当前位置:网站首页>Embedded-c Language-5
Embedded-c Language-5
2022-07-05 17:05:00 【Orange peel does not stop school】
One 、 function ( The core )
1.1. clear :
whatever C Program ,C The source file contains two parts : A pair of variables ( Including arrays ) And a bunch of functions
1.2. The concept of function :
A function is a combination of statements , It is used to realize some relatively independent and universal functions
analysis : Code without functions is extremely tedious , The code is written repeatedly , Increase the workload of development : Just write the above repeated code once , Other files can only be used , Reduce development effort
programme :
vim add.c
// Write an addition function add
int add(int x, int y)
{
if(x < 0 || y < 0) {
printf(" Please re-enter a positive number .\n");
return -1; // Let the program end , Can't continue to run
}
// You can add only if the entered number is a positive number
sum = a + b;
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
return sum;
}vim main1.c
int main(void)
{
int a;
int b;
int sum = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
sum = add(a, b);
return 0;
} vim main2.c
int main(void)
{
int a;
int b;
int sum = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
sum = add(a, b);
return 0;
} vim main3.c ....main250.c Just use it easily add Function
1.3. Function features :
1. Consisting of one or more statements
2. Can be reused
1.4. The function uses three steps :
a) Function declaration :
1. Function declaration function : Tell compiler , In the future, this function can be used by others or yourself , Function declarations do not allocate memory space
2. Syntax of function declaration :extern Return value data type Function name ( Formal parameter table );
Suggest : Function declaration plus extern( Improve the readability of the code ), In theory, there is no need to add
3. Function declaration features :
1. If the function is defined before the function is called , Function declarations can be omitted , Otherwise, it must be declared that
2. There is no statement in this statement , So the compiler gcc It will give a default function ,, form :
extern int Function name ();
3. The naming of function names follows the naming rules of identifiers
b) Function definition :
1. Function definition function : Is the concrete implementation process of a function , It will contain a bunch of statements , It can be used by others or yourself in the future , Function definitions allocate memory
2. Syntax of function definitions :
Return value data type Function name ( Formal parameter table )
{
A bunch of function body statements ;
} // The function of curly braces is to circle statements with
for example :
int add(int x, int y) //x=100,y=200
{
return x + y;
}
x = 250; // Report errors
y = 251; // Report errors
int main(void)
{
sum = add(100, 200) = 300; //main Function USES add function
return 0;
}
1.5 Function definition features :
1. Return value data type : It is to return a number to the code using this function after the function runs , Then this number must have a corresponding data type , If the function does not return a value , The data type of the return value is void keyword .
2. Formal parameter table : Is a bunch of variable definitions , These variables can only be used inside the body of this function , You can't use the function , The values of formal parameters are assigned by the code that uses these functions , There are multiple variables of formal parameters , Comma , Separate , If the code using the function doesn't want to pass parameters to the function , When defining a function, the formal parameter table is written void
Suggest : The number of formal parameter table variable definitions should not exceed 4 individual , Less than or equal to 4 individual , Otherwise, it will affect the efficiency of function
for example :
int add(int x, int y, int z, int m) {} // good
int add(int x, int y, int z, int m, int n) {} // The execution efficiency of the code is reduced
3. The return value of the function :
If the function needs to return a number , With keywords return, for example :return Return value
Bear in mind : If you forget to write return Return value ,gcc In the future Returns a random number
Be careful : The number type of the return value should be consistent with the data type of the return value when the function is defined , If it's not consistent , There will be implicit conversions , May cause data loss
for example :
int add(int x, int y)
{
int sum = x + y;
return sum;
}
If the function no return value , You don't have to write return Or write return Leave nothing behind !
for example :
void add(int x, int y)
{
printf("%d\n", x+y);
return; // Or don't write
}c) Function call :
1. Function call function : Commonly known as using functions , Call function , Access function
2. Function call syntax : A variable that receives the return value of a function = Function name ( Argument table );
3. Function call features :
Argument table : Is the value assigned to the formal parameter table of the function
for example : sum = add(100, 200);//100,200 It's a real parameter , Give... In the future add Functional x,y
The memory space of arguments and formal parameters are independent , The address is different , But the data stored inside is the same !
