当前位置:网站首页>Explore pointers and pointer types in depth
Explore pointers and pointer types in depth
2022-07-06 03:10:00 【iYYu】
Catalog
Preface
This is the advanced level of pointer , If you don't understand the primary pointer, please poke : Primary pointer .
The basic concept of pointer :
- A pointer is a variable , It's used to store the address , The address uniquely identifies a piece of memory space .
- The size of the pointer variable is 4/8 Bytes ( according to 32/64 Bit platform ).
- Pointers are typed , The type of pointer determines the pointer ± Step size of integer , The range that can be accessed during pointer dereference operation .
- Simple operation of pointer .
1. Character pointer
Among the pointer types, we know that one pointer type is character pointer char* ;
int main()
{
char ch = 'a';
char* pc = &ch;
*pc = 'b';
return 0;
}
It can also be written in the following form :
int main()
{
char* pc = "abcd";
// Is there a string stored in the pointer
printf("%s\n", pc);
return 0;
}
Not at all , It's actually a string First element address a Store to pointer pc in ,%s Just give the starting address of the string , Print all the way to \0 Before .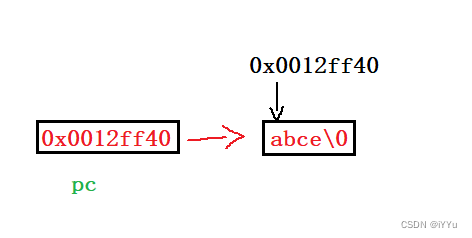
Because this string is a constant string , Cannot be modified , It is not safe to put pointer variables that are not decorated , Add const modification , So that it cannot be modified , In this way, the string is well protected .
const char* pc = "abcd";
An interview question :
int main()
{
char* p1 = "abcd";
char* p2 = "abcd";
char arr1[] = "abcd";
char arr2[] = "abcd";
if (p1 == p2)
puts("p1 == p2");
else
puts("p1 != p2");
if (arr1 == arr2)
puts("arr1 == arr2");
else
puts("arr1 != arr2");
return 0;
}
// What is the result of the output ?

So what is the difference between these two forms ? Drawing analysis :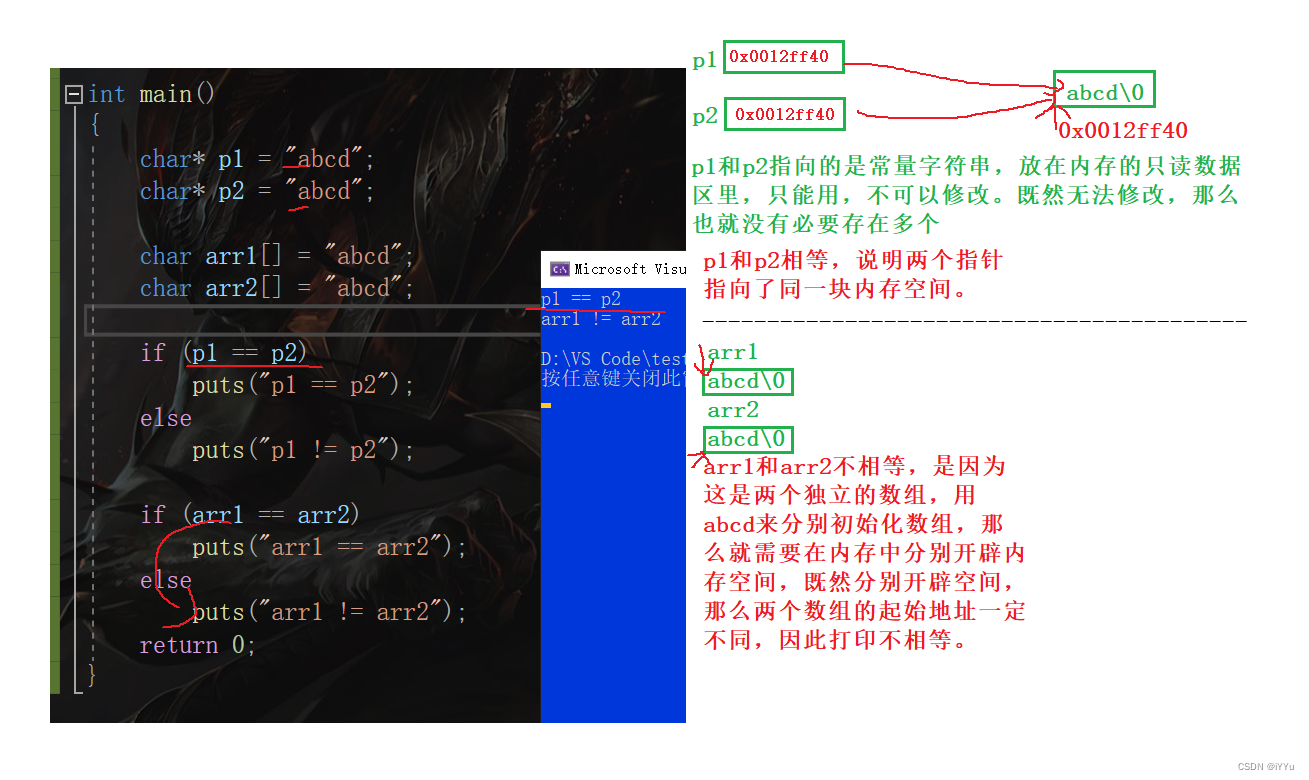
2. Array pointer
Before exploring array pointers , Let's review what is a pointer array :
Pointer array - It's an array . Is an array used to store pointer variables .
