当前位置:网站首页>[LZY learning notes -dive into deep learning] math preparation 2.5-2.7
[LZY learning notes -dive into deep learning] math preparation 2.5-2.7
2022-07-03 10:18:00 【DadongDer】
2.5 Automatic differentiation
Deep learning framework through ⾃ Calculate the derivative dynamically , namely ⾃ Dynamic differential (automatic differentiation) To speed up the derivation . In the actual , According to the model we designed , The system will build ⼀ Calculation charts (computational graph), To track which data is calculated and which operations are combined to produce ⽣ Output .
⾃ Dynamic differentiation enables the system to subsequently Back propagation gradient . this ⾥, Back propagation (backpropagate) It means tracking the whole calculation diagram , Fill in the partial derivative of each parameter .
Sharing by a netizen , Explain the calculation diagram and BP
An example
import torch
x = torch.arange(4.0)
# Not every time ⼀ Allocate new memory when deriving parameters
# Because we often update the same parameters thousands of times , Allocating new memory every time may soon run out of memory
# A scalar function about a vector x The gradient of is with x Vectors of the same shape
x.requires_grad_(True)
# Equivalent to x=torch.arange(4.0,requires_grad=True)
print(x.grad)
y = 2 * torch.dot(x,x) # y = 2 x⊤ x
print(y)
# Call the back propagation function to automatically calculate y About x The gradient of each component
y.backward()
print(x.grad)
# f(x) = 2*x0*x0 + 2*x1*x1 + 2*x2*x2 + 2*x3*x3
# df(x)/dx0 = 4*x0 when x0 = 0, df(x)/dx0 = 0
# df(x)/dx1 = 4*x1 when x1 = 1, df(x)/dx0 = 4
# df(x)/dx2 = 4*x2 when x2 = 2, df(x)/dx0 = 8
# df(x)/dx3 = 4*x3 when x3 = 4, df(x)/dx0 = 12
print(x.grad == 4*x)
# By default ,PyTorch It accumulates gradients , We need to clear the previous value
x.grad.zero_()
y = x.sum()
# f(x) = x0 + x1 + x2 + x3
# df(x)/dx0 = df(x)/dx1 = df(x)/dx2 = df(x)/dx3 = 1
y.backward()
print(x.grad)
Back propagation of non scalar variables
When y When it's not scalar , vector y About vectors x The derivative of ⾃ However, the explanation is ⼀ Matrix . about ⾼ Step sum ⾼ Dimensional y and x, The result of derivation can be ⼀ individual ⾼ Order tensor .
Gradient in partial derivative of Advanced Mathematics , The gradient indicates the direction in which a scalar function rises or falls most violently at a certain point and the directional derivative of that direction .
x = torch.arange(4.0,requires_grad=True)
y = x * x # By element
# Yes ⾮ Scalar modulation ⽤backward Need to transmit ⼊⼀ individual gradient Parameters , This parameter specifies the differential function about self Gradient of .
# Just want to find the sum of partial derivatives , So deliver ⼀ individual 1 The gradient of is appropriate ( ride 1 Adding up is sum)
y.sum().backward() # y.backward(torch.ones(len(x)))
print(x.grad)
Separation of computing
You want to move some calculations out of the recorded calculation graph .
import torch
x = torch.arange(4.0,requires_grad=True)
y = x * x # Non scalar
u = y.detach()
z = u * x # Non scalar
z.sum().backward()
print(x.grad == u) # tensor([True, True, True, True])
x.grad.zero_()
y.sum().backward() # Non scalar
print(x.grad == 2 * x) # tensor([True, True, True, True])
Python Gradient calculation of control flow
send ⽤⾃ Dynamic differential ⼀ One advantage is that : Even if the calculation diagram of the construction function needs to pass Python control flow ( for example , Conditions 、 Loop or any function call ), We can still calculate the gradient of the variable .
import torch
def f(a):
b = a * 2
while b.norm() < 1000:
b = b * 2
if b.sum() > 0:
c = b
else:
c = 100 * b
return c
a = torch.randn(size=(), requires_grad=True)
d = f(a)
d.backward()
print(a.grad == d / a)
# tensor(True)
Summary
Deep learning framework can ⾃ Calculate the derivative dynamically : We first attach the gradient to the variable on which we want to calculate the partial derivative . Then we record ⽬ Calculation of benchmark value , Execute its back propagation function , And access the resulting gradient .
