当前位置:网站首页>AtCoder Beginner Contest 258「ABCDEFG」
AtCoder Beginner Contest 258「ABCDEFG」
2022-07-05 10:18:00 【Chels.】
A - When?
Title Description :
Ask from
21:00StartkWhen is it in minutes
Ideas :
Just write whatever you want
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod7 1000000007
#define mod9 998244353
#define m_p(a,b) make_pair(a, b)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define debug(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n";
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair <int,int> pii;
#define MAX 300000 + 50
int n, m, k, x;
int tr[MAX];
void work(){
cin >> n;
if(n < 60){
printf("21:%02d\n", n);
}
else{
n %= 60;
printf("22:%02d\n", n);
}
}
int main(){
io;
work();
return 0;
}
B - Number Box
Title Description :
Here you are.
n * nMatrix , Every point has a number , The upper and lower bounds of this matrix 、 The left and right boundaries are connected , You can choose any starting point , Then fix one direction , The directions are up and down, left and right, up and down, left, left, down, right, up and down 8 A direction , Ask to leave n After step, you will get a length of n String , Ask the one with the largest lexicographic order among the possible strings
Ideas :
Enumerate each starting point , Enumerate each direction , Just run violently
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod7 1000000007
#define mod9 998244353
#define m_p(a,b) make_pair(a, b)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define debug(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n";
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair <int,int> pii;
#define MAX 300000 + 50
int n, m, k, x;
char tr[15][15];
int dx[] = {
1, 0, -1, 0, -1, -1, 1, 1};
int dy[] = {
0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 1, -1, 1};
void work(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
cin >> tr[i][j];
}
}
vector<string>v;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
for(int k = 0; k < 8; ++k){
int num = 0;
string s = "";
while(num < n){
int x = (i + dx[k] * num - 1 + n * n) % n + 1;
int y = (j + dy[k] * num - 1 + n * n) % n + 1;
s += tr[x][y];
++num;
}
v.push_back(s);
}
}
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << v.back() << endl;
}
int main(){
io;
work();
return 0;
}
C - Rotation
Title Description :
Given a length of n String , Conduct Q operations , Two kinds of operations , As follows :
op = 1: Delete the following x Characters , And put it in frontop = 2: Output No x What is a character
Ideas :
We can think of a string as a string connected from beginning to end , We just need to record the starting point , The operation 1 In fact, it makes the starting point move to the left x position , We only need to take a reasonable mold to maintain , operation 2 Also through our starting point and x If you want to add a module and output the characters at the corresponding position
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod7 1000000007
#define mod9 998244353
#define m_p(a,b) make_pair(a, b)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define debug(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n";
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair <int,int> pii;
#define MAX 500000 + 50
int n, m, k, x, op;
char tr[MAX];
void work(){
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)cin >> tr[i];
int fi = 0;
while(m--){
cin >> op >> x;
if(op == 1){
fi = (fi - x + 2 * n) % n;
}
else{
cout << tr[(fi + x - 1) % n] << endl;
}
}
}
int main(){
io;
work();
return 0;
}
D - Trophy
Title Description :
Yes n A level , Each level has an entry animation and the time required to pass the level , Each time you enter a new level, you must watch the entry animation and pass this level before unlocking the next level , And you don't need to watch the entrance animation when you choose the level again after passing the level , Just need to pass the customs , You are now at the checkpoint 1 Doorway , You must pass the customs x A level , this x A level can have duplicate levels , Ask the minimum time it takes
Ideas :
Simple greed
Note that the maximum value should be larger , Because the limit data will actually exceed 1e18, For this reason, I insisted wa 了 20 minute ( Split
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod7 1000000007
#define mod9 998244353
