当前位置:网站首页>Go语言实现原理——Map实现原理
Go语言实现原理——Map实现原理
2022-07-05 22:53:00 【生命中有太多不确定】
本文目录
Map实现原理
1、概述
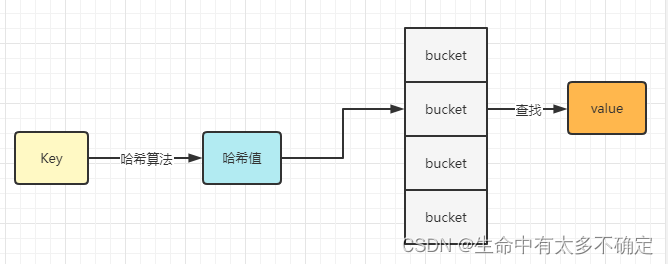
Map这一数据结构在很多语言中都存在,其查询的效率非常高,时间复杂度在O(1)的级别,其底层原理使用的是哈希表,通过计算key的hash值,找到其所在的bucket,然后再通过bucket寻找其value, 流程如下图所示
2、哈希碰撞
由于bucket的数量有限,而k-v对的数量会越来越多,因此,在通过哈希值查找对应的bucket的时候可能出现多个哈希值对应一个bucket的情况,这就是hash碰撞。为解决这个问题,可以通过拉链法或开放地址法来解决此类问题
2.1、拉链法
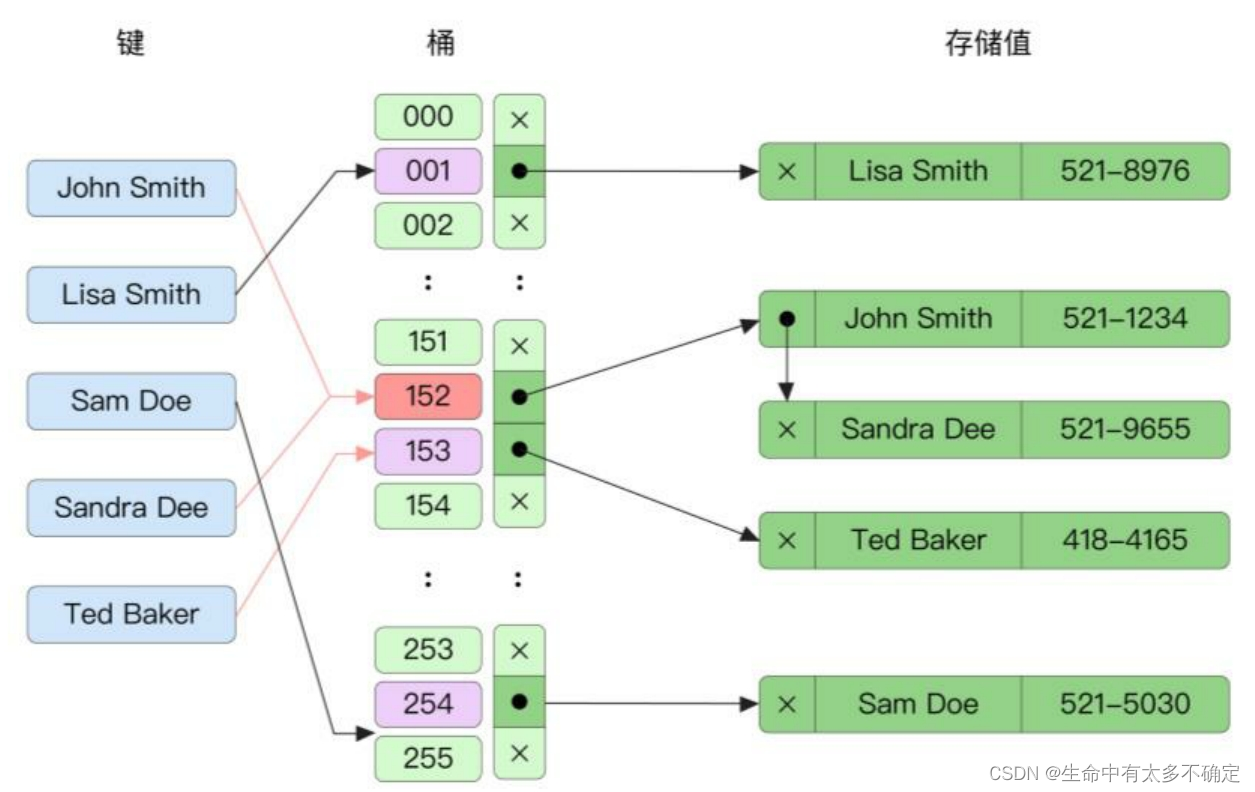
如果多个元素被放在一个bucket中,则会将他们以链表的形式组织起来,在查找到对应的bucket后,只需要对其进行遍历即可。
缺点:由于使用链表组织数据,因此需要额外的指针,并且也无法高效利用CPU高速缓存
2.2、开放地址法
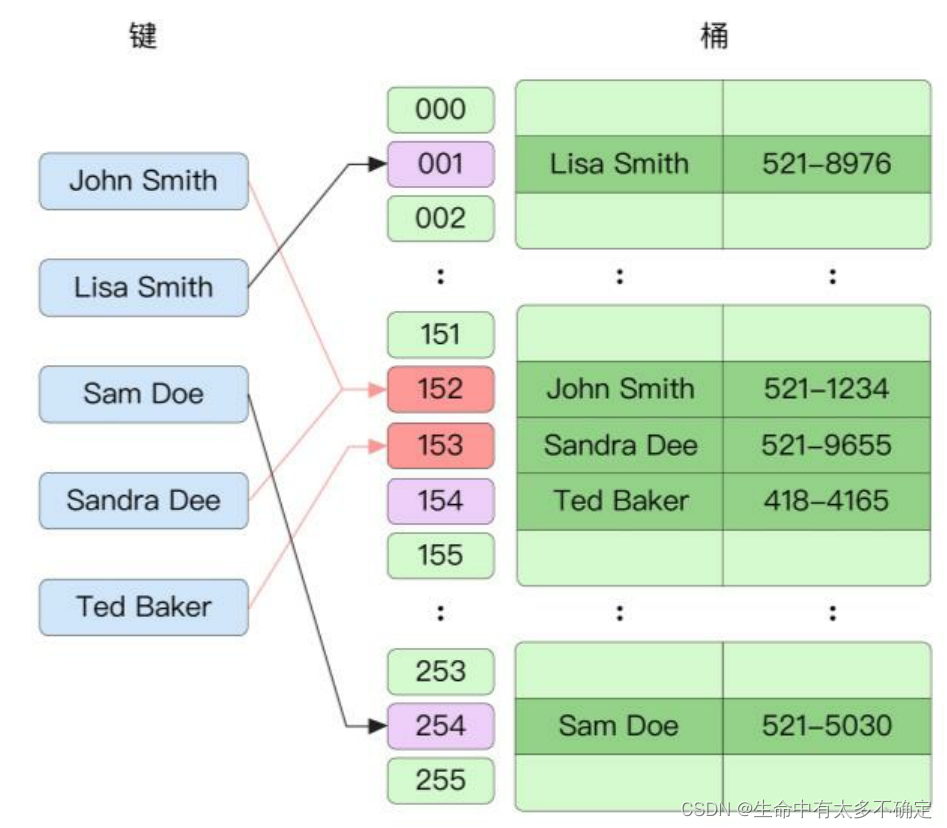
和拉链发不一样的是,对于同一个bucket中的元素,采用的是数组的形式进行保存的,Go语言采用的正式这种方式来解决哈希冲突,在查找元素时是按顺遍历的,此方式能够较好的利用CPU的高速缓存。
3、常用操作
3.1、声明与创建
var m1 map[int]string // m1为nil,不能进行操作
var m2 = make(map[int]int) // m2不为nil,默认长度为0
3.2、获取值
var m = make(map[int]int)
v1 := m[1]
fmt.Println(v1) // 0
v2, ok := m[2]
fmt.Println(v2, ok) // 0 false
通过上面例子不难看出,如果获取一个不存在的元素,将会得到此类型的”零值“,因此,更推荐使用第二种方法来从map中获取元素,通过第二个参数就可以判断是否存期望的值
3.3、赋值操作
var m = make(map[int]int)
// 赋值:map[key] = value
m[1] = 666
fmt.Println(m[1]) // 666
// 删除:delete(map,key)
delete(m, 1)
fmt.Println(m[1]) // 0
3.4、key的比较性
在Go语言中,map的key必须要具备可比较性。除了切片、函数、map, 不具备可比较性,其他类型几乎都具备可比较性。值得一提的是,结构体的可比较性,取决于其所有属性,如果所有则字段都是可比较的,则该结构体具有可比较性,反之则不具备可比较性。
