当前位置:网站首页>6. Scala operator
6. Scala operator
2022-07-05 00:33:00 【liangzai2048】
List of articles
Operator
Scala The use of operators and Java The use of operators is basically the same , Only a few details are different .
Arithmetic operator
- Basic grammar
| Operator | operation | Example | result |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Plus sign | +3 | 3 |
| - | Minus sign | b=4;-b | 4 |
| + | Add | 5+5 | 10 |
| - | reduce | 6-4 | 2 |
| * | ride | 3*4 | 12 |
| / | except | 5/5 | 1 |
| % | modulus ( Remainder ) | 7%5 | 2 |
| + | String addition | “He”+“llo” | “Hello” |
For division marks "/" , Its integer and decimal division are different : Division between integers , Keep only the whole part and discard the decimal part .
Case study
package day03
object Test01_TestOperator {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1、 Arithmetic operator
val result1 = 10 / 3
println(result1)
val result2: Double = 10 / 3
println(result2)
//float and double When doing decimal operations, there will be a deviation in accuracy
val result3: Double = 10.0 / 3
println(result3)
println(result3.formatted("%5.2f")) // There is not enough space in front of formatted output
val result4: Int = 10 % 3
println(result4)
}
}
Running results :
3.0
3.3333333333333335
3.33
1
Relational operator ( Comparison operator )
- Basic grammar
| Operator | operation | Example | result |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | Equivalent to | 4==3 | false |
| != | It's not equal to | 4!=3 | true |
| < | Less than | 4<3 | false |
| > | Greater than | 4>3 | true |
| <= | Less than or equal to | 4<=3 | false |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | 4>=3 | true |
- Case study
Java example
public class TestOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Comparison operator
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = new String("hello");
Boolean isEqual = s1 == s2;
System.out.println(isEqual);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
}
}
Running results :
false
true
Scala example
package day03
object Test01_TestOperator {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 2、 Comparison operator
val s1: String = "hello"
val s2: String = new String("hello")
println(s1 == s2) // Judge whether the two values are equal
println(s1.equals(s2)) // Judge whether the two values are equal
println(s1.eq(s2)) // Determine if the addresses are equal
}
}
Output results :
true
true
false
Logical operators
- Basic grammar
Used to connect multiple conditions ( General classes will be relational expressions ), The end result is also a Boolean
Assume : Variable A by true,B by false
| Operator | describe | example |
|---|---|---|
| && | Logic and | (A && B ) The result of operation is false |
| II | Logic or | (A II B) The result of operation is true |
