当前位置:网站首页>Implementation of a sequence table
Implementation of a sequence table
2022-07-31 03:17:00 【blue cat knight】
目录
Construction of basic functions
3.尾插(Insert data from the tail)
序言
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储.在数组上完成数据的增删查改
The implementation of the sequence table can generally be divided into two types:静态的顺序表(It is stored in the form of a fixed-length array) 和 动态的顺序表(使用动态开辟的数组进行存储)
静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景.静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空
间开多了浪费,开少了不够用.所以现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态的分配空间
大小,所以下面我们实现动态顺序表.
About the frame structure:
The basic function of the sequence table 增 删 查 找 改 插入 几大功能,We do this with functions 下面 我们 先来 对 Structure is constructed, One more declaration of the base function,This completes the basic framework.
typedef struct SeqList
{
int* a;
int size; // 存储数据的个数
int capicity; // Because we have a dynamic sequence table here,We need a capacity.
}SL;
// 初始化
void SeqListInit(SL* psl);
// 检查空间,如果满了,进行增容
void CheckCapacity(SL* psl);
// 顺序表尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SL* psl, int x);
// 顺序表尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SL* psl);
// 顺序表头插
void SeqListPushFront(SL* psl, int x);
// 顺序表头删
void SeqListPopFront(SL* psl);
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SL* psl, int x);
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SL* psl, size_t pos, int x);
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SL* psl, size_t pos);
// 顺序表销毁
void SeqListDestory(SL* psl);
// 顺序表打印
void SeqListPrint(SL* psl);Construction of basic functions
1.初始化数据
将 a 指针置为空 以及把size 和 capicity 的大小置为 0 ;
void SeqListInit(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->size = psl->capicity = 0;
}
2.销毁数据
void SeqListDestory(SL* psl);
void SeqListDestory(SL* psl)
{
if (psl->a)
{
free(psl->a);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->capicity = psl->size = 0;
}
}
3.尾插(Insert data from the tail)
Because we have a dynamic sequence table here Think about it when inserting data 我们的capicity容量是否充足?
Here we are going to use a function;void CheckCapacity(SL* psl)
Determine whether there is enough memory area for inserting data 不够的话 We will do dynamic expansion;
检查扩容
void CheckCapacity(SL* psl)
void CheckCapacity(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
if (psl->capicity == psl->size)
{
int newcapicity = psl->size == 0 ? 4 : (psl->size) * 2;
int* tmp = (int*)realloc(psl->a,sizeof(int)*newcapicity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("ralloc fail");
return;
}
psl->a = tmp;
psl->capicity = newcapicity;
}
}Now let's construct the tail plug again:
void SeqListPushBack(SL* psl, int x)
{
assert(psl);
CheckCapacity(psl);
psl->a[psl->size] = x;
psl->size++;
}4.尾删
这个比较简单,We explained earlier in the struct size is used to count data;It is based on when we print the data size 来进行打印的.Now since the issue of printing data is mentioned So let's write a function that prints data first
打印数据
void SeqListPrint(SL* psl);
void SeqListPrint(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", psl->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}尾删
直接把 size to reduce 就行了;因为我们是根据sizeThe size of the data to determine the storage.
void SeqListPopBack(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
if (psl->size == 0)
{
return;
}
psl->size--;
}
5.头插
在 Insert a data at the beginning; 同样是插入 同样也需要 检查扩容;Actually here's the head plug 效率不高 Also traverse the mobile data;
void SeqListPushFront(SL* psl, int x)
{
assert(psl);
CheckCapacity(psl);
int i = 0;
for (i = psl->size+1; i > 0; i--)
{
psl->a[i] = psl->a[i-1];
}
psl->a[0] = x;
psl->size++;
}6.头删
void SeqListPopFront(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
assert(psl->size > 0);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < psl->size-1;i++)
{
psl->a[i] = psl->a[i + 1];
}
psl->size--;
}7.顺序表查找
Find the subscript where a data is located 返回值为 int 如果不存在 则返回 -1.
int SeqListFind(SL* psl, int x)
{
assert(psl);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
{
if (psl->a[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}8.顺序表在pos位置插入x
Insert to cite 检查扩容
void SeqListInsert(SL* psl, size_t pos, int x)
{
assert(psl);
CheckCapacity(psl);
size_t i = 0;
for (i = psl->size + 1; i > pos; i--)
{
psl->a[i] = psl->a[i - 1];
}
psl->a[pos] = x;
psl->size++;
}9.顺序表删除pos位置的值
利用 SeqListFind 来找出 pos 位置的下标 利用for遍历 数组 从 This subscript position 依次向前覆盖;
void SeqListErase(SL* psl, size_t pos)
{
assert(psl);
int A = SeqListFind(psl, pos);
int i = 0;
for (i = A; i < psl->size-1; i++)
{
psl->a[A] = psl->a[A + 1];
}
psl->size--;
}改进和优化
我们知道 data in our data sheet Not necessarily all plastic In order to facilitate us to modify the data;
We can use it in advance #define 来 定义 类型的名称;
以上代码 The assertion part is not sufficient,需要进行优化.
边栏推荐
- STM32问题合集
- 选好冒烟测试用例,为进入QA的制品包把好第一道关
- 数据库实现分布式锁
- 品牌广告投放平台的中台化应用与实践
- VS QT——ui不显示新添加成员(控件)||代码无提示
- C primer plus study notes - 8, structure
- Redis实现分布式锁
- What skills do I need to learn to move from manual testing to automated testing?
- With 7 years of experience, how can functional test engineers improve their abilities step by step?
- 华为分布式存储FusionStorage知识点总结【面试篇】
猜你喜欢