#define m_p(a,b) make_pair(a, b)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define debug(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n";
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair <int,int> pii;
#define MAX 300000 + 50
ll n, m, k, x;
ll ar[MAX], br[MAX];
void work(){
cin >> n >> x;
ll minx = 8e18;
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
cin >> ar[i] >> br[i];
ans += ar[i] + br[i];
minx = min(minx, ans + (max(0ll, x - 1)) * br[i]);
--x;
}
cout << minx << endl;
}
int main(){
io;
work();
return 0;
}
E - Packing Potatoes
Title Description :
n Items , Every object has a weight
w[i],n Items are arranged in order ,n After the items are finished, continue to repeat this indefinitely n Items , Now there are countless boxes that want to pack these items , The rule is : If the weight of the box after adding the current item is greater than or equal toK, Then seal the box , Change an empty box to load items , Otherwise, continue to installNow here you are Q Time to ask , Ask you every time
X[i]There are several items in a box
Ideas :
At first glance, I thought it was to find the circular section
Because the order of items has been determined , And
KAlso make sure , So if you encounter withiThe item is the starting item of an empty box , That must start to produce a cycleSo we can calculate the number of
iWhen an item is the starting item of an empty box , The subscript of the starting item of the next empty box isid[i]The method is to dichotomy on the basis of prefix and , And record with
iThe item is the number of items that the starting item of the empty box can holdThere are two cases :
- When
sum[n] - sum[i - 1] >= K, Then just two points directly- otherwise , Let's put the
Ksubtractsum[n] - sum[i - 1], Then it becomes an object1For starting items , Then onsum[n]Take the mold , Another dichotomyAfter dichotomy , Let's simulate this process , Use an array to record the last occurrence
iThe box subscript of the starting item of the empty box , If it happened before , It means that there is a cycle , It's probably like this :
For every question we ask , Let's subtract the front head first according to the subscript , Just go to the circulation section again
This inscription has many details , Especially the two points and subscripts , I just wrote the wrong subscript at the starting point of two points wa For a long time
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod7 1000000007
#define mod9 998244353
#define m_p(a,b) make_pair(a, b)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define debug(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n";
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair <int,int> pii;
#define MAX 300000 + 50
ll n, m, k, x;
ll tr[MAX];
ll sum[MAX];
ll fuck[MAX];
ll num[1000005];
ll id[MAX];
ll vis_id[MAX];
void work(){
cin >> n >> m >> x;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
cin >> tr[i];
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + tr[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
ll p = x;
if(sum[n] - sum[i - 1] >= x){
id[i] = (lower_bound(sum + i, sum + 1 + n, x + sum[i - 1]) - sum);
fuck[i] = id[i] + 1 - i;
id[i] = id[i] % n + 1;
}
else{
p = p - (sum[n] - sum[i - 1]);
fuck[i] = n - i + 1 + n * (p / sum[n]);
p %= sum[n];
id[i] = (lower_bound(sum + 1, sum + 1 + n, p) - sum);
fuck[i] = fuck[i] + id[i];
id[i] = id[i] % n + 1;
}
}
ll idd = 1;
ll len = 0;
ll r = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= 1000000; ++i){
if(vis_id[idd]){
len = i - vis_id[idd];
r = vis_id[idd] - 1;
break;
}
vis_id[idd] = i;
num[i] = fuck[idd];
idd = id[idd];
}
while(m--){
cin >> x;
if(x <= r)cout << num[x] << endl;
else{
x -= r;
x = (x - 1) % len + 1;
cout << num[r + x] << endl;
}
}
}
int main(){
io;
work();
return 0;
}
F - Main Street
Title Description :
Input B,K, On a two-dimensional plane , There are countless parallel lines x Axis and y Axis line ,
x = n, y = n, These are small roads , among ,x = Bn, y = BnThese straight lines are roads , When people walk on the road , The cost between two adjacent points is1, While walking on the path , The cost between two adjacent points isK, Ask from(Sx, Sy)Set out to(Gx, Gy)What's the minimum cost of
Ideas :
obviously , We should take the main road as far as possible , And for each point , Must belong to a