3.5、并发问题
// 测试并发读写
// 并发读写会报错 fatal error: concurrent map read and map write
func test1() {
m := make(map[int]int)
go func() {
for {
m[0] = 5
}
}()
go func() {
for {
_ = m[1]
}
}()
select {
}
}
// 测试并发读
func test2() {
m := make(map[int]int)
go func() {
for {
_ = m[0]
}
}()
go func() {
for {
_ = m[1]
}
}()
select {
}
}
// 测试并发写
// 报错: fatal error: concurrent map writes
func test3() {
m := make(map[int]int)
go func() {
for {
m[0] = 5
}
}()
go func() {
for {
m[1] = 5
}
}()
select {
}
}
通过上面的案例不难看出,Go语言中的Map只支持并发读,之所以这样设计,是因为在大多数场景下Map都是读多写少的,如果为了那一点点的安全性让每个方法都互斥会有点得不偿失,因此,在性能与并发安全上选择了前者。
4、底层结构
4.1、哈希表结构体
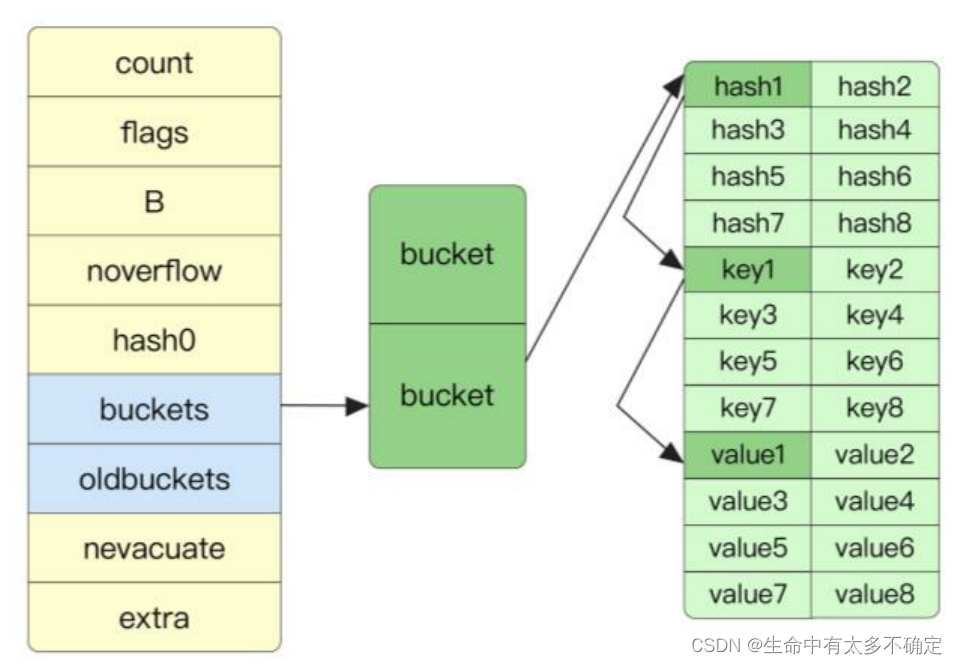
Map结构体
// A header for a Go map.
type hmap struct {
// Note: the format of the hmap is also encoded in cmd/compile/internal/reflectdata/reflect.go.
// Make sure this stays in sync with the compiler's definition.
count int // # live cells == size of map. Must be first (used by len() builtin)
flags uint8
B uint8 // log_2 of # of buckets (can hold up to loadFactor * 2^B items)
noverflow uint16 // approximate number of overflow buckets; see incrnoverflow for details
hash0 uint32 // hash seed
buckets unsafe.Pointer // array of 2^B Buckets. may be nil if count==0.
