当前位置:网站首页>【纯音听力测试】基于MATLAB的纯音听力测试系统
【纯音听力测试】基于MATLAB的纯音听力测试系统
2022-07-05 00:49:00 【fpga和matlab】
1.软件版本
matlab2017b
2.系统原理
语音是人类进行交流沟通的最基本方式,而人类的耳朵则是接收语音信号的唯一器官,但是对于听力障碍患者来讲,由于无法正常接收来自他人的语音信号,其无法进行正常的交流和沟通,严重影响了他们的日常生活[01]。早期,由于各种条件的限制,他们往往被社会忽略,而随着经济的不断发展,社会的不断进步,听力问题则受到了人们越来越多的重视,通过研究发现,导致听力问题的主要原因有有长时间生活在噪声环境中,导致听力逐渐受到损伤,先天性的听力障碍,外界影响受伤受损等[02]。到目前为止,我国听力障碍人士超过3000万,一种大部分是老年人,还有一部分是新生儿。而在全世界,听力障碍人士则超过6亿人,听力障碍正成为影响全人类健康的一个重要疾病,如果不采取正确的措施,在未来将会导致更加严重的问题。而其中大部分人则可以通过早期听力测试及早发现问题进行治疗来避免的,但是长期以来,由于缺乏各种有效的测试方法,导致很多人成为听力障碍患者。因此,开发一种行之有效的听力测试方法是一个十分重要的研究方向。目前,关于听力测试主要可以分为纯音听力测试,言语测听以及听力分辨能力测试等。通过这些测试,然后根据相关标准对测试结果进行打分,从而对患者的听力水平给出一个客观准确的评价指标,为后期患者的听力康复工作起到指导性工作。其中纯音听力测试是一个重要的听力测试项目,在临床应用中处于举足轻重的地位。其主要测试方法是通过观测、记录患者对不同频率,声强的声音信号的自然反应来了解患者的实际听力情况。
基于纯音听力测试的测听系统。整个系统具备如下几个方面的功能:
第一、系统可以产生不同频率,不同声强以及不同持续时间的纯音信号;
第二、对于同一频率的纯音信号,可以改变其声强,得到多个不同声强的纯音信号;
第三、可以记录不同受试者的测试记录;
第四、具有良好的用户使用人机交互界面;
根据国家标准GB-16403,本文制定如下的纯音听力阈值测试的整体步骤:
第一、设置纯音信号的起始频率为1000Hz,初始的声压设置为0dB作为初始声压级,并且以5dB为间隔进行等间隔逐渐增大声压,直到受试者听到声音为止,并记录不同声压下对应的受试者的听力反馈结果。
第二、然后在以5dB为间隔降低声压级,直到受试者听不到声音为止,然后再以5dB为间隔进行等间隔逐渐增大声压,直到受试者听到声音为止,如此发反复测试3次以上,记录每次一次受试者可以听见声音的阈值。
第三、改变频率测试点,变为2kHz,然后重复步骤一和步骤二结果,并记录相关测试结果;然后再增加频率测试点,重复步骤一和步骤二,直到频率测试点增加到20000Hz为止。
然后在纯音频率分辨率测试方面,根据国际通用标准,我们设置11个频率点:125Hz,250Hz,500Hz,,750Hz,1000Hz,1500Hz,2000Hz,3000Hz,4000Hz,6000Hz,8000Hz,其具体测试步骤如下所示:
第一、选择第一个频率测试点,产生频率为125Hz的纯音信号;
第二、然后选择10个受试者,分别对其进行测试,记录各个受试者的听力反馈情况。然后将频率点设置为第二个频率值250H在,重复对10个受试者进行测试,记录各个受试者的听力反馈情况。通过这种方法,依次将11个频率点进行测试,直到完成所有频率点的测试。
3.核心源码
·声音录制模块
声音录制模块的MATLAB基本GUI界面如下图所示:
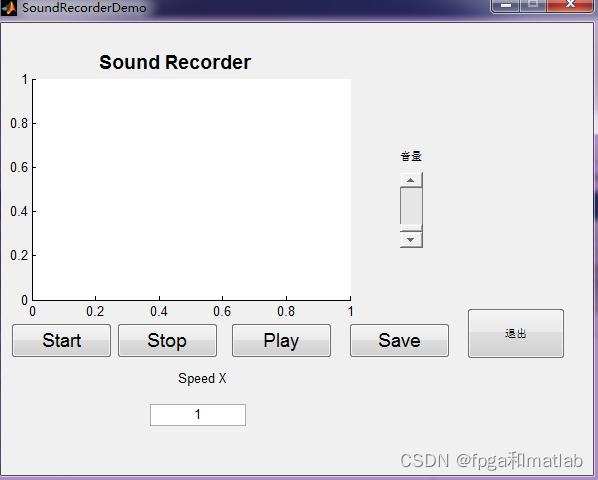
图1声音录制模块
从图1可知,声音录制模块包括开始录制、停止录制、播放、保存以及音量控制等功能,同时在播放过程中,可以自动显示语速(Speed X)。该模块的主要功能是录制一些需要进行语言类测试的语音样本。
·音乐测试模块
音乐测试模块的MATLAB基本GUI界面如下图所示:
图2音乐测试模块
·纯音信号产生模块
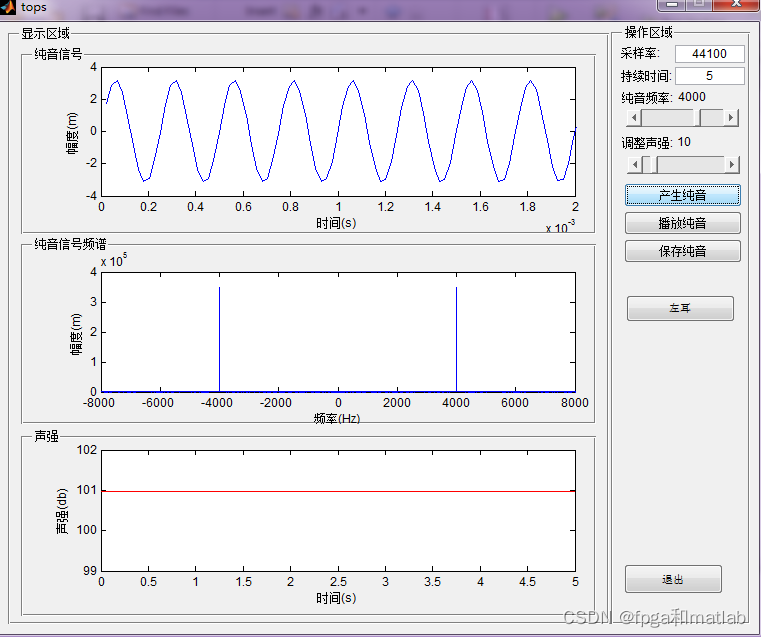
纯音信号产生模块的MATLAB基本GUI界面如下图所示:

