当前位置:网站首页>Mysql database (basic)
Mysql database (basic)
2022-07-07 04:59:00 【This is~】
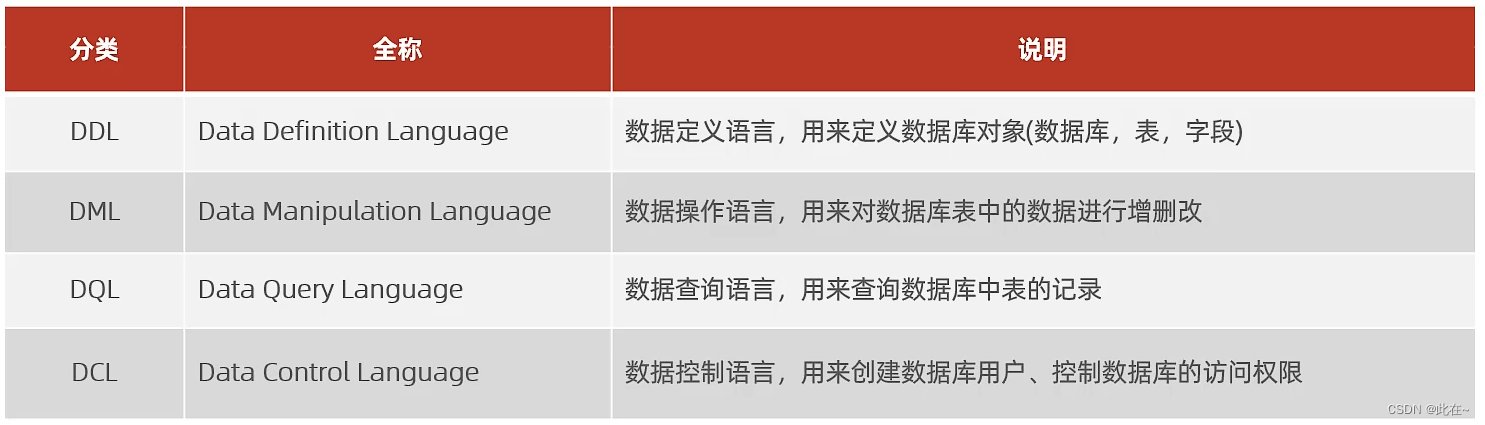
MySQL database
1.SQL
1.1 SQL General grammar and classification
1.1.1 SQL General grammar

1.1.2 SQL Sentence classification
1.2 SQL Common operations DDL
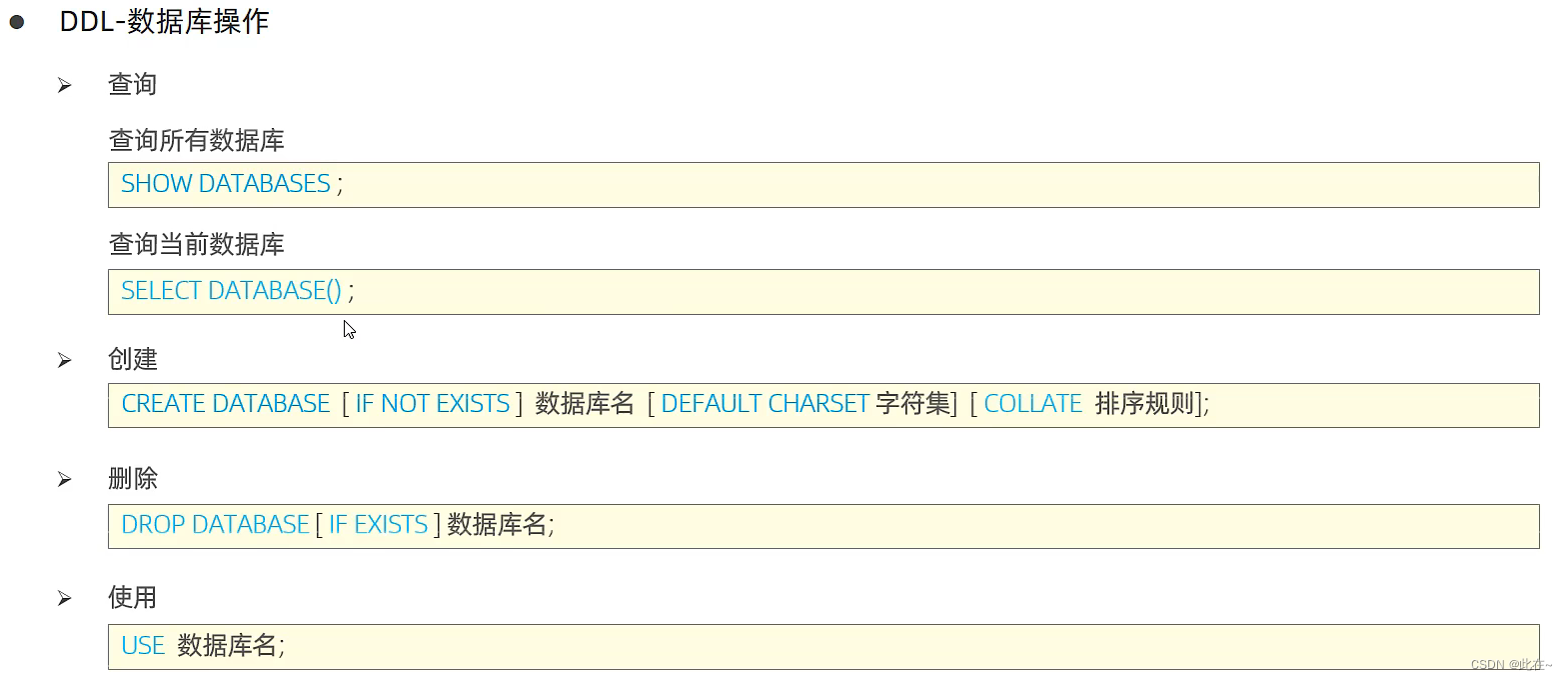
1.2.1 Database operation
1.2.2 Table operation creation & Inquire about


