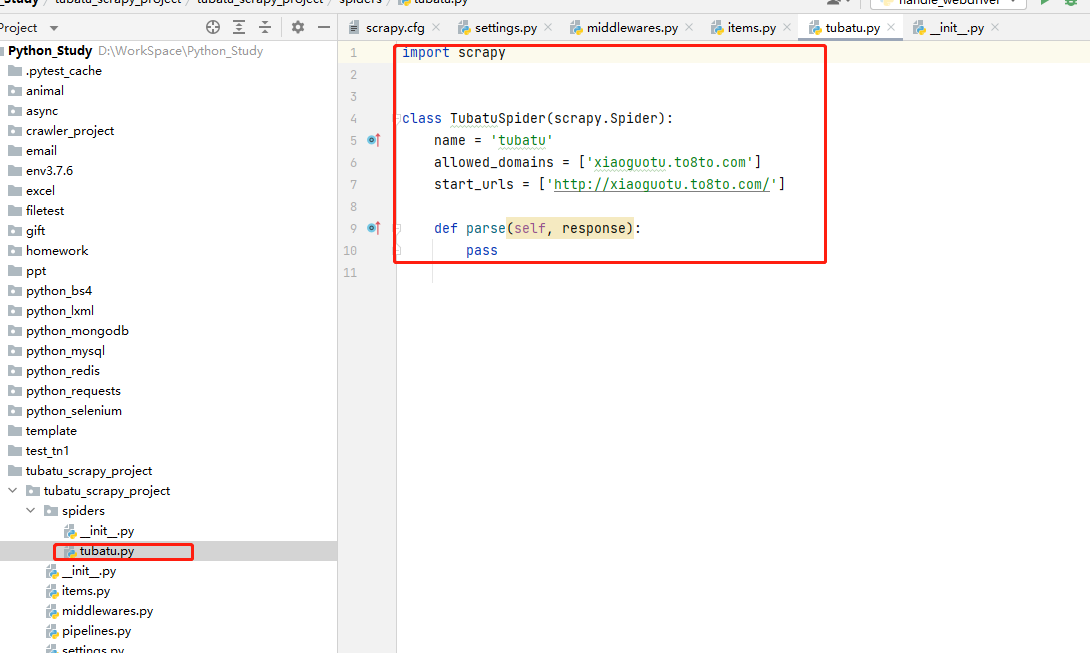
Run crawler
Mode one :cmd start-up
cd To spiders Under the table of contents , Execute the following command , Start the crawler :
scrapy crawl Reptile name
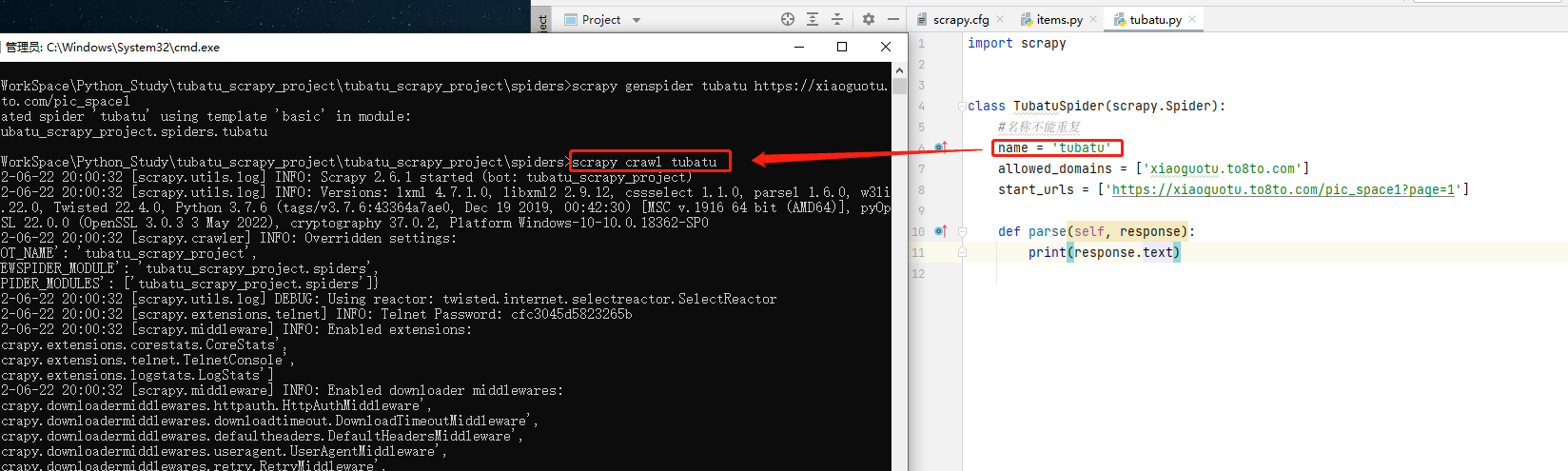
Mode two :py File to start the
Create under Project main.py file , Create startup script , perform main.py Startup file , The code example is as follows :
code- Crawler file
import scrapy class TubatuSpider(scrapy.Spider): # The name cannot be repeated name = 'tubatu' # Allow crawlers to crawl the domain name allowed_domains = ['xiaoguotu.to8to.com'] # Crawler file to be started after the project is started start_urls = ['https://xiaoguotu.to8to.com/pic_space1?page=1'] # The default parsing method def parse(self, response): print(response.text)
code- Startup file
from scrapy import cmdline # In us scrapy Inside the project , For the convenience of operation scrapy The files created during the project # Use cmdlie.execute() Method to execute the crawler start command :scrapy crawl Reptile name cmdline.execute("scrapy crawl tubatu".split()) #execute Each command that the method needs to run is a separate string , Such as :cmdline.execute(['scrapy', 'crawl', 'tubatu']), So if the command is an entire string , need split( ) Segmentation ;#
code- Running results
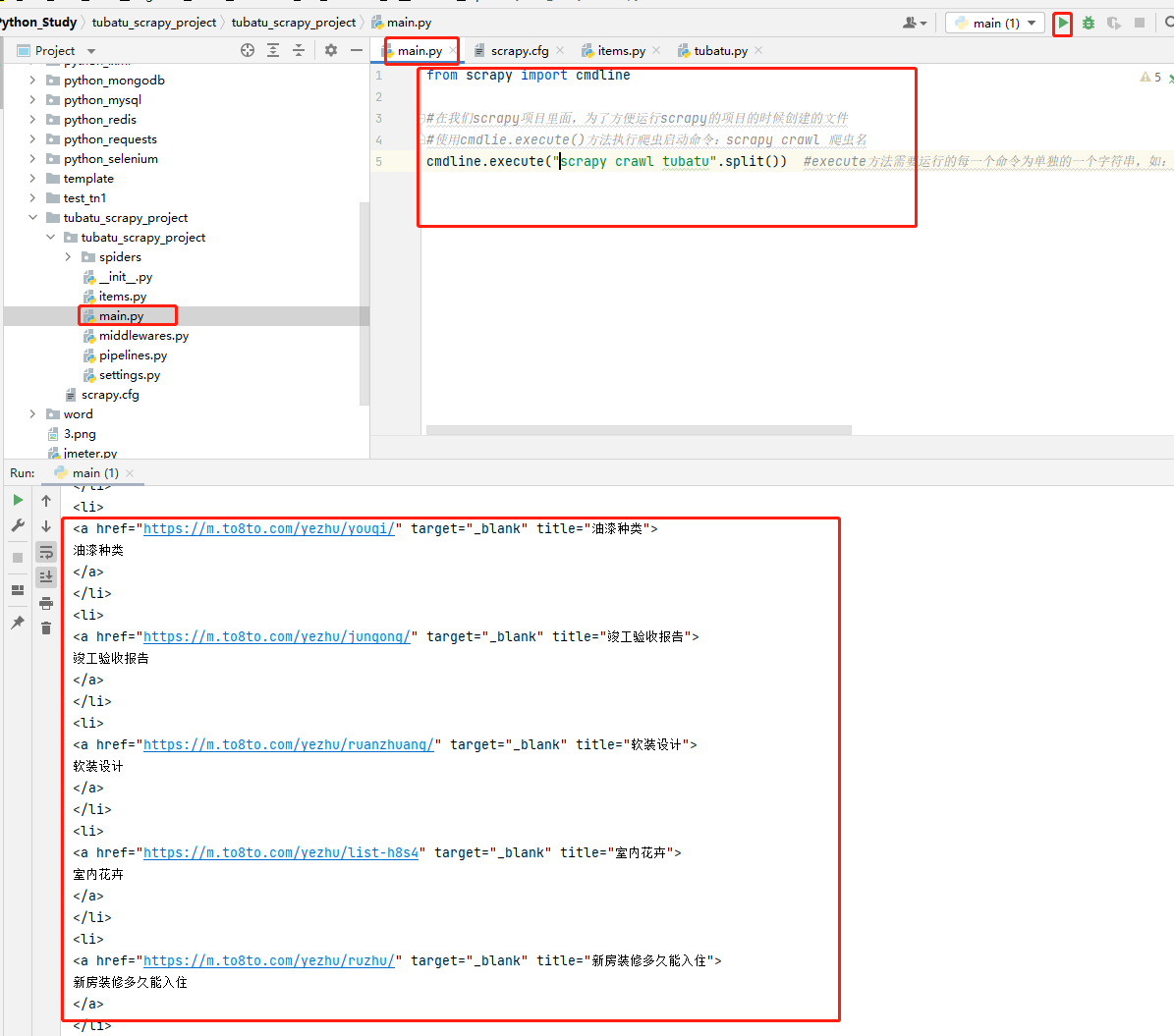
The sample project
Crawl the information of Tu Batu decoration website . Store the crawled data locally MongoDB In the database ;
The following figure shows the project organization , The document marked in blue is this time code Code for
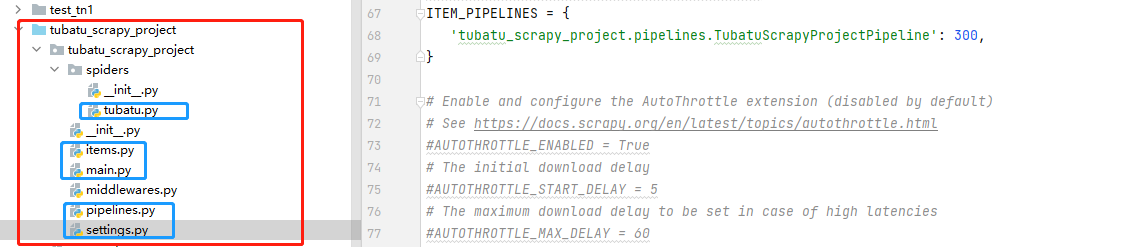
tubatu.py
