当前位置:网站首页>Functions in C language (detailed explanation)
Functions in C language (detailed explanation)
2022-07-04 05:57:00 【Small protrusion ~】
Catalog
2.c Classification of functions in language :
3. The parameters of the function
3.1 The actual parameter ( Actual parameters )
3.2 Formal parameters ( Shape parameter )
5. Nested calls and chained access to functions
6. Function declaration and definition
7.2 Two necessary conditions for recursion
1. What is a function
In Wikipedia , The definition of function is Subroutines . Subroutines It's a piece of code in a large program , Consists of one or more statement blocks , He is responsible for completing a specific task , And compared to other code , With relative independence .
Generally, there will be input Parameters And it has a return value , Provide encapsulation of the process and hiding of details . These codes are usually integrated into software
Parts library .
2.c Classification of functions in language :
2.1. Library function
Why are there library functions ?
In the early c Language has no function , He only stipulates your grammar , such as for How to write loops and so on, and then the rules of various grammatical details are very clear , Is that the code you write can be edited . But one day ,A When you want to print a message on the screen A It implements a similar printf1 Functions of the function . At that time ,B say , I also want a print function , So he wrote a printf2, later c say , He also wants to print . What about him , Also wrote a printf3 function .
These people don't know each other , So let's take a look at . When each of us implements the function of printing , This code , It becomes redundant .
What is the second ? Low development efficiency , Each of us is repeating the creation theory , You write one , He also wrote a , Others write another . It is written with similar functions , Of course, the development efficiency is low .
The third is not standard , What you write is the same function , But the implementation method may be different . The parameters may also be different , The return value type may also be different .
So for the above reasons . Can you implement some commonly used functions into functions ? At that time , There is the concept of library function , As long as the parameters of this function are specified . The return type specification is dead . The function name is dead , Then his use method must be exactly the same , The emergence of library functions makes our code development efficiency higher . The code is more standardized .
notes : However, the use of library functions must include the corresponding header file
Here are two websites that recommend learning :cppreference.com
cplusplus.com - The C++ Resources Network
So how to learn library functions ?
Here we have a simple look :http://www.cplusplus.com

This is a c The library of , We can quickly find the functions we used in the left part , Then I will take you to learn with an example Library function .
 strcpy This function is contained in string.h In this header file , This function requires two arguments The pointer , The return value is a character pointer , The pointer is the address ,char * strcpy ( char * destination, const char * source );
strcpy This function is contained in string.h In this header file , This function requires two arguments The pointer , The return value is a character pointer , The pointer is the address ,char * strcpy ( char * destination, const char * source );
Copies the C string pointed by source into the array pointed by destination, including the terminating null character (and stopping at that point).
Translate it into source Point to the C Copy string to destination In the array that points to , Include terminated empty characters ( And stop at that point ). Include '\0' character .
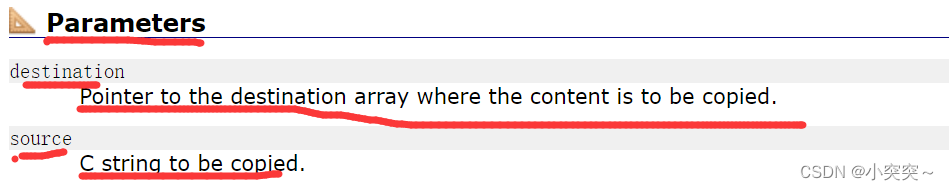
Pointer to the destination array where the content is to be copied.
Pointer to the target array , Where the contents of the target array are copied .
C string to be copied.
To be copied c character string

The return value is destiination,destiination It's a character pointer .
To sum up , Namely strcpy The function copies one string to another .
2. Custom function
If library functions can do everything , What do programmers do ? Therefore, it is more important to customize functions . Custom functions are the same as library functions , There's a function name , Return value types and function parameters . But the difference is that these are all designed by ourselves . This gives programmers a lot of room to play .
Composition of functions :
ret_type fun_name(para1, * )
{
statement;// Statement item
}
ret_type Return type
fun_name Function name
para1 Function parameter
Give me an example , At a glance .

3. The parameters of the function
3.1 The actual parameter ( Actual parameters )
The parameters that are actually passed to the function , It's called the actual parameter . The argument can be : Constant 、 Variable 、 expression 、 Functions, etc . Whatever the type of argument is , When you make a function call , They all have to have certain values , In order to pass these values to the parameter .
3.2 Formal parameters ( Shape parameter )
Formal parameters refer to the variables in brackets after the function name , Because formal parameters are only instantiated when the function is called ( Within distribution
Storage unit ), So it's called formal parameter . Formal parameters are automatically destroyed when the function call is completed . So formal parameters are only valid in functions .