give an example : Establish the current database 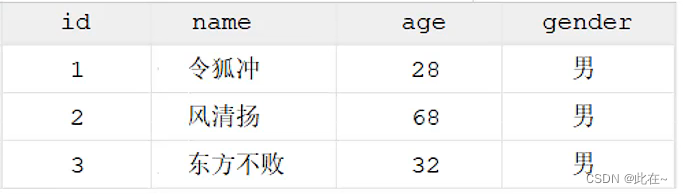
Explain :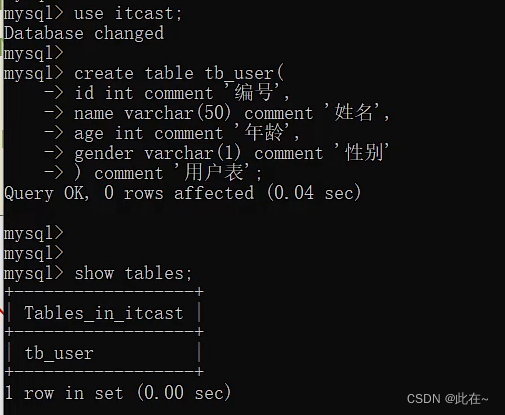
Look at the table structure 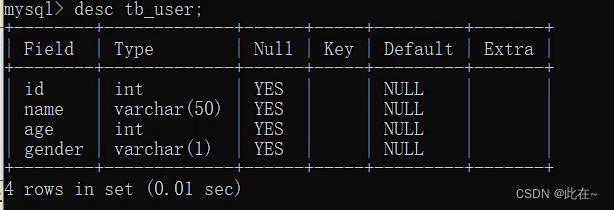
1.2.3 Data types and cases
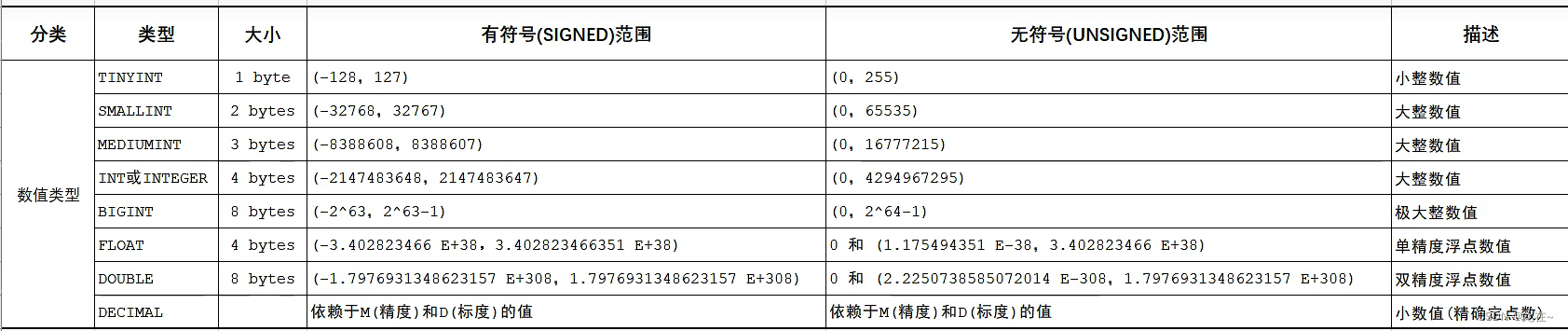
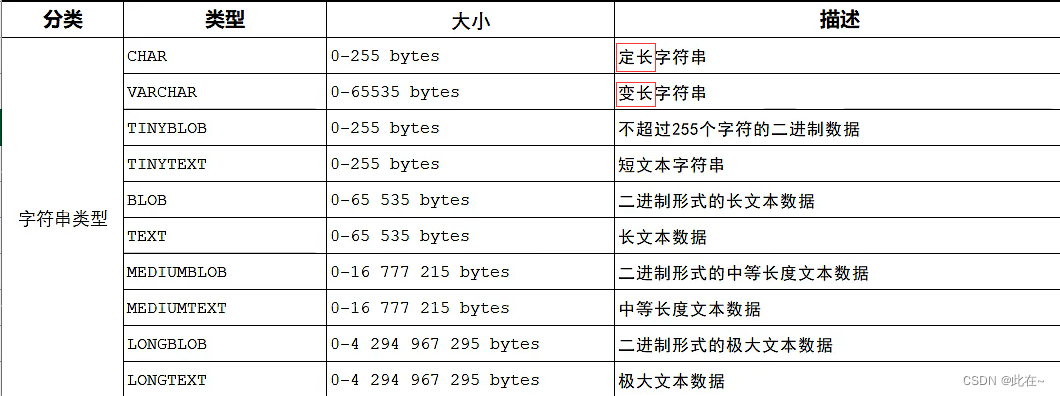
char Than varchar Higher performance
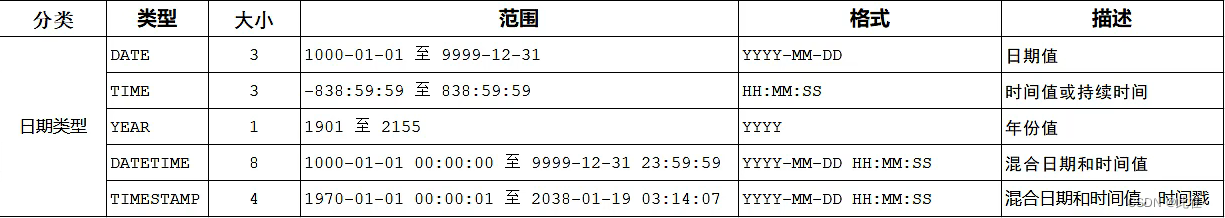
Case study :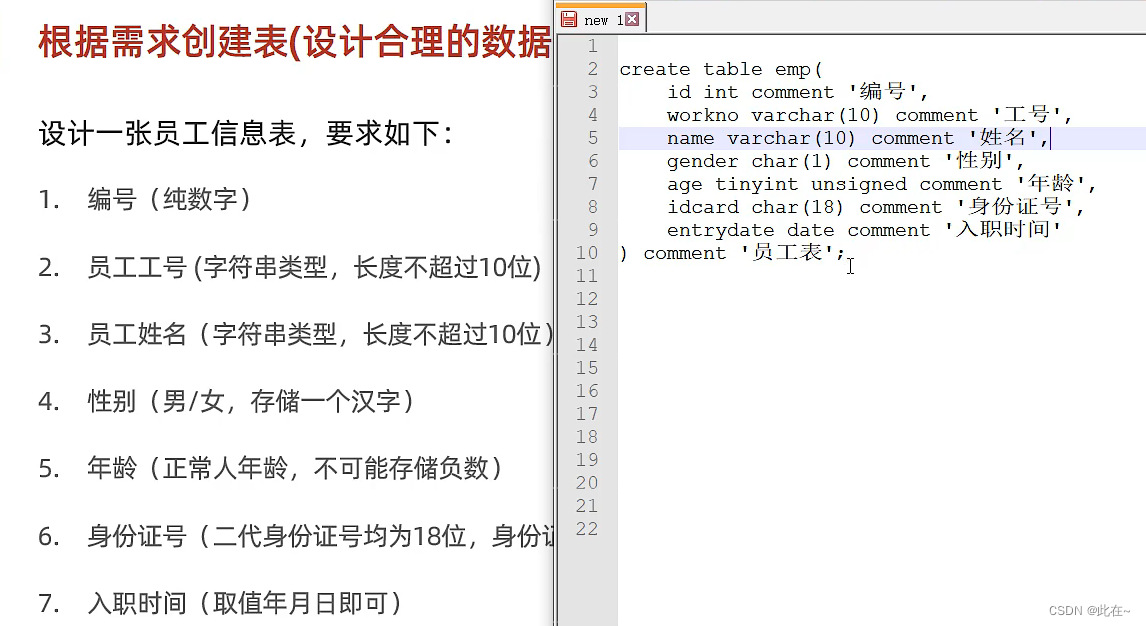
perform :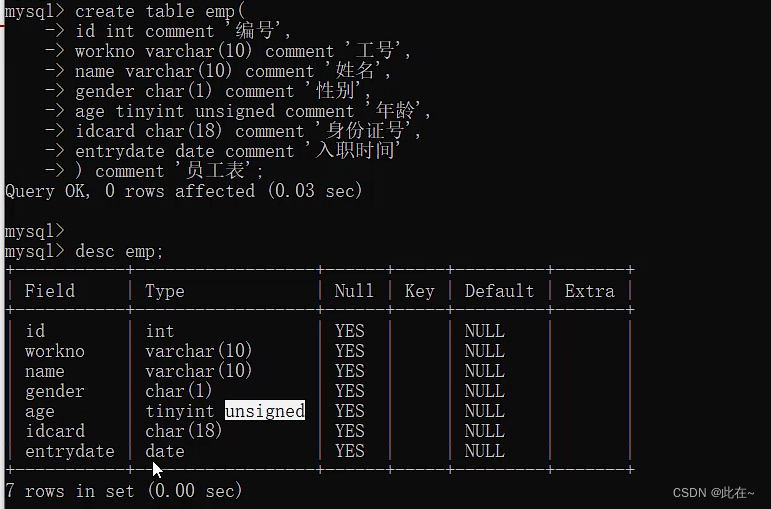
1.2.4 Table operation modification & Delete

Explain :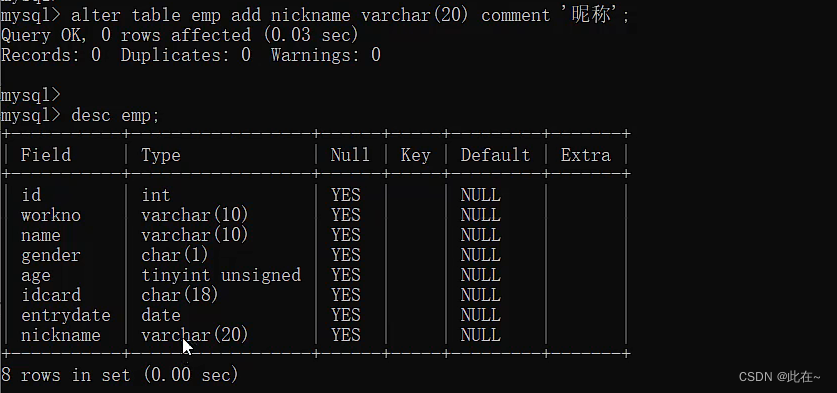

Explain :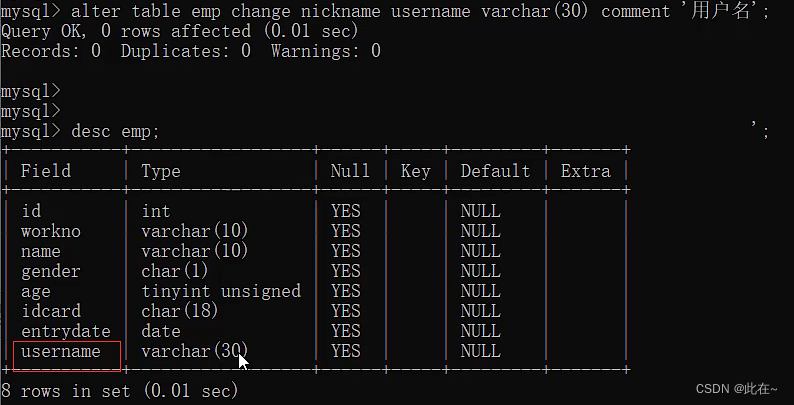

Explain :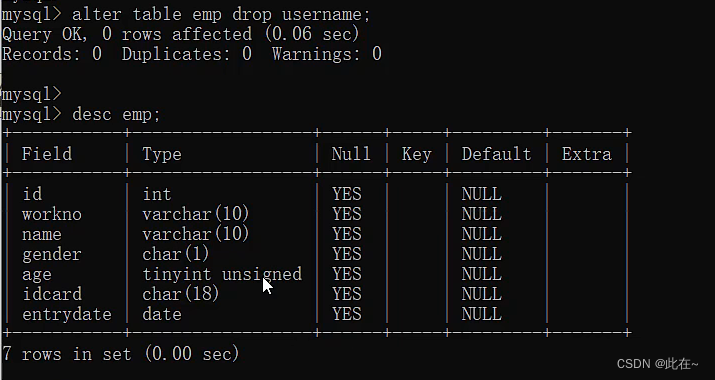
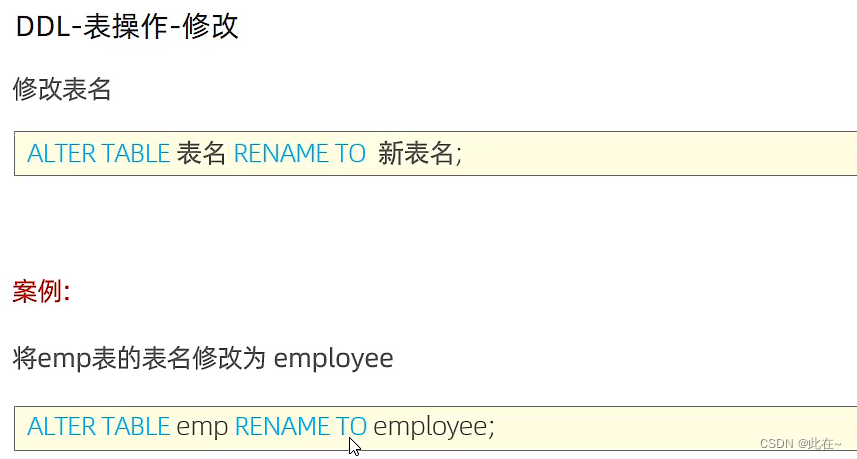
Explain :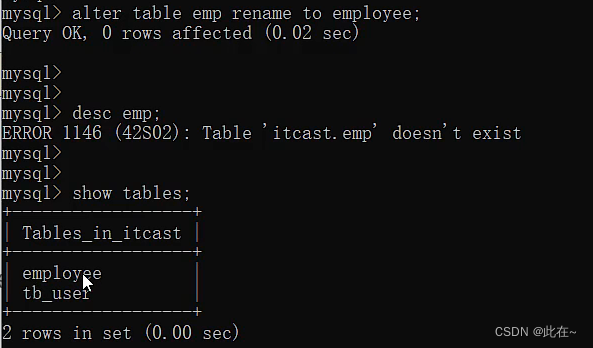