d) The form used by the function :
form 1: No parameter no return value
for example : void Function name (void)
{
Function statement ;
}
form 2: No parameter return value
for example :int Function name (void)
{
Function statement ;
}
form 3: Ginseng (1 Parameters ) No return value
for example :void Function name (int x)
{
Function statement ;
}
form 4: Ginseng ( Multiple parameters , It is recommended to be less than or equal to 4 individual ) No return value
for example :void Function name (int x, int y, int m, int n)
{
Function statement ;
}
form 5: With parameter and return value
for example :int Function name (int x, int y, int m, int n)
{
Function statement ;
}
form 6: The parameter may have a return value ( This is not recommended )
for example :int Function name ()
{
Function statement ;
}
e)return Key words and exit function
return keyword : Implement function return
exit function : Let the program end forcibly , To use this function, you need to add a header file :#include <stdlib.h>
f) Arguments and formal arguments
A formal parameter is a copy of an argument Copy , When an argument passes a parameter to a formal parameter , Is to copy the number in the argument to the formal parameter
1.5. Functions and arrays
a) The previous code is to study how functions operate variables , That is, how the function operates the memory allocated through variables
b) Function to access array programming formula
/* Define functions that access arrays */
void Function name ( The first address of the array , Length of array )
{
You can view array elements
You can modify array elements
}
for example :
void array_function(int a[], int lenght)
{
// View the values of array elements
printf("%d\n", a[ Subscript ]);
// Modify the value of array elements
a[ Subscript ] = The new value ;
}
Shape parameter :int a[] The essence is the first address of an array , Not an array , Because defining array syntax like this is not acceptable , When a function accesses an element through this address , It can be used as an array
clear : You cannot use variables , Because if it's a variable , A formal parameter is a copy of an argument , You can only change formal parameters, but not actual parameters , To change , at present Only function and array techniques can be used
2. Scope and visibility
2.1. clear :C Language variables by data type ( Memory size ) branch :12 Kind of (char....double)
2.2. clear :C Language variables are divided into two categories according to scope and visibility : Local and global variables
2.3. Definition of local variables : Variables defined within a function
for example :
void A (void)
{
int a = 250; // local variable
}
2.4. Global variable definition : Variables defined outside functions
for example :
int g_b = 520; // Global variables
void A (void)
{
int a = 250; // local variable
}
int g_c = 521; // Global variables
2.5.static keyword
If you define variables before Add static Keyword modification , Indicates that this variable is a static variable
If the defined variable is not preceded by static Keyword modification , Indicates that this variable is a non static variable
for example :
int a = 250; // Nonstatic variable
static int a = 250; // Static variables
2.6. Conclusion : Final C Language variables are classified by scope and visibility , Finally, it is divided into four categories :
Local non static variables / Local static variable / Global non static variables / Global static variables
2.7. Explain the characteristics of local non-static variables in detail :
a) form 1:
void A(void)
{
printf("a = %d\n", a); // Can not be , Report errors ,gcc There is no defined error in the compilation times
int a = 250; // Define local nonstatic variables
printf("a = %d\n", a); // Sure
}b) form 2:
void A(void)
{
if(1) {
int a = 250;
printf("a = %d\n", a); // Sure
}
printf("a = %d\n", a); // Can not be , Report errors ,gcc There is no defined error in the compilation times
}c) The formal parameter of the function
void A(int a) //a It can be used in the whole function body , Out of the function can not be used
d) Local non static variables characteristic
1. This variable is used in : Start at the defined place and then go down to Recent curly braces end
Be careful :if...else/switch...case/for/while/do-while
2. Assigned by this variable Memory life cycle : From where it is defined, the operating system allocates memory to variables , Until recently, the curly bracket operating system immediately reclaimed the memory of variables , Only the next time you run this code can you reallocate memory for variables
2.8. Explain the characteristics of local static variables in detail :
a) form 1:
void A(void)
{
printf("a = %d\n",a);// Can not be , Report errors ,gcc There is no defined error in the compilation times
static int a = 250; // Local static variable
printf("a = %d\n",a); // Sure
}b) form 2:
void A(void)
{
if(1) {
static int a = 250; // Local static variable
printf("a = %d\n",a); // Sure
}
