当前位置:网站首页>Tensorflow customize the whole training process
Tensorflow customize the whole training process
2022-07-06 01:35:00 【@zhou】
Create a machine learning problem
f ( x ) = 3 x + 7 f(x) = 3x + 7 f(x)=3x+7
For a machine learning problem , There are the following steps :
- Get training data .
- Defining models .
- Define the loss function .
- Traverse the training data , Calculate the loss from the target value .
- Calculate the gradient of this loss , And use optimizer Adjust variables to fit data .
- The result of the calculation is .
Build data
Supervised learning uses input ( Usually expressed as x) And the output ( Expressed as y, Commonly known as labels ). The goal is to learn from paired inputs and outputs , So that you can predict the output value according to the input .TensorFlow Almost every input data in is represented by tensor , And it's usually a vector . In supervised learning , Output ( That is, think of the predicted value ) It's also a tensor . This is done by putting Gauss ( Normal distribution ) Some data synthesized by adding noise to the points on the line , And visualize these data .
x = np.random.random([1000]) * 5
noise = np.random.random([1000])
y = 3 * x + 7
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.scatter(x, y, c="b")
plt.show()
Customize the model we need
We inherit tf.module class , And define two variables , Its attribute is trainable_variables.
class selfmodel(tf.Module):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.v1 = tf.Variable(1.0, trainable=True)
self.v2 = tf.Variable(2.0, trainable=True)
def __call__(self, x):
y = self.v1 * x + self.v2
return y
Define the loss function
We use the mean square deviation here to calculate the loss
def loss(target_y, predicted_y):
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(target_y - predicted_y))
Define the cycle training function
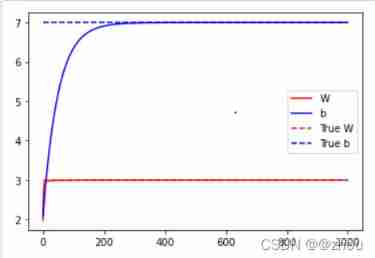
We use epcohs Function to get the two variables we need v 1 , v 2 v1,v2 v1,v2, After each training v 1 , v 2 v1, v2 v1,v2 Record , Finally, visualization
def train(model, x, y,epochs,optimizer):
v1, v2 = [], []
for j in range(epochs):
with tf.GradientTape() as gd:
y_pred = model(x) # This needs to be inside
loss_score = loss(y, y_pred)
grad = gd.gradient(loss_score, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grad, model.trainable_variables))
v1.append(model.v1.numpy())
v2.append(model.v2.numpy())
return (model, v1, v2)
The end result shows
I'm defining epcohs When , If the setting is too small , Will lead to v 1 , v 2 v1,v2 v1,v2 Can't get the right result
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD()
model = selfmodel()
epochs = 1000
(model, v1, v2) = train(model, x, y,epochs, opt)
# draw
plt.plot(range(epochs), v1, "r",
range(epochs), v2, "b")
plt.plot([3] * epochs, "r--",
[7] * epochs, "b--")
plt.legend(["W", "b", "True W", "True b"])
plt.show()
Problems in the code
# The code in this case will report an error , Say our grad The result is (none, none),
# because y_pred = model(x) It should be written in with Inside
# The following will write the correct way , The reason for this error is loss Function in
# Yes molel.trainable_variables When seeking derivative , Gradient not found
y_pred = model(x)
with tf.GradientTape() as t:
l = loss(y, y_pred)
grad = t.gradient(l, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD()
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grad, model.trainable_variables))
# Correct writing
with tf.GradientTape() as t:
y_pred = model(x)
l = loss(y, model(x))
grad = t.gradient(l, model.trainable_variables)
print(model.trainable_variables)
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD()
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grad, model.trainable_variables))
边栏推荐
- ORA-00030
- VMware Tools安装报错:无法自动安装VSock驱动程序
- 2022年广西自治区中职组“网络空间安全”赛题及赛题解析(超详细)
- Huawei Hrbrid interface and VLAN division based on IP
- SPIR-V初窥
- Kotlin basics 1
- [solved] how to generate a beautiful static document description page
- PHP error what is an error?
- Mathematical modeling learning from scratch (2): Tools
- ctf. Show PHP feature (89~110)
猜你喜欢

现货白银的一般操作方法

Basic operations of databases and tables ----- default constraints

Leetcode skimming questions_ Sum of squares
【Flask】官方教程(Tutorial)-part1:项目布局、应用程序设置、定义和访问数据库
How to upgrade kubernetes in place
Unity | two ways to realize facial drive

Blue Bridge Cup embedded stm32g431 - the real topic and code of the eighth provincial competition
ORA-00030

伦敦银走势中的假突破
Alibaba-Canal使用详解(排坑版)_MySQL与ES数据同步
随机推荐
Remember that a version of @nestjs/typeorm^8.1.4 cannot be obtained Env option problem
3D vision - 4 Getting started with gesture recognition - using mediapipe includes single frame and real time video
General operation method of spot Silver
About error 2003 (HY000): can't connect to MySQL server on 'localhost' (10061)
Luo Gu P1170 Bugs Bunny and Hunter
Folio. Ink is a free, fast and easy-to-use image sharing tool
3D模型格式汇总
How to see the K-line chart of gold price trend?
Huawei converged VLAN principle and configuration
Redis守护进程无法停止解决方案
[技术发展-28]:信息通信网大全、新的技术形态、信息通信行业高质量发展概览
VMware Tools installation error: unable to automatically install vsock driver
MUX VLAN configuration
PHP error what is an error?
Internship: unfamiliar annotations involved in the project code and their functions
Unreal browser plug-in
A Cooperative Approach to Particle Swarm Optimization
How does the crystal oscillator vibrate?
Unity VR resource flash surface in scene
c#网页打开winform exe