1.3 Database common operations DML

1.3.1 Insert
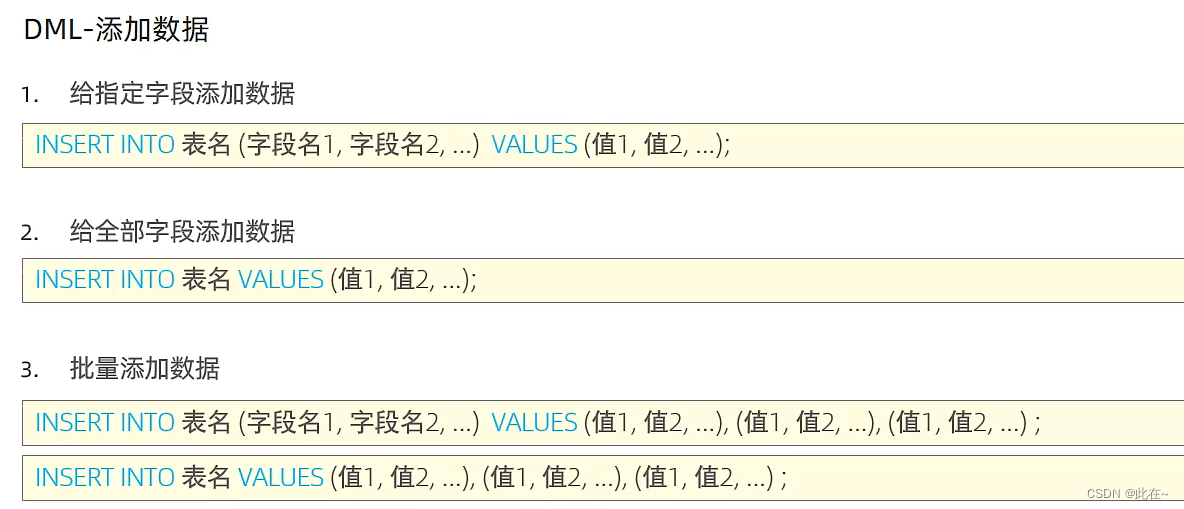
Be careful :
1.3.2 Update and delete

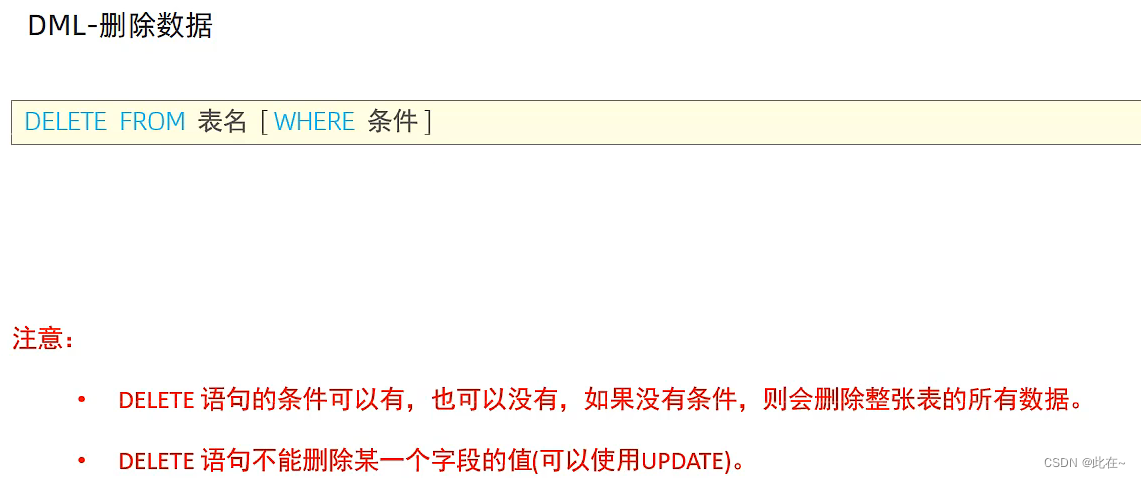
1.4 Data query —DQL


1.4.1 DQL Basic query

Try not to use select * from Table name ;, Don't even use all fields , Affect efficiency
1.4.2 DQL Conditions of the query

Conditions 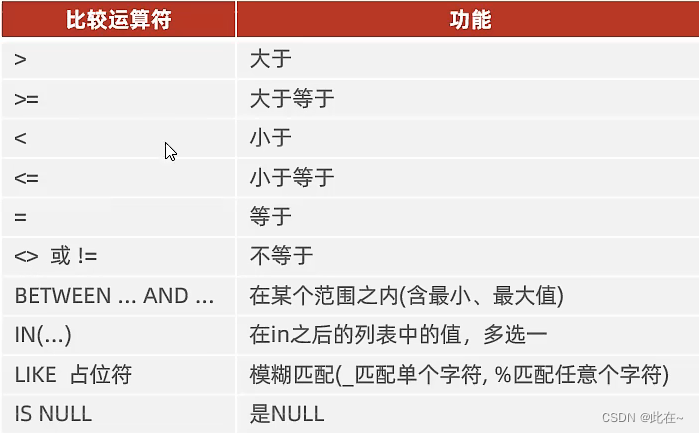
between…and… Must be small to capital 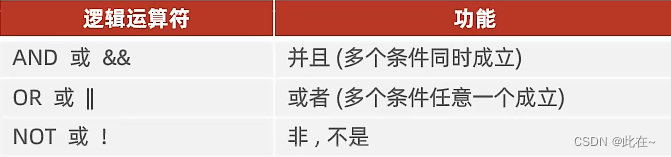
give an example :
-- Age equals 30
select * from employee where age = 30;
-- Age is less than 30
select * from employee where age < 30;
-- Less than or equal to
select * from employee where age <= 30;
-- No ID card
select * from employee where idcard is null or idcard = '';
-- Have ID card
select * from employee where idcard;
select * from employee where idcard is not null;
-- It's not equal to
select * from employee where age != 30;
-- Age 20 To 30 Between
select * from employee where age between 20 and 30;
select * from employee where age >= 20 and age <= 30;
-- The following statement does not report an error , But I can't find any information
select * from employee where age between 30 and 20;
-- The gender is female and the age is less than 30
select * from employee where age < 30 and gender = ' Woman ';
-- Age equals 25 or 30 or 35
select * from employee where age = 25 or age = 30 or age = 35;
select * from employee where age in (25, 30, 35);
-- The name is two words
select * from employee where name like '__';
-- The last ID card is X
select * from employee where idcard like '%X';
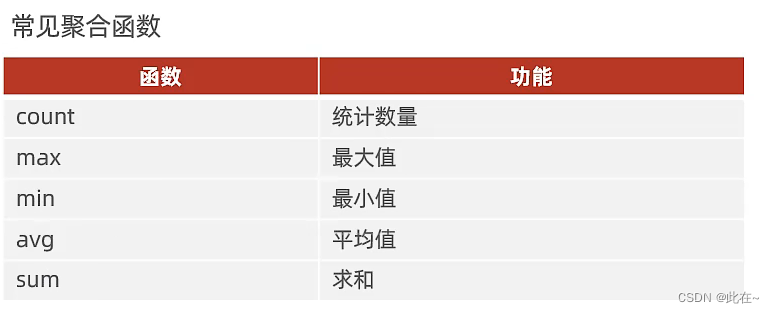
1.4.3 Aggregate functions


give an example :
-- The statistical address is employees in Guangdong Province
select count(id) from employee where workaddress = " Guangdong province, ";
-- Count the maximum age of employees
select max(age) from emp
1.4.4 Group query

-- Group by sex , Count the number of men and women ( Show only the number of groups ,
-- It doesn't show which is male and which is female )
select count(*) from employee group by gender;
-- Group by sex , Count the number of men and women
select gender, count(*) from employee group by gender;
-- Group by sex , Count the average age of men and women
select gender, avg(age) from employee group by gender;
-- Age is less than 45, And grouped according to the working address
select workaddress, count(*) from employee where
age < 45 group by workaddress;
-- Age is less than 45, And grouped according to the working address , Get the number of employees greater than or equal to 3 My work address
select workaddress, count(*) address_count from employee where
age < 45 group by workaddress having address_count >= 3;

1.4.5 Sort query

give an example :
-- Sort in ascending order by age
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY age ASC;
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY age;
-- Two field sorting , Sort in ascending order by age , If the age is the same, it will be sorted in descending order according to the entry time
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY age ASC, entrydate DESC;
1.4.6 Paging query

-- Query the data on the first page , Exhibition 10 strip
SELECT * FROM employee LIMIT 0, 10;
-- Check page two
SELECT * FROM employee LIMIT 10, 10;
1.4.7 DQL Execution order
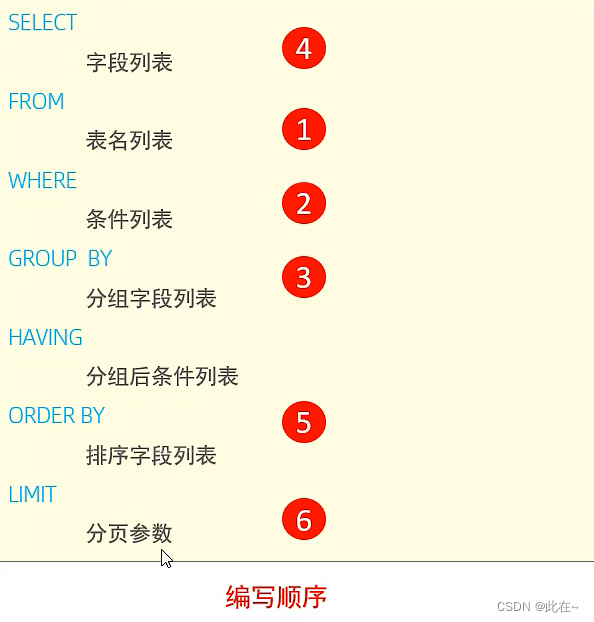
1.5 DCL Data control language

1.5.1 DCL Manage users
Query the user
USER mysql;
SELECT * FROM user;
Create user :
CREATE USER ' user name '@' Host name ' IDENTIFIED BY ' password ';
Change user password :
ALTER USER ' user name '@' Host name ' IDENTIFIED WITH
mysql_native_password BY ' New password ';
Delete user :
DROP USER ' user name '@' Host name ';
give an example :
-- Create user test, Only on the current host localhost visit
create user 'test'@'localhost' identified by '123456';
-- Create user test, Can be accessed from any host
create user 'test'@'%' identified by '123456';
create user 'test' identified by '123456';
-- Change Password
alter user 'test'@'localhost' identified with
mysql_native_password by '1234';
-- Delete user
drop user 'test'@'localhost';