1 import scrapy 2 from tubatu_scrapy_project.items import TubatuScrapyProjectItem 3 import re 4 5 class TubatuSpider(scrapy.Spider): 6 7 # The name cannot be repeated 8 name = 'tubatu' 9 # Allow crawlers to crawl the domain name , Beyond this directory, you are not allowed to crawl 10 allowed_domains = ['xiaoguotu.to8to.com','wx.to8to.com','sz.to8to.com'] 11 # Crawler file to be started after the project is started 12 start_urls = ['https://xiaoguotu.to8to.com/pic_space1?page=1'] 13 14 15 # The default parsing method 16 def parse(self, response): 17 # response It can be used directly in the back xpath Method 18 # response It's just one. Html object 19 pic_item_list = response.xpath("//div[@class='item']") 20 for item in pic_item_list[1:]: 21 info = {} 22 # Here is a point to not lose , It means that at present Item Now use again xpath 23 # It's not just xpath In positioning text() Content , Need to filter again ; Return to :[<Selector xpath='.//div/a/text()' data='0 Yuan gets the design plan , Limit the number of people to receive '>] <class 'scrapy.selector.unified.SelectorList'> 24 # content_name = item.xpath('.//div/a/text()') 25 26 # Use extract() Method to get item Back to data Information , Back to the list 27 # content_name = item.xpath('.//div/a/text()').extract() 28 29 # Use extract_first() Method to get the name , data ; The return is str type 30 # Get the name of the project , Project data 31 info['content_name'] = item.xpath(".//a[@target='_blank']/@data-content_title").extract_first() 32 33 # Get the URL 34 info['content_url'] = "https:"+ item.xpath(".