当前位置:网站首页>[C Advanced] file operation (2)
[C Advanced] file operation (2)
2022-07-04 08:51:00 【Three points of bitterness】
Catalog
1、 Random reading and writing of documents
3、 Determination of the end of file reading
1、 Random reading and writing of documents
(1)fseek
Create a file test.txt, There is... In it abcdef Such a string , We were reading the document before , The initial file pointer is to a Of , Read a character pointing to b, Read another point c…… At this time, it is read in sequence , This is the sequential reading and writing of files . Let's review :
#include<stdio.h> int main() { // Open file FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "r"); if (pf == NULL) { perror("fopen"); return 1; } // Read the file int ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //a ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //b ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //c // Close file fclose(pf); pf = NULL; return 0; }Can we read in the way we want , For example, read directly d, At this point, a function of file pointer positioning is involved :fseek
- fseek: Move a file pointer to a specific location
Locate the file pointer according to its position and offset .
int fseek ( FILE * stream, long int offset, int origin );
- Understand the three parameters :
- stream: For which stream
- offset: Offset
- origin: The starting position
- There are three options for starting position :
- SEEK_CUR:
1、 Shift the file forward from its current location 1 Bytes :
// Read the file int ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //a // Adjust file pointer fseek(pf, -1, SEEK_CUR); ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //a ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //b2、 Let files from The current position Offset backward 2 Bytes :
// Read the file int ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //a // Adjust file pointer fseek(pf, 2, SEEK_CUR); ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //d ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //e
- SEEK_END:
From file At the end of Start to shift forward 2 byte
// Read the file int ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //a // Adjust file pointer fseek(pf, -2, SEEK_END); ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //e ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //f
- SEEK_SET:
From file The starting position Start to shift back 3 byte
// Read the file int ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //a // Adjust file pointer fseek(pf, 3, SEEK_SET); ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //d ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //e
(2)ftell
Returns the offset of the file pointer from its starting position
long int ftell ( FILE * stream );
- for example :
// Read the file int ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //a // Adjust file pointer fseek(pf, 3, SEEK_SET); ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //d int ret = ftell(pf); printf("%d\n", ret);//4
(3)rewind
Return the file pointer to the beginning of the file
void rewind ( FILE * stream );
- for example :
// Read the file int ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //a // Adjust file pointer fseek(pf, -1, SEEK_END); ch = fgetc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //f // Return the file to its starting position rewind(pf); ch = getc(pf); printf("%c\n", ch); //a
2、 Text files and binaries
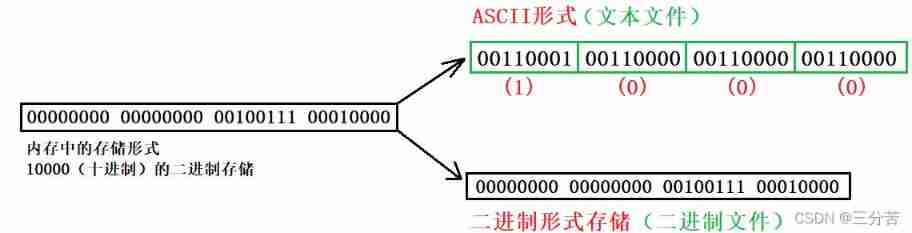
According to the organization of data , Data files are called text file perhaps Binary .
Data is stored in memory in binary form , If the output without conversion is to external memory , Namely Binary .
If it's required to use ASCII In the form of code , You need to convert before storing . With ASCII The file stored in the form of characters is text file .
- How is a data stored in memory ?
All characters are written in ASCII stored , Numerical data can be used either ASCII stored , It can also be stored in binary form .
If there are integers 10000, If the ASCII Code output to disk , The disk is occupied by 5 Bytes ( One byte per character ), And binary output , On the disk 4 Bytes (VS2013 test ).
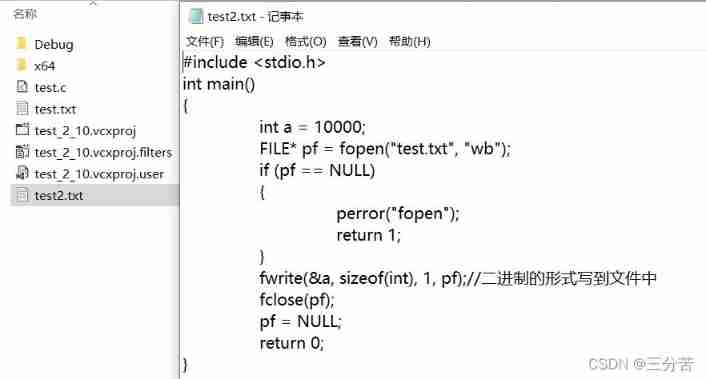
