当前位置:网站首页>Hard core, have you ever seen robots play "escape from the secret room"? (code attached)
Hard core, have you ever seen robots play "escape from the secret room"? (code attached)
2022-07-05 10:03:00 【Mr.Winter`】
Catalog
0 Preface
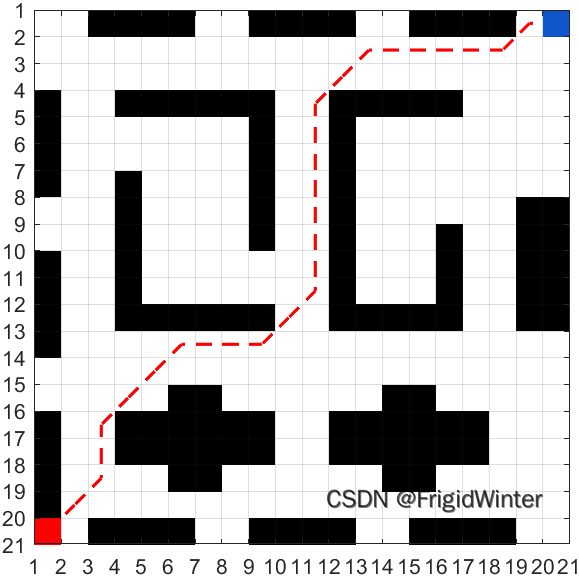
This paper makes an algorithm application based on Path Planning , That is, first construct two-dimensional Grid chamber , Release the entrance and exit of the secret room , Plan the escape route of the robot from the entrance to the exit , The dynamic diagram of simulation effect is as follows , After reading this article, I believe you can also do !
1 What is path planning ?
Modeling and positioning the environment through navigation technology 、 Control motion 、 Detect obstacles 、 Avoid obstacles , Mobile robots can complete many comprehensive tasks with the support of navigation technology , It has been widely used in entertainment 、 Medical care 、 mining 、 rescue 、 education 、 military 、 Space 、 Agriculture and other fields .
Path planning mainly solves the conflict free optimization problem of mobile robots from one position to another . According to whether the position and state of obstacles in the working environment change with time , Path planning technology can be roughly divided into
- Static path planning
- Dynamic path planning
in addition , According to the planning results of the path formed by the robot before or during the movement , Path planning technology can also be divided into
- Online planning
- Offline planning
Online path planning technology , Mobile robots acquire workspace information through local sensors attached to them , According to the changes of the working environment, the mobile robot can generate or update the optimal path in time . According to whether the target position of the robot has mobility , Path planning can be divided into
- Static target path planning
- Dynamic target road strength Planning
Various applications and job scenarios require different path planning algorithms .
2 Grid modeling : Construct a secret room
The main idea of grid method is to divide the region into non overlapping grids , Traverse from one grid to another with a connection graph , Traverse the grid without obstacles to complete the path planning from the initial position to the target position . The grid with obstacles is divided into two , The grid without obstacles is regressed into the algorithm . The initial position and target position are represented by grids , The planning result is represented by the path generated by grid connection .
This paper uses grid map to model the environment , The map generation function is as follows :
function map = generateMap(size, obstacle)
%%
% @breif: Generate grid map
% @prama[in]: size -> The size of the generated grid map
% @prama[in]: obstacle -> Static obstacles
% @retval: map -> grid map
%% Grid numerical meaning
% 1 ------ clearing
% 2 ------ Static obstacles
% 3 ------ Task point
% 4 ------ agent
%%
% Initialize the global grid map
map = ones(size(1), size(2));
% Initialize static obstacles
map(obstacle) = 2;
end
How to use this function ? Take a look at an example :
% Static obstacles
obs1 = 4:7;
obs2 = [41, 61, 81, 101];
obs3 = 368:372;
obs4 = [64,84, 104, 124, 144, 164, 165, 166, 167, 168, 169];
obs5 = [67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 92, 112, 132, 152, 172];
obs6 = [76, 77, 96, 97, 115, 116, 117, 118, 135, 136, 137, 138, 156, 157, 176, 177];
obs7 = [224, 225, 226, 227, 228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 244, 264, 284, 304, 252, 272, 292, 312, 311, 310, 309];
obstacle = [obs1, obs1 + 6, obs1 + 12, obs2, obs2 + 120, obs2 + 240, obs2 + 19,...