| ! | Logic is not | !(A && B ) The result of operation is true |
- Case study
package day03
object Test01_TestOperator {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 3、 Logical operators
def m(n: Int): Int = {
println("m Called ")
return n
}
val n = 1
println((4 > 5) && m(n) > 0) // A short circuit , The latter will not be called
println((4 > 5) & m(n) > 0)
// Determine whether a string is empty
def isNotRmpty(str: String): Boolean = {
return str != null && !("".equals(str.trim))
}
println(isNotRmpty(str = null))
}
}
Running results :
false
m Called
false
false
Assignment operator
- Basic grammar
An assignment operator is the value of an operation , Assign to the specified variable
| Operator | describe | example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Simple assignment operators , Assign the value of an expression to an lvalue | C= A+B take A+B The result of the expression is assigned to C |
| += | Add and then assign a value | C+=A be equal to C=C+A |
| -= | Subtract and then assign a value | C-=A be equal to C=C-A |
| *= | Multiply and assign a value | C*=A be equal to C=C*A |
| /= | Divide and assign a value | C/=A be equal to C=C/A |
| %= | The value is assigned after the remainder | C%=A be equal to C=C%A |
| <<= | Left shift assignment | C<<=2 be equal to C=C<< 2 |
| >>= | Right shift after assignment | C>>=2 be equal to C=C>>2 |
| &= | Bitwise and post assignment | C&=2 be equal to C=C&2 |
| ^= | Assign a value after bitwise XOR | C ^ =2 be equal to C=C ^ 2 |
| I= | Assign value by bit or after | CI=2 be equal to C=CI2 |
Be careful :Scala There is no ++、– The operator , Can pass +=、-= To achieve the effect of consent
- Case study
Java
public class TestOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Increase and decrease
int x = 15;
int y = x++;
System.out.println("x = " + x + ", y = " + y);
x = 15;
y = ++x;
System.out.println("x = " + x + ", y = " + y);
x = 23;
x = x ++; // Temporary variable assignment required x++ temp = x++; x = temp;
System.out.println(x); // Assign first and then add
}
}
Running results :
12
x = 16, y = 15
x = 16, y = 16
23
Scala
package day03
object Test01_TestOperator {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 4、 Assignment operator
var b: Byte = 10
// b += 1 // error
// println(b)
var i: Int = 12
i += 1
println(i)
// i++ //Scala Abandoned
}
}
Output results :
13
An operator
- Basic grammar
Variables in the following table a by 60,b by 13
| Operator | describe | example |
|---|---|---|
| & | Bitwise and operator | (a & b) Output results 12 , Binary interpretation : 0000 1100 |
| I | bitwise or operator | (a I b) Output results 61 , Binary interpretation : 0011 1101 |
| ^ | bitwise exclusive or operator | (a ^ b) Output results 49 , Binary interpretation : 0011 0001 |