1.5.2 DCL Access control
Common permissions 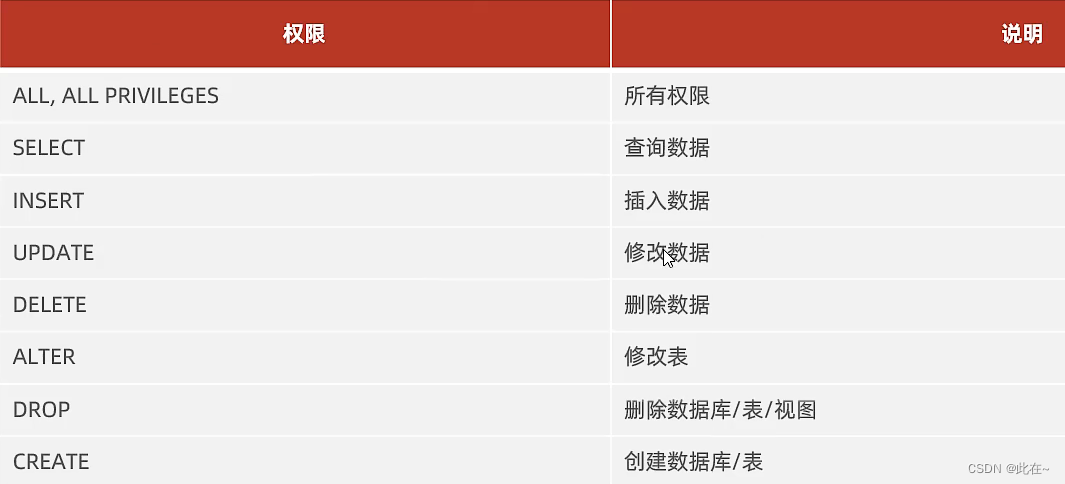
DCL - Access control
Query authority :
SHOW GRANTS FOR ' user name '@' Host name ';
Grant authority :
GRANT Permission list ON Database name . Table name TO ' user name '@' Host name ';
Revoke authority :
REVOKE Permission list ON Database name . Table name FROM ' user name '@' Host name ';

give an example :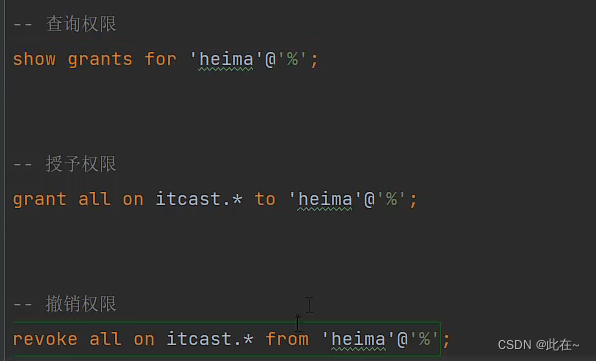
2. function
2.1 String function
Common functions :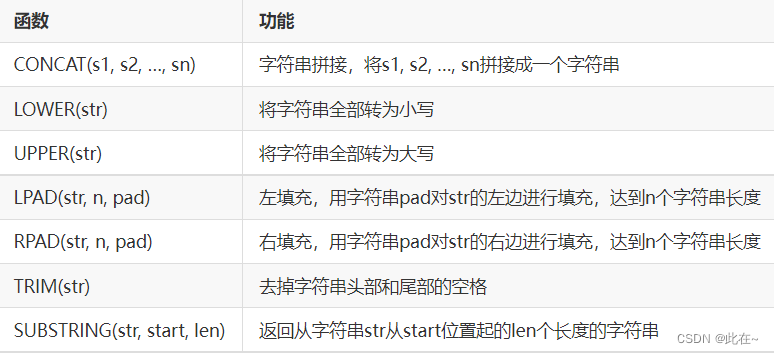
-- Splicing
SELECT CONCAT('Hello', 'World');
-- A lowercase letter
SELECT LOWER('Hello');
-- Capitalization
SELECT UPPER('Hello');
-- padding-left
SELECT LPAD('01', 5, '-');
-- Right fill
SELECT RPAD('01', 5, '-');
-- Remove the space
SELECT TRIM(' Hello World ');
-- section ( The starting index is 1)
SELECT SUBSTRING('Hello World', 1, 5);
2.2 Numerical function
Common numerical functions 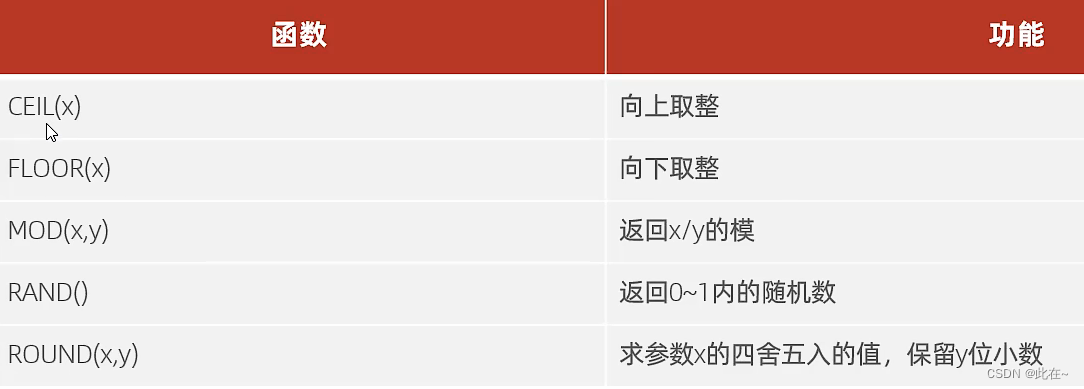

2.3 Date function
Common date functions
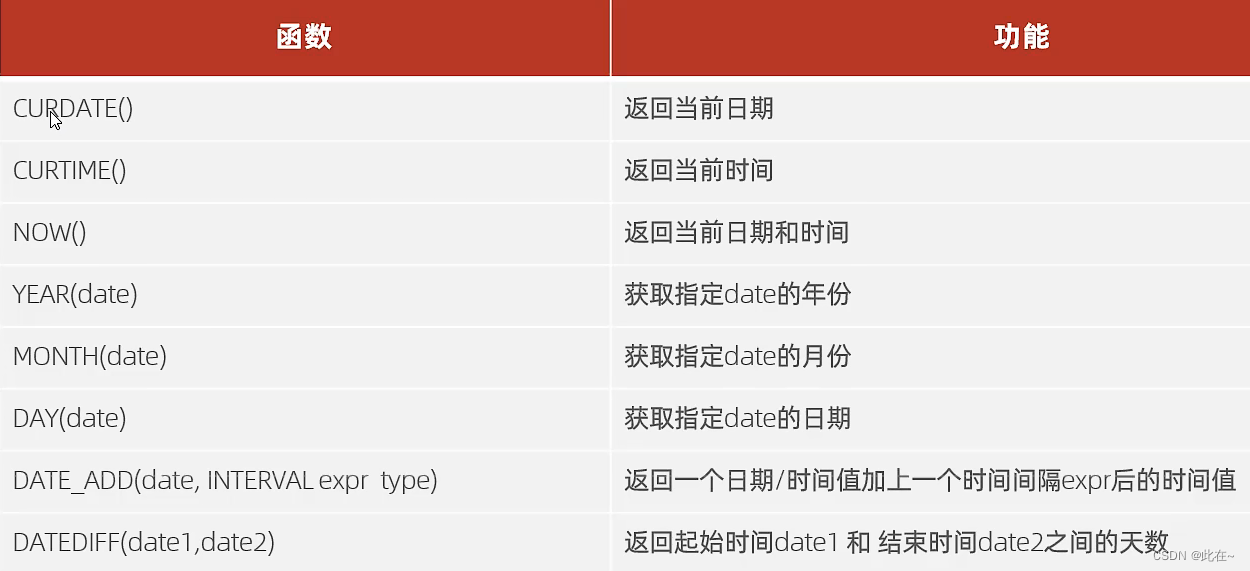
Case study :
2.4 Flow function
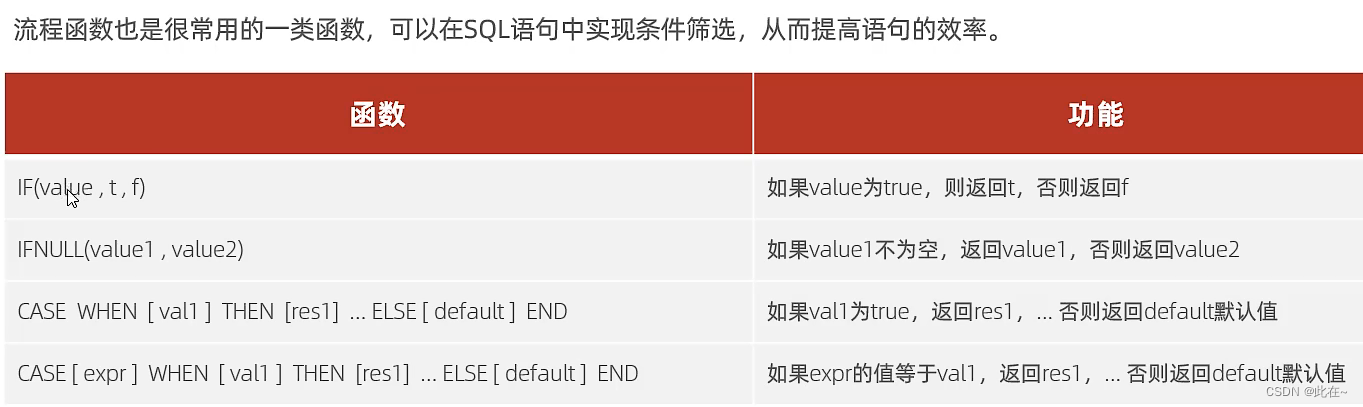
Case study 1
Case study 2
3. constraint
3.1 summary