2.6 probability
Basic probability theory
The process of sampling from the probability distribution is called sampling (sampling)
Assign probability to ⼀ The distribution of some discrete choices is called multinomial distribution (multinomial distribution)
In estimation ⼀ Dice ⼦ The fairness of , We hope from the same ⼀ In distribution ⽣ Into multiple samples . If ⽤Python Of for Loop to complete the task , The speed will be surprisingly slow ⼈. So we make ⽤ The function of the deep learning framework extracts multiple samples at the same time , Get any shape we want ⽴ Sample array .
import torch
from torch.distributions import multinomial
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# A probability distribution
fair_probs = torch.ones([6]) / 6
# Sample the data / Sampling
# sample 600 times with fair probs. theoritical output [100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100]
print(multinomial.Multinomial(600, fair_probs).sample())
# Calculate the relative frequency as an estimate of the true probability
counts = multinomial.Multinomial(1000, fair_probs).sample()
print(counts / 1000) # theoritical value: 1/6 ~= 0.167
# How the probability converges to the real probability over time
# Into the ⾏500 Group experiment , Extraction of each group 10 Samples
counts = multinomial.Multinomial(10, fair_probs).sample((500,))
cum_counts = counts.cumsum(dim=0) # Add by line
estimates = cum_counts / cum_counts.sum(dim=1, keepdims=True) # Keep the shape without dimension reduction
print(estimates)
# draw 6 line
for i in range(6):
plt.plot(estimates[:, i].numpy(), label=("P(die=" + str(i + 1) + ")"))
plt.axhline(y=0.167, color='black', linestyle='dashed') # axhline Draw parallel to x Horizontal reference line of axis
plt.gca().set_xlabel("Groups of experiments")
plt.gca().set_ylabel("Estimated probability")
plt.legend() # Add icons
plt.show()
axiom :
When processing the roll of dice , We will gather S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} Called sample space (sample space) Or result space (outcome
space), Each of these elements is the result (outcome)
event (event) yes ⼀ Random results of a given set of sample spaces 
A random variable :
Discrete random variable vs Continuous random variables ( Section )
In these cases , We quantify the probability of seeing a certain value as density (density). The height is just 1.80 The probability of meters is 0, But density is not 0.
Handle multiple random variables
① joint probability joint probability P(A = a, B = b)
A = a and B = b At the same time ⽣ The possibility is not ⼤ On A = a or B = b Single issue ⽣ The possibility of
② Conditional probability conditional probability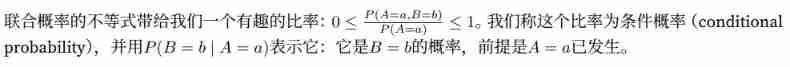
③ Bayes theorem Bayes’theorem
④ Marginalization 
⑤ independence
rely on (dependence) And alone ⽴(independence)
If two random variables A and B It's the only one ⽴ Of , It means events A The hair of ⽣ Follow B The occurrence of events ⽣⽆ Turn off .
Two random variables are unique ⽴ Of , If and only if the joint distribution of two random variables is their respective ⾃ The product of the distribution .
Expectation and variance : Summarize the key characteristics of probability distribution 
⼩ junction
• We can sample from the probability distribution .
• We can make ⽤ Joint distribution 、 Conditional distribution 、Bayes Theorem 、 Marginalization and independence ⽴ Sex hypothesis to analyze multiple random variables .
