At high level ,Java programmatic GC The problem belongs to a very typical kind of problem , The impact is often further magnified . Whether it's 「GC The frequency is too fast 」 still 「GC It takes too long. 」, because GC There's always been Stop The World problem , So it's easy to cause service timeout , Causing performance problems .
Our team is responsible for the advertising system to undertake a relatively large C End flow , During the peak period, the number of requests basically reached thousands QPS, I have met many times in the past GC Related online questions .
This article , I share a tricky one Young GC Time consuming online cases , At the same time, I will sort out YGC Related knowledge , I hope you'll get something . The content is divided into the following 2 Parts of :
1、 From once YGC It takes too long to talk about2、YGC Summary of the relevant knowledge points of
01 From once YGC It takes too long to talk about
This year, 4 month , After the new version of our advertising service goes online , Received a large number of service timeout alarms , You can see from the monitoring chart below : The amount of overtime suddenly increased ,1 Even thousands of interface timeouts have been reached in minutes . The following details the troubleshooting process of this problem .

1. Check and monitor
After receiving the alarm , We checked the monitoring system for the first time , Immediately found out YoungGC Long time consuming exceptions . our The program is probably in 21 spot 50 Left and right online , As you can see from the picture below : Before going online ,YGC It's basically done in tens of milliseconds , And when it goes online YGC It takes a lot longer , The longest is even up to 3 A second more .

because YGC The program will Stop The World , However, the service timeout set by our upstream system is in hundreds of milliseconds , So infer : Because YGC The time-consuming is too long, resulting in a large area of service overtime .
according to GC The routine troubleshooting process of the problem , We immediately removed a node , Then by the following command dump The heap memory file is used to keep the scene .
jmap -dump:format=b,file=heap pid
Finally, the online service is rolled back , After the rollback, the service immediately returned to normal , And then there's da da 1 Days of troubleshooting and repair process .
2. confirm JVM To configure
Use the following command , We checked again JVM Parameters of
ps aux | grep "applicationName=adsearch"
-Xms4g -Xmx4g -Xmn2g -Xss1024K-XX:ParallelGCThreads=5
-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC
-XX:+UseParNewGC
-XX:+UseCMSCompactAtFullCollection
-XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction=80
You can see that the heap memory is 4G, Both the new generation and the old generation are 2G, The new generation adopts ParNew The collector .
And then by order jmap -heap pid find out : A new generation of Eden Area is 1.6G,S0 and S1 All the districts are 0.2G.
This launch has not been modified JVM Any relevant parameters , At the same time, the number of requests for our service is basically the same as usual . So guess : The big probability of this problem is related to the online code .
3. Check code
Back to YGC To think about this problem , once YGC The process includes the following two steps :
1、 from GC Root Scanning objects , Tagging live objects2、 Copy the live object to S1 District or promotion to Old District
According to the monitoring chart below, we can see that : Under normal circumstances ,Survivor The utilization rate of the district has been maintained at a very low level ( Probably 30M about ), But after going online ,Survivor The utilization rate of the district began to fluctuate , It's almost full at the most 0.2G 了 . and ,YGC Time consuming and Survivor There is a positive correlation between the utilization rate of the area . therefore , We speculate : There are more and more objects with long life cycle , This leads to an increase in the time consumption of the annotation and copy process .

Back to the overall performance of the service : There is no significant change in upstream flow , Under normal circumstances , The response time of the core interface is basically in 200ms within ,YGC The frequency is about every 8 Seconds 1 Time .
Obviously , For local variables , In every time YGC After that, it can be recycled immediately . Then why are there so many objects in YGC And survived ?
We further lock the suspect in : On global variables or class static variables of a program . however diff This online code , We didn't find this kind of variable in the code .
4. Yes dump To analyze the heap memory file
After there is no progress in code checking , We started looking for clues from heap memory files , Use MAT The tool has imported section 1 Step dump Out of the pile of files , And then through Dominator Tree The view looks at all the large objects in the current heap .