classification :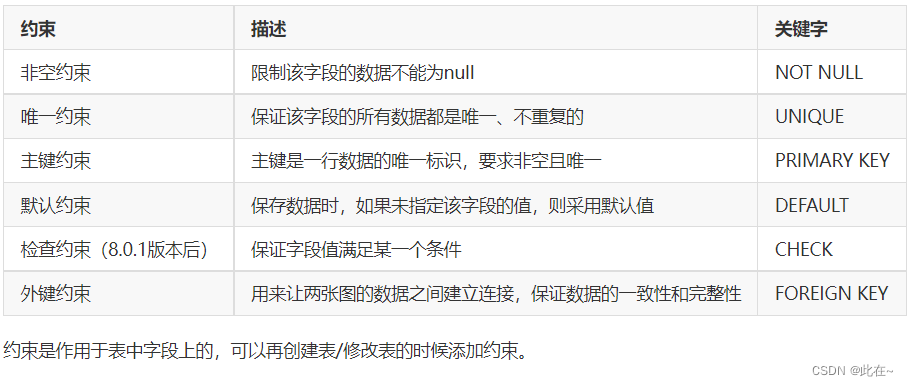
Case study :
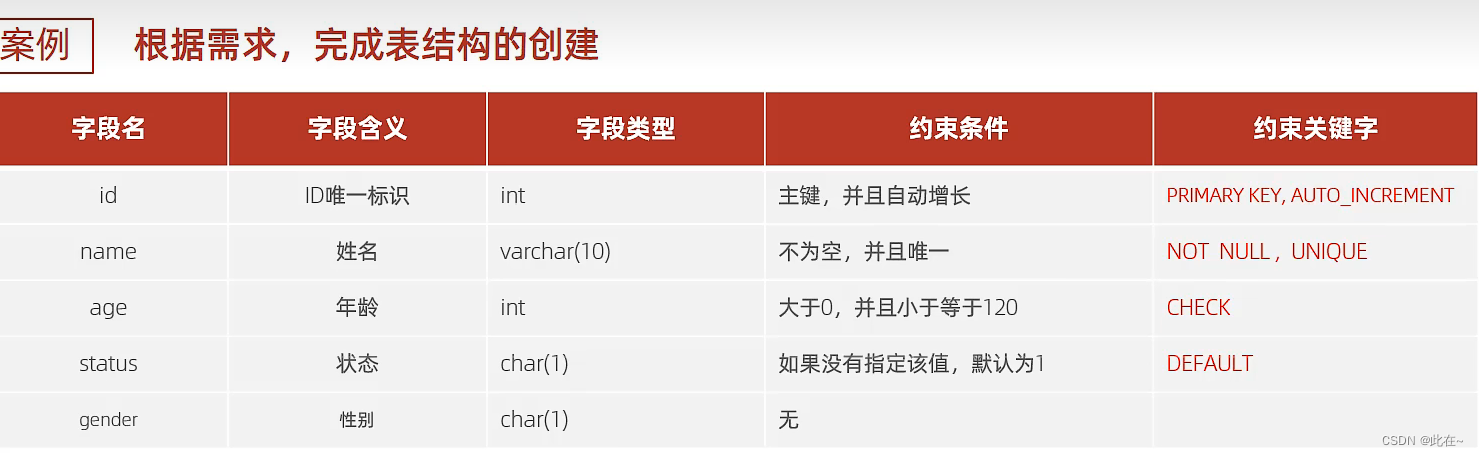
Explain :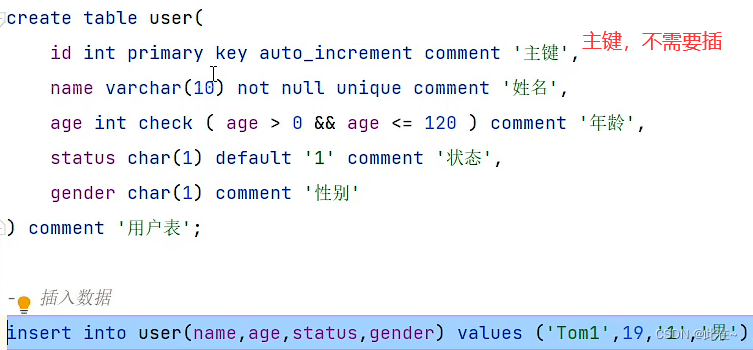
3.2 Foreign key constraints
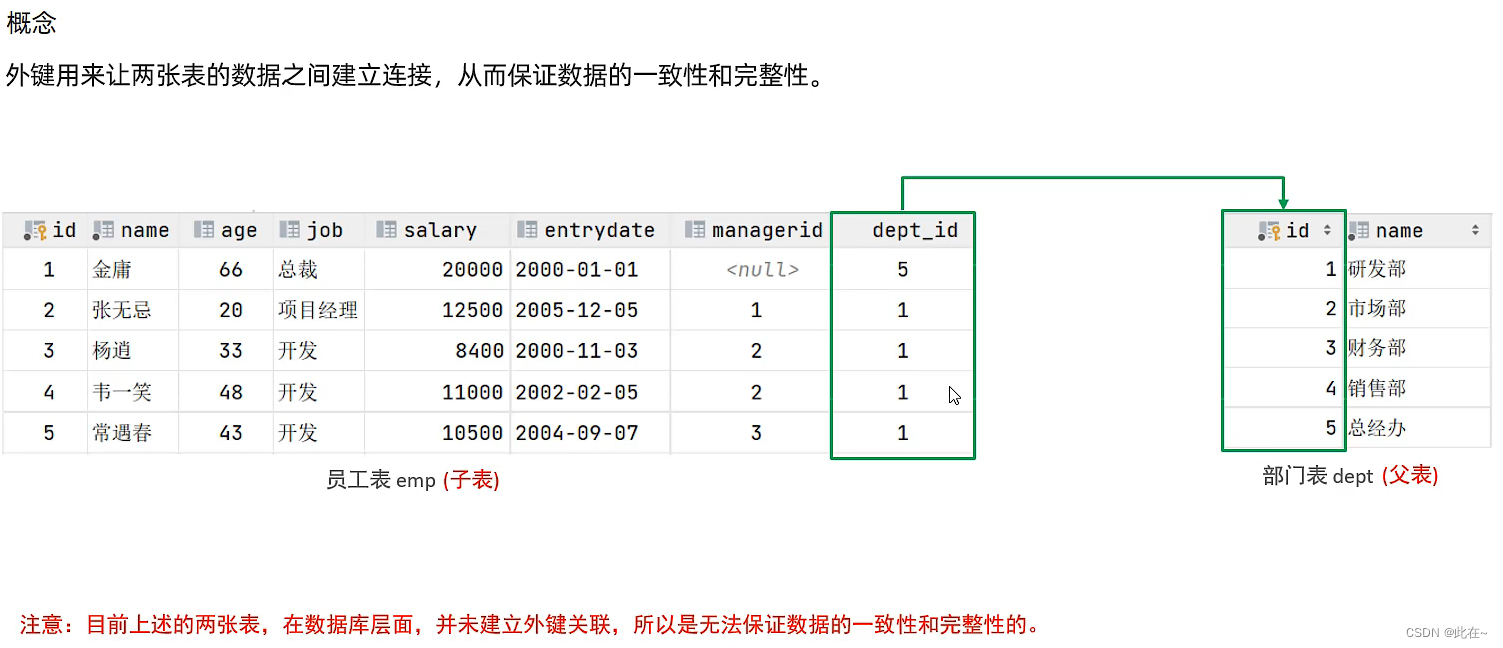

Add foreign keys
CREATE TABLE Table name (
Field name Field type ,
...
[CONSTRAINT] [ Name of the foreign key ] FOREIGN KEY( Foreign key field name ) REFERENCES Main table ( Name of main table )
);
ALTER TABLE Table name ADD CONSTRAINT Name of the foreign key FOREIGN KEY ( Foreign key field name ) REFERENCES Main table ( Name of main table );
– Example
alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key(dept_id) references dept(id);

ALTER TABLE Table name DROP FOREIGN KEY Foreign key name ;
3.3 Foreign key delete update behavior

Delete update behavior
ALTER TABLE Table name ADD CONSTRAINT Name of the foreign key FOREIGN KEY ( Foreign key field )
REFERENCES Main table name ( Main table field name ) ON UPDATE Behavior ON DELETE Behavior ;
4. Multi-table query
4.1 Multi table relation

