explain :
- The article mainly aims at the simple notes made in class , And after the interview for some of the content of the detailed explanation
- Repeated statements : The students who take part in the postgraduate entrance examination should make good endorsement , Problem. , Key research , come on. !!!
- This article is summarized from :【 computer network 】( The seventh edition ) Xie Xiren , The copyright of all contents belongs to the author of the book , Invasion and deletion
One Preface of data link layer
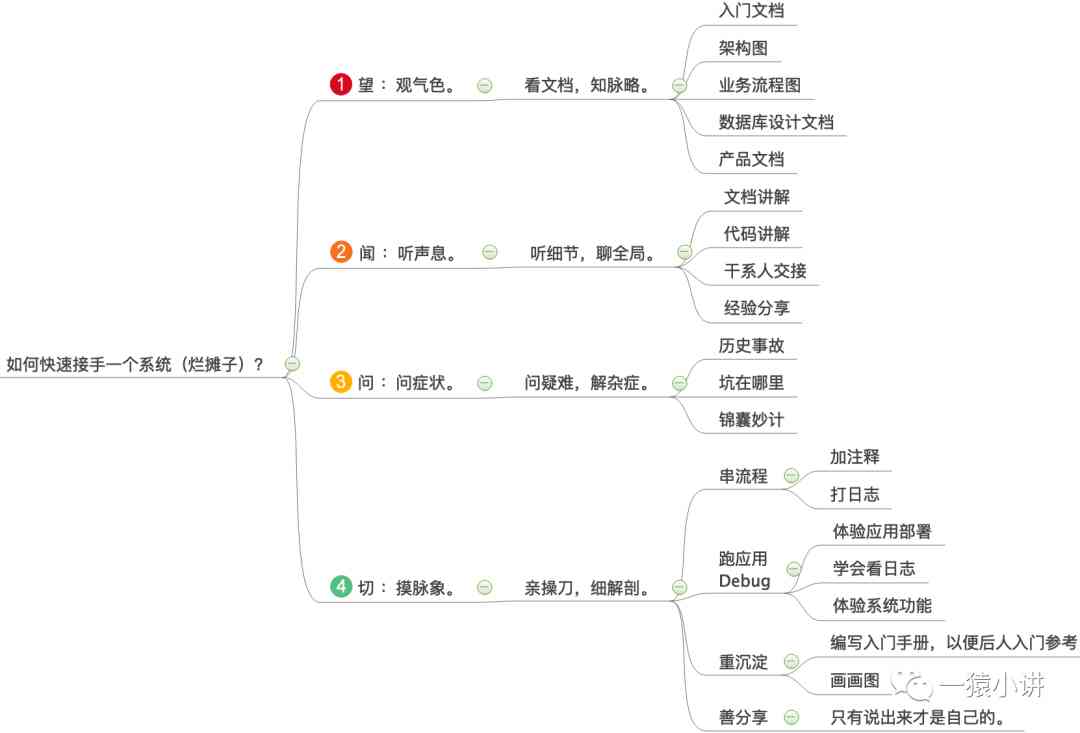
The data link layer is the lower layer of a computer network , There are two main types of channels used by the data link layer :
- Point to point channels . This channel uses one-on-one Point to point communication .
- Broadcast channel . This channel uses One to many broadcast communication mode , So it's complicated . There are many hosts connected on the broadcast channel , Therefore must A dedicated shared channel protocol is used to coordinate the data transmission of these hosts .
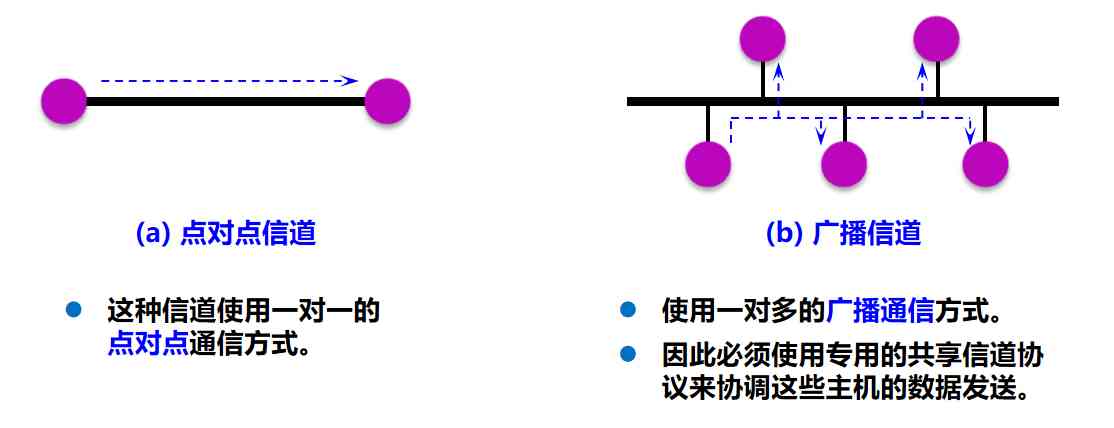
When we focus on the data link layer to find that problem , In many cases, we can Only the data link layers in the horizontal direction in the protocol stack are concerned , So when the host H1 Host computer H2 When sending data , We can Imagine that data is being sent from left to right in the data link layer along the horizontal method
Two Data link layer using point-to-point channel
( One ) Data links and frames
(1) link
link : A physical route from a node to an adjacent node , And any other switching node in the middle
- In data communication , The communication path between two computers often goes through many such links , Visible links are only part of a path
(2) The data link
The data link (data link): Apart from the physical circuit , There must also be communication protocols to control the transmission of these data . If the hardware and software to implement these protocols are added to the link , It's a data link
- The most common method now is to use adapters ( Network card ) The hardware and software to implement these protocols
- General adapters include the functions of data link layer and physical layer
Another term has been used . This is the Links are divided into physical links and logical links
- The physical link is the link mentioned above
- The logical link is the data link above , Is the physical link plus the necessary communication protocol
Add : The early riser data communication protocol used to be called Communication procedures , So in the data link layer , Protocol and protocol are synonyms
(3) frame
The data link layer transmits frames