图3纯音信号产生模块
从图3可知,纯音信号产生模块包括纯音信号采样率设置,持续时间设置,纯音信号频率设置(250Hz,500Hz,,750Hz,1000Hz,1500Hz,2000Hz,3000Hz,4000Hz,6000Hz,8000Hz),声强设置(10dB HL,15 dB HL,25 dB HL,35 dB HL,45 dB HL,50 dB HL,60 dB HL,70 dB HL,75 dB HL,85 dB HL),产生纯音,播放纯音,保存纯音以及伸到设置(双声道、左声道、右声道)。纯音信号产生模块同时可以显示纯音信号的时域波形,频域波形以及声强特征曲线。
纯音信号产生模块也是本系统的核心模块,通过该模块,我们可以测试得到受试者的听力阈值,即可以感知的听力频率范围和声强大小范围。为后期对听力障碍者的治疗康复提供治疗依据。
·测试结果分析模块
测试结果分析模块的MATLAB基本GUI界面如下图所示:
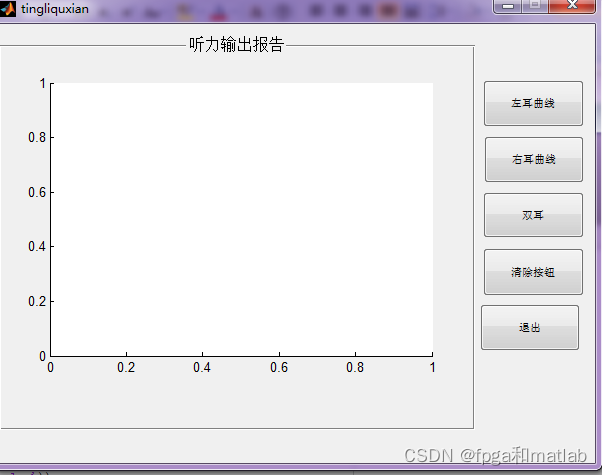
图4测试结果分析模块
从图4可知,测试结果分析模块包括左耳曲线、右耳曲线以及双耳曲线的测试结果数据。该模块的主要功能主要是对受试者的测试结果以数据曲线的形式进行显示。
function varargout = tops(varargin)
% TOPS MATLAB code for tops.fig
% TOPS, by itself, creates a new TOPS or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = TOPS returns the handle to a new TOPS or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% TOPS('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in TOPS.M with the given input arguments.
%
% TOPS('Property','Value',...) creates a new TOPS or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before tops_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to tops_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help tops
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 26-Apr-2019 22:46:55
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @tops_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @tops_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before tops is made visible.
function tops_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to tops (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for tops
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes tops wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = tops_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function edit1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit1 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit2 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit3 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