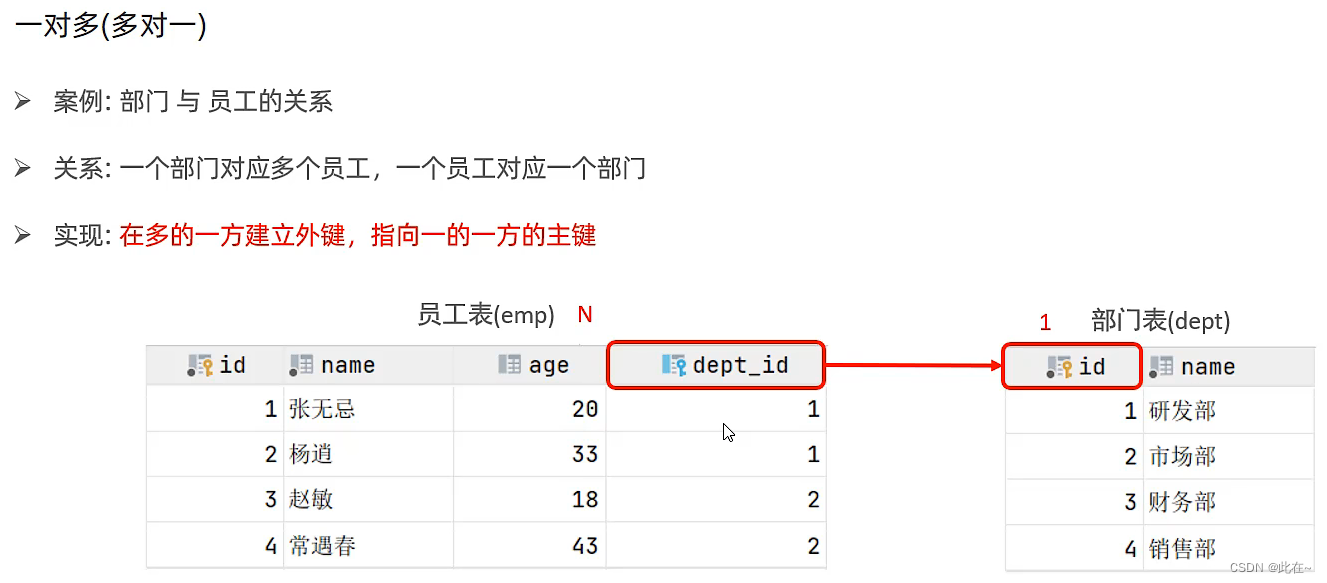
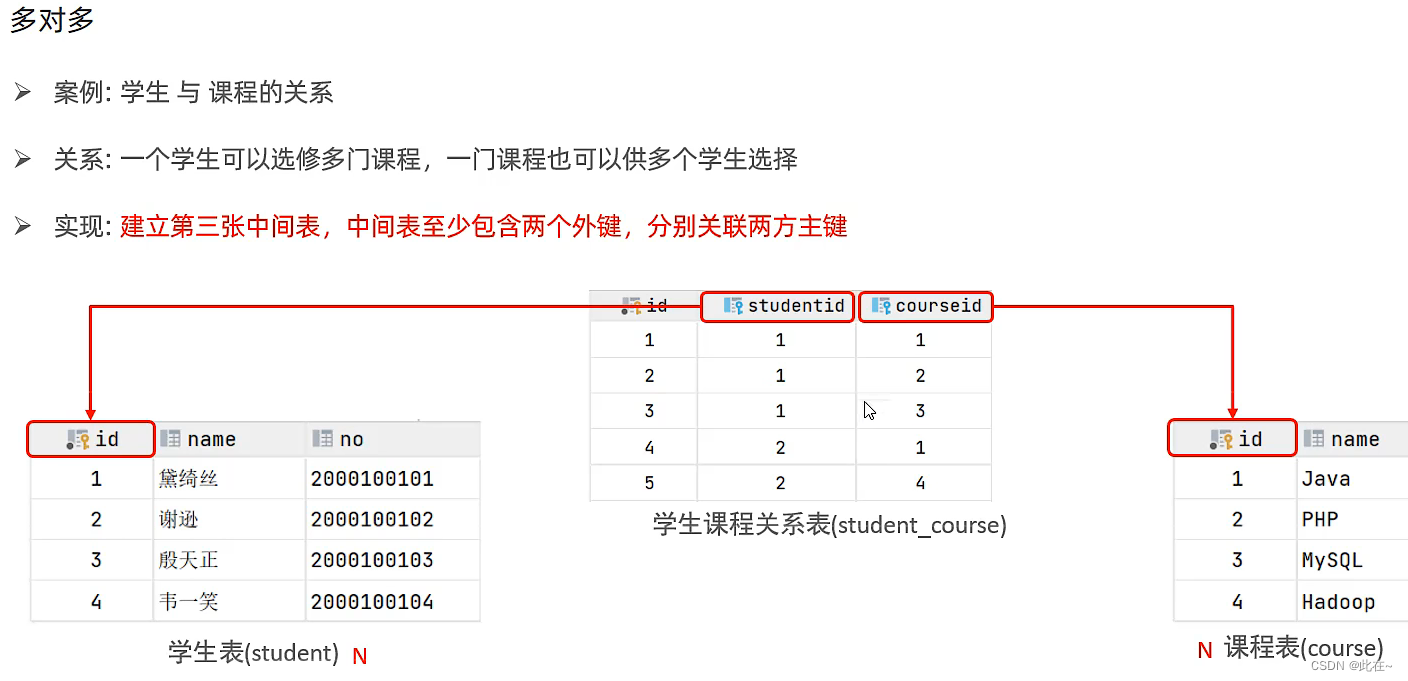
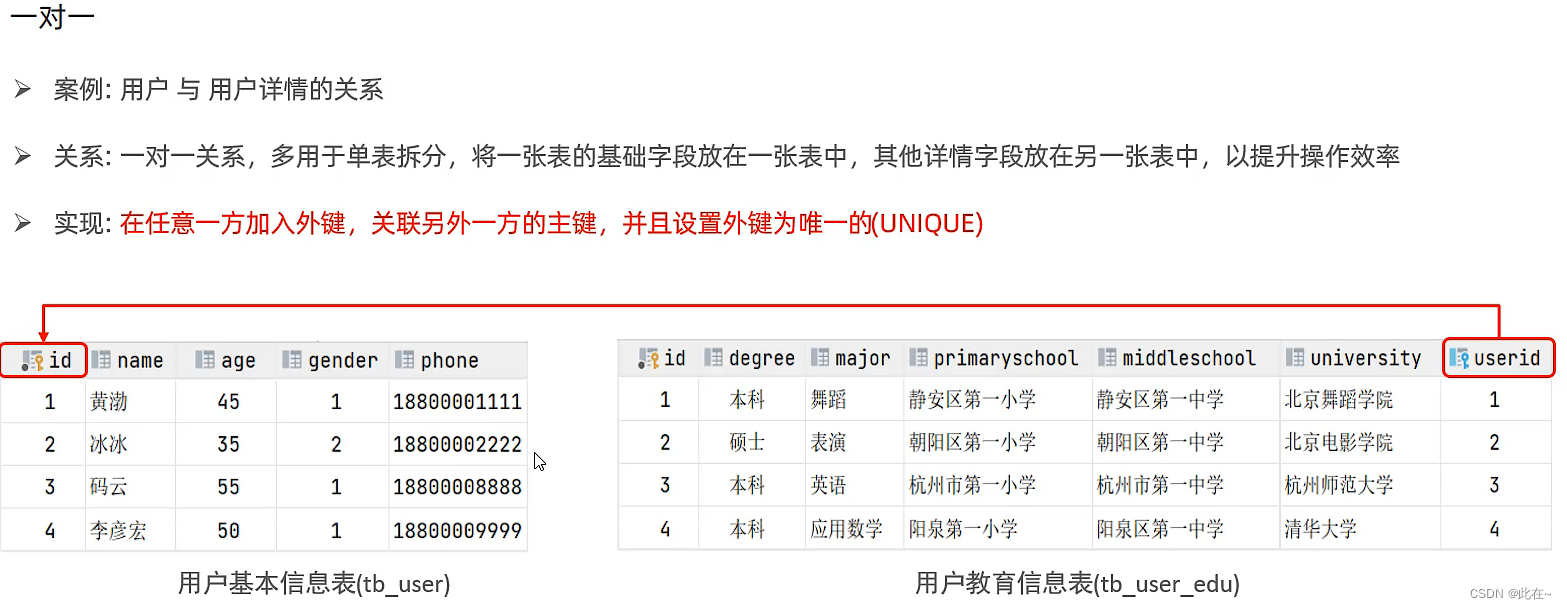
4.2 Overview of multi table query
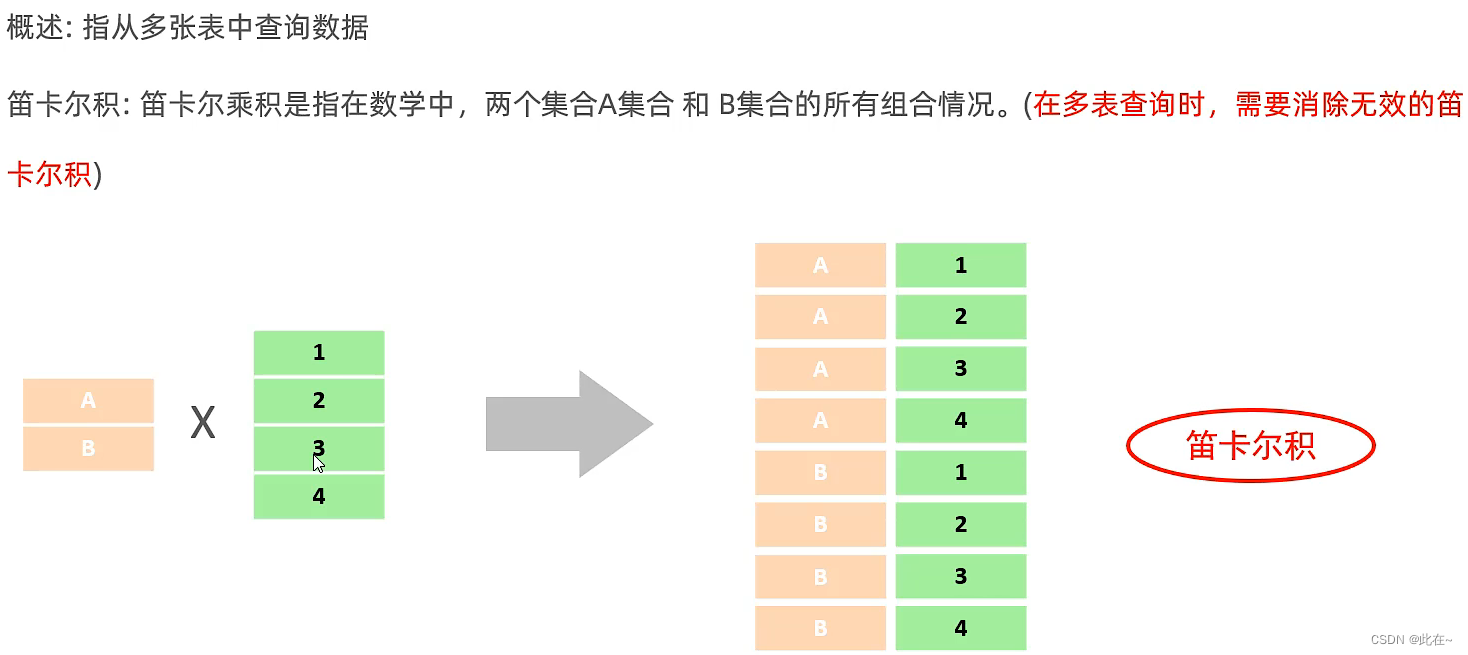
Merge query ( The cartesian product , Will show all the combined results )
select * from employee, dept;
Eliminate invalid Cartesian product : Use the corresponding connection table
select * from employee, dept where employee.dept = dept.id;

4.3 Internal connection
The inner join query is the part of the intersection of two tables
Implicit inner join
SELECT Field list FROM surface 1, surface 2 WHERE Conditions ...;
Display inner connection
SELECT Field list FROM surface 1 [ INNER ] JOIN surface 2 ON Connection condition ...;
Explicit performance is better than implicit


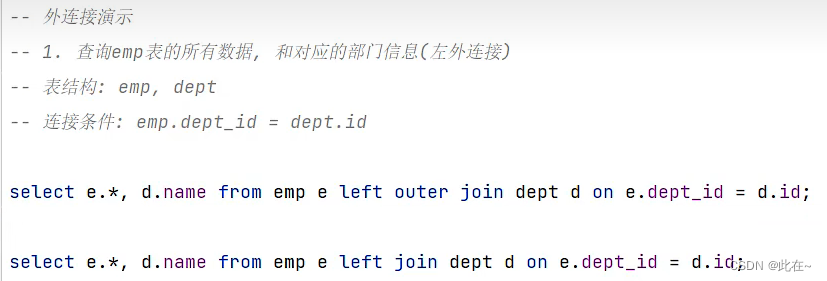
4.4 External connection

The left outer join :
Query all data in the left table , And the intersection of two tables
SELECT Field list FROM surface 1 LEFT [ OUTER ] JOIN surface 2 ON Conditions ...;
Equivalent to query table 1 All data for , Include table 1 And table 2 Intersection part data
Right connection :
Query all data in the right table , And the intersection of two tables
SELECT Field list FROM surface 1 RIGHT [ OUTER ] JOIN surface 2 ON Conditions ...;