obs2 + 139, obs2 + 259, obs3, obs3 + 20, obs4, obs5, obs6, obs6 + 160, obs7];
% Initialize map
map = generateMap([20, 20], obstacle);
% Print
plotMap(map);
This is the effect of printing , You can do as you like 、 The actual application scenario , Use your imagination to design by yourself “ The chamber of secrets ”.
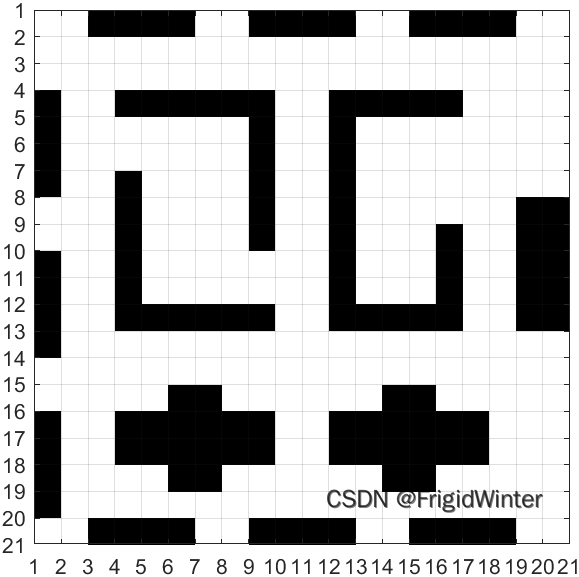
3 Release the first and last positions
Determine the head and end positions with grid coordinates .
start = [20, 1];
goal = [1, 20];
Use different colors to distinguish the first and last positions , And print it on the map .
function s = plotSquare(pts, size, G, color)
[ptsX, ptsY] = gridN2Xy(pts(:, 1) + size * (pts(:, 2) - 1), size, G);
ptsNum = length(ptsX);
for i=1:ptsNum
s = scatter(ptsX, ptsY, 270, 'Marker', 'square', 'MarkerEdgeColor', color, ...
"MarkerFaceColor", color);
end
end
4 Perform path planning
Here we use the simplest Greedy best first algorithm .
Greedy best first search is a heuristic search algorithm , It is an improvement of breadth first search algorithm ; The idea of the algorithm is Sort the nodes by the distance from the target , Then choose the node to be expanded at the cost of this distance .
- The breadth limited search algorithm is equivalent to a first in first out queue ;
- Limited depth search is equivalent to a last in first out stack ;
- Greedy best first search is equivalent to a priority queue sorted according to the distance from the destination .
Without obstacles , Greedy best first algorithm can usually find a shortest path and is more efficient than BFS higher , But in the case of obstacles , You may not find an optimal path .
The algorithm logic is as follows :
% Initialize parameters
open = [start, 0, h(start, goal), start]; % Open surface
close = []; % Closed surface
flag = false; % Planning end sign
next = [-1, 1, 14;... % Explore neighborhood
0, 1, 10;...
1, 1, 14;...
-1, 0, 10;...
1, 0, 10;...
-1, -1, 14;...
0, -1, 10;...
1, -1, 14];
neighborNum = length(next(:, 1));
while ~flag
% 【 Failure 】Open The table is empty and the target has not been found
if isempty(open(:,1))
return;
end
% 【 success 】 The target point appears in Open In the table
gIndex = locList(goal, open, [1:2]);
if gIndex
close = [open(gIndex, :); close];
cost = open(gIndex, 3);
flag = true;
break;
end
% Cost assessment
[val, index] = min(open(:, 4));
curNode = open(index, :);
close = [curNode; close]; % Minimum cost node in Closed surface
open(index, :) = []; % Minimum cost node out Open surface
% Evaluate the neighborhood expansion node of the current node
for i=1:neighborNum
% Initialize neighborhood nodes
neighborNode = [curNode(1) + next(i, 1), ...
curNode(2) + next(i, 2), ...
curNode(3) + next(i, 3), ...