int arr[10];// Shape array
char brr[10];// A character array
...
int* crr[10];// Integer pointer array - An array of plastic pointers
char* drr[10];// Character pointer array
The function of pointer array :
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1,2,3 };
int brr[] = {
2,3,4 };
int crr[] = {
3,4,5 };
// Define an array of pointers
int* prr[3] = {
arr, brr, crr };
// The array name is equivalent to the address of the first element
// Put the first three elements of the array in prr in
// It's the address , therefore prr The type of is integer pointer type
return 0;
}
This kind of writing , In fact, it is simulated as a two-dimensional array , How to understand this ?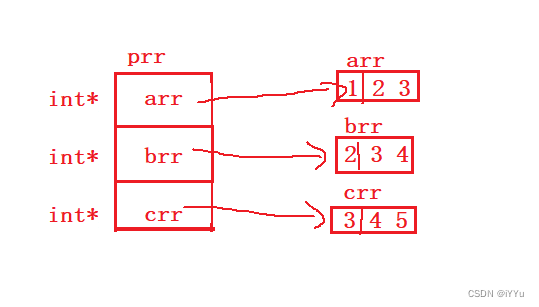
The meaning of that code , Know the layout of the pointer array , Then visit and print prr The contents of the array are almost the same as those of a two-dimensional array :
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1,2,3 };
int brr[] = {
2,3,4 };
int crr[] = {
3,4,5 };
int* prr[3] = {
arr, brr, crr };
// Three elements , Corresponding subscript 0 1 2
// Find the corresponding first element address
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
// Then use a subscript to offset backward to find each element in the array
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
{
//prr[i][j] == *(prr[i] + j) == *(*(prr+i)+j)
printf("%d ", *(prr[i] + j));
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
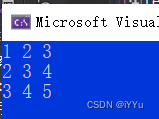
Use a pointer array to skillfully combine three one-dimensional arrays , It's like a two-dimensional array , This is a function of pointer array .
Two dimensional arrays are stored continuously in memory , These three one-dimensional arrays are not necessarily , So it's simulating a two-dimensional array .
2.1 Definition of array pointer
After understanding the pointer array , Next, explore array pointers :
Shaping the pointer - Pointer to the shape
Character pointer - Pointer to character
…
Array pointer - Is a pointer - Pointer to array .
What are the meanings of the following two statements :
int *p1[10];
int (*p2)[10];
//p1, p2 What are the differences ?

[ ] The priority of is higher than that of the asterisk , So we have to add () To guarantee p The first and * combination .
2.2 & Array name VS Array name
To figure out how array pointers are used , We must understand again Array name and & Array name The meaning of :
The array name is usually the address of the first element , But there are Two accidents :
- sizeof( Array name )
there arr It's the whole array , The total size of the array is calculated .