4.5 Self join
Query the connection between the current table and itself , Self join must use table alias
grammar :
SELECT Field list FROM surface A Alias A JOIN surface A Alias B ON Conditions ...;
Self connect query , It can be internal connection query , It can also be an external connection query
give an example :

4.6 The joint query union,union all

grammar :
SELECT Field list FROM surface A ...
UNION [ALL]
SELECT Field list FROM surface B ...
give an example :
Be careful :
UNION ALL There will be duplicate results ,UNION Can't Joint queries are better than using or Efficient , Will not invalidate the index
4.7 Subquery

4.7.1 Scalar subquery

give an example :
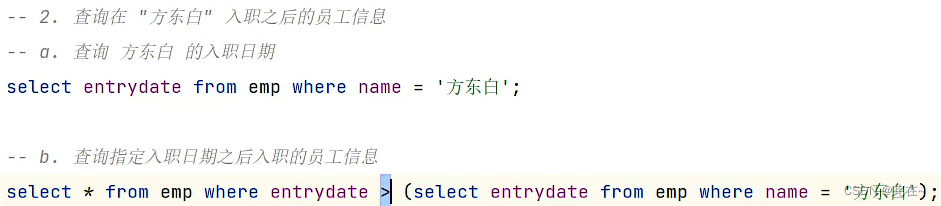
4.7.2 Column query
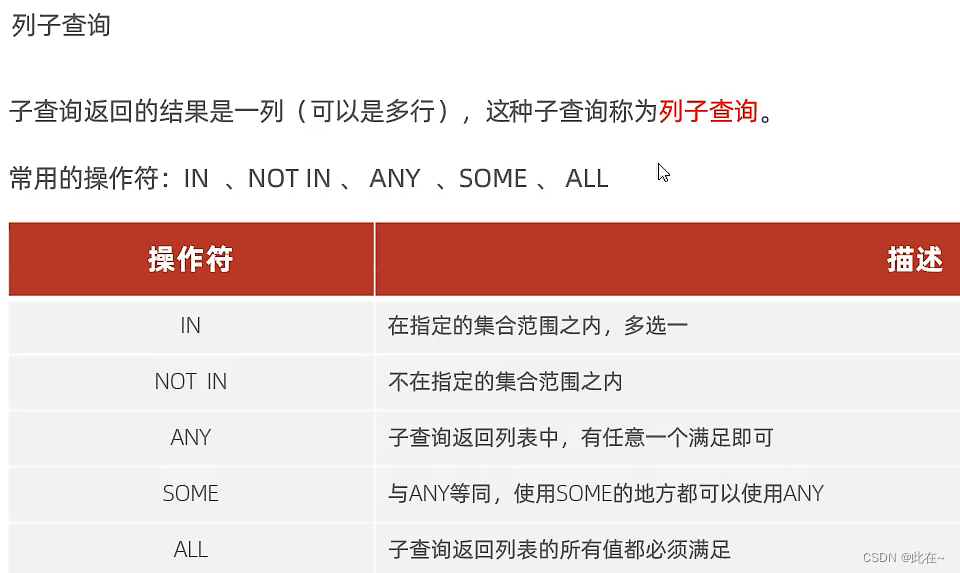
give an example :
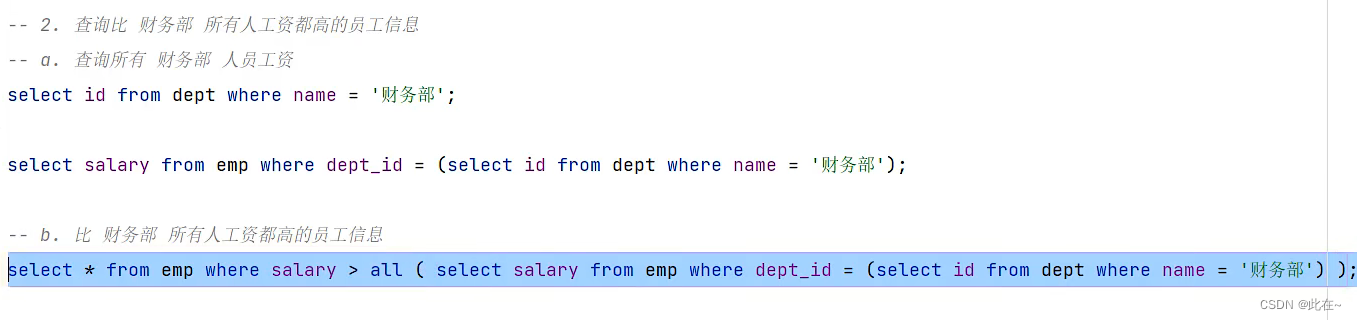

4.7.3 Line sub query

give an example :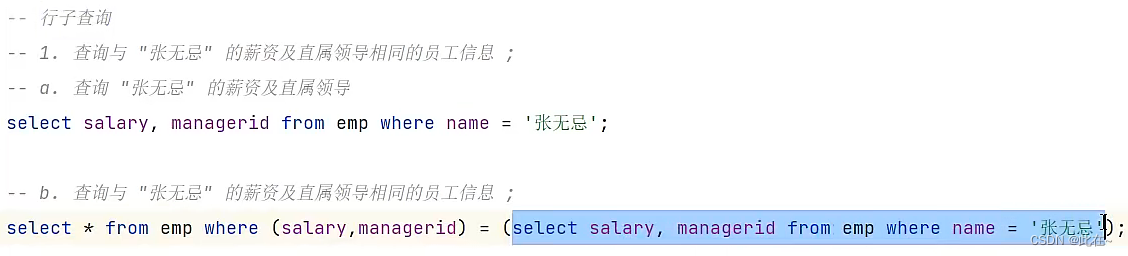
4.7.4 Table sub query

give an example 1.
give an example 2.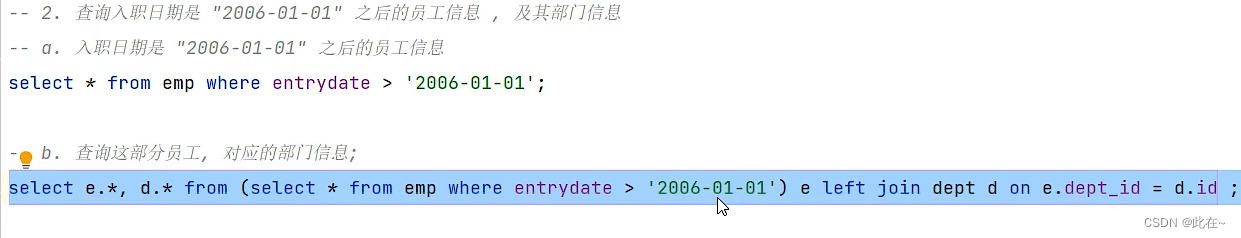
5. Business
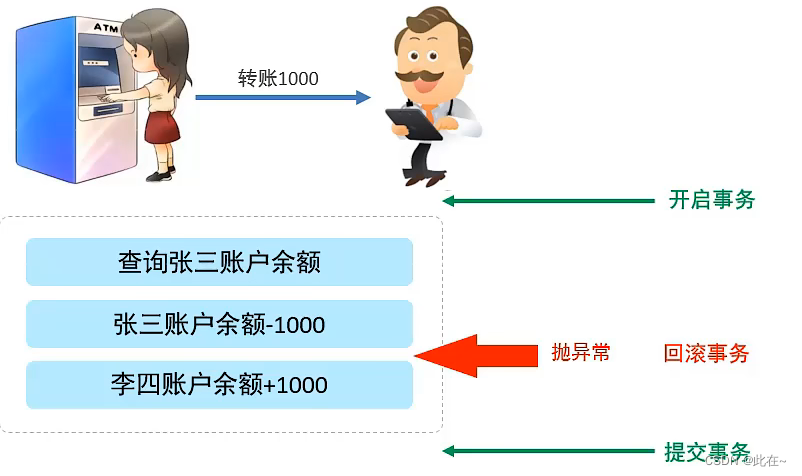
Business Is a collection of operations , The transaction will submit or revoke the operation request to the system as a whole , That is, these operations Or at the same time , Or fail at the same time .