With 7 years of experience, how can functional test engineers improve their abilities step by step?
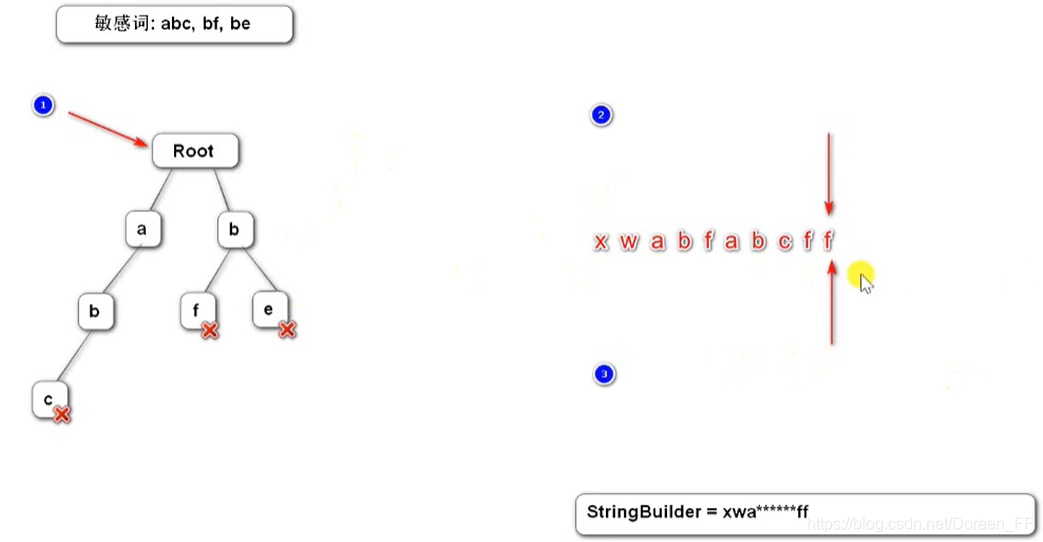
4. Sensitive word filtering (prefix tree)

