当前位置:网站首页>Read the basic grammar of C language in one article
Read the basic grammar of C language in one article
2022-07-05 17:05:00 【Embedded universe】
List of articles
Preface —— sketch C History of language development
C The development of language can be traced back to 1972 year . His creation is due to writing Unix Operating system ,Unix The operating system was originally written in assembly language , The biggest advantage of assembly language is that the code runs fast . But its shortcomings are also very obvious , That is, if the code goes wrong, debugging is difficult , The biggest problem is due to poor code portability , Cannot cross platform , Because some instructions of assembly language are strongly related to the platform . This obviously reduces efficiency , And it gets in the way of Unix The development of . And then there was B Language , however B Language also has some limitations , And with Unix The great development of , Make in B Developed on the basis of language C Language . Let's remember such a great man ,C The father of language —— Dennis · Ricci (Dennis Ritchie) .
after one's words C After a brief history of language, we will proceed C The basic grammar of language introduces !
One 、 Start with a program ——Hello World
We go straight through a Hello World Program to introduce our grammar .hello world Program can be said to be a convention of programming language, commonly known as .hello world Which translates as Hello world , In fact, it is a greeting to the world , Tell the world , I'm coming . Actually, write this hello world Another meaning of the program is that as long as the program can run normally, it means that there is no problem with its local running environment , So when you learn any programming language, you can try hello world This program !
Source code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}
Running results :
Hello World!
The code above is very simple , Is to print a sentence to the screen terminal " hello world! " .
Now let's analyze it :
(1)#include<stdio.h> : This is actually a standard library file , There are many standard functions in this standard library file , By introducing this library file, we can use the functions inside .
(2)int main(){} : Here is the definition of a return value of int Type variable main function , It is worth noting that all of us C The programs are all from main Function starts to run , And to main After running . In other words, as long as it is C The program must be defined main function .
(3)printf(“Hello World!\n”); : The function of this sentence is to output a hello world.printf() Namely stdio.h A function inside , We will explain his function in detail in the following article .
(4)return 0; : Function return value , The type of the return value should be consistent with the first type of the function .
Two 、C Basic grammar of language
1. Constants and variables
Constant , As the name suggests, it is a constant quantity , image 1, 2, 3, 1.1, -100 Wait, such numbers are constants , And we cannot assign values to constants .
Variable , As the name suggests, it is the amount of change , To define variables, we usually assign data types to variables , Such as char a; int b; ( Define character variables a, Define shaping variables b). And variables can be assigned .
2. data type
When defining variables , We usually assign data types to them , Next we will introduce C The data type of the language .
Basic data type :
char : Character . yes signed char Shorthand for type , That is, signed character type , Abbreviation character type . Take up a byte in memory , Range of values -128~127.
unsigned char : No sign character type . In memory 1 Bytes , Range of values 0~255. A character is a character enclosed in single quotation marks . It should be noted that , There can be at most one character in a single quotation mark .
short : Short . yes signed short Shorthand for type , That is, signed short integer , Short integer . In memory 2 Bytes , Range of values -32768~32767.
unsigned short : Unsigned short . In memory 2 Bytes , Range of values 0~65535.
int : integer . yes signed int Shorthand for type , That is, signed integer , It's called integer for short . In memory 4 Bytes (16 Bit and below are 2 byte ), Range of values -2147483648~2147483647.
unsigned int : Unsigned integer . In memory 4 Bytes (16 Bit and below are 2 byte ), Range of values 0~4294967295.
long : Long integer . yes signed long Shorthand for type , That is, signed long integer , Short for long integer . In memory 4 Bytes (64 In a bit operating system, it's 8 byte ).
unsigned log: Unsigned long . In memory 4 Bytes (64 In a bit operating system, it's 8 byte ).
long long: Long plastic surgery , In memory 8 Bytes .
float : Single precision floating point , In memory 4 byte .
double : Double precision floating point , In memory 8 byte .
Empty type :
void : Empty type , In memory 1 byte .
Construct data types :
Array : Such as char buf[10]; It can store multiple data of the same type .
Structure : struct, It can store multiple data of different types .
Shared body : union, It can store multiple data of different types , The data in the community share the same address space .
Pointer types :
* : for example char* int* etc. , Pointer type size 32 The bit operating system is always 4 byte , 64 Bit operation is 8 byte .