It must be internal A separate Put an array name
- & Array name
The array name here still represents the whole array ,& The array name takes out the address of the entire element .( Unit is byte )
What's the difference ?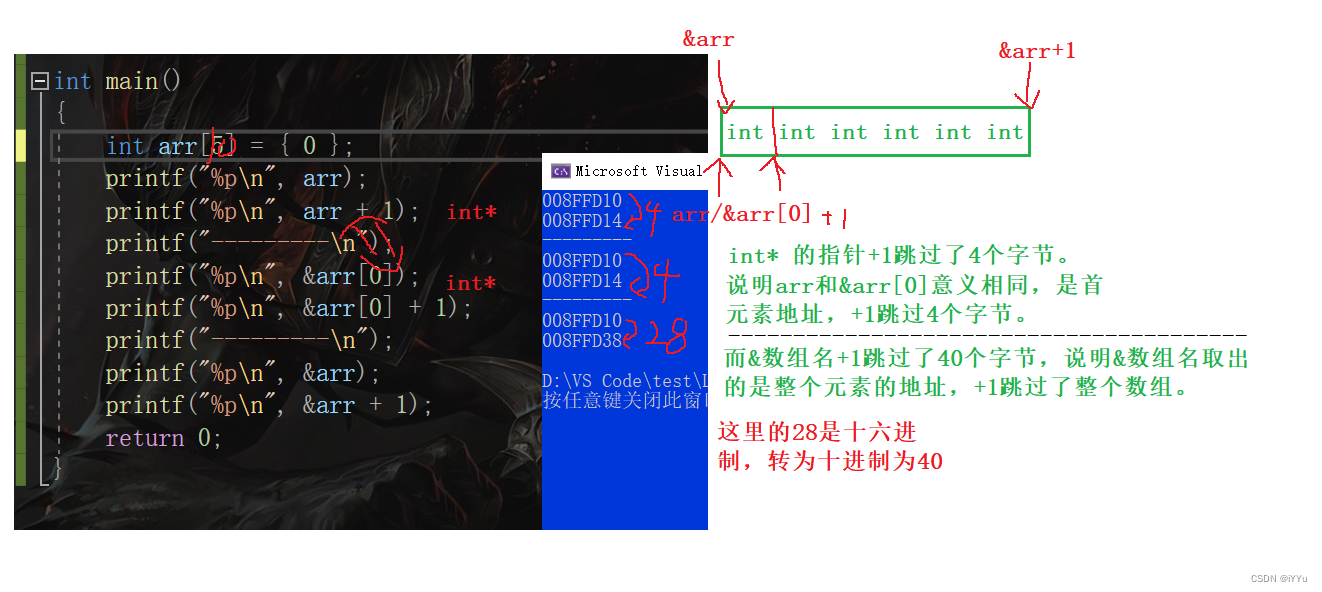
Code instructions :
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {
0 };
// The address of the first element of the array is placed in int* The pointer to
int* p1 = arr;
// Take the address of the entire array and put it in the array pointer p2 in
int (*p2)[5] = &arr;
// The difference between these two pointers :
//p1 The address of the first integer element is stored , Point to first element , Can't represent the entire array .
// and p2 The whole array is stored arr The address of , It points to an array .
return 0;
}
Removing the name is its type :int* \ int (*)[5].
The following square brackets must contain the number of elements of the array , Otherwise, it will warn .
2.3 Application of array pointer
Understand the basic concept of array pointer , Next, we will explore the usage of array pointers :
Print array elements :
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {
1,2,3,4,5 };
int (*p)[5] = &arr;
// The address of the entire array
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", *(*p + i));
/// First, dereference p Found array arr The address of the first element
// namely *p == arr
// Address +i Find each element in the dereference backward offset
}
return 0;
}
This usage is awkward , In fact, it is very unreasonable .
The normal way of writing should be :
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {
1,2,3,4,5 };
int* p = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", *(p + i));
// The address of the first element p The pointer to
//p+i Find the address of each element
// Dereference found element
}
return 0;
}
Compared with the first method, the clarity of this method is self-evident .
The function of array pointer is not reflected in one-dimensional array , In two-dimensional or multi-dimensional arrays, array pointers are wonderful .
Next, explore the correct usage of array pointers .
Function to print a two-dimensional array :
// There are two ways of writing :
// The array is passed to the parameter group and received :int arr[3][4]
// The first element address is actually uploaded from the array parameters
// Here, how to write formal parameters in the form of pointers ?
