当前位置:网站首页>【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks
【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks
2022-07-04 09:37:00 【weixin_45965693】
Get!New
1.super(MLP, self).__init__(**kwargs):这句话调用nn.Block的__init__函数,它提供了prefix(指定名字)和params(指定模型参数)
net3 = MLP(prefix='another_mlp_')
2.net.name_scope():调用nn.Block提供的name_scope()函数。nn.Dense的定义放在这个scope里面。它的作用是给里面的所有层和参数的名字加上前缀(prefix)使得他们在系统里面独一无二。
卷积神经网络
卷积:input/output 2channel
池化(pooling):和卷积类似,每次看一个小窗口,然后选出小窗口中的最大或平均元素作为输出。
LeNet
两层卷积+两层全连接
权重格式:input_filter×output_filter×height×width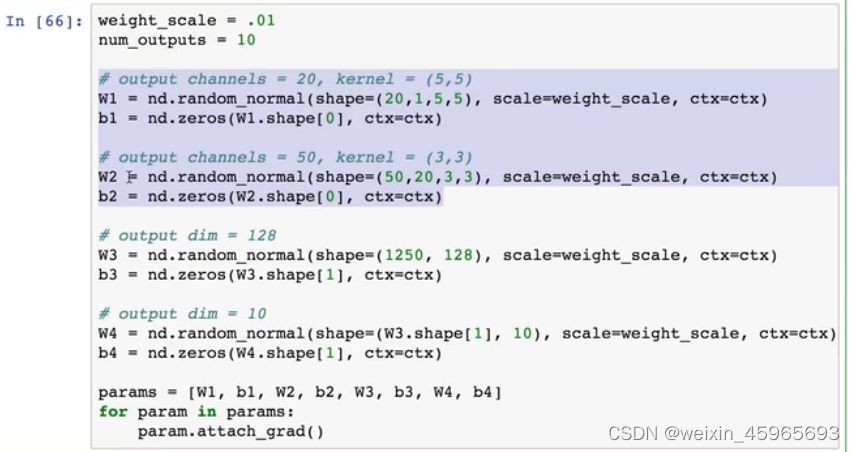
当输入数据有多个通道的时候,每个通道会有对应的权重,然后会对每个通道做卷积之后在通道之间求和
c o n v ( d a t a , w , b ) = ∑ i c o n v ( d a t a [ : , i , : , : ] , w [ 0 , i , : , : ] , b ) conv(data,w,b)=\sum_{i}conv(data[:,i,:,:],w[0,i,:,:],b) conv(data,w,b)=i∑conv(data[:,i,:,:],w[0,i,:,:],b)
卷积模块通常是“卷积层-激活层-池化层”。然后转成2D矩阵输出给后面的全连接层。
def net(X, verbose=False):
X = X.as_in_context(W1.context)
# 第一层卷积
h1_conv = nd.Convolution(data=X, weight=W1, bias=b1, kernel=W1.shape[2:], num_filter=W1.shape[0])
h1_activation = nd.relu(h1_conv)
h1 = nd.Pooling(data=h1_activation, pool_type="max", kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2))
# 第二层卷积
h2_conv = nd.Convolution(data=h1, weight=W2, bias=b2, kernel=W2.shape[2:], num_filter=W2.shape[0])
h2_activation = nd.relu(h2_conv)
h2 = nd.Pooling(data=h1_activation, pool_type="max", kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2))
h2 = nd.flatten(h2)
# 第一层全连接
h3_linear = nd.dot(h2, W3) + b3
h3 = nd.relu(h3_linear)
# 第二层全连接
h4_linear = nd.dot(h3, W4) + b4
if verbose:
print('1st conv block:', h1.shape)
print('2nd conv block:', h2.shape)
print('1st dense:', h3.shape)
print('2nd dense:', h4_linear.shape)
print('output:', h4_linear)
return h4_linear

gluon
不用管输入size
net = gluon.nn.Sequential()
with net.name_scope():
net.add(gluon.nn.Conv2D(channels=20, kernel_size=5, activation='relu'))
net.add(gluon.nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2))
net.add(gluon.nn.Conv2D(channels=50, kernel_size=3, activation='relu'))
net.add(gluon.nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2))
net.add(gluon.nn.Flatten())
net.add(gluon.nn.Dense(128,activation="relu"))
net.add(gluon.nn.Dense(10))
创建神经网络block
nn.block是什么?–提供灵活的网络定义