A digital pipeline is often drawn between two equivalent data link layers , The unit of data transmitted on this digital pipeline is frame
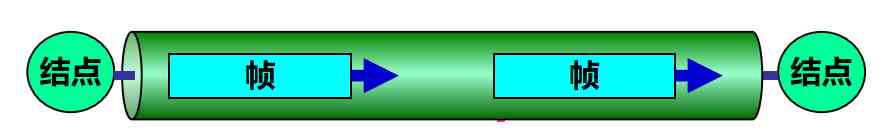
The data link layer does not need to consider the details of how the physical layer implements bit transmission . It can even be simpler to imagine sending frames directly to each other in a horizontal direction between two data link layers
( Two ) Three basic questions
There are many kinds of data link layer protocols , But three basic problems are common , Package into frames 、 Transparent transmission 、 Error control
(1) Package into frames
Package into frames (framing) This is to add a head and tail before and after a piece of data , And then it forms a frame
An important role of the head and tail is to carry out Frame delimitation
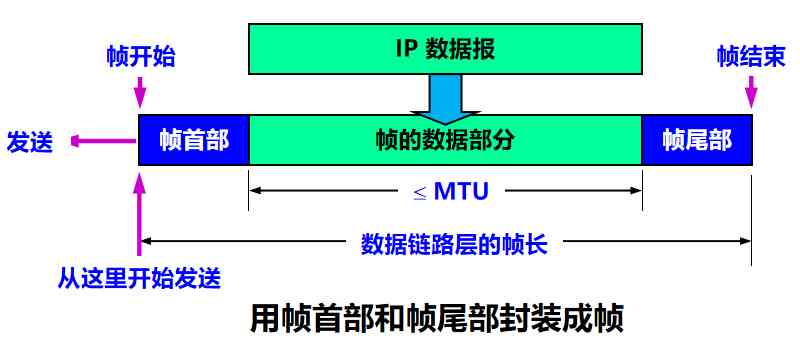
When data is printed by ASCII Code composition of the text file , Special frame bounds can be used
Control characters SOH (Start Of Header) Put at the front of a frame , Indicates the beginning of the first frame . Another control character EOT (End Of Transmission) Indicates the end of the frame

ASCII Code is 7 Bit code , It can be made up of 128 Different ASCII code , The printable ones are 95 individual , Non printable 33 individual , Please note that ,SOH and EOT Are the names of control characters , Their hexadecimal codes are 01( Binary is 00000001) and 04(00000100)SOH( or EOT) Not at all S,O,H ( or E,O,T) Three characters
(2) Transparent transmission
If the binary code of a byte in the data is exactly the same as SOH or EOT equally , The data link layer will incorrectly “ Find the border of the frame ”
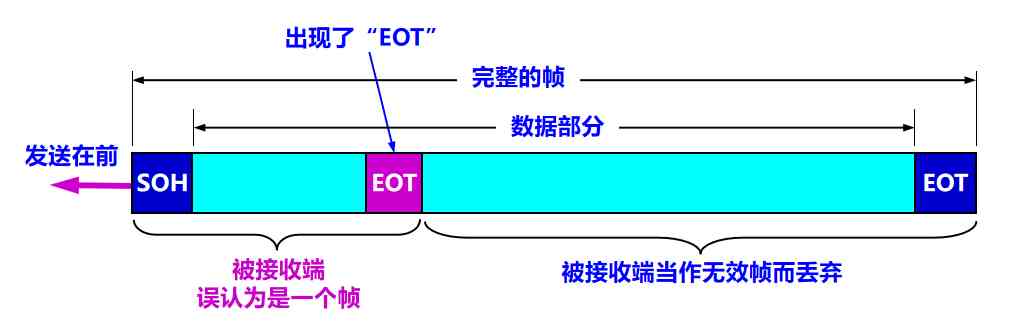
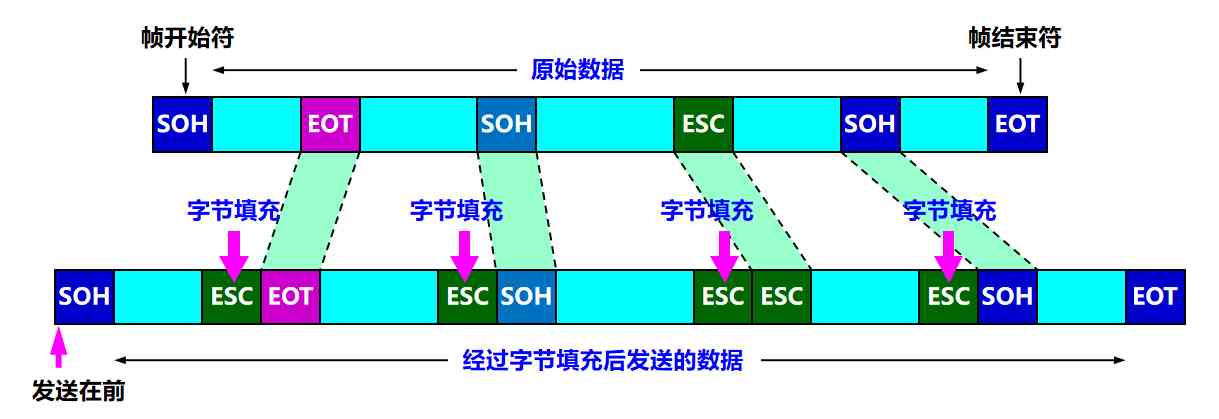
resolvent : Byte padding (byte stuffing) Or character fill (character stuffing)
- The control characters appear in the data in the data link layer of the sender “SOH” or “EOT” Insert an escape character before “ESC”( Its hexadecimal code is 1B)
- The data link layer of the receiver deletes the inserted escape characters before sending the data to the network layer
- If the escape character also appears in the data , Then insert an escape character before the escape character ESC. When the receiver receives two consecutive escape characters , Just delete the first one
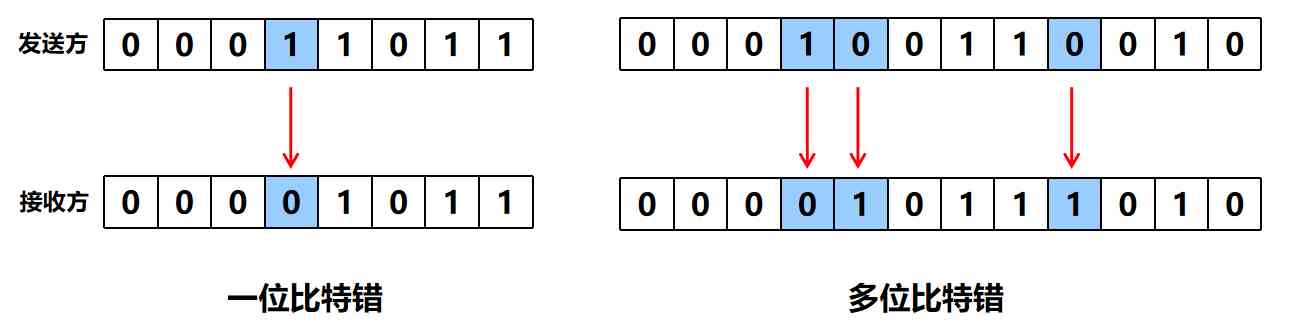
(3) Error detection
Bit errors may occur during transmission :1 Could become 0, and 0 It could become 1
A: Cyclic redundancy test
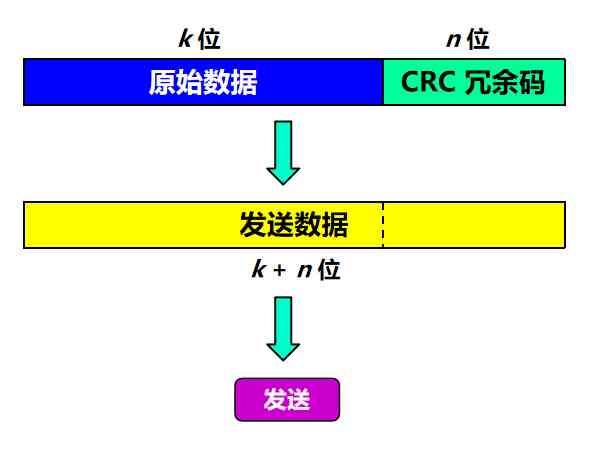
In frames transmitted at the data link layer , widely Cyclic redundancy test is used CRC Error detection techniques