The names of formal parameters and arguments can be the same , It doesn't matter .
4. Function call :
4.1 Value transfer call
The formal and actual parameters of a function occupy different memory blocks , Modification of a parameter does not affect the argument .
Write a function to exchange the contents of two shaping variables
void swap(int p1, int p2)
{
int tmp = 0;
tmp = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf(" Exchange before ,a = %d b = %d\n", a, b);
swap(a, b);
/*int p1 = &a;
int p2 = &b;
swap(p1, p2);*/
printf(" After exchanging ,a = %d b = %d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}
It can be seen that , I clearly passed in the parameters , Why haven't the parameters been exchanged yet ? We are going to use important address calls .
4.2 Address call
Address call is a way to call a function by passing the memory address of the created variable outside the function to the function parameter . This parameter transfer method can establish a real relationship between the function and the variables outside the function , In other words, the variables outside the function can be directly manipulated inside the function .
void swap(int* p1 , int* p2)
{
int tmp = 0;
tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf(" Exchange before ,a = %d b = %d\n", a, b);
swap(&a, &b);
/*int p1 = &a;
int p2 = &b;
swap(p1, p2);*/
printf(" After exchanging ,a = %d b = %d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}In argument , I will a,b The address of was passed in , Formal parameters are used again p1 and p2 Two pointers store a,b The address of , Then use * Operator found a,b And modify the contents .
5. Nested calls and chained access to functions
5.1 Nested calls
#include <stdio.h>
void new_line()
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
void three_line()
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
new_line();
}
}
int main()
{
three_line();
return 0;
}Functions can be called nested , But you can't nest definitions .
5.2 Chained access
Take the return value of one function as the parameter of another function .


Why is this printed 4321 Well ? We need to check printf The return value of . So the result is 4321 No wonder .

6. Function declaration and definition
6.1 Function declaration :

The program is executed step by step , The following picture is the writing method in the textbook , When we call a function , There should be a function declaration , But if the function is written in main Function above , There is no need to declare .

1. Tell the compiler that there is a function called , What are the parameters , What is the return type . But does it exist , function
The statement does not determine .
2. The declaration of a function usually precedes the use of the function . To satisfy the requirement of declaration before use .
3. The declaration of the function is usually placed in the header file .
6.2 Function definition :
The definition of a function refers to the concrete implementation of a function , Explain the function realization .

7. Function recursion
7.1 What is recursion ?
The programming skill of program calling itself is called recursion ( recursion). Recursion as an algorithm is widely used in programming languages . A procedure or function has a method that directly or indirectly calls itself in its definition or description , It usually transforms a large and complex problem into a smaller problem similar to the original problem to solve , The recursion strategy only needs a few programs to describe the repeated calculation needed in the process of solving problems , Greatly reduces the amount of code in the program . The main way to think about recursion is : Turn the big thing into a small one
7.2 Two necessary conditions for recursion
There are restrictions , When this constraint is met , Recursion doesn't continue .
After each recursive call, it gets closer and closer to this constraint
I will explain some topics of recursion in detail in the next article , I hope you will like it a little !
边栏推荐
- JSON Web Token----JWT和傳統session登錄認證對比
- 配置交叉编译工具链和环境变量
- 19. Framebuffer application programming
- Programmers don't talk about morality, and use multithreading for Heisi's girlfriend
- Component、Container容器常用API详解:Frame、Panel、ScrollPane
- 报错cvc-complex-type.2.4.a: 发现了以元素 ‘base-extension‘ 开头的无效内容。应以 ‘{layoutlib}‘ 之一开头。
- One click filtering to select Baidu online disk files
- el-select如何实现懒加载(带搜索功能)
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor 与 BeanPostProcessor 相关子类概述
- 接地继电器DD-1/60
猜你喜欢
AWT常用组件、FileDialog文件选择框

Input displays the currently selected picture

C # character similarity comparison general class
HMS v1.0 appointment. PHP editid parameter SQL injection vulnerability (cve-2022-25491)

Programmers don't talk about morality, and use multithreading for Heisi's girlfriend

How to configure static IP for Kali virtual machine

Overview of relevant subclasses of beanfactorypostprocessor and beanpostprocessor

AWT common components, FileDialog file selection box
JS扁平化数形结构的数组
实用的小工具指令
随机推荐
el-select如何实现懒加载(带搜索功能)
Detectron: train your own data set -- convert your own data format to coco format
Sword finger offer II 038 Daily temperature
left_ and_ right_ Net normal version
70000 words of detailed explanation of the whole process of pad openvino [CPU] - from environment configuration to model deployment
How to implement lazy loading in El select (with search function)
每周小结(*63):关于正能量
VB. Net GIF (making and disassembling - optimizing code, class library - 5)
安装 Pytorch geometric
How to determine whether an array contains an element
【无标题】
lightroom 导入图片灰色/黑色矩形 多显示器
如何获取el-tree中所有节点的父节点
JS flattened array of number shape structure
724. Find the central subscript of the array
How to configure static IP for Kali virtual machine
Programmers don't talk about morality, and use multithreading for Heisi's girlfriend
Actual cases and optimization solutions of cloud native architecture
报错cvc-complex-type.2.4.a: 发现了以元素 ‘base-extension‘ 开头的无效内容。应以 ‘{layoutlib}‘ 之一开头。
(4) Canal multi instance use