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // previous bucket array of half the size, non-nil only when growing
nevacuate uintptr // progress counter for evacuation (buckets less than this have been evacuated)
extra *mapextra // optional fields
}
借助翻译软件可以得知大部分字段的作用,这里就不重复解释了,这里介绍一下没有英文注释的flag字段,这个字段的作用记录当前map的状态,前面提到的并发问题正是借助了这个字段进行判断的
Bucket结构体
// A bucket for a Go map.
type bmap struct {
// tophash generally contains the top byte of the **hash** value
// for each key in this bucket. If tophash[0] < minTopHash,
// tophash[0] is a bucket evacuation state instead.
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8
// Followed by bucketCnt keys and then bucketCnt elems.
// NOTE: packing all the **keys** together and then all the **elems** together makes the
// code a bit more complicated than alternating key/elem/key/elem/... but it allows
// us to eliminate padding which would be needed for, e.g., map[int64]int8.
// Followed by an overflow pointer.
}
在源码中可以看到bucketCnt在运行时为8,在这个结构体中只有一个tophash属性,它是一个长度为8的数组,通过注释可以得知它存储的是hash值,通过后面的英文解释可以得知,紧跟着的应该是key和value,在获取的时候是通过计算偏移量得到的。因此,在运行时实际的结构应该是下面的样子
// A bucket for a Go map.
type bmap struct {
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8
key [bucketCnt]T
value [bucketCnt]T
......