At the sending end , First, divide the data into groups . Suppose that each group k A bit
In each group M( Data to be transmitted ) We will add the n Bit redundancy code , And send it out together
How to calculate redundancy code :
- Using binary modules 2 The operation is carried out 2^n ride M Arithmetic , This is equivalent to M Add later n individual 0
- Got (k + n) The number of bits divided by the pre-determined length is (n + 1) The divisor of bits P, The quotient is Q And the remainder is R, remainder R Divisor P Less 1 position , namely R yes n position
- Put the remainder R As redundant code splicing in data M Back , Send it together
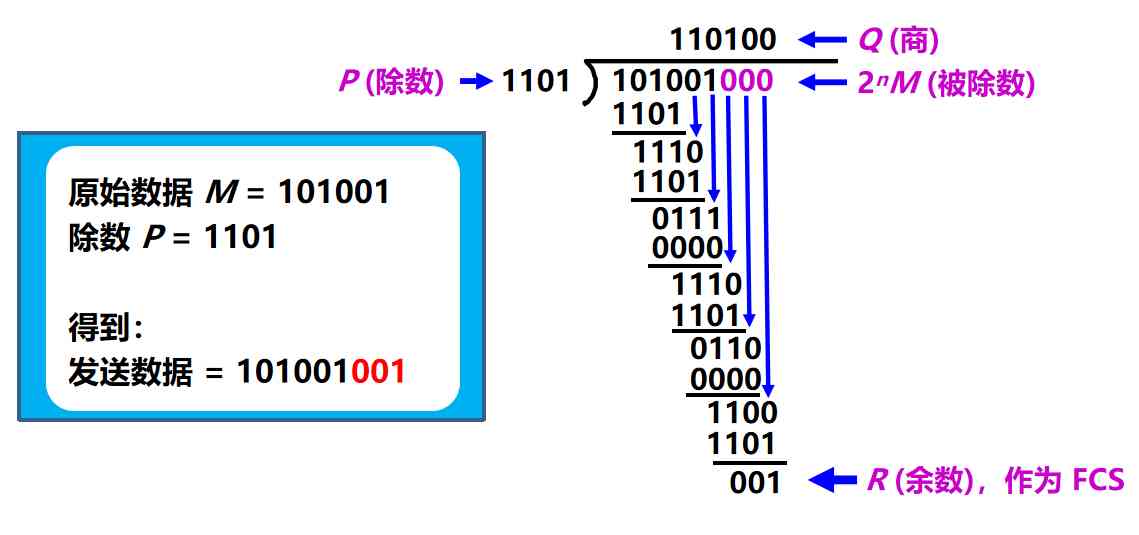
give an example :
Now? k = 6, M = 101001
set up n = 3, Divisor P = 1101
The divisor is 2^nM = 101001000
model 2 The result of the operation is : merchant Q = 110101, remainder R = 001
Put the remainder R Add as redundancy code in data M Send out the back of . The data sent is :2nM + R, namely :101001001, common (k + n) position
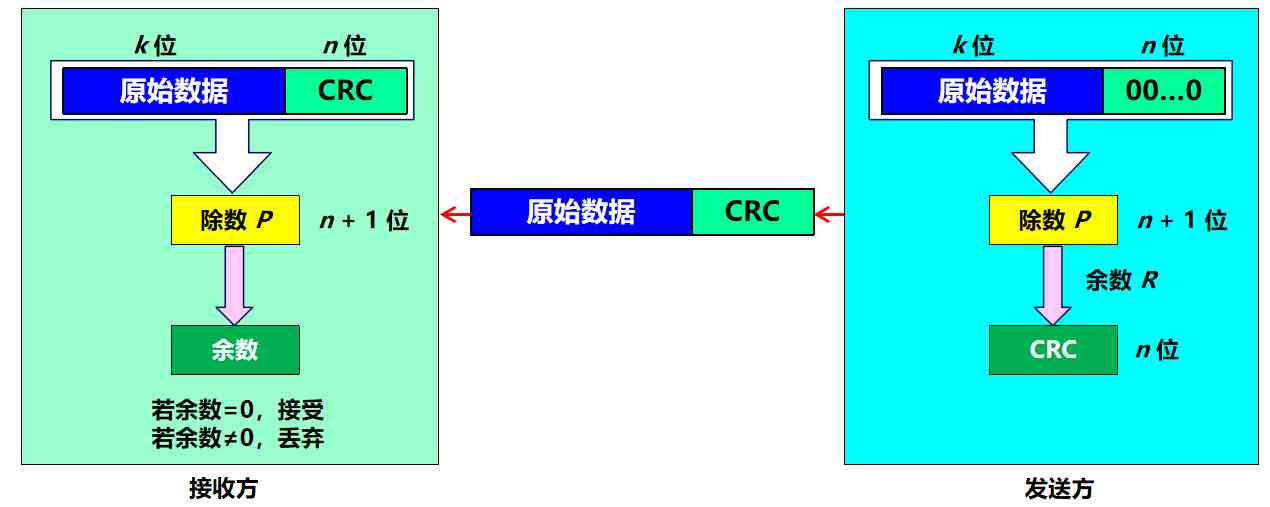
How to judge the receiver
- If we get the remainder R = 0, Then determine that there is no error in this frame , Just accept it (accept)
- If the remainder R ≠ 0, It is determined that there is an error in this frame , Just throw away
But this detection method can not determine which bit or several bits are wrong
As long as they are strictly selected , And use a divisor with enough digits P, Then the probability of undetectable errors is very small
B: Frame check sequence FCS
The redundant code added to the end of the data is called the frame check sequence FCS (Frame Check Sequence)
Cyclic redundancy test CRC And frame check sequence FCS It's not the same as
-
CRC It is a common method of error detection , and FCS Is the redundancy code added after the data
-
FCS It can be used CRC This method leads to , but CRC It's not used to get FCS The only way
Be careful :
Only cyclic redundancy check CRC Error detection technology can only achieve error free acceptance (accept)
-
“ Accept without error ” Refer to :“ All accepted frames ( That is, the discarded frames are not included ), We can all be very close to 1 The probability of these frames is that there is no error in the transmission process ”
-
in other words :“ There is no transmission error in any frame received by the data link layer of the receiver ”( The frame with error will be discarded and not accepted )
Just use CRC Error detection technology cannot be implemented “ Error free transmission ” or “ Reliable transmission ”
It should be clear ,“ No bit error ” And “ No transmission error ” It's a different concept