在gluon里,nn.block是一个一般化的部件。整个神经网络可以是一个nn.Block,单个层也是一个nn.Block。我们可以(近似)无限地【嵌套】nn.Block来构建新的nn.Block。主要提供:
- 存储参数
- 描述
forward如何执行 - 自动求导
class MLP(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(MLP, self).__init__(**kwargs)
with self.name_scope():
self.dense0 = nn.Dense(256)
self.dnese1 = nn.Dense(10)
def forward(self, x):
return self.dense1(nd.relu(self.dense0(x)))
class FancyMLP(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(FancyMLP, self).__init__(**kwargs)
with self.name_scope():
self.dense = nn.Dense(256)
self.weight = nd.random_uniform(shape=(256,20))
def forward(self, x):
x = nd.relu(self.dense(x))
print('layer 1:',x)
x = nd.relu(nd.dot(x, self.weight)+1)
print('layer 2:',x)
x = nd.relu(self.dense(x))
return x
fancy_mlp = FancyMLP()
fancy_mlp.initialize()
y = fancy_mlp(x)
print(y.shape)
nn.Sequential是什么?–定义更加简单nn.Sequential是一个nn.Block容器,它通过add来添加nn.Block。它自动生成forward()函数,其就是把加进来的nn.Block逐一运行。
class Sequential(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Sequential, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def add(self, block):
self._children.append(block)
def forward(self, x):
for block in self._children:
x = block(x)
return x
add layer
net = nn.Sequenctial()
with net.name_scope():
net.add(nn.Dense(256, activation="relu"))
net.add(nn.Dense(10))
net.initialize()
nn下面的类基本都是nn.Block子类,他们可以很方便地嵌套使用
class RecMLP(nn.Block):
def __init__(self. **kwargs):
super(RecMLP, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.net = nn.Sequential()
with self.name_scope():
self.net.add(nn.Dense(256, activation="relu"))
self.net.add(nn.Dense(128, activation="relu"))
self.net.add(nn.Dense(64, activation="relu"))
def forward(self, x):
return nd.relu(self.dense(self.net(x)))
rec_mlp = nn.Sequential()
rec_mlp.add(RecMLP())
rec_mlp.add(nn.Dense(10))
print(rec_mlp)
初始化模型参数
访问:params = net.collect_params()
class MyInit(init.Initializer):
def __init__(self):
super(MyInit, self).__init__()
self._verbose = True
def __init__weight(self, __, arr):
# 初始化权重,使用out=arr后我们不需要指定形状
nd.random.uniform(low=5, high=10, out=arr)
def __init__bias(self, __, arr):
# 初始化偏移
arr[:] = 2
params.initialize(init=MyInit(), force_reinit=True)
print(net[0].weight.data(), net[0].bias.data())
共享模型参数
net.add(nn.Dense(4, in_units=4, activation="relu"))