It was immediately discovered that NewOldMappingService This class takes up a lot of space , Locate through the code : This is the third party client In bag , Provided by our company's commodity team , It is used to realize the conversion between new and old categories ( Recently, the commodity team is reforming the category system , To be compatible with the old business , New and old categories need to be mapped ).
Take a closer look at the code , We found a lot of static in this class HashMap, It is used to cache all kinds of data needed in the conversion of new and old categories , In order to reduce RPC call , Improve conversion performance .

thought , Very close to the truth of the problem , But in-depth investigation found that : All static variables of this class are initialized when the class is loaded , Although it will occupy 100 many M Of memory , But there will be no new data after that . also , This class dates back to 3 It was launched in January ,client The version of the package has never changed .
After the above analysis , The static state of this class HashMap Will live forever , After many rounds YGC after , And finally promoted to the senior generation , It shouldn't be YGC The reason why it takes so long . therefore , For the time being, we have ruled out this suspicious point .
5. analysis YGC Handle Reference Time consuming
Team for YGC There is little experience in troubleshooting problems , I don't know how to analyze it further . Basically swept all the cases that can be found on the Internet , We found that the causes focus on these two categories :
1、 It takes too long to label live objects : For example, it's overloaded Object Class Finalize Method , Cause to label Final Reference It takes too long ; perhaps String.intern Improper use of methods , Lead to YGC scanning StringTable drawn-out .
2、 Long period objects accumulate too much : For example, improper use of local cache , There are too many survivors ; Or lock contention causes serious thread blocking , The life cycle of local variables becomes longer .
For 1 Class problem , It can be displayed by the following parameters GC Handle Reference Time consuming -XX:+PrintReferenceGC. After adding this parameter , You can see different types of reference The processing time is very short , Therefore, this factor is excluded .

6. And then we go back to the analysis of long-term objects
Further back , We added a variety of GC Parameters try to find clues, but there is no result , It seems that you have to run out of skills , There's no idea . Comprehensive monitoring and analysis : Only long-lived objects should cause us this problem .
For hours , Finally, it turns around , A little partner starts again from MAT A second suspicion was found in heap memory .

You can see from the screenshot above : Ranked first among large objects 3 Bit ConfigService Classes come into our view , One of the class ArrayList The variable actually contains 270W Objects , And most of them are the same elements .
ConfigService This class is in a third party Apollo The package , However, the source code has been re transformed by the company's architecture department , You can see from the code that : The problem is that 11 That's ok , Every time you call getConfig The method is always going to List Add elements to it , And it's not reprocessed .