//a[@target='_blank']/@href").extract_first() 35 36 # project id 37 content_id_search = re.compile(r"(\d+)\.html") 38 info['content_id'] = str(content_id_search.search(info['content_url']).group(1)) 39 40 # Use yield To send asynchronous requests , It uses scrapy.Request() Method to send , This method can be passed on to cookie etc. , You can enter this method to check 41 # Callback function callback, Write only the method name , Do not call methods 42 yield scrapy.Request(url=info['content_url'],callback=self.handle_pic_parse,meta=info) 43 44 if response.xpath("//a[@id='nextpageid']"): 45 now_page = int(response.xpath("//div[@class='pages']/strong/text()").extract_first()) 46 next_page_url="https://xiaoguotu.to8to.com/pic_space1?page=%d" %(now_page+1) 47 yield scrapy.Request(url=next_page_url,callback=self.parse) 48 49 50 def handle_pic_parse(self,response): 51 tu_batu_info = TubatuScrapyProjectItem() 52 # The address of the picture 53 tu_batu_info["pic_url"]=response.xpath("//div[@class='img_div_tag']/img/@src").extract_first() 54 # nickname 55 tu_batu_info["nick_name"]=response.xpath("//p/i[@id='nick']/text()").extract_first() 56 # The name of the picture 57 tu_batu_info["pic_name"]=response.xpath("//div[@class='pic_author']/h1/text()").extract_first() 58 # Name of the project 59 tu_batu_info["content_name"]=response.request.meta['content_name'] 60 # project id 61 tu_batu_info["content_id"]=response.request.meta['content_id'] 62 # Project URL 63 tu_batu_info["content_url"]=response.request.meta['content_url'] 64 #yield To piplines, We go through settings.py It's enabled inside , If not enabled , Will not be available 65 yield tu_batu_info
items.py