Use at the data link layer CRC test , It can realize bit error free transmission , But it's not reliable transmission yet
To do it “ Error free transmission ”( That is, you receive what you send ) We have to add the confirmation and retransmission mechanism
None of the data link layer protocols described in this article are reliable transmission protocols
( 3、 ... and ) PPP agreement
For point-to-point links , The most widely used data link layer protocol is the point-to-point protocol PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol)
PPP The agreement has three components :
- One will IP The method of data packet encapsulation to serial link
- Link control protocol LCP (Link Control Protocol)
- Network control protocol NCP (Network Control Protocol)
(1) PPP What the agreement should meet
- Simple —— This is the first requirement
- Package into frames —— Special characters must be specified as the frame delimiter
- transparency —— The transparency of data transmission must be guaranteed
- Multiple network layer protocols —— It can support multiple network layer protocols on the same physical link
- Multiple types of links —— It can run on multiple types of links
- Error detection —— It can detect the frame received by the receiver , And immediately discard the frame with error
- Check connection status —— It can automatically detect whether the link is in normal working state in time
- Maximum transfer unit —— A maximum transport unit must be set for each type of point-to-point link MTU Standard defaults for , Facilitate interoperability between implementations
- Network layer address negotiation —— A mechanism must be provided so that two network layer entities communicating can know or configure each other's network layer address through negotiation
- Data compression negotiation —— A method must be provided to negotiate the use of data compression algorithms
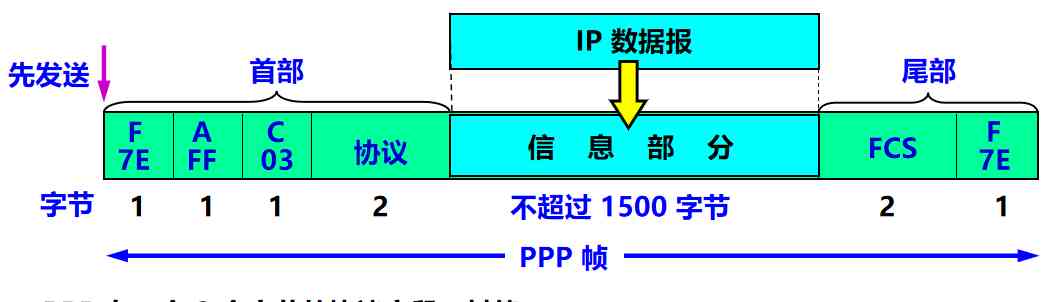
(2) PPP The frame format of the protocol
- PPP The head and tail of the frame are 4 Fields and 2 A field
- Flag fields F = 0x7E ( Symbol “0x” The following characters are represented in hexadecimal . Hexadecimal 7E The binary representation of is 01111110)
- Address field A Set as 0xFF. The address field doesn't actually work
- Control field C Usually set to 0x03
- PP It's byte oriented , be-all PPP The length of the frame is all integer bytes

PPP There is one 2 Byte protocol field , Its value :
- if 0x0021, Then the information field is IP The datagram .
- if 0x8021, Then the information field is network control data .
- if 0xC021, Then the information field is PPP Link control data .
- if 0xC023, Then the information field is the authentication data .