void print(???, int r, int c)
{
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][4] = {
1,2,3,4,2,3,4,5,3,4,5,6 };
print(arr, 3, 4);
return 0;
}
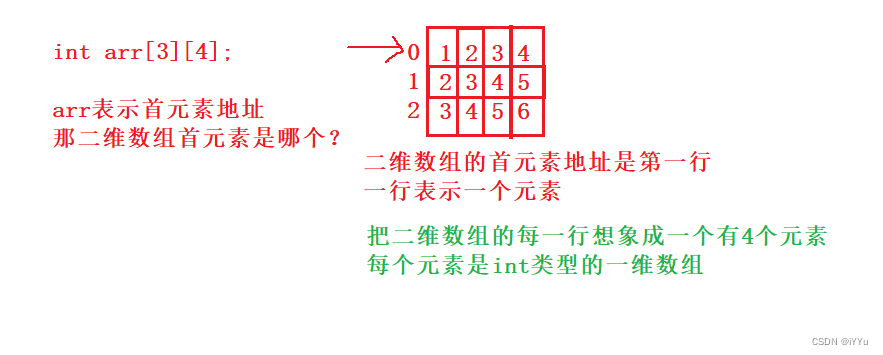
Since the name of a two-dimensional array is the address of its first row of one-dimensional array , Then the formal parameter should set a pointer to the address of one-dimensional array :
(*pa) Is a pointer , Pointing to the array , The array has four elements (*pa)[4], Each element is int type
int (*pa)[4]
void print(int (*pa)[4], int r, int c)
{
//pa+i Point to i That's ok
for (int i = 0; i < r; ++i)
{
//pa+i Dereference to get the address of the first element of the current line
for (int j = 0; j < c; ++j)
{
// First element address +j Then dereference to get the current element
printf("%d ", *(*pa + i) + j));
//printf("%d ", pa[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][4] = {
1,2,3,4,2,3,4,5,3,4,5,6 };
print(arr, 3, 4);
return 0;
}
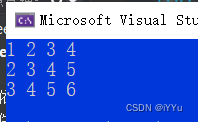
Why array pointers +1 Skip an array :
pa The type of is an array pointer :int (*)[4]
pa Is to point to an array , Array 4 A plastic element
therefore pa+1 Skip one 4 individual int Array of elements .
Having learned about pointer arrays and array pointers, review and see what the following code means :
int arr[5];
//arr Is an integer array
int *parr1[10];
//parr1 Is an array of integer pointers
int (*parr2)[10];
//parr2 Is an integer array pointer
int (*parr3[10])[5];
//parr3 Is an array that holds array pointers
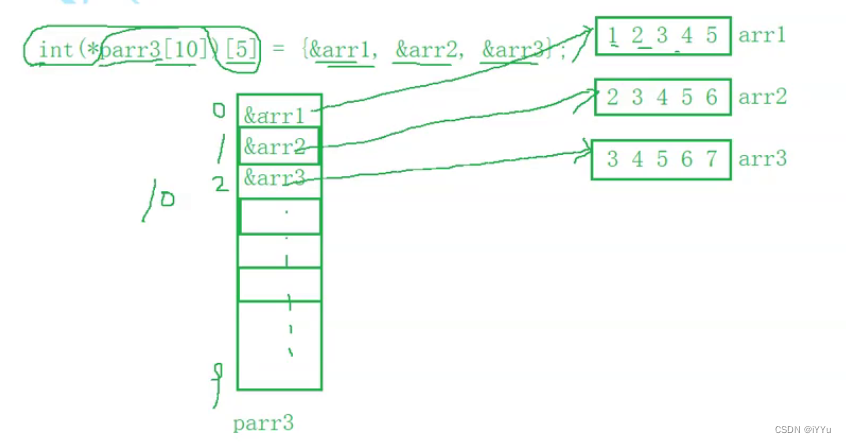
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1,2,3 };
int brr[] = {
1,0,1 };
int crr[] = {
1,2,3 };
int (*parr[3])[3] = {
&arr, &brr, &crr };
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
int (*pa)[3] = parr[i];
// hold parr The elements of the array are assigned to the array pointer in turn pa
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
{
//pa It's No i The address of an array
// First, dereference to get the address of the first element of the current array
// recycling j Offset dereference to get each element separately
printf("%d ", (*pa)[j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
3. Array parameter passing and pointer parameter passing
When writing code, it is inevitable to 【 Array 】 perhaps 【 The pointer 】 Pass to function , How to design the parameters of the function ?
3.1 One dimensional array parameters
void test(int arr[])//ok?
{
}
void test(int arr[10])//ok?
{
}
void test(int *arr)//ok?
{
}
void test2(int *arr[20])//ok?
{
}
void test2(int **arr)//ok?
{
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
0};
int *arr2[20] = {
0};
test(arr);
test2(arr2);
return 0;
}
The above parameter transfer forms are correct .
3.2 Two dimensional array parameters
void test(int arr[3][5])//ok?1
{
}
void test(int arr[][])//ok?2
{
}
void test(int arr[][5])//ok?3
{
}
void test(int *arr)//ok?4
{
}
void test(int* arr[5])//ok?5
{
}
void test(int (*arr)[5])//ok?6
{
}
void test(int **arr)//ok?7
{
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {
0};
test(arr);
return 0;
}
2:error, reason : Two dimensional array parameters , Function parameter design can only omit the first [ ] The number of .