1 # Define here the models for your scraped items 2 # 3 # See documentation in: 4 # https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html 5 6 import scrapy 7 8 9 class TubatuScrapyProjectItem(scrapy.Item): 10 # define the fields for your item here like: 11 # name = scrapy.Field() 12 13 # Decoration name 14 content_name=scrapy.Field() 15 # decorate id 16 content_id = scrapy.Field() 17 # request url 18 content_url=scrapy.Field() 19 # nickname 20 nick_name=scrapy.Field() 21 # The image url 22 pic_url=scrapy.Field() 23 # The name of the picture 24 pic_name=scrapy.Field()
piplines.py
1 # Define your item pipelines here 2 # 3 # Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting 4 # See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html 5 6 7 # useful for handling different item types with a single interface 8 from itemadapter import ItemAdapter 9 10 from pymongo import MongoClient 11 12 class TubatuScrapyProjectPipeline: 13 14 def __init__(self): 15 client = MongoClient(host="localhost", 16 port=27017, 17 username="admin", 18 password="123456") 19 mydb=client['db_tubatu'] 20 self.mycollection = mydb['collection_tubatu'] 21 22 def process_item(self, item, spider): 23 data = dict(item) 24 self.mycollection.insert_one(data) 25 return item
settings.py
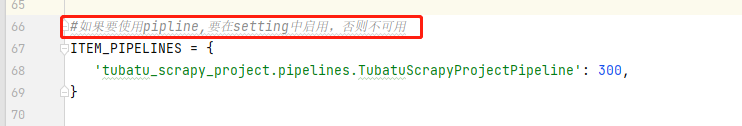
main.py
1 from scrapy import cmdline 2 3 # In us scrapy Inside the project , For the convenience of operation scrapy The files created during the project 4 # Use cmdlie.execute() Method to execute the crawler start command :scrapy crawl Reptile name 5 cmdline.execute("scrapy crawl tubatu".split()) #execute Each command that the method needs to run is a separate string , Such as :cmdline.execute(['scrapy', 'crawl', 'tubatu']), So if the command is an entire string , need split( ) Segmentation ;#

![[observation] with the rise of the](/img/9a/8bbf98e6aed80638f4340aacec2ea9.jpg)