3. keyword
C The keywords of the language are 32 individual , These keywords are already defined , We can't change it at will , And these keywords have their special significance .
void : Declares that the function returns no value or takes no arguments , Declare no type pointer ( Basically, these three functions )
char : Declare character type variables or functions
short : Declare short integer variables or functions
int : Declare an integer variable or function
long : Declare long integer variables or functions
float : Declare floating-point variables or functions
double : Declare a double precision variable or function
enum : Declare enumeration type
unsigned : Declare an unsigned type variable or function
signed : Declare a symbolic type variable or function
struct : Declare a structural variable or function
union : Declare federated data types
const : Declare read-only variable
auto : Declare automatic variables Generally not used
do: The body of a loop statement
while : The loop condition of a loop statement
for : A circular statement
if: Conditional statements must Branch
else : Conditional statement negates Branch ( And if Continuous use )
switch : Used for branch statements
case : Switch statement Branch
continue : End the current cycle , Start next cycle
break: Jump out of current loop
default : In the switch statement “ other ” Branch
goto : Jump statements without conditions
sizeof : Calculate the data type length
volatile : Explain that variables can be implicitly changed during program execution
static : Declare static variables
register: Declare register variables
typedef: Used to alias data types
extern: Declare variables are being declared in other files ( It can also be seen as a reference variable )
return : Program return statement
4. identifier
When we define variable names or function names , We will define the identifier , for example int a; This defines a int Type variables a , This a It's an identifier , Empathy , We can also define char b; float c; These variables are identifiers , The name of the variable is our own ,C Language has requirements for identifiers :
(1) Identifiers can only be made of letters 、 Numbers 、 Underline composition .
(2) Identifiers can only start with letters or underscores .
(3) Identifiers cannot be with C Language keyword conflict .
although C The identifier of a language can be named by ourselves , But in order to develop good coding habits , It is still recommended that you know the meaning of the name when naming . Otherwise, if the code capacity is huge , You may not know what you are doing with this identifier .
5. notes
If a piece of code is annotated , When the program is running code , Will not run the code in the comments , The contents in the comments will be automatically ignored when the program is running . The content in the comments is usually to annotate or explain the code , Make it easy for yourself or others to read the code . Can be interpreted as , The code is written by people and run by computers , Notes are written for people to see .
C There are three ways to add comments to languages .
(1)// Double slash notes , Is the content after the double slash in the comment line .
(2)/* */ This annotation method is to annotate all the contents between the two symbols , If the annotation is multi line, this method can be used faster .
(3)#if 0
The content in the middle will be annotated
#else
The content in the middle will work normally
#endif
In fact, the third method cannot be regarded as annotation in a strict sense , But this practice can also achieve the purpose of annotation .
6. Hexadecimal number
stay C There are octal numbers that can be recognized in the language 、 Decimal system 、 Hexadecimal .
Octal numbers require numbers 0 start , Such as 012 It's an octal number , His decimal system is 10
We are very familiar with decimal numbers , Such as 10, 12 etc.
Hexadecimal numbers need 0x start , Such as 0xa It's a hexadecimal number , His decimal system is 10
namely 012, 10, 0xa Their values are equal , Just different base .
7. Operator
C There are many language operators , Depending on the operands , Operators can be divided into monocular operators 、 Binocular operator 、 Ternary operator . If you use an operator, you only need one operand to complete , We call this operator a monocular operator , And so on . We know that four operations in mathematics have priority , Empathy . We C There are also operational priorities in languages .
c The relationship between all operators and priorities in the language can be seen in the following figure .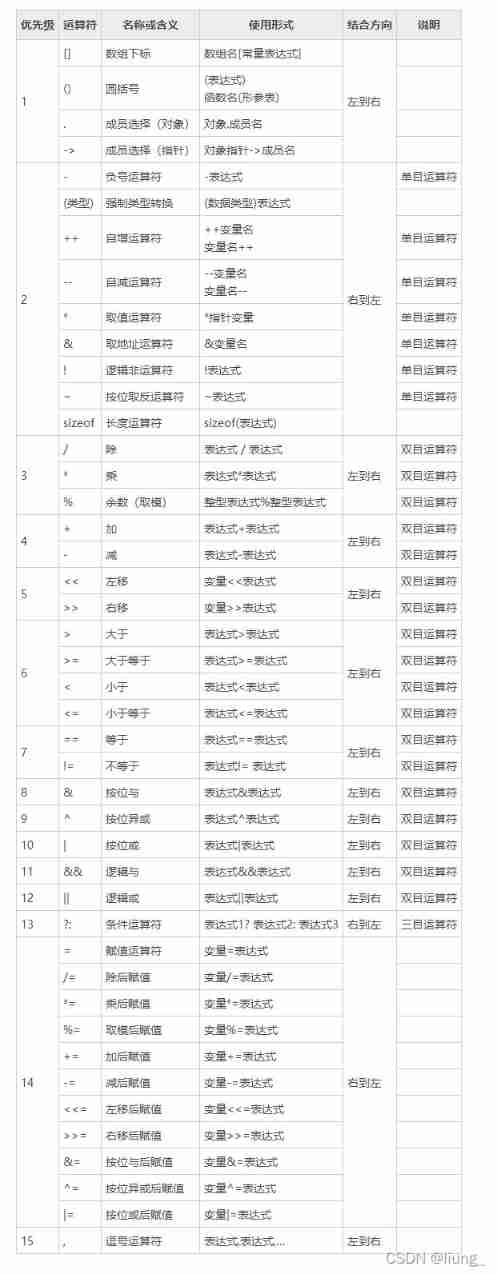
8. Escape character
because C Some characters in language should be given special meanings , In order to ensure that it does not conflict with its original intention , Therefore, the concept of importing escape characters . Escape character is to use \ Change the original meaning of characters , Give it a new meaning .