Because for a two-dimensional array , I don't know how many lines there are , But you have to know how many elements in a row .
So it's easy to calculate .
4:error, reason : The array name of a two-dimensional array represents the address of the first element , Is the address on the first line .
The first line can be seen as containing 5 The address of an array of integer elements , Since the address of the array is placed at the first level, the pointer must be wrong , You should use array pointers .
5:error, reason :arr The first and [ ] combination , It's an array , Each element is int*, So wrong .
7:error, reason : The secondary pointer stores the primary pointer , The address of the array cannot be stored in the secondary pointer .
3.3 First level pointer parameter transfer
If the formal parameter part of the function is a first-order pointer , So what can the actual parameters be written when calling ?
void print(int *p)
{
}
int main()
{
> int a = 10;
print(&a);
> int* pa = &a;
print(pa);
> int arr[10];
print(arr);
return 0;
}
If the formal parameter is a first-order pointer , The argument can be passed to the address of the shaping 、 Integer pointer and array name ( It's all pointers ).
3.4 The secondary pointer transmits parameters
If the formal parameter part of the function is a secondary pointer , Then what can the actual parameters be written when calling ?
void test(int** ptr)
{
}
int main()
{
int* p1;
test(&p1);
int* *p2 = &p1;
test(p2);
int* arr[10];
test(arr)
return 0;
}
A formal parameter is a secondary pointer , Arguments can : Take the first level pointer of the address 、 Second level pointer and pointer array .
4. A function pointer
An array pointer is a pointer to an array , and A function pointer is a pointer to a function .
& The array name takes out the address of the array :
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {
0 };
int(*pa)[5] = &arr;// Array pointer
return 0;
}
that & Is the address of the function taken out by the function name ?
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
// Get the address of the function
printf("%p\n", &Add);
return 0;
}
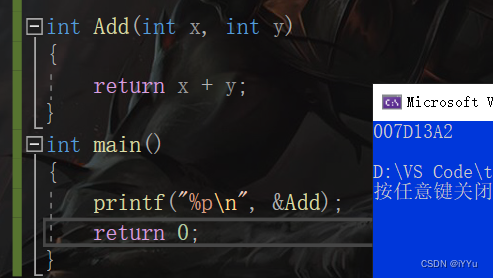
So functions also have addresses .
For functions :& Function name and function name are the address of the function .
So withprintf("%p\n", Add);There is no difference between .
Get the address of the function , Save it , How to write ?
In fact, it is very similar to array pointers :
(*pf) Indicates that it is a pointer ,(*pf)() This pair of parentheses indicates that it refers to a function ( Function call operator ()), The function parameter type it points to is int, int, The return type is int,int (*pf)(int, int), The pointer pf Stored functions Add The address of .
int (*pf)(int, int) = &Add
int (*pf)(int x, int y) The parameter name can be omitted without writing , As long as the parameter type .
Since there is the type of function pointer , Then it must have its function , Next, explore the role of function pointers :
Take out a plastic address and put it in a pointer , Dereference the pointer to find and modify it , For function pointers , It's the same thing .
For example, using pointers to call functions indirectly :
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
// Call directly
//int ret = Add(2, 3);
// Take the address and put it in the pointer pf in
int (*pf)(int, int) = &Add;
// This & The symbol can be omitted
// Call indirectly with pointer
// Dereference pointer , Pass parameters while calling functions
int ret = (*pf)(2, 3);
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
notes : This kind of writing is also right ,
int ret = pf(2, 3);, Don't write * Number , Exactly equivalent toint ret = Add(2, 3);This explains why you can omit the asterisk , The asterisk above is for easier understanding .
But if you write the form above, you must use parentheses , Otherwise, it's not a function pointer .
Through the understanding of the above code , You may feel that the function pointer is a little superfluous , It's all the same , Calling by pointer also complicates the code , In fact, function pointers are more complex in this environment .
But function pointers are very useful in other environments , After that, I will introduce its other wonderful functions .
Let's first look at two interesting pieces of code :
// Code 1
( *( void (*)() )0 )();
// Code 2
void ( *signal(int , void(*)(int) ) )(int);
first :
the second :
Although it explains its meaning , But it's not too convenient to understand , Function parameters are function pointers , The return type is also a function pointer , Some winding .