0, curNode(1), curNode(2)
];
neighborNode(4) = h(neighborNode(1:2), goal);
% Obstacle judgment
if map(neighborNode(1), neighborNode(2)) == 2
continue;
end
% to update Open surface
open = updateOpen(neighborNode, open, close);
end
end
% Back to the path
path = backPath(close, start);
end
5 Demonstration test
In the secret room we built , Choose different entrances and exits , Test whether the robot can plan the legal path to escape from the secret room , Here is an additional test case, as shown in the following figure
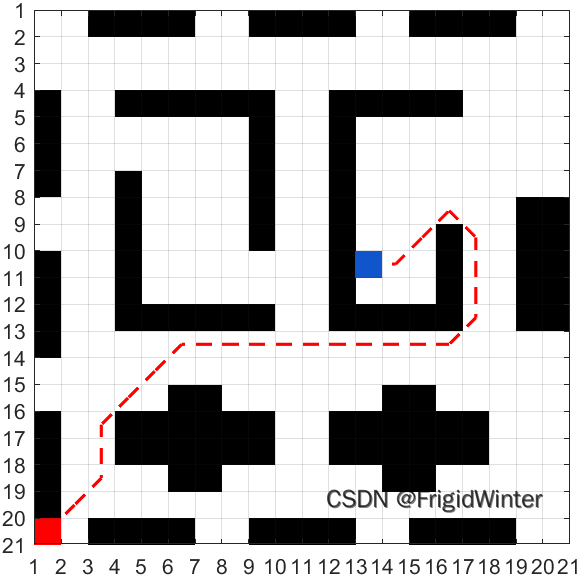
Good effect ~
More wonderful Columns :
- 《 Robot principle and technology 》
- 《ROS From entry to mastery 》