}
在后面的英文注释部分也解释了,之所以这样组织数据,是为了节省因对其而填充的空间
4.2、溢出桶
通过上面对结构体的分析可以知道,bucket结构体中的数据是存储在数组中的,而数组的长度固定是8,当往map进行存储时,bucket中的数据可能会超过8。对于这种情况,Go语言的做法是创建一个新的bucket,这个新的bucket叫做溢出桶,原bucket,和溢出桶会组织一个链,换句话说,原bucket会有一个指针指向这个溢出桶。
4.3、map重建
在使用key获取value的时候,会先找到对应的bucket,然后回去遍历这里面的元素,如果此bucket没有找到就会检查是否有溢出桶,如果有则会遍历溢出桶。我们知道遍历的效率是非常差的,因此,为了提高性能,需要增加原bucket的数量,由于map中bucket是以数组的方式组织起来的,因此需要在扩容时需要申请一块更大的内存,然后将旧的bucket复制到新的数组中去。
扩容条件
// If we hit the max load factor or we have too many overflow buckets,
// and we're not already in the middle of growing, start growing.
if !h.growing() && (overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) || tooManyOverflowBuckets(h.noverflow, h.B)) {
hashGrow(t, h)
goto again // Growing the table invalidates everything, so try again
}
根据英文注释以及方法名称不难看出,当负载因子达到一定阈值或者溢出桶太多的时候(溢出桶和正常的桶数量一样多的时候),便会触发map重建
负载因子
下面是负载因子的计算公式:
负 载 因 子 = 元 素 数 量 / b u c k e t 数 量 负载因子 = 元素数量/bucket数量 负载因子=元素数量/bucket数量
负载因子可以得到目前对空间的大致使用情况,如果当前负载因子很小,说明元素数量远比申请的容量要小,例如:负载因子为1,那么平均每个bucket就只有一个元素,因为每个bucket能存放8个元素,从平均的角度来看,大约只使用到了1/8的空间。
// Maximum average load of a bucket that triggers growth is 6.5.
// Represent as loadFactorNum/loadFactorDen, to allow integer math.
loadFactorNum = 13
loadFactorDen = 2
通过上述源码可以得知,在运行时map的默认最大负载因子为6.5,也就是13÷2的结果,也就是说,当map的负载因子达到6.5的时候会进行扩容操作
扩容策略
func hashGrow(t *maptype, h *hmap) {
// If we've hit the load factor, get bigger.
// Otherwise, there are too many overflow buckets,
// so keep the same number of buckets and "grow" laterally.
bigger := uint8(1)
if !overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) {
bigger = 0
h.flags |= sameSizeGrow
}
oldbuckets := h.buckets
newbuckets, nextOverflow := makeBucketArray(t, h.B+bigger, nil)
//......
}
map结构体重的B字段与bucket数量的关系是: 2 B = b u c k e t s 2^B = buckets 2B=buckets,也就是说B每增加1,bucket就会增加一倍
在上述源码中,不难看出,如果是因为负载因子导致的扩容,bigger为1,那么B会增加1,也就是buckets的数量会翻倍,如果是因为溢出桶的数量太多导致的扩容,bigger为0,桶的数量会保持不变,进行横向“增长”。
4.4、删除原理
在使用delete(map,key)删除map中的元素的时候,会将bucket中对应位置上的值设置成emptyOne, 如果该值后面都没有值,则会设置成emptyRest, 这样做的好处是,遇到emptyRest的时候便不会继续向后遍历了。如下图所示
边栏推荐
- Data type, variable declaration, global variable and i/o mapping of PLC programming basis (CoDeSys)
- [speech processing] speech signal denoising and denoising based on Matlab GUI low-pass filter [including Matlab source code 1708]
- Registration and skills of hoisting machinery command examination in 2022
- 基于STM32的ADC采样序列频谱分析
- 东南亚电商指南,卖家如何布局东南亚市场?