printf("a = %d\n",a);// Can not be , Report errors ,gcc There is no defined error in the compilation times
}c) Characteristics of local static variables :
1. This variable is used in : From the place of definition to the end of the nearest curly bracket
2. The memory life cycle allocated by this variable : Allocate memory from the defined place until the end of the program , Primary distribution , The program doesn't end , Not assigned next time , Then the last use , The program doesn't end , The memory will not be reallocated next time
3. Heartfelt advice : Use less such variables
2.9. Explain global non static variables in detail :
a) form 1
void B(void)
{
printf("g_a = %d\n", g_a); // Can not be ,gcc An undefined error is reported
}
int g_a = 10; // Define and initialize global non static variables
void A(void)
{
printf("g_a = %d\n", g_a); // Sure , Function internal access to global non static variables
}
void C(void)
{
printf("g_a = %d\n", g_a); // Sure , Function internal access to global non static variables
}
...b) form 2: Definition and use of global non static variables In different source files Conduct
Bear in mind : If a source file specifies a global non static variable , Another source file wants to directly access this global non static variable , Just declare this global non static variable
Syntax for declaring global non static variables :extern data type Global non static variable name ;
Conclusion : Once declared , You can access global non static variables defined in other files
vim var1.c Add the following
int g_a = 250; // Define global non static variables
// Definition A function
void A(void)
{
printf("A function :g_a = %d\n", g_a); // View and print global non static variables
}
// Definition B function
void B(void)
{
g_a = 520; // Modify global non static variables
}vim var2.c Add the following
/* Definition D function */
void D(void)
{
printf("%d\n", g_a); //gcc Compiler error , No definition
}
// Due to cross file access functions , Declare functions
extern void A(void);
extern void B(void);
// In order to use var1.c Global non static variables of , Declare it
extern int g_a;
/* Defined function C*/
void C(void)
{
printf("%d\n", g_a); // You can visit
}
int main(void)
{
A();
B();
A();
printf("%d\n", g_a);
return 0;
}Compile command :gcc -o var var1.c var2.c // take var1.c and var2.c Compile to generate an executable file var
c) Bear in mind : Global non static variables characteristic
1. The scope of use of this variable : There are two situations
1. If it is Access to this document , The scope starts from the defined place and then goes down. All functions can access , The previous function cannot be accessed
2. If it is Different documents ( Cross file ) Visit between , The scope starts from the declared place and then goes down. All functions can access , The previous function cannot be accessed
2. The memory life cycle allocated by this variable : Starting from , When a program is run, the operating system allocates memory for it , Until the end of the program , The operating system reclaims its memory
3. Bear in mind : Global non static variables are rarely used in actual development , Use with caution , It is prone to disordered access ! If you must , Be sure to remember that mutually exclusive access protection , But this kind of mutually exclusive protection reduces the efficiency of code execution
2.10. Explain the global static variables :
a) form : The definition and use access of global static variables are in the same file , And this Global static variables can only be used in this file , Other source files are not accessible
vim var3.c
void B(void)
{
printf("g_a = %d\n", g_a); // Can not be ,gcc An undefined error is reported
}
static int g_a = 10; // Define initialization global static variables , It can only be used for var3.c in
void A(void)
{
printf("g_a = %d\n", g_a); // Sure , Function internal access to global non static variables
}
void C(void)
{
printf("g_a = %d\n", g_a); // Sure , Function internal access to global non static variables
}vim var4.c
extern void A(void); // Declare functions A
extern void B(void); // Declare functions B
extern int g_a; // Declare global static variables g_a
int main(void)
{
A();
B();
printf("g_a = %d\n", g_a); //gcc Report errors
return 0;
}compile :gcc -o var var3.c var4.c
b) Global static variable characteristics :
1. This variable is used in : Can only be used in files that define variables (var3.c), And is All other functions can be accessed from the defined place down in turn , Previous functions are not accessible
2. This variable allocates the life cycle of memory : Starting from , When the program is run, the operating system will allocate memory for it until the end of the program , The operating system reclaims its memory
3. Global static variables should also be used sparingly , Use with caution , If you have to visit , Remember to mutually exclusive access , However, it is less likely than global non-static variables to have disorder !