5.1 Commit transaction
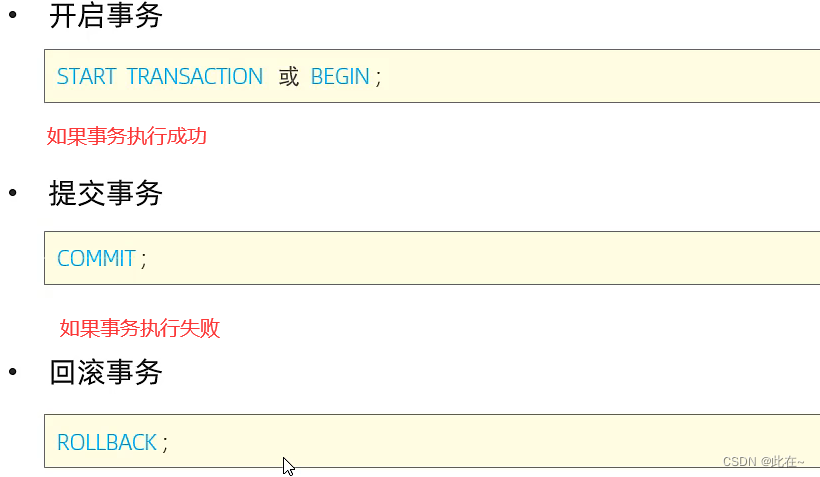
Mode one :
Mode two :
Basic operation :
-- 1. Check Zhang San's account balance
select * from account where name = ' Zhang San ';
-- 2. The balance of three accounts -1000
update account set money = money - 1000 where name = ' Zhang San ';
-- After this statement goes wrong, Zhang San Qian decreases, but Li Si qian does not increase
simulation sql sentence in wrong
-- 3. Transfer the balance of Li Si's account +1000
update account set money = money + 1000 where name = ' Li Si ';
-- ***************** I'm the dividing line *********************
-- View transaction submission method
SELECT @@AUTOCOMMIT;
-- Set the transaction submission method ,1 For automatic submission ,0 For manual submission , This setting is only valid for the current session
SET @@AUTOCOMMIT = 0;
-- Commit transaction
COMMIT;
-- Roll back the transaction
ROLLBACK;
-- After setting manual submission, the above code is changed to :
select * from account where name = ' Zhang San ';
update account set money = money - 1000 where name = ' Zhang San ';
update account set money = money + 1000 where name = ' Li Si ';
commit;
Mode two :
-- Open transaction
start transaction;
select * from account where name = ' Zhang San ';
update account set money = money - 1000 where name = ' Zhang San ';
update account set money = money + 1000 where name = ' Li Si ';
-- Commit transaction
commit;
-- Roll back the transaction
rollback;
5.2 Four characteristics of transactions ACID
- Atomicity (Atomicity): Transaction is an indivisible minimum operation , All or nothing , All or nothing
- Uniformity (Consistency): When the transaction completes , All data must be kept in a consistent state
- Isolation, (Isolation): The isolation mechanism provided by the database system , Ensure that transactions run in an independent environment that is not affected by external concurrent operations
- persistence (Durability): Once a transaction is committed or rolled back , Its changes to the data in the database are permanent ( disk )
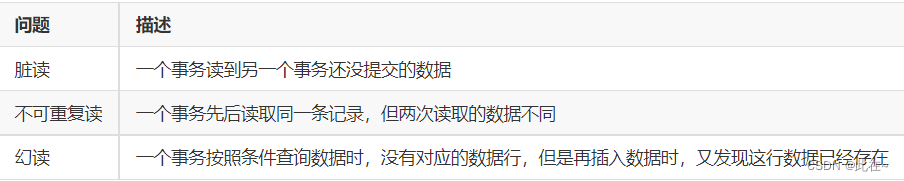
5.3 Concurrent transaction problems
5.4 Concurrent transaction demonstration and isolation level
Concurrent transaction isolation level
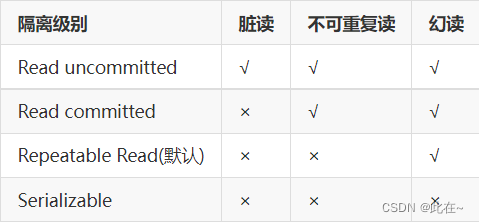
√ Indicates that the problem will occur at the current isolation level
- Serializable Lowest performance ;
- Read uncommitted The highest performance , Data security is the worst
- Higher isolation level , The worse performance , The more secure
View transaction isolation level :SELECT @@TRANSACTION_ISOLATION;
Set the transaction isolation level :SET [ SESSION | GLOBAL ] TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL {READ UNCOMMITTED | READ COMMITTED | REPEATABLE READ | SERIALIZABLE };
SESSION It's the conversation level , Indicates that it is valid only for the current session ,GLOBAL Indicates that it is valid for all sessions
边栏推荐
- 组织实战攻防演练的5个阶段
- Depth first traversal template principle of tree and graph
- 一文搞懂常见的网络I/O模型
- In depth analysis of kubebuilder
- 深入解析Kubebuilder
- Servicemesh mainly solves three pain points
- Inventory host list in ansible (I wish you countless flowers and romance)
- Ansible reports an error: "MSG": "invalid/incorrect password: permission denied, please try again“
- JS variable
- leetcode 53. Maximum subarray maximum subarray sum (medium)
猜你喜欢

Why do many people misunderstand technical debt

动态生成表格
Vscode 如何使用内置浏览器?
Depth first traversal template principle of tree and graph

Common Oracle SQL statements

How does vscade use the built-in browser?
Introduction to namespace Basics
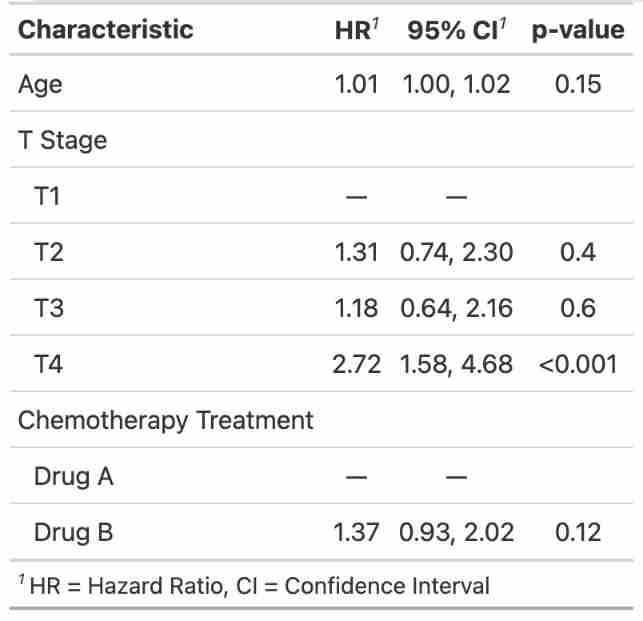
A row of code r shows the table of Cox regression model
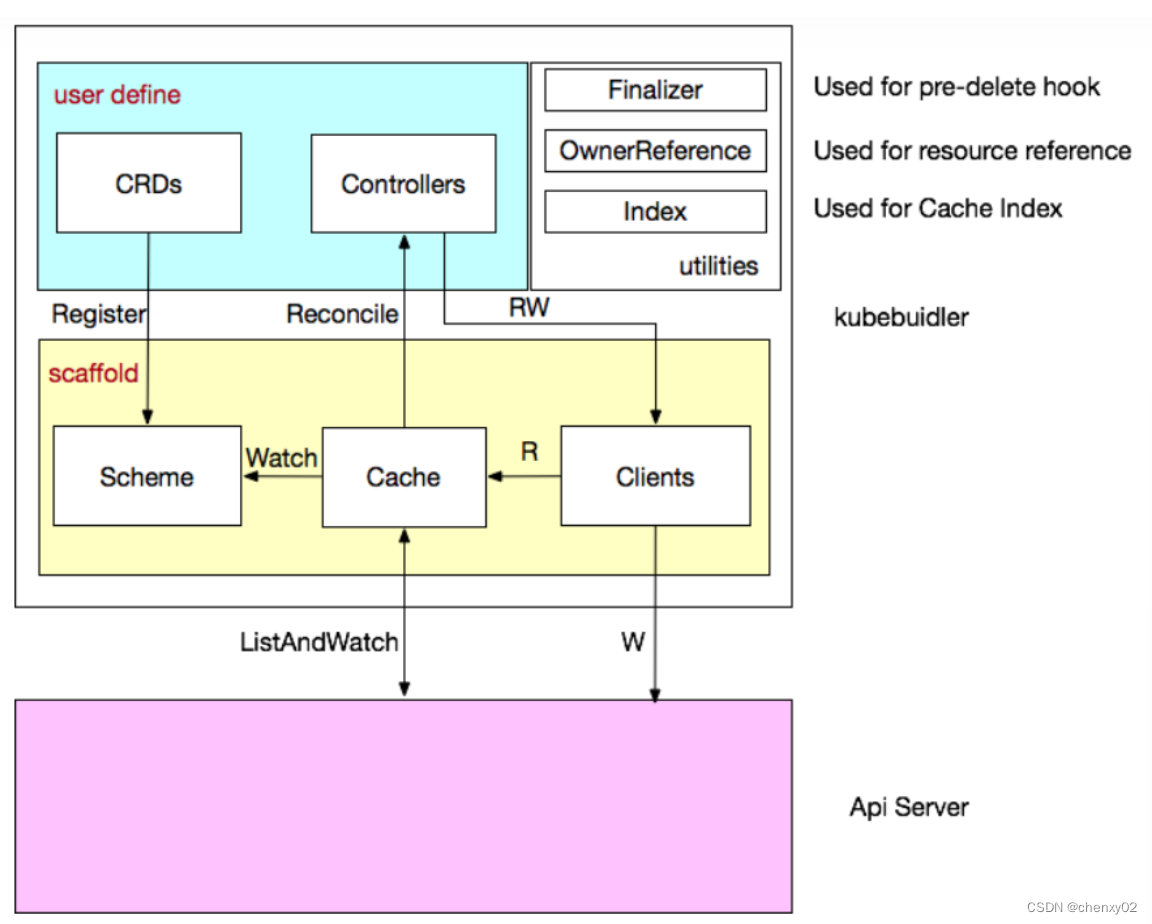
深入解析Kubebuilder
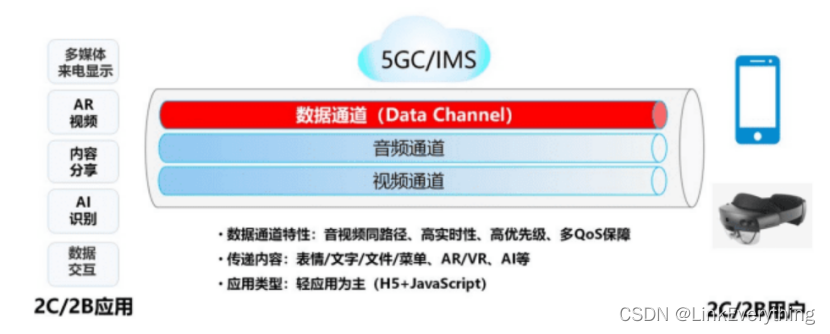
5G VoNR+之IMS Data Channel概念
随机推荐
A line of R code draws the population pyramid
Function pointer and pointer function in C language
窗口可不是什么便宜的东西
谈谈讲清楚这件事的重要性
ServiceMesh主要解决的三大痛点
Terms used in the Web3 community
Appium practice | make the test faster, more stable and more reliable (I): slice test
Talk about the importance of making it clear
全国气象数据/降雨量分布数据/太阳辐射数据/NPP净初级生产力数据/植被覆盖度数据
【Android Kotlin协程】利用CoroutineContext实现网络请求失败后重试逻辑
树与图的深度优先遍历模版原理
Time complexity & space complexity
Is there any way to bookmark the code in the visual studio project- Is there a way to bookmark code in a Visual Studio project?
R language principal component PCA, factor analysis, clustering analysis of regional economy analysis of Chongqing Economic Indicators
STM32 system timer flashing LED
sscanf,sscanf_ S and its related usage "suggested collection"
深入解析Kubebuilder
The worse the AI performance, the higher the bonus? Doctor of New York University offered a reward for the task of making the big model perform poorly
架构实战训练营|课后作业|模块 6
Flask project uses flask socketio exception: typeerror: function() argument 1 must be code, not str