B*BIn the box of , Then there must be a vertical line from this point to the four boundaries of the grid 4 Foot drop ( May coincide ), These are the four ways to get to the main road at this point , We use doubleforLoop to enumerate the methods of two points to reach the road , That is to say4 * 4 = 16Kind of plan , We need to know what is the shortest distance between two points on the roadIf the two points here are not in the same
B*BInside the square , Or in the same block , But not on the opposite side parallel to each other , Then the cost is the Manhattan distance between the two , If it is in the same block and the two points are on the opposite side , Then we need to discuss , Discuss whether it is on the opposite side of the top and bottom or on the opposite side of the left and right , On this basis , The minimum distance between two points should also be taken as the minimum value in the following three cases
There are three paths , We take the minimum value of these three paths , The purple one is to take the main road first and then the small road , So when calculating, the path must take
K
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000007
#define sd(n) scanf("%d",&n)
#define sdd(n,m) scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)
#define m_p(a,b) make_pair(a, b)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define debug(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n";
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair <ll, ll> pii;
#define y1 y114514
#define MAX 300000 + 50
ll b, k, sx, sy, gx, gy;
vector<pii>ar, br;
void cal(ll x, ll y, vector<pii>&ar){
ar.push_back(m_p(x - x % b, y));
ar.push_back(m_p(x, y - y % b));
ar.push_back(m_p(x, y + b - y % b));
ar.push_back(m_p(x + b - x % b, y));
}
ll getans(ll x1, ll y1, ll x2, ll y2){
ll ans = (abs(x1 - sx) + abs(y1 - sy) + abs(x2 - gx) + abs(y2 - gy)) * k;
if(x1 % b == 0 && x2 % b == 0 && y1 / b == y2 / b){
ans += min({
abs(x1 - x2) * k + abs(y1 - y2), abs(x1 - x2) + 2 * b - y1 % b - y2 % b, abs(x1 - x2) + y1 % b + y2 % b});
}
else if(y1 % b == 0 && y2 % b == 0 && x1 / b == x2 / b){
ans += min({
abs(y1 - y2) * k + abs(x1 - x2), abs(y1 - y2) + x1 % b + x2 % b, 2 * b - x1 % b - x2 % b + abs(y1 - y2)});
}
else {
ans += abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2);
}
return ans;
}
void work(){
cin >> b >> k >> sx >> sy >> gx >> gy;
ar.clear();br.clear();
cal(sx, sy, ar);
cal(gx, gy, br);
ll ans = 8e18;
ans = min(ans, (abs(sx - gx) + abs(sy - gy)) * k);
for(int i = 0; i < ar.size(); ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < br.size(); ++j){
ans = min(ans, getans(ar[i].first, ar[i].second, br[j].first, br[j].second));
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main(){
io;
int tt;cin>>tt;
for(int _t = 1; _t <= tt; ++_t){
work();
}
return 0;
}
G - Triangle
Title Description :
Ask how many triples exist
(i, j, k), Satisfyi<j<kAndiandjThere's a side between ,jandkThere's a side between ,iandkThere's a side between
Ideas :
Let's enumerate
iandj, use bitset take&To optimize , seekkThe number ofBe careful
bitsetWhat is stored is an inverted string, in fact , We need toreverseonce
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod7 1000000007
#define mod9 998244353
#define m_p(a,b) make_pair(a, b)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define debug(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n";
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair <int,int> pii;
#define MAX 300000 + 50
int n, m, k, x;
bitset<3005>b[3005];
string s;
void work(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
cin >> s;
reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
b[i] = bitset<3005>(s);
}
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
for(int j = i + 1; j <= n; ++j){
if(b[i][j - 1] == 1){
ans += (b[i] & b[j]).count();
}
}
}
cout << ans / 3 << endl;
}
int main(){
io;
work();
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- > Could not create task ‘:app:MyTest.main()‘. > SourceSet with name ‘main‘ not found.问题修复
- Timed disappearance pop-up
- 伪类元素--before和after
- Swift saves an array of class objects with userdefaults and nssecurecoding
- Events and bubbles in the applet of "wechat applet - Basics"
- Excerpt from "sword comes" (VII)
- Comment obtenir le temps STW du GC (collecteur d'ordures)?