(3) PPP The protocol solves the problem of transparent transmission
- When PPP Use in Sync Transmission link , Provisions of the agreement Hardware is used to complete bit filling ( and HDLC Do the same thing )
- When PPP Use in asynchronous When transmitting , Just use a special one Character filling
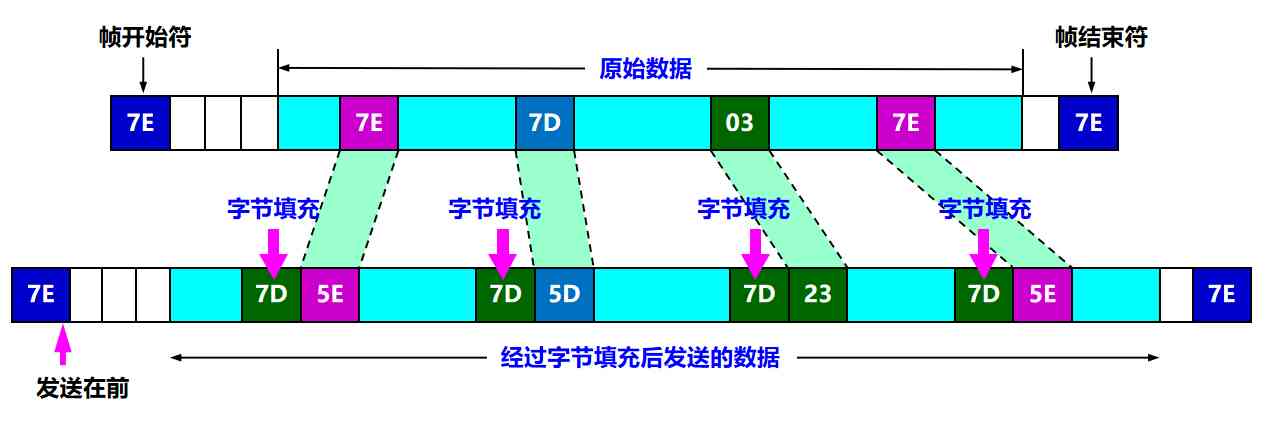
A: Character padding
Put every... That appears in the information field 0x7E Byte to 2 Byte sequence (0x7D, 0x5E)
If a... Appears in the message field 0x7D Bytes of , Turn it into 2 Byte sequence (0x7D, 0x5D)
If... Appears in the message field ASCII Code control characters ( That is, the value is less than 0x20 The characters of ), Add a... Before the character 0x7D byte , At the same time, change the encoding of the character
B: Zero bit fill
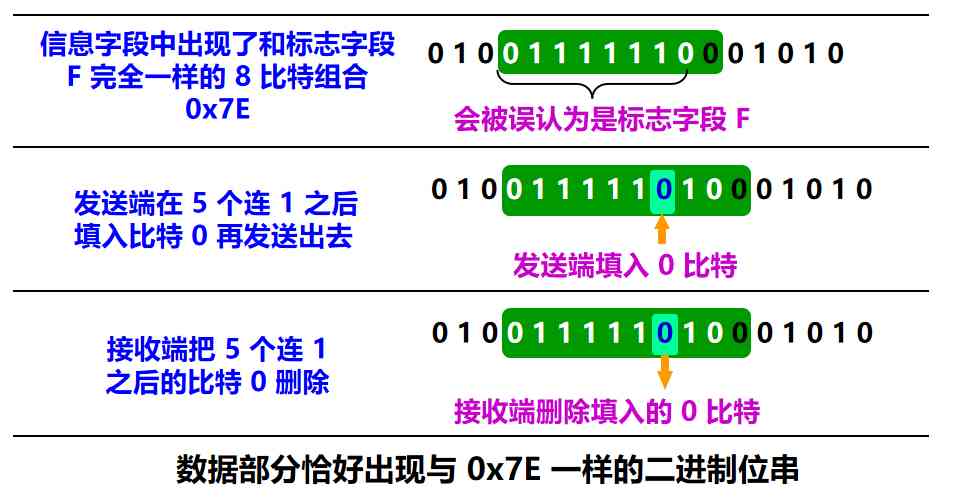
PPP Protocol used SONET/SDH Link time , Use synchronous transfer ( A continuous stream of bits ). At this time PPP The protocol adopts zero bit filling method to realize transparent transmission
At the sending end , As long as we find that there is 5 One continuous 1, Fill in a... Immediately 0
The receiving end scans the bit stream in the frame . Whenever I find 5 One continuous 1 when , Just put this 5 One continuous 1 The latter one 0 Delete
(4) Reliable transmission using serial numbers and confirmations is not provided
PPP The reason why the agreement Don't use The sequence number and confirmation mechanism are based on the following considerations :
When the probability of errors in the data link layer is small , Use the simpler PPP The agreement is more reasonable
In the Internet Environment ,PPP The data put in the information field of is IP The datagram . The reliable transmission of data link layer does not guarantee that the transmission of network layer is also reliable
Frame check sequence FCS Field to ensure error free acceptance
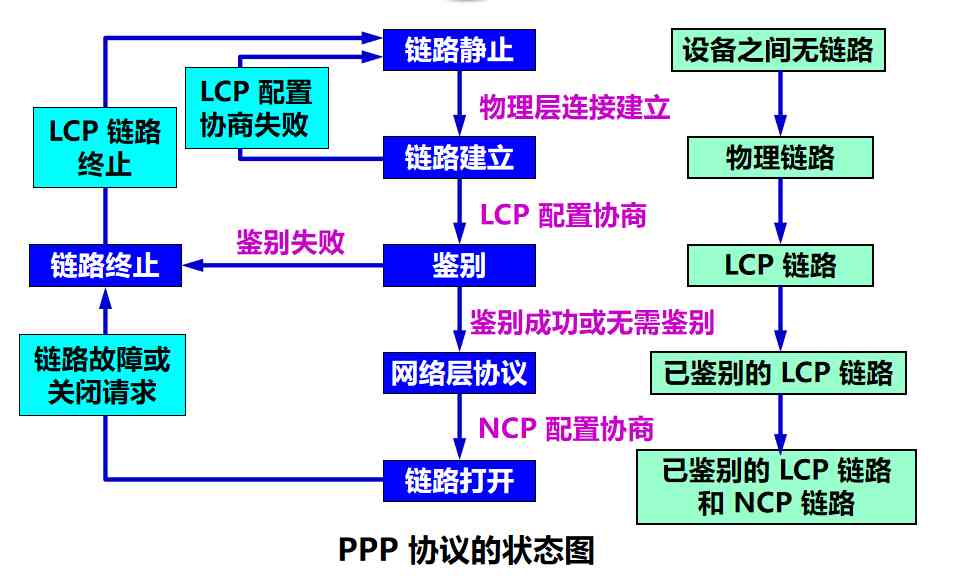
(5) PPP Working status of the agreement
When users dial in ISP when , The modem of the router confirms the dialing , And establish a physical connection
PC The machine sends a series of LCP grouping ( To encapsulate into many PPP frame )
These groups and their response choices are PPP Parameters , And network layer configuration ,NCP For new access PC Machine assigns a temporary IP Address , send PC Machine becomes a host on the Internet
At the end of the communication ,NCP Release network layer connection , Take back what was allotted IP Address . next ,LCP Release data link layer connection . The last thing to release is the connection of the physical layer
so ,PPP Protocol is not a pure data link layer protocol , It also includes the physical layer and the network layer
3、 ... and Use the data link layer of the broadcast channel
( One ) Data link layer of LAN
The main characteristics of LAN are :
- The network is owned by one unit
- The geographical scope and number of stations are limited
LAN has the following main advantages :
-
With broadcast function , Easy access to the whole network from one site , Hosts on LAN can share all kinds of hardware and software resources connected to LAN
-
Facilitate the expansion and gradual evolution of the system , The position of each equipment can be adjusted and changed flexibly
-
Improve the reliability of the system 、 Availability and survivability
The topological structure of Internet :
(1) Two standards of Ethernet
DIX Ethernet V2 It's the first LAN product in the world ( Ethernet ) The statute of
IEEE 802.3 Is the first IEEE Ethernet standard for
-
DIX Ethernet V2 Standards and IEEE Of 802.3 There's only a small difference in standards , So you can put 802.3 Local area network is abbreviated as “ Ethernet ”
-
Strictly speaking, ,“ Ethernet ” It should mean conformity with DIX Ethernet V2 Standard lan
(2) Two sublayers of data link layer
In order to make the data link layer better adapt to a variety of LAN standards ,IEEE 802 The Committee divides the data link layer of LAN into two sub layers :
- Logical link control LLC (Logical Link Control) Sublayer
- Media access control MAC (Medium Access Control) Sublayer
Content related to access to the transmission media is placed in MAC Sublayer , and LLC The sublayer has nothing to do with the transmission media
No matter what protocol is used in LAN , Yes LLC The sublayers are transparent
(3) Function of adapter
Network interface board is also called Communication adapter (adapter) or Network interface card NIC (Network Interface Card), or “ network card ”
An important function of the adapter :
- Serial / Parallel transformation
- Caching data
- Install device drivers on your computer's operating system
- Implement Ethernet protocol
( Two ) CSMA/CD agreement
The original Ethernet was to connect many computers to a bus . It is easy to realize broadcast communication . It was thought that such a connection method was simple and reliable , Because there are no active devices on the bus .