Our advertising service is in apollo A large number of advertising strategy configurations are stored in , And most requests call ConfigService Of getConfig Method to get the configuration , So it's constantly going to static variables namespaces Add a new object to , This leads to this problem .
thus , The whole problem finally came to light . This BUG It's because the architecture department is dealing with apollo client The package was accidentally introduced when customized development , It's obviously not carefully tested , And it was released to the central warehouse just before we went online , The version of the company's basic component library is through super-pom In a unified way , The business has no perception .
7. Solution
For quick verification YGC It takes too long because of this problem , We use the old version of... Directly on a server apollo client The package has been replaced , And then the service was restarted , It's been observed that nearly 20 minute ,YGC Back to normal .
Last , We Inform the architecture department to repair BUG, It's redistributed super-pom , It completely solved the problem .
02 YGC Summary of the relevant knowledge points of
Through the above case , You can see YGC The problem is actually more difficult to investigate . comparison FGC perhaps OOM,YGC It's very simple , We only know the changes and time consuming of the new generation memory , meanwhile dump Out of the heap memory must be carefully checked .
in addition , If you don't know YGC The process of , It's going to be more difficult to investigate . here , I am right. YGC Relevant knowledge points to do next comb , To facilitate a more comprehensive understanding of YGC.
1. 5 A new understanding of the new generation
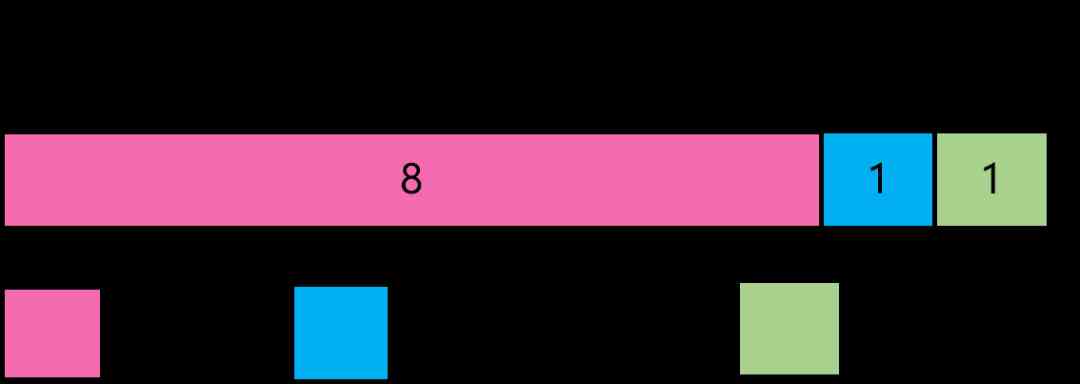
YGC In the new generation , First of all, we should make clear the division of Cenozoic reactor structure . The new generation is divided into Eden Area and two Survivor District , among Eden:from:to = 8:1:1 ( The proportion can be determined by the parameter –XX:SurvivorRatio To set ), This is the most basic understanding .
Why there is a new generation ?
If there are no generations , All objects are in one area , Every time GC You need to scan the whole heap , There are efficiency problems . After generations , The recycling frequency can be controlled separately , And use different recycling algorithms , Make sure GC Performance is globally optimal .
Why the new generation will adopt replication algorithms ?
The objects of the new generation live and die , about 90% Can be quickly recycled , The cost of replication algorithm is low , At the same time, it can ensure that there is no debris in space . Although the tag collation algorithm can guarantee no fragmentation , But because of the large number of objects to be cleaned up by the new generation , Organize the surviving objects before the objects to be cleaned , It requires a lot of mobile operations , Time complexity is higher than replication algorithm .
Why the new generation needs two Survivor District ?
To save space, consider , If we use the traditional replication algorithm , only one Survivor District , be Survivor Area size needs to be equal to Eden Area size , At this point, the space consumption is 8 * 2, And two pieces Survivor You can keep the new object always in Eden Zone creation , The living object is in Survivor Transfer between the two , Space consumption is 8+1+1, Obviously, the latter is more space efficient .
What is the actual available space of the new generation ?
YGC after , There's always a piece of Survivor The zone is free , So the new generation of available memory space is 90%. stay YGC Of log In or through jmap -heap pid Command to view the space of the new generation , If you find that capacity Only 90%, Don't be surprised .
Eden How do regions speed up memory allocation ?
HotSpot Virtual machines use two techniques to speed up memory allocation . Namely bump-the-pointer and TLAB(Thread Local Allocation Buffers).
because Eden Zones are continuous , therefore bump-the-pointer When an object is created , Just check if there is enough memory behind the last object , So as to speed up the memory allocation .
TLAB Technology is for multithreading , stay Eden Assign an area to each thread in the , Reduce lock conflicts in memory allocation , Speed up memory allocation , Improve throughput .
2. A new generation of 4 Seed recycler

SerialGC( Serial recycler ), One of the oldest , Single thread execution , Fit list CPU scene .
ParNew( Parallel recycler ), Multithread the serial collector , Suitable for more CPU scene , It needs to go with the older generation CMS The recyclers are used together .
ParallelGC( Parallel recycler ), and ParNew The difference is that it focuses on throughput , The desired pause time can be set , It automatically adjusts the heap size and other parameters as it works .
G1(Garage-First Recyclers ),JDK 9 And later versions of the default collector , Both the new generation and the old generation , Break the heap into a series of Region, The memory blocks are not required to be continuous , The new generation is still parallel collection .
The above recyclers all adopt replication algorithm , It's all exclusive , During the execution period Stop The World.
3. YGC The trigger time of
When Eden When space is not enough , It will trigger YGC. Combined with the memory allocation of new generation objects, take a look at the detailed process :
1、 The new object will try to allocate on the stack first , If you can't, try in TLAB Distribute , Otherwise, if we want to meet the conditions of large objects, we should allocate them to the old generation , Finally, I think about Eden Area application space .
2、 If Eden There's no proper space in the zone , The trigger YGC.
3、YGC when , Yes Eden Area and From Survivor The surviving objects of the zone are processed , If the condition of dynamic age judgment is satisfied or To Survivor If there is not enough space, you will enter the old generation directly , If there is not enough space in the old days , It will happen promotion failed, Trigger old age recycling . Otherwise, copy the live object to To Survivor District .
4、 here Eden Area and From Survivor The remaining objects in the zone are garbage objects , It can be directly erased and recycled .
Besides , In the old days, if we used CMS Recyclers , In order to reduce the CMS Remark The time of the phase , It may also trigger once YGC, There is no expansion here .
4. YGC Implementation process of
YGC The replication algorithm used , It is divided into the following two steps :
1、 lookup GC Roots, Copy the object it refers to to to S1 District2、 Recursively traverses the first 1 The object of the step , Copy its referenced object to S1 District or promotion to Old District
The whole process mentioned above needs to suspend the business thread (STW), however ParNew The new generation of recyclers can be executed in parallel with multiple threads , Improve processing efficiency .
YGC Through reachability analysis algorithm , from GC Root( The starting point of reachable objects ) Start looking down , Mark the current surviving object , The remaining unmarked objects are the objects that need to be recycled .