- 《 Computer vision course 》
- 《 machine learning 》
- 《 Numerical optimization method 》
- …
Private messages enter AI Technology exchange group , Whoring for nothing 30G E-books and teaching resources , Regularly release AI Knowledge dry goods 、 Free technology books and other benefits !
边栏推荐
- Common fault analysis and Countermeasures of using MySQL in go language
- Openes version query
- Kotlin Compose 多个条目滚动
- Kotlin compose and native nesting
- tongweb设置gzip
- Wechat applet - simple diet recommendation (2)
- How to improve the operation efficiency of intra city distribution
- [JS sort according to the attributes in the object array]
- [sorting of object array]
- oracle 多行数据合并成一行数据
猜你喜欢
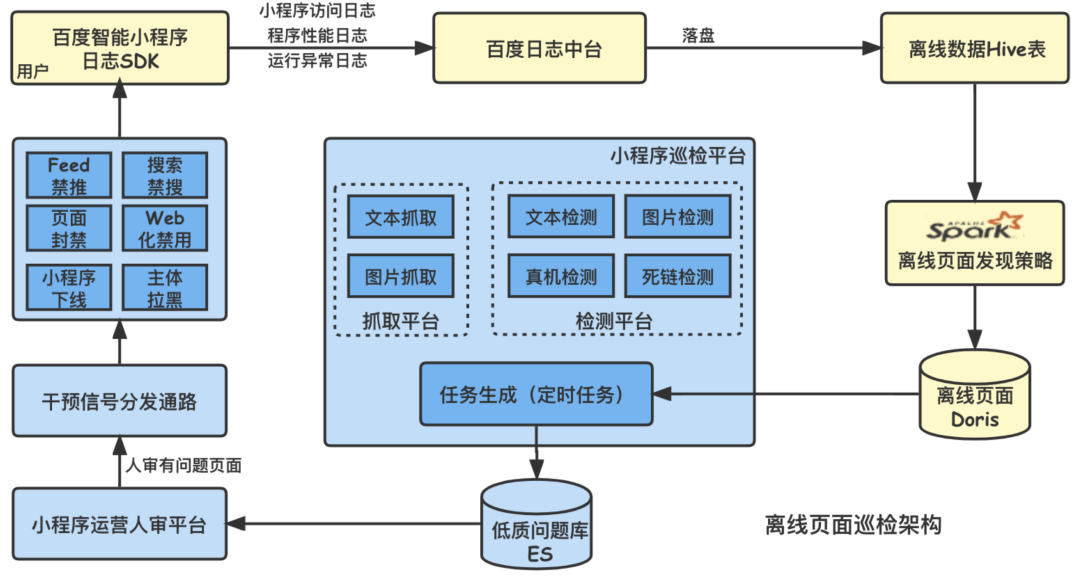
百度智能小程序巡檢調度方案演進之路
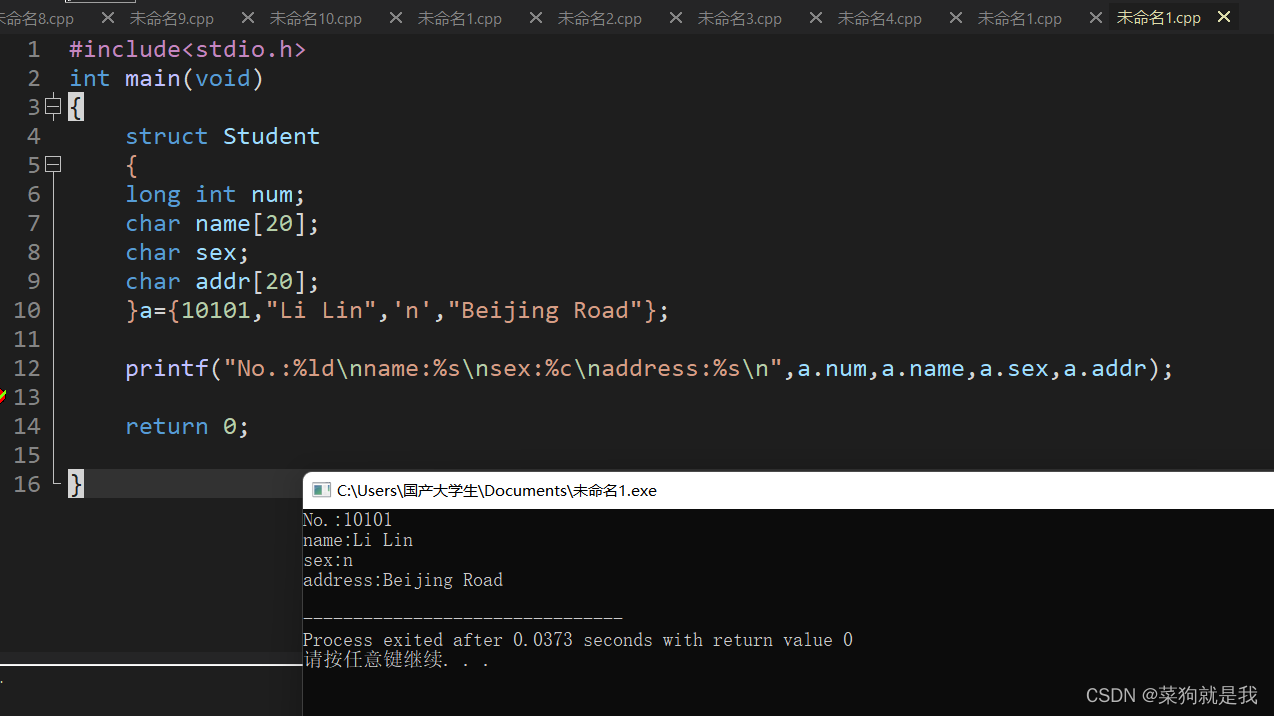
First understanding of structure
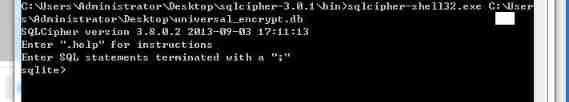
How Windows bat script automatically executes sqlcipher command

百度智能小程序巡检调度方案演进之路
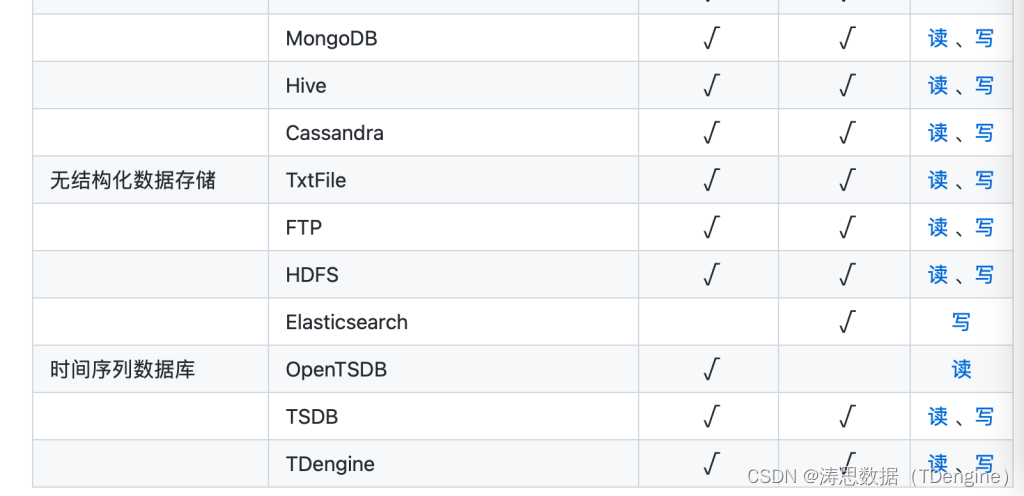
Tdengine can read and write through dataX, a data synchronization tool

Community group buying has triggered heated discussion. How does this model work?
![[listening for an attribute in the array]](/img/1f/96eb85ee0af83d601918bcd04e405e.png)
[listening for an attribute in the array]
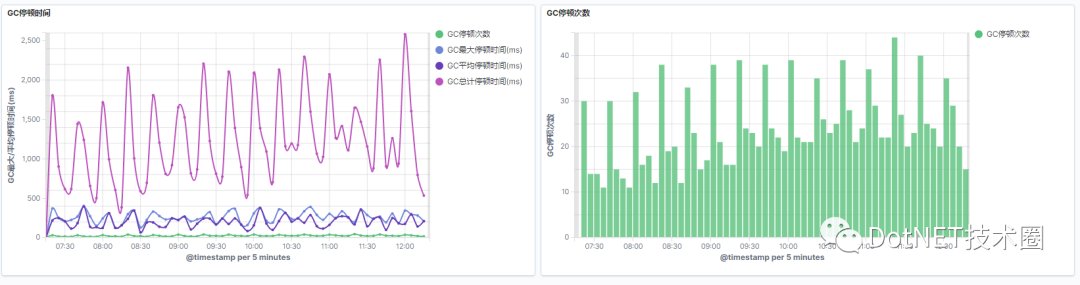
How to get the STW (pause) time of GC (garbage collector)?