- Leecode learning notes
- Leetcode buys and sells stocks
- Nangou Gili hard Kai font TTF Download with installation tutorial
- Basic knowledge of database (interview)
- Nail error code Encyclopedia
猜你喜欢
第十七周作业
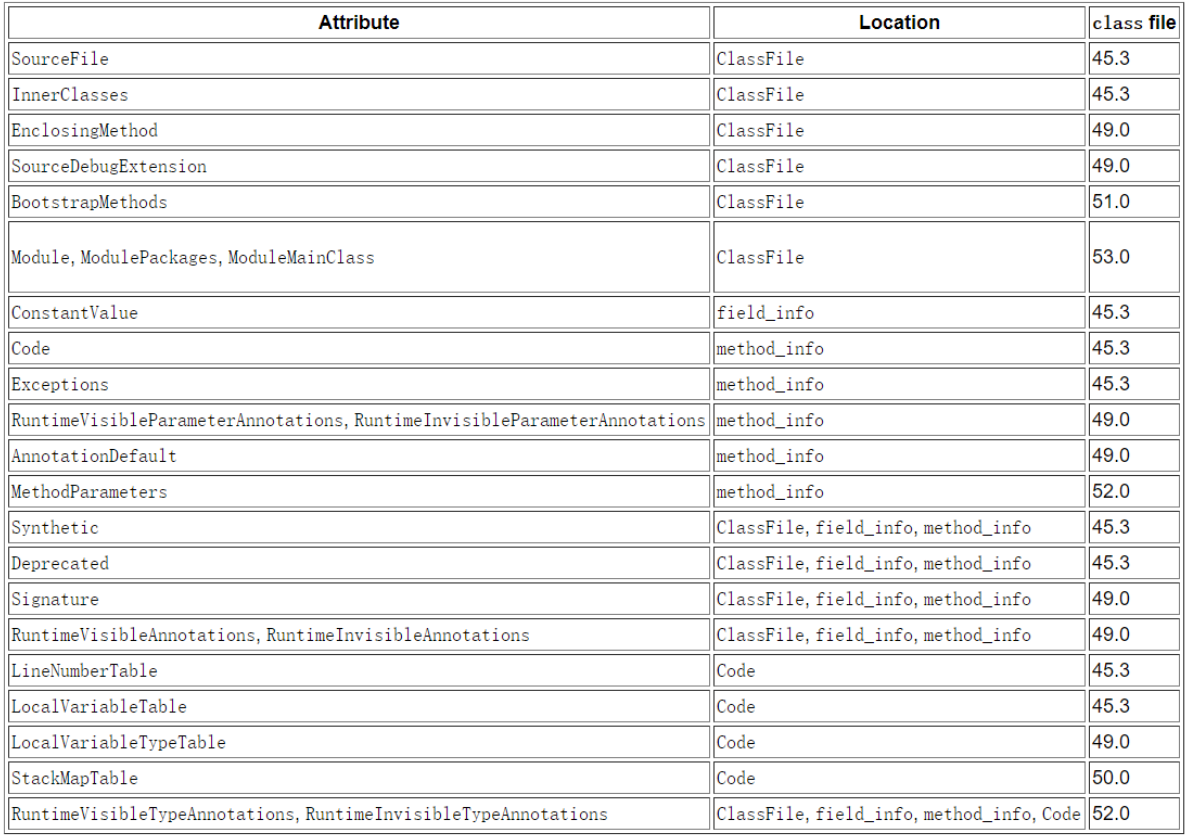
Un article traite de la microstructure et des instructions de la classe
Metasploit (MSF) uses MS17_ 010 (eternal blue) encoding:: undefined conversionerror problem
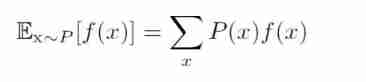
Expectation, variance and covariance
I closed the open source project alinesno cloud service
2022 R2 mobile pressure vessel filling review simulation examination and R2 mobile pressure vessel filling examination questions
Hcip day 11 (BGP agreement)
audiopolicy

Debian 10 installation configuration
![[secretly kill little buddy pytorch20 days] - [Day2] - [example of picture data modeling process]](/img/41/4de83d2c81b9e3485d503758e12108.jpg)
[secretly kill little buddy pytorch20 days] - [Day2] - [example of picture data modeling process]
随机推荐
Overview of Fourier analysis
东南亚电商指南,卖家如何布局东南亚市场?
Hcip day 11 (BGP agreement)
Fix the memory structure of JVM in one article
Boring boring
Nacos installation and service registration
Hainan Nuanshen tea recruits warmhearted people: recruitment of the product experience recommender of Nuanshen multi bubble honey orchid single cluster
透彻理解JVM类加载子系统
Detailed explanation of pointer and array written test of C language
Week 17 homework
My experience and summary of the new Zhongtai model
Media query: importing resources
Three. JS VR house viewing
一文搞定class的微观结构和指令
fibonacci search
Activate function and its gradient
傅里叶分析概述
2.13 summary
Use of metadata in golang grpc
[speech processing] speech signal denoising and denoising based on Matlab GUI low-pass filter [including Matlab source code 1708]