net.add(nn.Dense(4, in_units=4, activation="relu", params=net[-1].params))
定义一个简单的层
下面代码定义一个层将输入减掉均值。
from mxnet import nd
from mxnet.gluon import nn
class CenteredLayer(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(CenteredLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def forward(self, x):
return x - x.mean()
layer = CenteredLayer()#没有模型参数,不用initialize
layer(nd.array([1,2,3,4,5]))
Alexnet:深度卷积神经网络
net = nn.Sequential()
# 使用较大的11 x 11窗口来捕获物体。同时使用步幅4来较大幅度减小输出高和宽。这里使用的输出通
# 道数比LeNet中的也要大很多
net.add(nn.Conv2D(96, kernel_size=11, strides=4, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2),
# 减小卷积窗口,使用填充为2来使得输入与输出的高和宽一致,且增大输出通道数
nn.Conv2D(256, kernel_size=5, padding=2, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2),
# 连续3个卷积层,且使用更小的卷积窗口。除了最后的卷积层外,进一步增大了输出通道数。
# 前两个卷积层后不使用池化层来减小输入的高和宽
nn.Conv2D(384, kernel_size=3, padding=1, activation='relu'),
nn.Conv2D(384, kernel_size=3, padding=1, activation='relu'),
nn.Conv2D(256, kernel_size=3, padding=1, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2),
# 这里全连接层的输出个数比LeNet中的大数倍。使用丢弃层来缓解过拟合
nn.Dense(4096, activation="relu"), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Dense(4096, activation="relu"), nn.Dropout(0.5),
# 输出层。由于这里使用Fashion-MNIST,所以用类别数为10,而非论文中的1000
nn.Dense(10))

trick:丢弃法 dropout —— 应对过拟合
通常是对输入层或者隐含层做以下操作:
- 随机选择一部分该层的输出作为丢弃元素
- 把丢弃元素乘以0
- 把非丢弃元素拉伸
每一次都激活一部分的模型跑
def dropout(X, drop_prob):
assert 0 <= drop_prob <= 1
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
# 这种情况下把全部元素都丢弃
if keep_prob == 0:
return X.zeros_like()
# 随机选择一部分该层的输出作为丢弃元素
mask = nd.random.uniform(0, 1, X.shape) < keep_prob
return mask * X / keep_prob
num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2 = 784, 10, 256, 256
W1 = nd.random.normal(scale=0.01, shape=(num_inputs, num_hiddens1))
b1 = nd.zeros(num_hiddens1)
W2 = nd.random.normal(scale=0.01, shape=(num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2))
b2 = nd.zeros(num_hiddens2)
W3 = nd.random.normal(scale=0.01, shape=(num_hiddens2, num_outputs))
b3 = nd.zeros(num_outputs)
params = [W1, b1, W2, b2, W3, b3]
for param in params:
param.attach_grad()
drop_prob1, drop_prob2 = 0.2, 0.5
def net(X):
X = X.reshape((-1, num_inputs))
H1 = (nd.dot(X, W1) + b1).relu()
if autograd.is_training(): # 只在训练模型时使用丢弃法