You can use typedef To optimize the function declaration :
typedef unsigned int u_int;
// It's just a way of unsigned int Rename it to u_int
// Optimize the function pointer
void(*)(int)
// hold void (*)(int) The type is renamed to pf_t
Now modify the code :
typedef void (*pf_t)(int);
int main()
{
void (* signal(int, void (*)(int) ) )(int);
pf_t signal(int, pf_t);
return 0;
}
Here is the function of function pointer .
Write a simple calculator , This computer contains addition and subtraction ( The principle of multiplication and division is the same , Just understand its meaning , No longer implemented ):
// choose 1 Add
// choose 2 Subtraction
// choose 0 sign out
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
void menu()
{
puts("*******************");
puts("***** 1. Add ****");
puts("***** 2. Sub ****");
puts("***** 0. exit ****");
puts("*******************");
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please input function :");
there:
scanf("%d", &input);
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
switch (input)
{
case 1:
printf(" Please enter two operands :");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", Add(x, y));
break;
case 2:
printf(" Please enter two operands :");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", Sub(x, y));
break;
case 0:
printf("Exit calcu!\n");
break;
default:
printf(" error ! Please re-enter :\n");
goto there;
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
test result :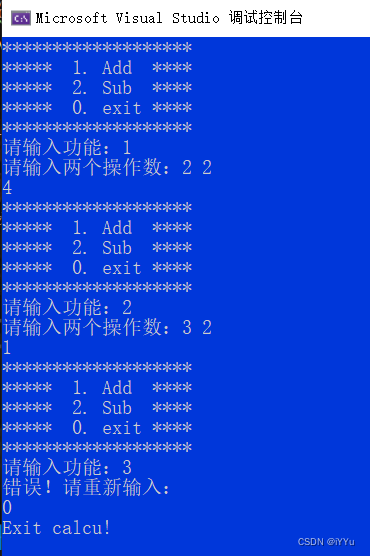
Although the running result is ok , But it is not difficult to find that the implementation of the code is somewhat redundant , If you add multiplication and division, the repeated part of the code will be more .
At this time, it reflects the cleverness of function pointers :
Encapsulate a function calc To be responsible for adding and subtracting , Because the function name is the function address , You can take the address of the function that implements addition and subtraction as calc Parameters of , choice 1 Pass in Add Address of function , choice 2 Pass in Sub The address of , Then use the function pointer to find and call the current function .
void menu()
{
puts("********************");
puts("***** 1. Add *****");
puts("***** 2. Sub *****");
puts("***** 0. exit *****");
puts("********************");
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
// Calculation
// Function pointer should be set for formal parameter
void calc(int (*pf)(int, int))
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
printf(" Please enter two operands :");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", pf(x, y));
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please input function :");
there:
scanf("%d", &input);
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
switch (input)
{
case 1:
calc(Add);
break;
case 2:
calc(Sub);
break;
case 0:
printf("Exit calcu!\n");
break;
default:
printf(" error ! Please re-enter :\n");
goto there;
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
Here, function pointers are cleverly used to achieve relatively simple code , If there is no concept of function pointer , Of course, there is no way to write in this form .
This form is also called a callback function , Through function pointers , Call the function it points to back at the appropriate time .
5. Function pointer array
Putting the function pointer in the array is the function pointer array .
The above two functions Add and Sub, Because the function name is the address of the function , Put these two functions into the array , The elements of an array are function pointers , And arrays are called function pointer arrays :
Let's deduce how to write its type , Actually, it is similar to function pointer :
int (*pf)(int, int) = Add;- This is the function pointer .
Actually pf Replace it with an array , It's an array of function pointers :int (*arr[2])(int, int) = {Add, Sub};( The number of elements can be omitted ).
arr The first and [ ] combination , It's an array , Put the array name arr and [ ] move aside , It's the type of it : A function pointer , Each element of it is a function pointer .
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
// Function pointer array
int (*arr[2])(int, int) = {
Add, Sub};
return 0
}
Access this array :
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
int (*arr[2])(int, int) = {
Add,Sub };
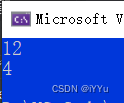
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
int ret = arr[i](8, 4);
printf("%d\n", ret);
}
return 0;
}
Since there is a form of function pointer array , It will certainly have its role , Use this array , Then optimize the calculator above .
You don't just want to add, subtract, multiply, divide , Also want to achieve x & y、x | y、x ^ y… wait
If you want to add more functions , So the corresponding case Statements are also bound to increase , The whole code is not easy to read , What can be done to simplify the code ?
At this time, use the function pointer array , Can greatly optimize the code , Make it very concise .