2.11.static Keyword summary ( The written examination questions are required ):
1.static Decorated global variables can only be used in this file , The rest of the files are inaccessible
2.static Modified function ( When defining a function ) For this document only , The rest of the files are not callable
3.static Modified variables and functions are relatively safe to use in the future , It plays the role of indirect protection , The probability of disorder is reduced
边栏推荐
- Sentinel-流量防卫兵
- Yarn common commands
- 如何安装mysql
- 【 brosser le titre 】 chemise culturelle de l'usine d'oies
- China Radio and television officially launched 5g services, and China Mobile quickly launched free services to retain users
- C# TCP如何限制单个客户端的访问流量
- 【testlink】TestLink1.9.18常见问题解决方法
- How to install MySQL
- American chips are no longer proud, and Chinese chips have successfully won the first place in emerging fields
- Solve cmakelist find_ Package cannot find Qt5, ECM cannot be found
猜你喜欢
腾讯音乐上线新产品“曲易买”,提供音乐商用版权授权
Fleet tutorial 09 basic introduction to navigationrail (tutorial includes source code)

The two ways of domestic chip industry chain go hand in hand. ASML really panicked and increased cooperation on a large scale
【Web攻防】WAF检测技术图谱

采用药丸屏的iPhone14或引发中国消费者的热烈抢购

Application of threshold homomorphic encryption in privacy Computing: Interpretation
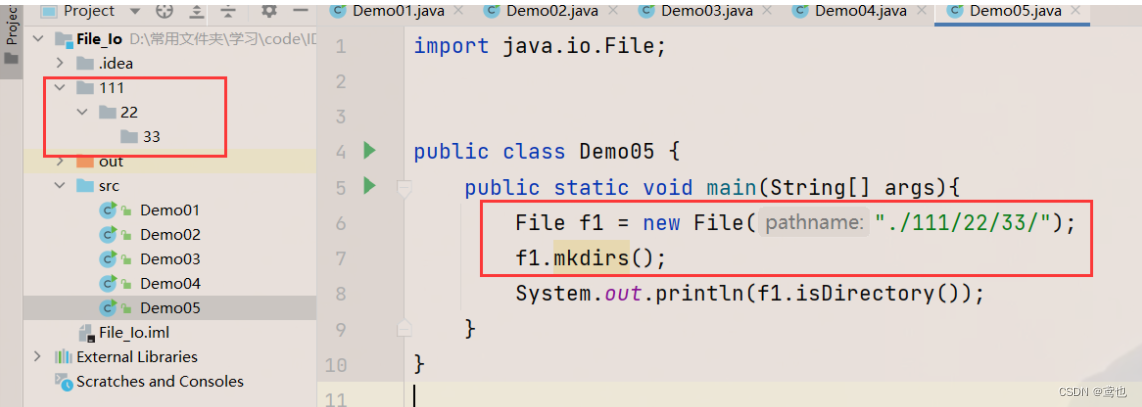
File operation --i/o
![[61dctf]fm](/img/22/3e4e3f1679a27d8b905684bb709905.png)
[61dctf]fm
拷贝方式之DMA

The survey shows that the failure rate of traditional data security tools in the face of blackmail software attacks is as high as 60%
随机推荐
Use byte stream to read Chinese from file to console display
PHP人才招聘系统开发 源代码 招聘网站源码二次开发
dried food! Semi supervised pre training dialogue model space
Can you help me see what the problem is? [ERROR] Could not execute SQL stateme
Games101 notes (III)
Apple has abandoned navigationview and used navigationstack and navigationsplitview to implement swiftui navigation
Allusions of King Xuan of Qi Dynasty
Jarvis OJ Webshell分析
养不起真猫,就用代码吸猫 -Unity 粒子实现画猫咪
【Web攻防】WAF检测技术图谱
【机器人坐标系第一讲】
How was the middle table destroyed?
【性能测试】jmeter+Grafana+influxdb部署实战
Solve cmakelist find_ Package cannot find Qt5, ECM cannot be found
Cs231n notes (bottom) - applicable to 0 Foundation
Basic introduction to the control of the row component displaying its children in the horizontal array (tutorial includes source code)
精准防疫有“利器”| 芯讯通助力数字哨兵护航复市
Data verification before and after JSON to map -- custom UDF
Jarvis OJ shell traffic analysis
It is forbidden to copy content JS code on the website page