- How to judge that the thread pool has completed all tasks?
- 学习笔记5--高精地图解决方案
- Interview: is bitmap pixel memory allocated in heap memory or native
猜你喜欢
ArcGIS Pro creating features

Timed disappearance pop-up

苹果 5G 芯片研发失败?想要摆脱高通为时过早
Constraintlayout officially provides rounded imagefilterview
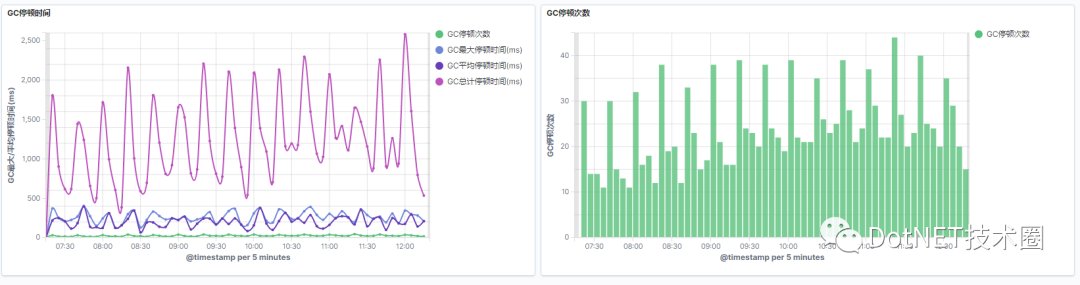
Comment obtenir le temps STW du GC (collecteur d'ordures)?
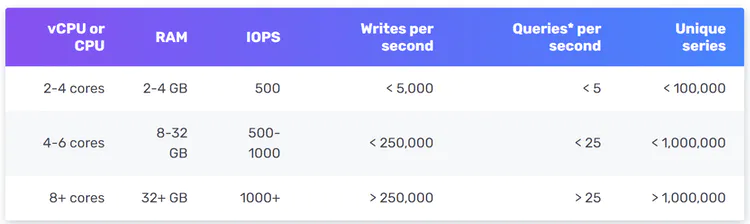
【系统设计】指标监控和告警系统
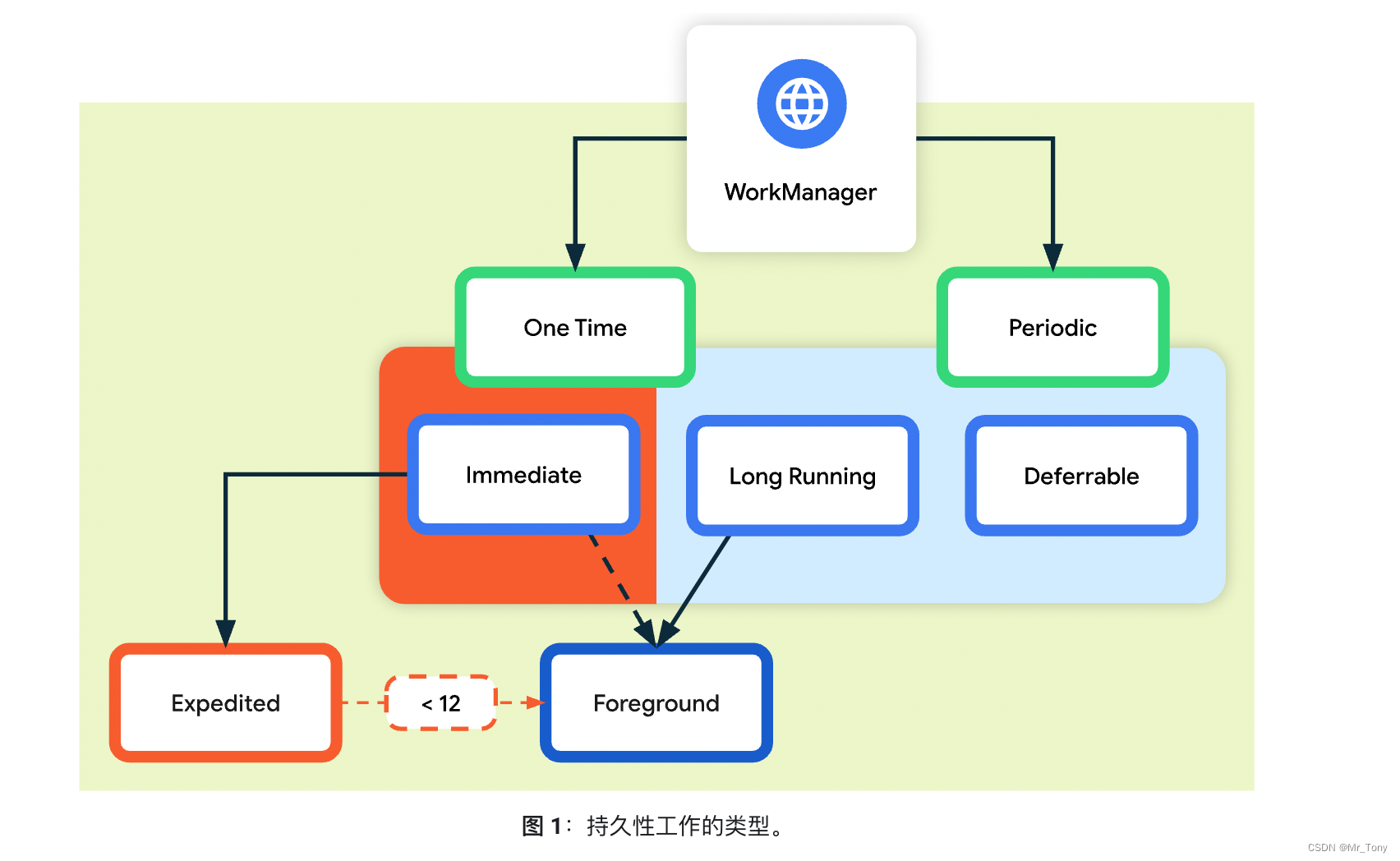
WorkManager学习一
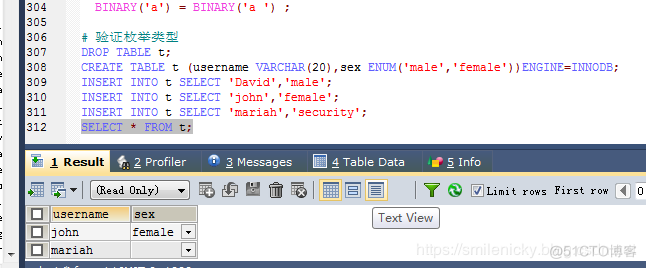
MySQL character type learning notes
Kotlin compose multiple item scrolling

如何獲取GC(垃圾回收器)的STW(暫停)時間?
随机推荐
php解决redis的缓存雪崩,缓存穿透,缓存击穿的问题
@Serializedname annotation use
Lepton 无损压缩原理及性能分析
Swift set pickerview to white on black background
Wechat applet - simple diet recommendation (4)
Jupiter notebook shortcut key
flink cdc不能监听mysql日志,大家遇到过这个问题吧?
WorkManager学习一
mongoDB副本集
Matrix processing practice
How to get the STW (pause) time of GC (garbage collector)?
Events and bubbles in the applet of "wechat applet - Basics"
MySQL字符类型学习笔记
Implementation of smart home project
各位大佬,我测试起了3条线程同时往3个mysql表中写入,每条线程分别写入100000条数据,用了f
[C language] the use of dynamic memory development "malloc"
leetcode:1200. 最小绝对差
Energy momentum: how to achieve carbon neutralization in the power industry?
Swift uses userdefaults and codable to save an array of class objects or structure instances
Zblogphp breadcrumb navigation code