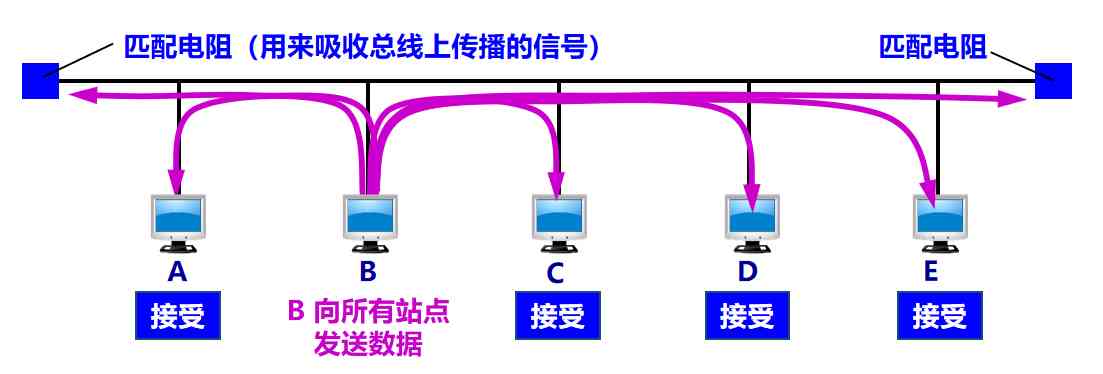
In order to achieve one-to-one communication , Write the hardware address of the receiving station into the destination address field in the header of the frame . Only if the destination address in the data frame is consistent with the hardware address of the adapter , To receive this data frame
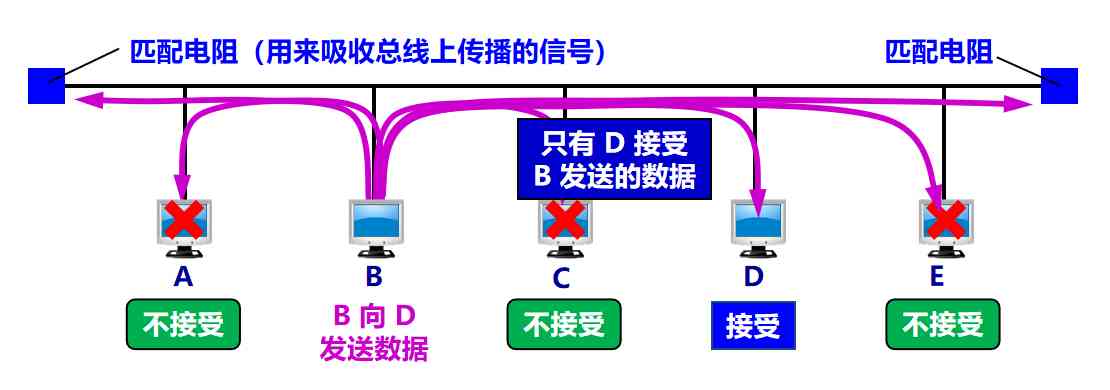
The bus also has disadvantages . If multiple computers or multiple sites send at the same time , There will be a send collision or conflict , Send failed .
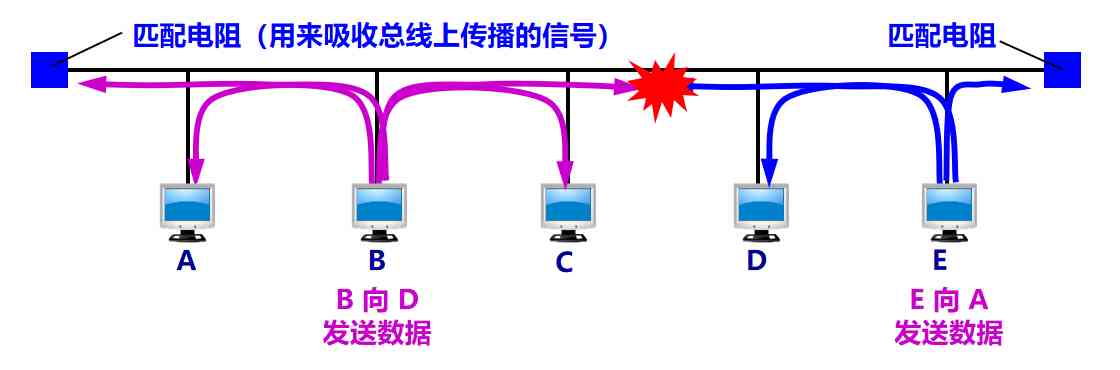
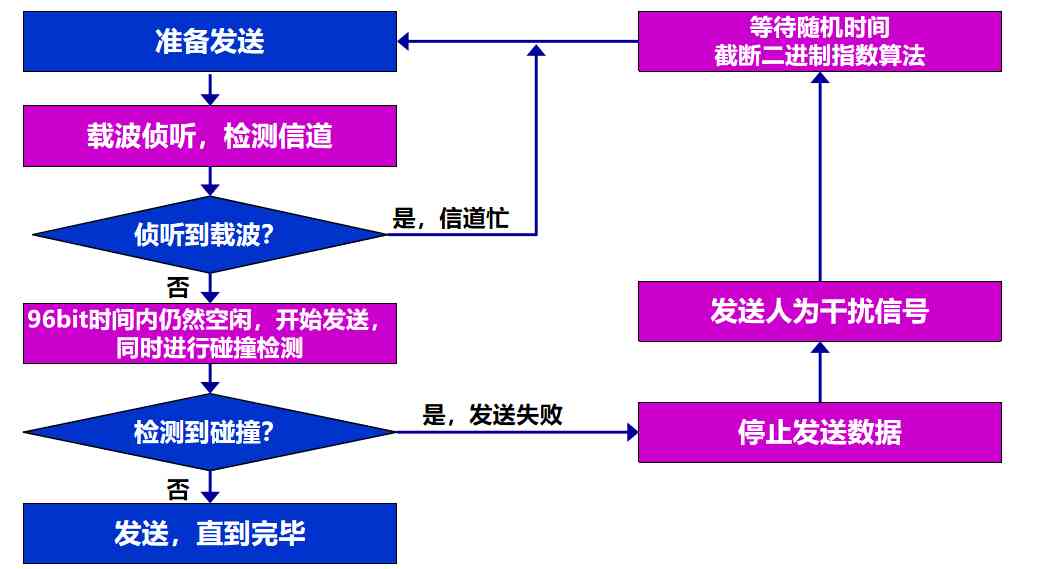
(1) Two important measures taken by Ethernet
① Adopt a more flexible working mode without connection
- You can send data directly without having to establish a connection first
- The transmitted data frames are not numbered , Also does not require the other party to send back confirmation
- The reason for this is that the quality of the LAN channel is very good , The probability of error due to channel quality is very small
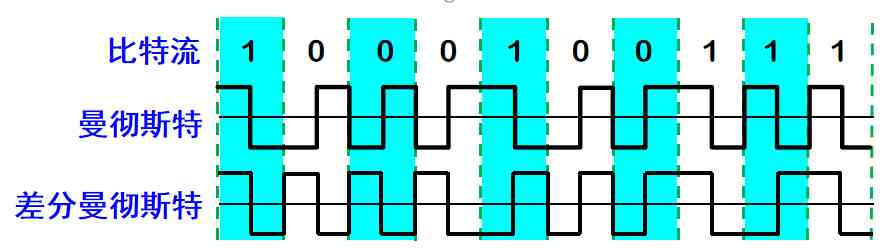
② All data sent over Ethernet uses Manchester (Manchester) code
- The disadvantages of Manchester coding are : It takes up twice the bandwidth of the original baseband signal
(2) CSMA/CD Key points of the agreement
CSMA/CD meaning : Carrier monitoring multipoint access / collision detection (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection)
“ Multipoint access ” It means that many computers are connected to a bus by means of multi-point access
“ carrier sense ” It means that each station should check whether there are other computers sending data on the bus before sending data , If there is , Do not send data for the time being , In case of collision
There's nothing on the bus “ carrier ”. therefore , “ carrier sense ” It is to use electronic technology to detect whether there are data signals sent by other computers on the bus