H1 = dropout(H1, drop_prob1) # 在第一层全连接后添加丢弃层
H2 = (nd.dot(H1, W2) + b2).relu()
if autograd.is_training():
H2 = dropout(H2, drop_prob2) # 在第二层全连接后添加丢弃层
return nd.dot(H2, W3) + b3
VGG:使用重复元素的非常深的网络
def vgg_block(num_convs, num_channels):
blk = nn.Sequential()
for _ in range(num_convs):
blk.add(nn.Conv2D(num_channels, kernel_size=3,
padding=1, activation='relu'))
blk.add(nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2))
return blk
def vgg(conv_arch):
net = nn.Sequential()
# 卷积层部分
for (num_convs, num_channels) in conv_arch:
net.add(vgg_block(num_convs, num_channels))
# 全连接层部分
net.add(nn.Dense(4096, activation='relu'), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Dense(4096, activation='relu'), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Dense(10))
return net
net = vgg(conv_arch)
批量归一化 batch-norm
好处:收敛更快
每层归一化
每个channel归一化
均值0,方差1
测试时用整个数据的均值和方差
但是党训练数据极大时,这个计算开销很大。因此,我们用移动平均的方法来近似计算(mvoing_mean和moving_variance)
def batch_norm(X, gamma, beta, is_training, moving_mean, moving_variance, eps = 1e-5, moving_momentum = 0.9):
assert len(X.shape) in (2,4)
# 全连接:batch_size x feature
if len(X.shanpe) == 2:
# 每个输入维度在样本上的平均和方差
mean = X.mean(axis=0)
variance = ((X - mean)**2.mean(axis=0))
# 2D卷积:batch_size × channel × height × width
else:
# 对每个通道算均值和方差,需要保持4D形状使得可以正确的广播
mean = X.mean(axis=(0,2,3), keepdims=True)
variance = ((X - mean)**2).mean(axis=(0,2,3), keepdims=True)
# 变形使得可以正确广播
moving_mean = moving_mean.reshape(mean.shape)
moving_variance = moving_variance.reshape(mean.shape)
# 均一化
if is_training:
X_hat = (X - mean) / nd.sqrt(variance + eps)
#!!! 更新全局的均值和方差
moving_mean[:] = moving_momentum * moving_mean + (1.0 - moving_momentum) * mean
moving_variance[:] = moving_momentum * moving_variance + (1.0 - moving_momentum) * variance
else:
#!!! 测试阶段使用全局的均值和方差
X_hat = (X - moving_mean) / nd.sqrt(moving_variance + eps)
# 拉伸和偏移
return gamma.reshape(mean.shape) * X_hat + beta.reshape(mean.shape)
在gluon中使用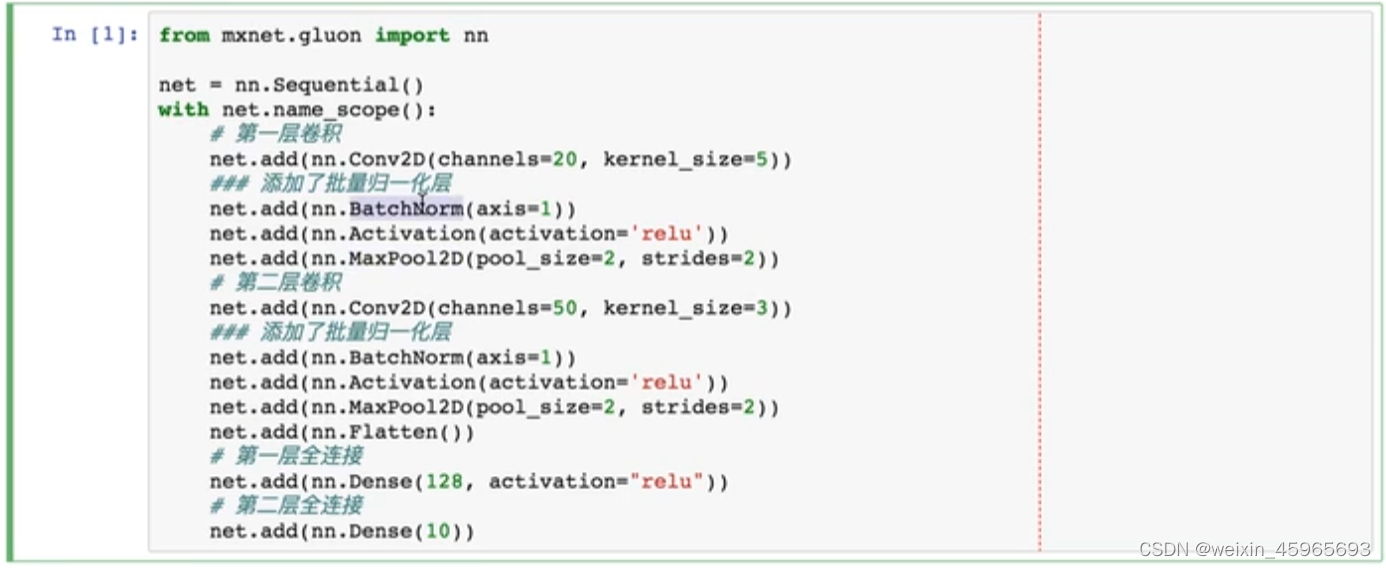
边栏推荐
- 入职中国平安三周年的一些总结
- Whether a person is reliable or not, closed loop is very important
- Histogram equalization
- el-table单选并隐藏全选框
- xxl-job惊艳的设计,怎能叫人不爱
- Mmclassification annotation file generation
- pcl::fromROSMsg报警告Failed to find match for field ‘intensity‘.