- test :( Store in binary form )
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int a = 10000; FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "wb"); if (pf == NULL) { perror("fopen"); return 1; } fwrite(&a, sizeof(int), 1, pf);// The binary form is written to the file fclose(pf); pf = NULL; return 0; }We put test.txt Put the contents of the document in VS2022 Look inside the compiler :
- 10000 Binary system :0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 0111 0001 0000
- Convert it to hexadecimal :00 00 27 10
3、 Determination of the end of file reading
(1) Misused feof
Keep in mind : During file reading , Out-of-service feof The return value of the function is directly used to determine whether the end of the file .
feof It is applied when the file reading ends , The judgment is that the read failed and ended , Or end of file .
1. Whether the reading of text file is finished , Determine whether the return value is EOF ( fgetc ), perhaps NULL ( fgets )
- for example :
- fgetc Judge whether it is EOF .
- fgets Determine whether the return value is NULL .
2. Judgment of reading end of binary file , Judge whether the return value is less than the actual number to be read .
- for example :
fread Judge whether the return value is less than the actual number to be read .
- Example :
Suppose we put a piece of code in test.txt In file
Now write the code test.txt A copy of the document , Generate test2.txt file
#include<stdio.h> int main() { FILE* pfread = fopen("test.txt", "r"); if (pfread == NULL) { return 1; } FILE* pfwrite = fopen("test2.txt", "w"); if (pfwrite == NULL) { fclose(pfread); return 1; } // File opened successfully // Read and write files int ch = 0; while ((ch = fgetc(pfread)) != EOF) { // Writing documents fputc(ch, pfwrite); } // Judge why it ended if (feof(pfread)) { printf(" End of file flag encountered , The file ends normally \n"); } else if (ferror(pfread)) { printf(" File read failed end \n"); } // Close file fclose(pfread); pfread = NULL; fclose(pfwrite); pfwrite = NULL; return 0; }
And test.txt The contents of the document are exactly the same
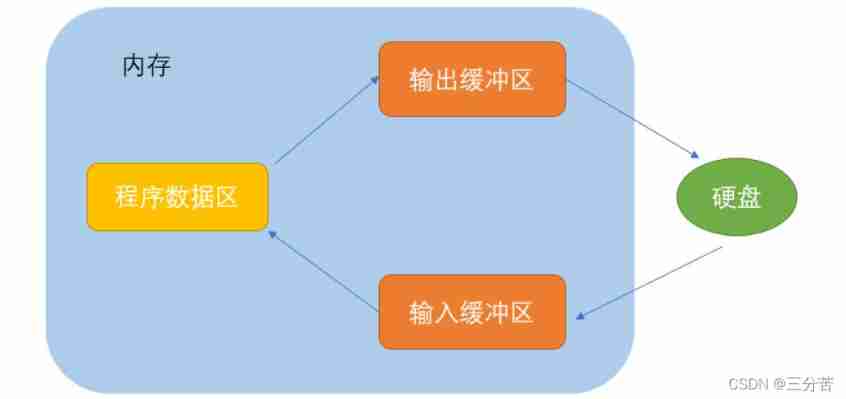
4、 File buffer
It means that the system automatically opens up a block in memory for each file being used in the program “ File buffer ”. Data output from memory to disk is first sent to a buffer in memory , After the buffer is filled, it is sent to the disk together . If you read data from disk to computer , Then read the data from the disk file and input it into the memory buffer ( Fill the buffer ), And then send the data from the buffer to the program data area one by one ( Program variables, etc ). The size of the buffer depends on C The compiler system decides .
- Purpose : Improve the efficiency of the operating system .
- Example :
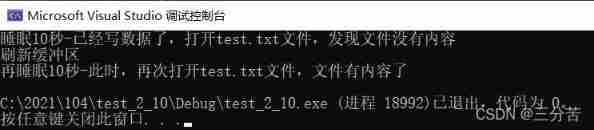
#include <stdio.h> #include <windows.h> int main() { FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "w"); fputs("abcdef", pf);// Put the code in the output buffer first printf(" sleep 10 second - The data has been written , open test.txt file , Found no content in the file \n"); Sleep(10000); printf(" Refresh buffer \n"); fflush(pf);// When the buffer is flushed , Write the data in the output buffer to a file ( disk ) // notes :fflush In high version VS It can't be used on printf(" Sleep again 10 second - here , Open again test.txt file , There's something in the file \n"); Sleep(10000); fclose(pf); // notes :fclose When closing a file , It also flushes the buffer pf = NULL; return 0; }
- Conclusion :
Because there is a buffer ,C Language when operating files , You need to flush the buffer or close the file at the end of the file operation . If you don't do , May cause problems in reading and writing files .
边栏推荐
- The upper layer route cannot Ping the lower layer route
- What sparks can applet container technology collide with IOT
- Newh3c - routing protocol (RIP, OSPF)
- awk从入门到入土(7)条件语句
- Sequence model
- Awk from entry to earth (18) GAW K line manual
- Bishi blog (13) -- oral arithmetic test app
- 20220701 barbarat lemma proof
- Technology sharing | MySQL parallel DDL
- Basic operations of databases and tables ----- view data tables
猜你喜欢