| ~ | Bitwise negation operator | (~a) Output results -61 , Binary interpretation : 1100 0011 , In the complement form of a signed binary number |
| << | Left move operator | a<<2 Output results 240, Binary interpretation : 0011 0000 |
| >> | Move right operator | a>> Output results 15, Binary interpretation : 0000 1111 |
- Case study
package day03
object Test01_TestOperator {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 5、 An operator
val a = 60
println(a << 3)
println(a >> 2)
val j: Short = -13
println(j << 2)
println(j >> 2)
println(j >>> 2) // unsigned right shift
}
}
Output results :
480
15
-52
-4
1073741820
The essence of operators
In the face of the object
package day03
object Test01_TestOperator {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 6、 The essence of operators
val j1: Int = 12
val j2: Int = 37
println(j1.+(j2))
println(j1 + (j2))
println(1.34.*(25))
println(1.34 * 25)
println(7.5 toInt).toString
}
}
Output results :
49
49
33.5
33.5
7
After all ! Give the pretty boy a compliment !(*゚ヮ゚)*
边栏推荐
- Consolidated expression C case simple variable operation
- Five papers recommended for the new development of convolutional neural network in deep learning
- 图解网络:什么是网关负载均衡协议GLBP?
- P3304 [SDOI2013]直径(树的直径)
- GDB常用命令
- Summer challenge brings you to play harmoniyos multi terminal piano performance
- 【雅思阅读】王希伟阅读P4(matching1)
- leetcode494,474
- 2022.07.03 (LC 6108 decryption message)
- 公司要上监控,Zabbix 和 Prometheus 怎么选?这么选准没错!
猜你喜欢
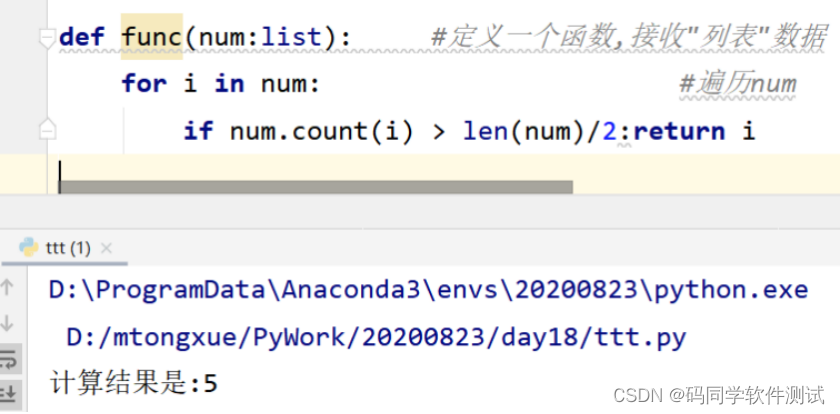
Tester's algorithm interview question - find mode
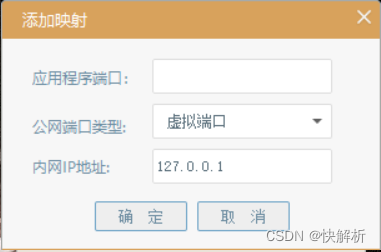
What is the difference between port mapping and port forwarding
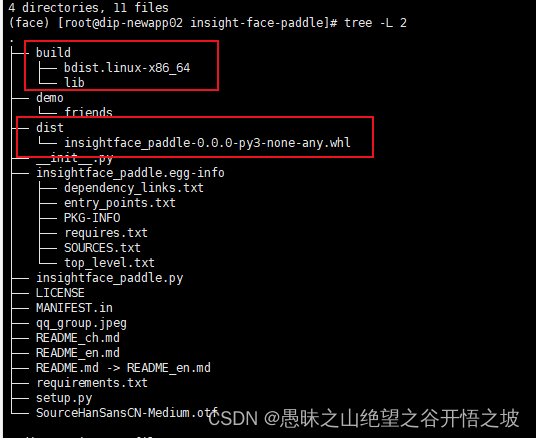
Face recognition 5- insight face padding code practice notes
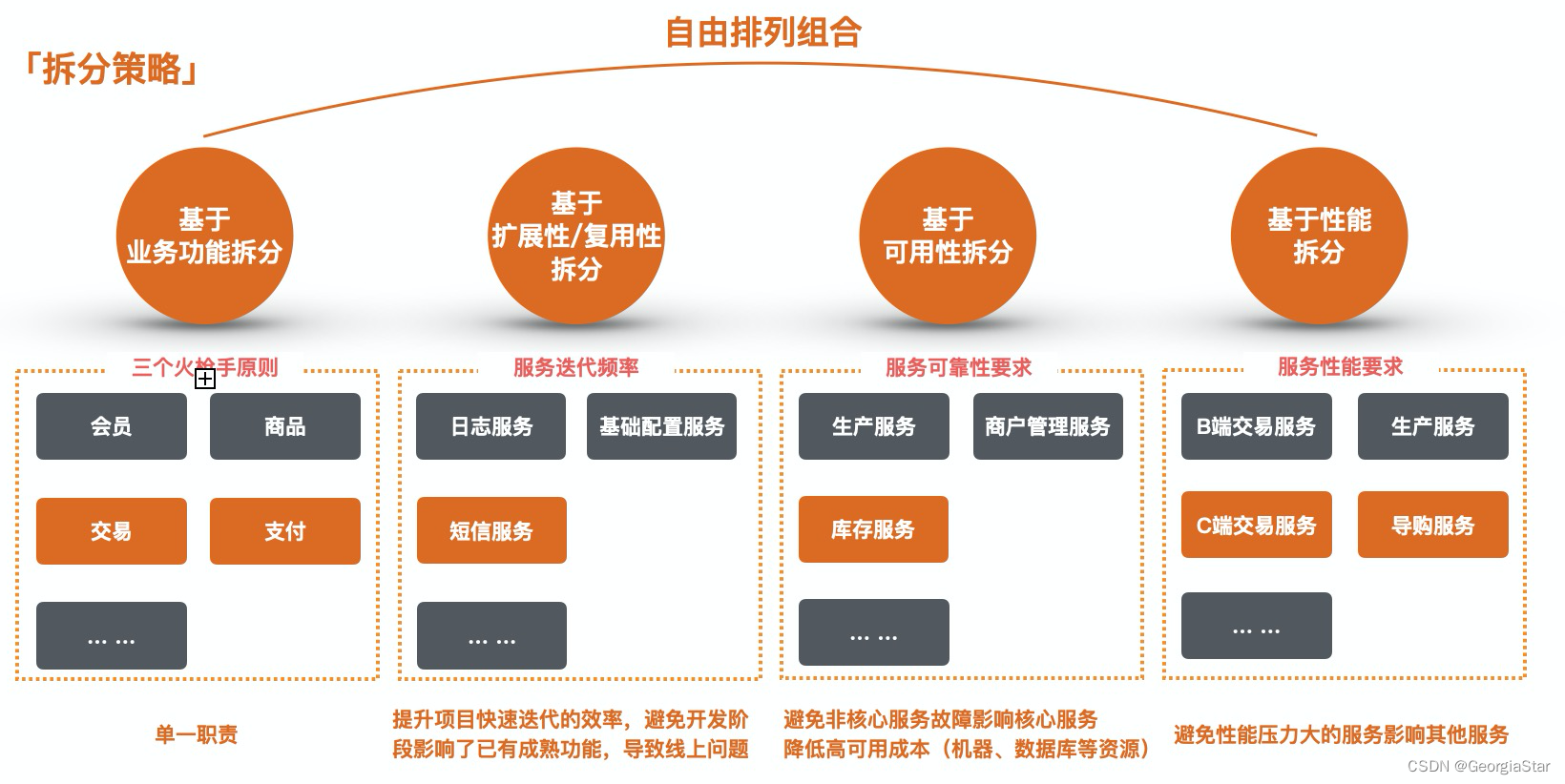
Microservice

2022.07.03(LC_6108_解密消息)

abc 258 G - Triangle(bitset)

图解网络:什么是网关负载均衡协议GLBP?
![[论文阅读] TUN-Det: A Novel Network for Thyroid Ultrasound Nodule Detection](/img/25/e2366cabf00e55664d16455a6049e0.png)
[论文阅读] TUN-Det: A Novel Network for Thyroid Ultrasound Nodule Detection

How to do the project of computer remote company in foreign Internet?
Learn C language from scratch day 024
随机推荐
微服务(Microservice)那点事儿
Tester's algorithm interview question - find mode
Face recognition 5- insight face padding code practice notes
分布式BASE理论
const、volatile和restrict的作用和用法总结
Hologres query management and timeout processing
leetcode518,377
abc 258 G - Triangle(bitset)
图解网络:什么是网关负载均衡协议GLBP?
JS convert pseudo array to array
AcWing164. 可达性统计(拓扑排序+bitset)
Kibana index, mapping, document operation
2022.07.03(LC_6109_知道秘密的人数)
Parsing of XML
Sorting selection sorting
ORB(Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF)
lambda表达式
P4408 [NOI2003] 逃学的小孩(树的直径)
Advanced template
Acwing164. Accessibility Statistics (topological sorting +bitset)