Code implementation : First, you need to create a function pointer array -int (*arr[])(int, int) = { 0,Add,Sub };
Put one at the front 0, Push the subscript of the two functions back by one , Therefore, it can be based on input The entered value directly corresponds to its subscript .
If input = 0; Exit the calculator directly , If input>=1 && input <=2, Use the array subscript to realize the corresponding · Function call , Otherwise, re-enter , Code implementation :
void menu()
{
puts("********************");
puts("***** 1. Add *****");
puts("***** 2. Sub *****");
puts("***** 0. exit *****");
puts("********************");
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
int (*pfArr[])(int, int) = {
0,Add,Sub };
int input = 0;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please select the function :");
there:
scanf("%d", &input);
if (!input)
{
puts("Exit calc!");
}
else if (input >= 1 && input <= 2)
{
printf(" Please enter two operands :");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
int ret = pfArr[input](x, y);
printf("%d\n", ret);
}
else
{
puts(" Please re-enter !");
goto there;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
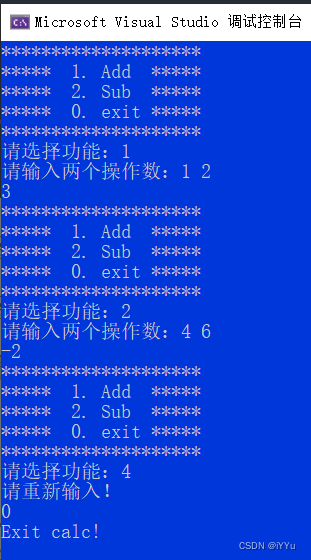
Very clever , Using function pointer array greatly simplifies the code .
If you want to add some functions later , You only need to implement the functions to be added , Add the function name to the array , Modify the judgment conditions again , It is very convenient to call and the code is simple .
6. A pointer to an array of function pointers
Function pointer array , It's also an array , Then there will be its address , Get the address of the array , It should be stored to point 【 Function pointer array 】 The pointer to , Then how to write the form of the pointer ?
int (*pfArr[])(int, int) = { 0,Add,Sub };This is an array of function pointers , Change according to this form :
First, it's a pointer (*ppfArr), It points to an array (*ppfArr)[ ], Each element of the array is a function pointer ( *(*ppfArr)[ ] )(), The argument to the function is int, int, The return value is intint ( *(*ppfArr)[] )(int, int) = &pfArr;
This is the pointer to the array of function pointers .
int main()
{
// This is an array of function pointers
int (*pfArr[])(int, int) = {
0,Add,Sub };
// A pointer to an array of function pointers
int (*(*ppfArr)[3])(int, int) = &pfArr;
return 0;
}
Since it's a pointer , It can also be stored in an array , That is to say 【 A pointer to an array of function pointers 】 Array of , This is also an array , Since it is an array …
7. Callback function
A callback function is a function called through a function pointer . If you put a pointer to a function ( Address ) Pass as argument to another function , When this pointer is used to call the function it points to , Let's just say this is a callback function .
The callback function is not called directly by the function's implementer , It's called by another party when a particular event or condition occurs , Used to respond to the event or condition .
First introduced qsort Function usage .
qsort yes C A library function of language , A sort function implemented using the idea of quick sort , It can sort any data .