- 华为联机对战如何提升玩家匹配成功几率
- On Multus CNI
- Get the source code in the mask with the help of shims
猜你喜欢
MATLAB小技巧(25)竞争神经网络与SOM神经网络
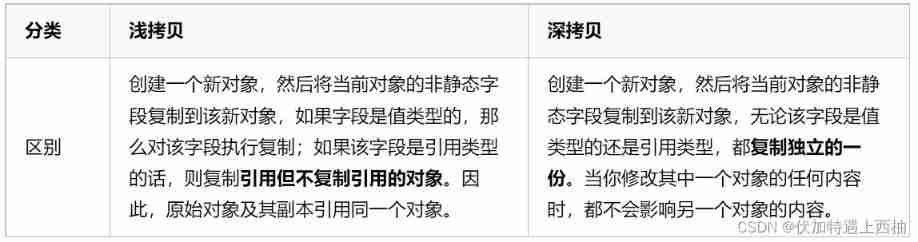
Four common methods of copying object attributes (summarize the highest efficiency)
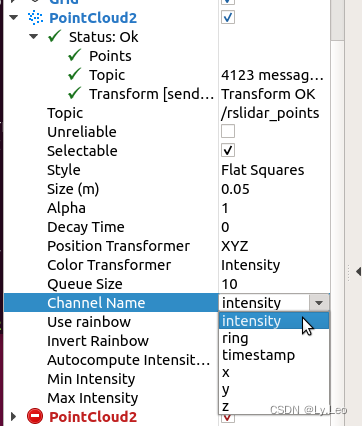
pcl::fromROSMsg报警告Failed to find match for field ‘intensity‘.

Baidu R & D suffered Waterloo on three sides: I was stunned by the interviewer's set of combination punches on the spot
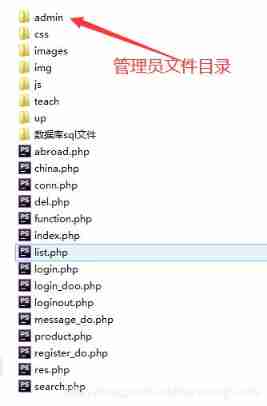
PHP is used to add, modify and delete movie information, which is divided into foreground management and background management. Foreground users can browse information and post messages, and backgroun

Application of safety monitoring in zhizhilu Denggan reservoir area
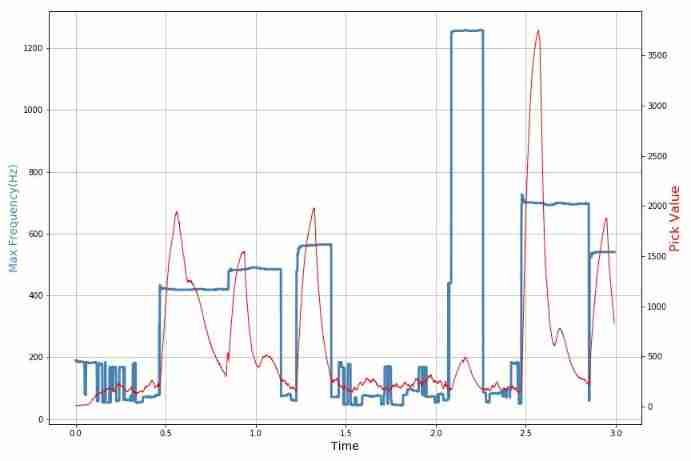
Daughter love: frequency spectrum analysis of a piece of music
el-table单选并隐藏全选框

uniapp 处理过去时间对比现在时间的时间差 如刚刚、几分钟前,几小时前,几个月前
直方图均衡化
随机推荐
What are the advantages of automation?
Laravel文档阅读笔记-How to use @auth and @guest directives in Laravel
Luogu deep foundation part 1 Introduction to language Chapter 4 loop structure programming (2022.02.14)
System.currentTimeMillis() 和 System.nanoTime() 哪个更快?别用错了!
PHP book borrowing management system, with complete functions, supports user foreground management and background management, and supports the latest version of PHP 7 x. Database mysql
Kotlin set operation summary
Hands on deep learning (33) -- style transfer
直方图均衡化
Kubernetes CNI 插件之Fabric
xxl-job惊艳的设计,怎能叫人不爱
Qtreeview+ custom model implementation example
Pueue data migration from '0.4.0' to '0.5.0' versions
Hands on deep learning (III) -- Torch Operation (sorting out documents in detail)
View CSDN personal resource download details
Logstack configuration details -- elasticstack (elk) work notes 020
Golang Modules
Are there any principal guaranteed financial products in 2022?
About the for range traversal operation in channel in golang
Exercise 7-3 store the numbers in the array in reverse order (20 points)
Devop basic command