华为分布式存储FusionStorage知识点总结【面试篇】

10. Redis implements likes (Set) and obtains the total number of likes
分布式与集群是什么 ? 区别是什么?
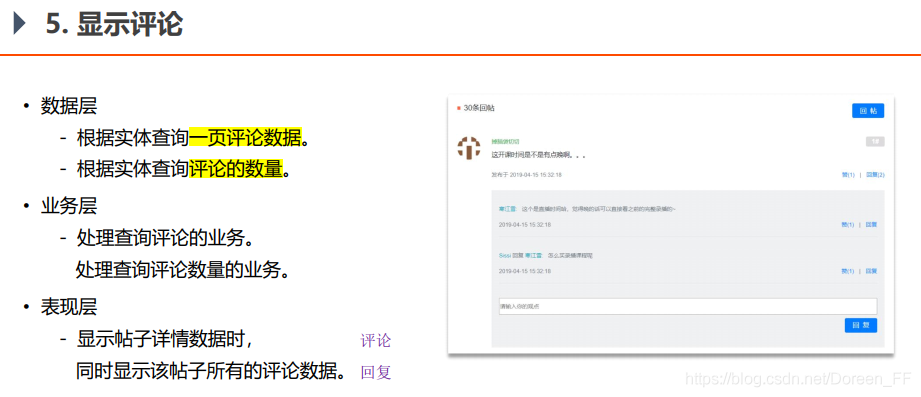
6. Display comments and replies
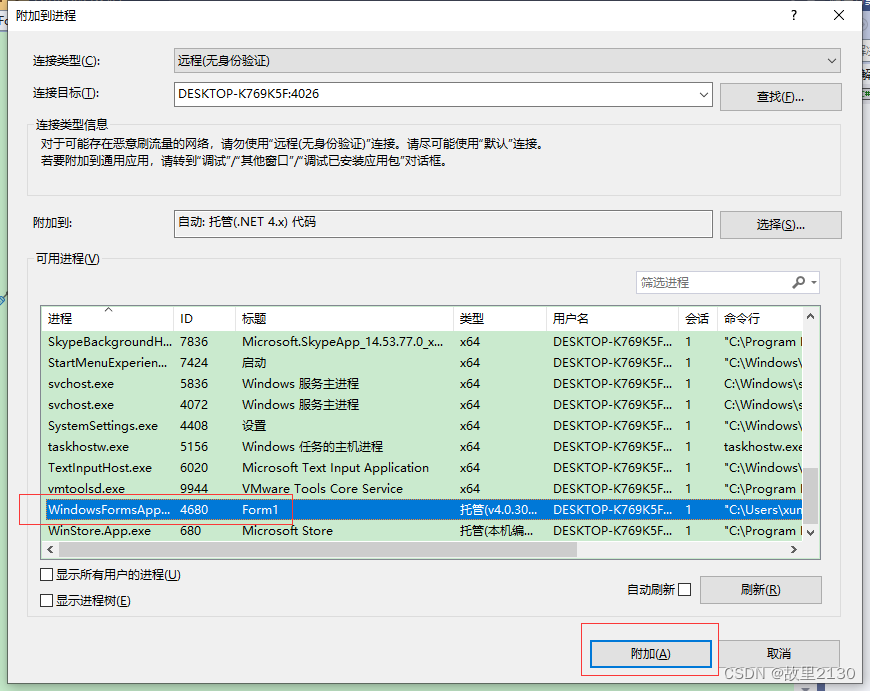
C#远程调试

LeetCode每日一练 —— OR36 链表的回文结构

加密公司向盗窃的黑客提供报价:保留一点,把剩下的归还
![[Compilation principle] Design principle and implementation of recursive descent parsing](/img/51/cd054a8246dc108520d6ff9ea26c60.png)
[Compilation principle] Design principle and implementation of recursive descent parsing
随机推荐
Redis implements distributed locks
What is SQALE
Modbus on AT32 MCUs
[Godot][GDScript] 2D cave map randomly generated
STM32 problem collection
Mysql 45讲学习笔记(二十四)MYSQL主从一致
6. Display comments and replies
JS function this context runtime syntax parentheses array IIFE timer delay self.backup context call apply
Moxa NPort 设备缺陷可能使关键基础设施遭受破坏性攻击
MultipartFile文件上传
【编译原理】递归下降语法分析设计原理与实现
下载jar包的好地方
SQL injection Less54 (limited number of SQL injection + union injection)
Problems that need to be solved in distributed system architecture
[Android] Room - Alternative to SQLite
some of my own thoughts
Graphical lower_bound & upper_bound
【动态规划】连续子数组的最大和
The els block moves the boundary to the right, and accelerates downward.
【HCIP】ISIS