cla(handles.axes1);
cla(handles.axes2);
global Fs;
global T;
global fc;
global tt;
global y;
global sy;
global LIMIT;
Fs = str2num(get(handles.edit1, 'string'));
T = str2num(get(handles.edit2, 'string'));
sy = LIMIT;
tt = [1/Fs:1/Fs:T];
y = 10^(sy/20)*sin(2*pi*fc*tt);
yfft = abs(fftshift(fft(y)));
N = length(yfft);
ff = Fs*[-N/2:1:N/2-1]/N;
axes(handles.axes1);
plot(tt,y);
xlim([0,0.002]);
xlabel('时间(s)');
ylabel('幅度(m)');
axes(handles.axes2);
plot(ff,yfft)
xlim([-2*fc,2*fc]);
xlabel('频率(Hz)');
ylabel('幅度(m)');
%取x的一个通道
x=y';
fs=Fs;
%将x从列向量转为行向量
x=x';
LL=length(x);
%语音分帧
framlen = 10;
M = fs*framlen/1000;
%m为Length/M后得到的余数
m = mod(LL,M);
if m >= M/2
x = [x,zeros(1,M-m)];
LL = length(x);
else
l = floor(LL/M);
x = x(1,1:M*l);
LL = length(x);
end
N = LL/M;
%计算声压级
s = zeros(1,M);
spl = zeros(1,N);
for k = 1:N
s = x((k-1)*M + 1:k*M);
spl(1,k) = SPLCal(s,fs,framlen);
end
t = 1:LL;
SPL = zeros(1,LL);
for r = 1:N
SPL(1,(r-1)*M+1:r*M) = spl(r);
end
axes(handles.axes3);
stairs(t/Fs,round(100*SPL)/100,'r');
xlabel('时间(s)');
ylabel('声强(db)');
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global Fs;
global T;
global fc;
global tt;
global y;
global sy;
global LIMIT;
sound(y,Fs)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global Fs;
global T;
global fc;
global tt;
global y;
global sy;
global LIMIT;
tmps = clock;
Names = ['savewav','---',num2str(Fs),'---',num2str(fc),'---',num2str(tmps(1)),num2str(tmps(2)),num2str(tmps(3)),num2str(tmps(4)),num2str(tmps(5)),num2str(tmps(6)),'.wav'];
wavwrite(y,Fs,Names)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton4.