(3) collision detection
because The propagation rate of electromagnetic wave on the bus is limited , When a station detects that the bus is idle , Or maybe the bus is not really idle
- A towards B A message sent , It will take a certain time to transmit to B
- B If in A The sent message arrived B Send your own frame before ( Because at this time B The carrier monitor can't detect A Messages sent ), At a certain time and A The transmitted frame collides
- The result of the collision is that both frames become useless
So you need to be in Collision detection during transmission , To detect conflicts
“ collision detection ” That is, when the computer sends data, it detects the signal voltage on the channel .
When several stations send data on the bus at the same time , The signal voltage swing on the bus will increase ( Superimpose on each other ).
When a station detects the signal voltage swing value When a certain threshold value is exceeded , I think At least two stations on the bus are sending data at the same time , Indicates a collision .
So-called “ Collision ” It's a conflict . therefore “ collision detection ” Also known as “ Collision detection ”
Every station that is sending data , Once a collision is found on the bus , Stop sending immediately , So as not to waste network resources , Then wait for a random period of time and send again
Use CSMA/CD Ethernet protocol Can not carry out full duplex communication, but can only carry out two-way alternate communication ( Half duplex communication ), Because the collision of the frame is invalid .
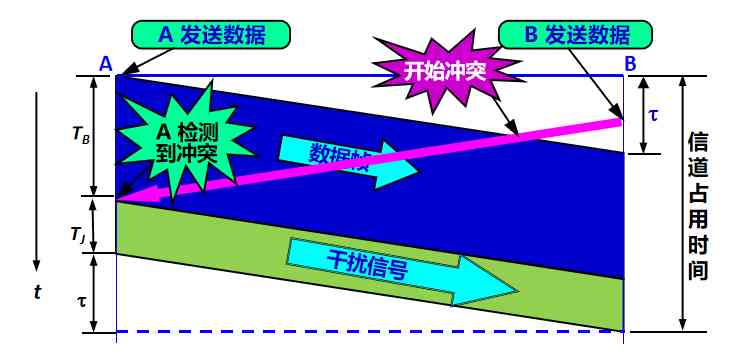
When sending data station Once a collision is found :
- (1) Stop sending data immediately ;
- (2) Continue to send several bits of Human interference signal (jamming signal), In order to let all users know now There has been a collision .