Common escape characters are :
\n : Line break
\t : Horizontal tabs , Equivalent to one Tab key
\v : Vertical tabs
\f : Change the page
\\ : Representing one \ character
\ddd : 1 To 3 Any character represented by an octal number ,d Represents any octal number
\xhh : 1 To 2 Any character represented by hexadecimal digits ,h Represents any hexadecimal number
9. C Language type conversion
C The type conversion of language can be divided into forced type conversion and implicit type conversion .
Cast :
Casting is to cast one type into another . It's our forced conversion .
Implicit type conversion .
Implicit type conversion is also converting one type to another . This conversion is done automatically by the compiler .
When doing forced type conversion , If a large type is converted to a small type, precision will be lost , This is worth noting .
3、 ... and 、 Sample code
So much has been said about C Grammar of language , Here we will pass a complete example to let you further understand it .
Source code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
/* Defining variables */
char a = 'x';
short b = 23;
int c = 10;
long d = 67;
float e = 3.14;
double f = 12.13;
printf("a = %c, b = %d, c = %d, d = %d, e = %f, f = %lf\n", a, b, c, d, e, f);
printf("%d, %d\n", a, 10); // Variables can be assigned at will , Constants cannot be .
printf("%d, %d, %d\n", 012, 10, 0xa); // Put octal 、 Decimal system 、 Hexadecimal numbers are printed in decimal .
/*C The language division operator is the acquisition quotient , The remainder operator is to get the remainder */
printf("%d %d %d\n", b+c, b/10, b%10);
/* octal 61 It's the decimal system 49,49 Corresponding ASCII The character is 1*/
printf("\61, \x32\n");
printf("c = %d\n", (int)e); // take float Type cast to int Type output
return 0;
}
Running results :
a = x, b = 23, c = 10, d = 67, e = 3.140000, f = 12.130000
120, 10
10, 10, 10
33 2 3
1, 2
c = 3
边栏推荐
- Twig数组合并的写法
- Jarvis OJ Telnet Protocol
- Embedded-c Language-5
- [729. My schedule I]
- Benji Banas membership pass holders' second quarter reward activities update list
- Games101 notes (I)
- Deep dive kotlin synergy (XXI): flow life cycle function
- [wechat applet] read the life cycle and route jump of the applet
- What is ROM
- Embedded-c language-6
猜你喜欢
composer安装报错:No composer.lock file present.
Embedded -arm (bare board development) -1
Jarvis OJ webshell analysis

采用药丸屏的iPhone14或引发中国消费者的热烈抢购

Android privacy sandbox developer preview 3: privacy, security and personalized experience

Etcd build a highly available etcd cluster

Flet tutorial 12 stack overlapping to build a basic introduction to graphic and text mixing (tutorial includes source code)
Games101 notes (II)
Jarvis OJ shell traffic analysis
Basic introduction to the control of the row component displaying its children in the horizontal array (tutorial includes source code)
随机推荐
Jarvis OJ shell流量分析
中国广电正式推出5G服务,中国移动赶紧推出免费服务挽留用户
叩富网开期货账户安全可靠吗?怎么分辨平台是否安全?
[Jianzhi offer] 66 Build product array
Is it safe to open futures accounts online? Will there be more liars online? Doesn't feel very reliable?
Benji Banas membership pass holders' second quarter reward activities update list
帮忙看看是什么问题可以吗?[ERROR] Could not execute SQL stateme
ECU简介
【微信小程序】一文读懂小程序的生命周期和路由跳转
Games101 notes (I)
Copy mode DMA
启牛商学院股票开户安全吗?靠谱吗?
How to install MySQL
PHP人才招聘系统开发 源代码 招聘网站源码二次开发
【Web攻防】WAF检测技术图谱
阈值同态加密在隐私计算中的应用:解读
Games101 notes (III)
How was the middle table destroyed?
File operation --i/o
深潜Kotlin协程(二十一):Flow 生命周期函数