function pushbutton4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
clc;
clear;
close all;
function edit4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit4 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit4 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit4_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on slider movement.
function slider1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'Value') returns position of slider
% get(hObject,'Min') and get(hObject,'Max') to determine range of slider
global Fs;
global T;
global fc;
global tt;
global y;
global sy;
global LIMIT;
t=(get(handles.slider1,'value'));
LIMIT = 5*round(t*17);
set(handles.text5,'String',num2str(LIMIT));
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function slider1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: slider controls usually have a light gray background.
if isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor',[.9 .9 .9]);
end
% --- Executes on slider movement.
function slider2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'Value') returns position of slider
% get(hObject,'Min') and get(hObject,'Max') to determine range of slider
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function slider2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: slider controls usually have a light gray background.
if isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor',[.9 .9 .9]);
end
% --- Executes on slider movement.
function slider3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'Value') returns position of slider
% get(hObject,'Min') and get(hObject,'Max') to determine range of slider
global Fs;
global T;
global fc;
global tt;
global y;
global sy;
global LIMIT;
t=(get(handles.slider3,'value'));
t2=floor(8*t)+1;t2
if t2==1
fc = 250;
end
if t2==2
fc = 500;
end
if t2==3
fc = 1000;
end
if t2==4
fc = 2000;
end
if t2==5
fc = 3000;
end
if t2==6
fc = 4000;
end
if t2==7