• Expectations and ⽅ Difference provides a real basis for the generalization of the key characteristics of probability distribution ⽤ Measurement form of .
2.7 Consult the documentation
Find all functions and classes in the module
Usually , We can ignore it by “__”( Double underline ) Start and end functions ( They are Python Special objects in ), Or in a single “_”( Underline ) Start function ( They are usually internal functions ).
import torch
# see PyTorch API Guidance of
# Query random numbers ⽣ All attributes in the module
print(dir(torch.distributions)) # Adjustable in the module ⽤ Which functions and classes
Find the usage of specific functions and classes
import torch
# How to make ⽤ A more specific description of a given function or class
# Look at the tensor ones function
help(torch.ones)
⼩ junction
• Officer, ⽅⽂ Files provide information beyond this book ⼤ Quantity description and ⽰ example .
• We can adjust ⽤dir and help Function or in Jupyter Make... In Notepad ⽤? and ?? see API Of ⽤ Law ⽂ files .
边栏推荐
- 20220531数学:快乐数
- LeetCode - 703 数据流中的第 K 大元素(设计 - 优先队列)
- Neural Network Fundamentals (1)
- CV learning notes - clustering
- getopt_ Typical use of long function
- Leetcode - the k-th element in 703 data flow (design priority queue)
- Opencv Harris corner detection
- 波士顿房价预测(TensorFlow2.9实践)
- My 4G smart charging pile gateway design and development related articles
- Positive and negative sample division and architecture understanding in image classification and target detection
猜你喜欢
Anaconda安装包 报错packagesNotFoundError: The following packages are not available from current channels:
Basic use and actual combat sharing of crash tool
Leetcode - 1670 design front, middle and rear queues (Design - two double ended queues)

Leetcode-106:根据中后序遍历序列构造二叉树
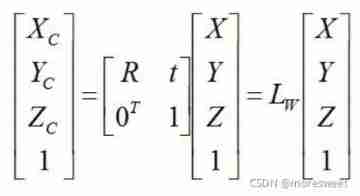
CV learning notes - camera model (Euclidean transformation and affine transformation)
Leetcode-112: path sum
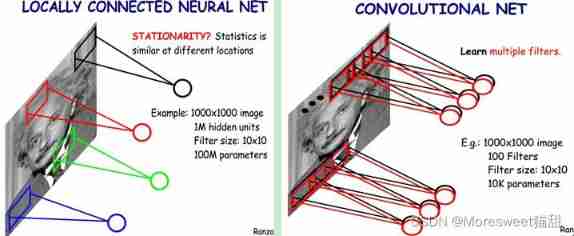
CV learning notes convolutional neural network

Leetcode - 895 maximum frequency stack (Design - hash table + priority queue hash table + stack)*

Flutter 退出当前操作二次确认怎么做才更优雅?

Neural Network Fundamentals (1)
随机推荐
LeetCode - 508. Sum of subtree elements with the most occurrences (traversal of binary tree)
LeetCode - 5 最长回文子串
Synchronous vs asynchronous
Policy Gradient Methods of Deep Reinforcement Learning (Part Two)
Google browser plug-in recommendation
Notes - regular expressions
My openwrt learning notes (V): choice of openwrt development hardware platform - mt7688
Yocto Technology Sharing Phase 4: Custom add package support
Leetcode - 460 LFU cache (Design - hash table + bidirectional linked hash table + balanced binary tree (TreeSet))*
LeetCode - 703 数据流中的第 K 大元素(设计 - 优先队列)
Leetcode-513:找树的左下角值
After clicking the Save button, you can only click it once
Leetcode-112: path sum
[graduation season] the picture is rich, and frugality is easy; Never forget chaos and danger in peace.
Wireshark use
20220604 Mathematics: square root of X
20220602数学:Excel表列序号
My notes on the development of intelligent charging pile (III): overview of the overall design of the system software
Leetcode interview question 17.20 Continuous median (large top pile + small top pile)
RESNET code details