Codeforces Global Round 21(A-E)

Educational Codeforces Round 115 (Rated for Div. 2)
Openfeign service interface call
Go zero micro service practical series (IX. ultimate optimization of seckill performance)
09 softmax regression + loss function

广和通高性能4G/5G无线模组解决方案全面推动高效、低碳智能电网

Codeforces Round #750 (Div. 2)(A,B,C,D,F1)

到底什么才是DaaS数据即服务?别再被其他DaaS概念给误导了

Codeforces Round #803 (Div. 2)(A-D)
CLion-控制台输出中文乱码
随机推荐
manjaro安装微信
Codeforces Round #750 (Div. 2)(A,B,C,D,F1)
Webapi interview question summary 01
Leetcode topic [array] - 121 - the best time to buy and sell stocks
What should I do if there is a problem with the graphics card screen on the computer
如何通过antd的upload控件,将图片以文件流的形式发送给服务器
FOC control
[error record] no matching function for call to 'cacheflush' cacheflush();)
Educational Codeforces Round 115 (Rated for Div. 2)
The basic syntax of mermaid in typera
Relationship and operation of random events
Codeforces Global Round 21(A-E)
Getting started with microservices: gateway gateway
C language - Introduction - Foundation - syntax - [variable, constant light, scope] (V)
C, Numerical Recipes in C, solution of linear algebraic equations, Gauss Jordan elimination method, source code
Sequence model
C#实现一个万物皆可排序的队列
Learn nuxt js
[attack and defense world | WP] cat
[BSP video tutorial] stm32h7 video tutorial phase 5: MDK topic, system introduction to MDK debugging, AC5, AC6 compilers, RTE development environment and the role of various configuration items (2022-