fc = 6000;
end
if t2==8
fc = 8000;
end
set(handles.text6,'String',num2str(fc));
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function slider3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: slider controls usually have a light gray background.
if isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor',[.9 .9 .9]);
end
4.测试结果
通过纯音信号产生模块产生需要测试的纯音信号,其结果如下图所示:
A03-23
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
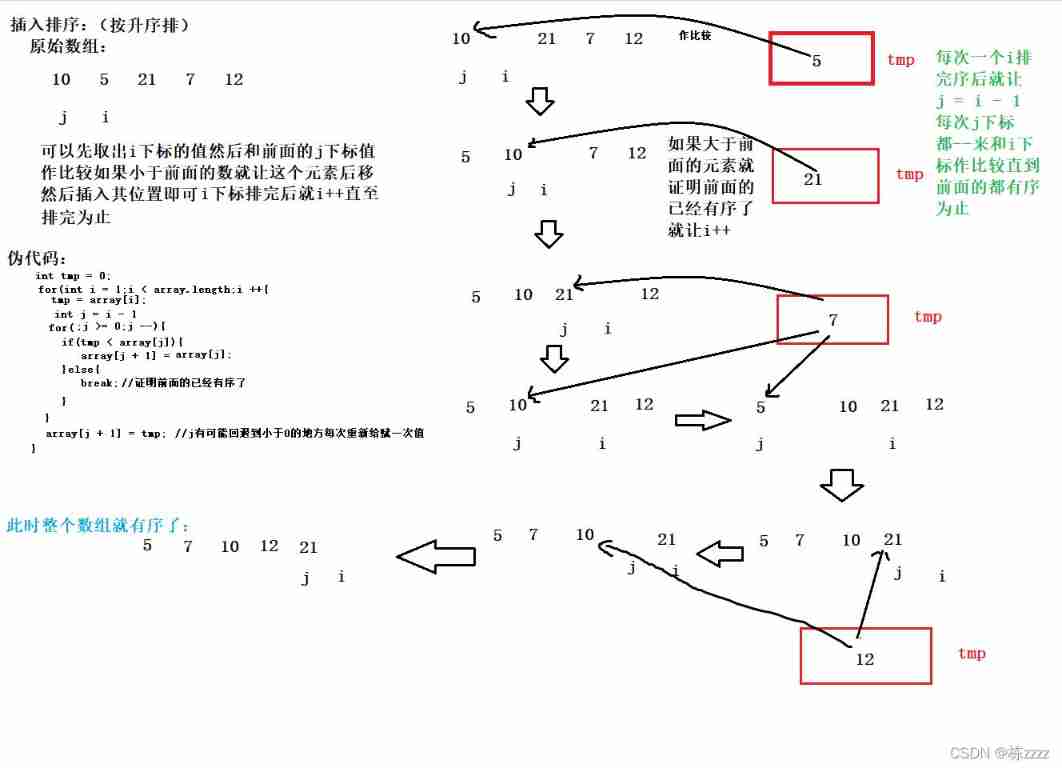
Insert sort of sort
Date time type and format in MySQL
pycharm专业版下载安装教程

Fs8b711s14 electric wine bottle opener MCU IC scheme development special integrated IC
OpenHarmony资源管理详解

BGP comprehensive experiment
SAP ui5 application development tutorial 107 - trial version of SAP ui5 overflow toolbar container control introduction
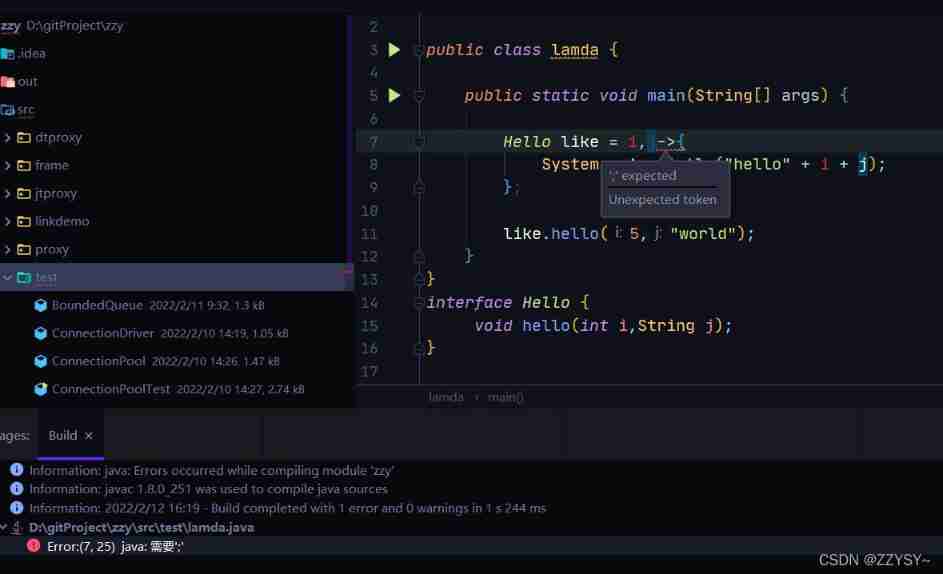
Several simplified forms of lambda expression

Some basic functions of enterprise projects are developed, and important things are saved to online first a
uniapp微信小程序拿来即用的瀑布流布局demo2(方法二)(复制粘贴即可使用,无需做其他处理)
随机推荐
【selenium自动化】常用注解
测试部新来了个00后卷王,上了年纪的我真的干不过了,已经...
2022.07.03 (lc_6111_counts the number of ways to place houses)
Hill sort of sorting
Detailed explanation of openharmony resource management
Specification for fs4061a boost 8.4v charging IC chip and fs4061b boost 12.6V charging IC chip datasheet
Expose testing outsourcing companies. You may have heard such a voice about outsourcing
海思3559万能平台搭建:YUV422的踩坑记录
大专学历,33岁宝妈又怎样?我照样销售转测试,月入13k+
[Yocto RM]11 - Features
Maximum number of "balloons"
RB technology stack
Hologres query management and timeout processing
Leetcode70 (Advanced), 322
SAP ui5 application development tutorial 107 - trial version of SAP ui5 overflow toolbar container control introduction
【微处理器】基于FPGA的微处理器VHDL开发
26.2 billion! These universities in Guangdong Province have received heavy support
TS快速入门-函数
2022.07.03(LC_6111_统计放置房子的方式数)
GDB common commands