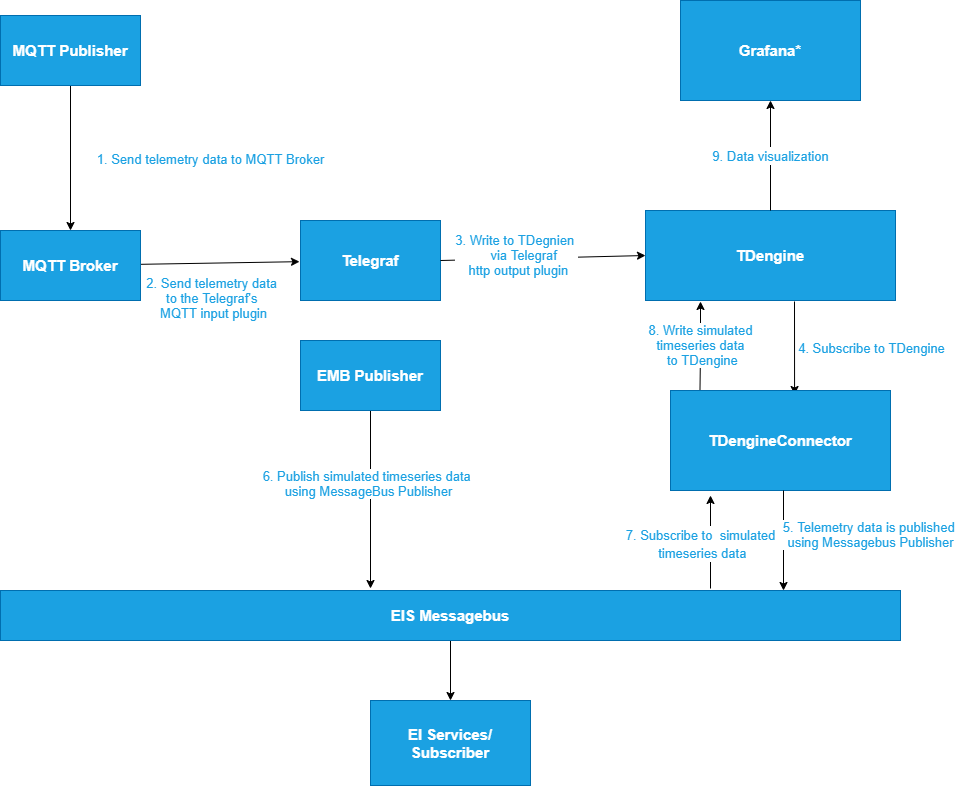
TDengine × Intel edge insight software package accelerates the digital transformation of traditional industries
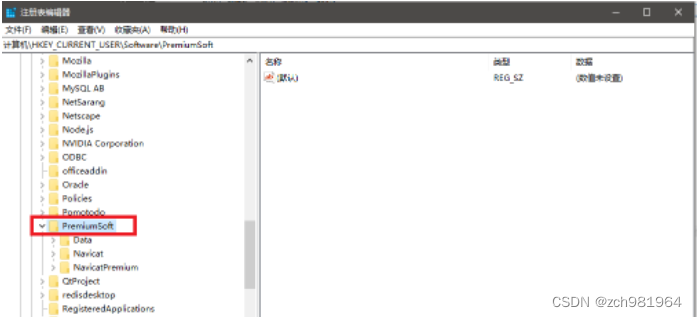
Solve the problem of no all pattern found during Navicat activation and registration
随机推荐
How Windows bat script automatically executes sqlcipher command
E-commerce apps are becoming more and more popular. What are the advantages of being an app?
Design and exploration of Baidu comment Center
Solve liquibase – waiting for changelog lock Cause database deadlock
View Slide
Tdengine can read and write through dataX, a data synchronization tool
[sorting of object array]
Understand the window query function of tdengine in one article
Wechat applet - simple diet recommendation (3)
Baidu app's continuous integration practice based on pipeline as code
揭秘百度智能测试在测试自动执行领域实践
Observation cloud and tdengine have reached in-depth cooperation to optimize the cloud experience of enterprises
小程序启动性能优化实践
The king of pirated Dall · e? 50000 images per day, crowded hugging face server, and openai ordered to change its name
Officially launched! Tdengine plug-in enters the official website of grafana
Roll up, break 35 - year - old Anxiety, animation Demonstration CPU recording Function call Process
[how to disable El table]
On July 2, I invite you to TD Hero online press conference
Idea debugs com intellij. rt.debugger. agent. Captureagent, which makes debugging impossible
(1) Complete the new construction of station in Niagara vykon N4 supervisor 4.8 software