qsort Parameters :void qsort( void *base, size_t num, size_t width, int (*cmp)(const void *e1, const void *e2 ) );
Four parameters :void* base- The starting position of the data to be sortedsize_t num- Number of elements of data to be sortedsize_t width- The size of the data element to be sorted ( byte )int (*cmp)(const void *e1, const void *e2 )- A function pointer ( Comparison function ), Call the function pointed to by this pointer , Parameters e1 and e2 Is the address of the two elements to be compared , Therefore, any type of data in this function can be compared .Be careful : The fourth function pointer points to a function whose parameters are
void*The pointer to , andvoid*The pointer to is a pointer without a specific type , Can receive any type of address , And because of this , thereforevoid*The pointer of cannot be dereferenced , Also can not ± The operation of integers ( Because I don't know what kind of address it is , The energy is set tovoid*type ), Therefore, you need to cast the type to the target type pointer .The return value of the comparison function :
utilize qsort To sort arrays :
int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(int), cmp_int);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
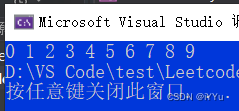
qsort Sort structure members :
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
};
int cmp_stu_by_name(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
// utilize strcmp To compare strings
return strcmp( ((struct Stu*)e1)->name, ((struct Stu*)e2)->name );
}
int cmp_stu_by_age(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return ((struct Stu*)e1)->age - ((struct Stu*)e2)->age;
}
int main()
{
struct Stu s[] = {
{
"zhangsan", 15}, {
"lisi",20}, {
"wangwu",25} };
int sz = sizeof(s) / sizeof(s[0]);
// Sort by name
qsort(s, sz, sizeof(s[0]), cmp_stu_by_name);
// Sort by age
qsort(s, sz, sizeof(s[0]), cmp_stu_by_age);
return 0;
}
Name sort 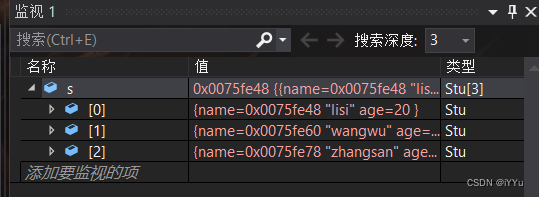
Age ranking :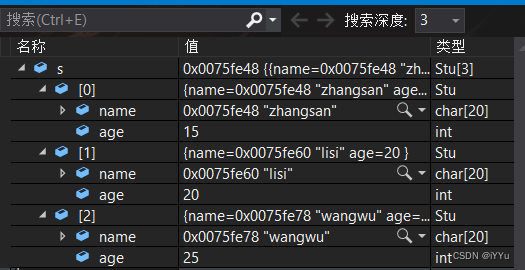
In understanding qsort Use of functions , Next, the ideological transformation based on bubble sorting qsort function :
void Swap(char* p1, char* p2, int width)
{
for (int i = 0; i < width; ++i)
{
char tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
++p1;
++p2;
}
}
int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return *(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2;
}
void bubble_sort(void* base, int num, int width, int(*cmp)(const void* e1, const void* e2))
{
for (int i = 0; i < num - 1; ++i)
{
int f = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < num - i - 1; ++j)
{
if (cmp( (char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width ) > 0)
{
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
f = 0;
}
}
if (f == 1)
{
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubble_sort(arr, sz, sizeof(int), cmp_int);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Running results :
The above is an in-depth exploration of the pointer , There are many pointer types that can easily be confused if you are not careful , So when learning the pointer, you should carefully and repeatedly watch a lot to master the pointer .
边栏推荐
- #PAT#day10
- Precautions for single chip microcomputer anti reverse connection circuit
- Misc (eternal night), the preliminary competition of the innovation practice competition of the National College Students' information security competition
- 银行核心业务系统性能测试方法
- CSP date calculation
- Tomb. Weekly update of Finance (February 7 - February 13)
- Taobao focus map layout practice
- Master data management theory and Practice
- Zhang Lijun: penetrating uncertainty depends on four "invariants"
- codeforces每日5題(均1700)-第六天
猜你喜欢

ERA5再分析资料下载攻略
故障分析 | MySQL 耗尽主机内存一例分析
Misc (eternal night), the preliminary competition of the innovation practice competition of the National College Students' information security competition
Linear regression and logistic regression

Software design principles
MySQL advanced notes
淘宝焦点图布局实战
XSS challenges bypass the protection strategy for XSS injection
![BUUCTF刷题笔记——[极客大挑战 2019]EasySQL 1](/img/37/c38a933ce7fa5d2b8fa597965ffcb2.png)
BUUCTF刷题笔记——[极客大挑战 2019]EasySQL 1
![[pointer training - eight questions]](/img/fd/1aa3937548a04078c4d7e08198c3a8.png)
[pointer training - eight questions]
随机推荐
Linear regression and logistic regression
Pat 1084 broken keyboard (20 points) string find
SD卡报错“error -110 whilst initialising SD card
Game theory matlab
[Yu Yue education] basic reference materials of digital electronic technology of Xi'an University of Technology
Web security SQL injection vulnerability (1)
全国大学生信息安全赛创新实践赛初赛---misc(永恒的夜)
Deeply analyze the chain 2+1 mode, and subvert the traditional thinking of selling goods?
淘宝焦点图布局实战
Reverse repackaging of wechat applet
PMP practice once a day | don't get lost in the exam -7.5
C # create self host webservice
Codeforces 5 questions par jour (1700 chacune) - jour 6
Precautions for single chip microcomputer anti reverse connection circuit
IPv6 jobs
Buuctf question brushing notes - [geek challenge 2019] easysql 1
codeforces每日5題(均1700)-第六天
MySQL advanced notes
继承day01
Technology sharing | what if Undo is too big