Can be used as YGC when GC Root The objects include the following :
1、 Objects referenced in the virtual machine stack2、 Static properties in the method area 、 Objects referenced by constants
3、 Objects referenced in the local method stack
4、 By Synchronized The object that the lock holds
5、 Record the class currently loaded SystemDictionary
6、 Record the string constant reference StringTable
7、 Objects with cross generational references
8、 and GC Root Be in the same place CardTable The object of
among 1-3 It's easy to think of , and 4-8 It's easy to be ignored , But most likely it's analysis YGC A clue to the question .
Another thing to note , For cross generation reference in the figure below , The object of old age A It has to be GC Root Part of , But if every time YGC When we go to scan the elderly , There must be efficiency problems . stay HotSpot JVM, Introduce card list (Card Table) To accelerate the markup of cross generational references .

Card Table, Simple understanding is a way of exchanging space for time , Because the number of objects with cross generation references is probably less than that 1%, Therefore, the heap space can be divided into the size of 512 Byte card page , If an object in the card page has a cross generation reference , You can use 1 Bytes to identify the card page is dirty state , Card page status is further maintained by write barrier technology .
End of traversal GC Roots after , So that we can find the first people to survive , Then copy it to S1 District . Next , It's a recursive process of finding and copying live objects .
S1 To facilitate the maintenance of memory areas , Two pointer variables are introduced : \_saved\_mark\_word and \_top, among \_saved\_mark\_word Represents the position of the current traversal object ,\_top Indicates the location of the current allocable memory , Obviously ,\_saved\_mark\_word To \_top Objects between are copied but not scanned .

As shown in the figure above , One object at a time ,\_saved\_mark\_word Will move forward , During this period, if there are new objects, they will also be copied to S1 District ,\_top It's going to move forward, too , until \_saved\_mark\_word Catch up \_top, explain S1 All objects in the zone have been traversed .
There is a detail to note : The target space of the copy object is not necessarily S1 District , It could be the old days . If the age of an object ( Experience of YGC frequency ) If the condition of dynamic age determination is satisfied, it will be promoted directly to the old generation . The age of the subject is preserved in Java The head of the object mark word In the data structure ( If you're right Java Concurrent locking is familiar with , I'm sure we know this data structure , It is suggested that you should refer to the materials to find out , There is no expansion here ).
At the end
This article through the online case analysis and combined with the principle to explain , In detail YGC Knowledge about . from YGC From a practical point of view , Again Just to summarize :
1、 First of all, be clear YGC Implementation principle of , For example, the heap memory structure of the younger generation 、Eden The memory allocation mechanism of the area 、GC Roots scanning 、 Object copy process, etc .
2、YGC The core steps of are tagging and copying , Most of them YGC The problem is all about these two steps , So we can combine YGC Check log and heap memory changes one by one , meanwhile d ump The heap memory file of It needs careful analysis .
If you're right JVM Performance tuning and GC The case is interesting , It is suggested to pay attention to the former Ali Daniel 「 You are stupid 」 Created PerfMa Community , There are a lot of high quality JVM article .
Author's brief introduction :985 master , Former Amazon Engineer , present 58 Transfer to technical director
Welcome to follow my personal public number :IT People's career advancement