The first (2) spot CSMA/CD Key points of the agreement :
( 3、 ... and ) Star topology of hub
Traditional Ethernet originally used thick coaxial cable , Later, it evolved to use the relatively cheap thin coaxial cable , Finally developed to use cheaper and more flexible twisted pair
Ethernet with twisted pair adopts star topology , In the center of the star, a very reliable device is added , It's called a hub (hub)
Traditional Ethernet uses coaxial cable , Bus topology is adopted
Twisted pair Ethernet using hub
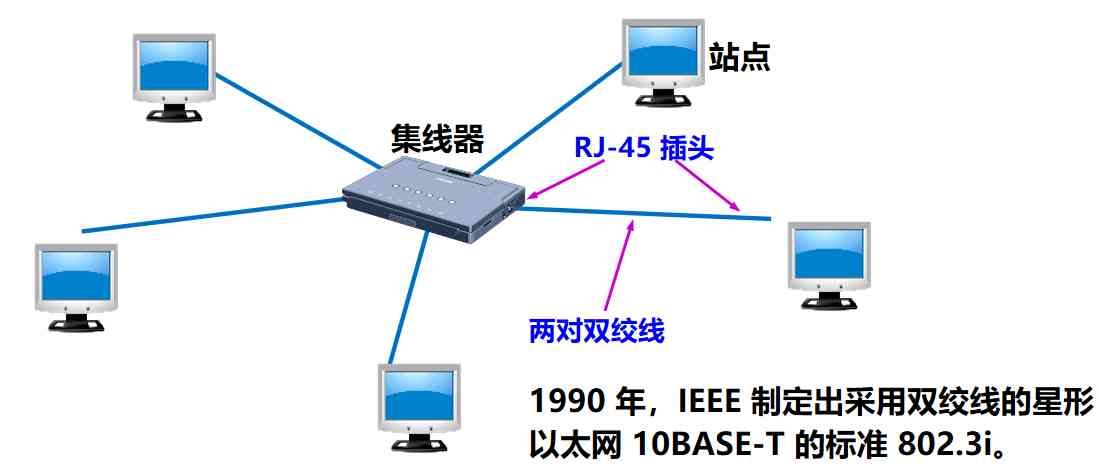
Hub is to use electronic devices to simulate the work of the actual cable , So the whole system still works like a traditional Ethernet
Ethernet using hub is still a bus network logically , Each workstation uses CSMA/CD agreement , And share the logical bus
Hub is very much like a multi interface transponder , Working on the physical level
The hub uses special chips , Adaptive crosstalk echo cancellation , Reduced near end crosstalk
( Four ) Ethernet channel utilization
(1) basic
Multiple stations working on the Ethernet at the same time may cause collision
When there is a collision , Channel resources are actually wasted . therefore , When the channel loss caused by collision is deducted , The total channel utilization of Ethernet cannot be achieved 100%
hypothesis x Is the end-to-end propagation delay of Ethernet one-way . The length of the contention period is 2x , That is, twice the end-to-end propagation delay . No interference signal is sent after collision is detected
Set the frame length to L (bit), The data transmission rate is C (bit/s), Then the transmission time of the frame is T0 = L/C (s)
A station collided while sending a frame . After a period of competition 2x after , There may be another collision . After several competing periods , One station sent it successfully . Suppose that the time required to send the frame is T0
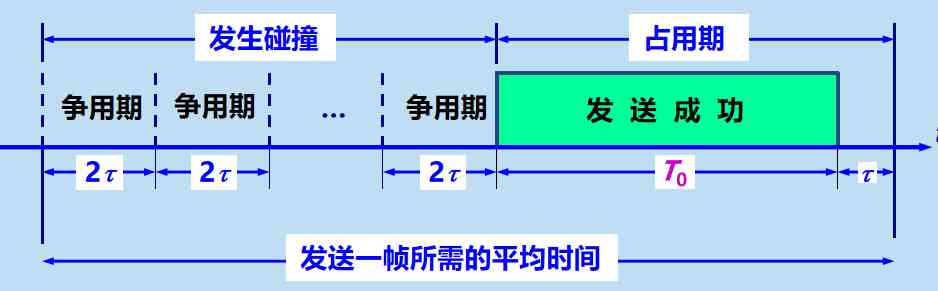
be aware , The time required for successful transmission of a frame is T0 + x , One more one-way end-to-end delay than the sending time of this frame x
This is because when a station sends the last bit , This bit has to be spread over the Ethernet
In the most extreme cases , The sending station is at one end of the transmission media , And the time it takes for bits to get to the other end of the media is x
To improve the channel utilization of Ethernet , It has to be reduced x And T0 The ratio of the
Parameters are defined in Ethernet a , It's Ethernet one-way end-to-end delay x Send time with frame T0 The ratio of the :
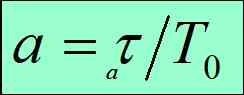
explain : The symbol of the essential molecule is shown in the figure , Because of the relative trouble of editor, number, formula, symbol, etc , So it's all used above x Instead of
In order to improve the utilization rate , Ethernet parameters a The value of should be as small as possible
For Ethernet parameters a The requirement is :
- When the data rate is fixed , The length of the Ethernet connection is limited , otherwise x It's going to be too big
- Ethernet frame length cannot be too short , otherwise T0 The value of will be too small , send a The value is too large
(2) Maximum channel utilization Smax
In an idealized situation , The data sent by each station on the Ethernet will not collide ( This is clearly not CSMA/CD, But a special scheduling method is needed ), Once the bus is idle, a certain station will send data immediately
The time taken to send a frame is T0 + x , And the transmission time of the frame itself is T0. therefore , We can calculate the ultimate channel utilization in the ideal case Smax by :
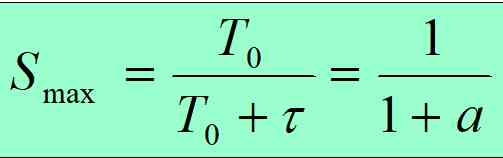
- Only when the parameter a Far less than 1 In order to get the maximum channel utilization as high as possible
- According to statistics , When the utilization of Ethernet reaches 30% Is already overloaded . A lot of network capacity has been consumed by online collisions
( 5、 ... and ) Ethernet MAC layer
In the LAN , The hardware address is also called the physical address , or MAC Address .
802 What the standard says “ Address ” Strictly speaking, it should be at every station “ name ” Or identifier .
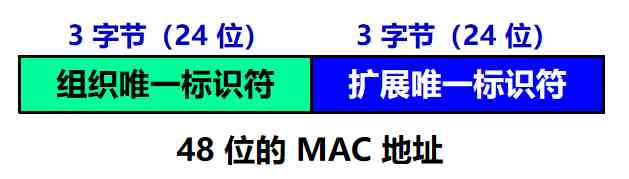
(1) MAC Address composition
- IEEE 802 The standard stipulates MAC The address field can be 6 byte ( 48 position ) or 2 byte ( 16 position ) One of the two
- IEEE The registration authority of RA Responsible for assigning address fields to manufacturers 6 The first three bytes of bytes ( That's high 24 position ), Called the organization unique identifier
- Address field 6 The last three of the bytes ( I.e. low position 24 position ) To be assigned by the manufacturer , Called extended unique identifier , It must be ensured that the adapter produced does not have a duplicate address
-
An address block can generate 224 Different addresses . such 48 Bit addresses are called MAC-48, Its common name is EUI-48
-
When making adapters ,6 Bytes of MAC The address has been solidified in the adapter's ROM, therefore ,MAC Address is also called hardware address (hardware address) Or physical address
-
“MAC Address ” It's actually the adapter address or the adapter identifier EUI-48
(2) Adapter check MAC
All adapters recognize at least the first two frames , That is, it can be identified Unicast and broadcast addresses
In a hybrid way (promiscuous mode) The Ethernet adapter works as long as “ hear ” Frames are received when they are transmitted over the Ethernet
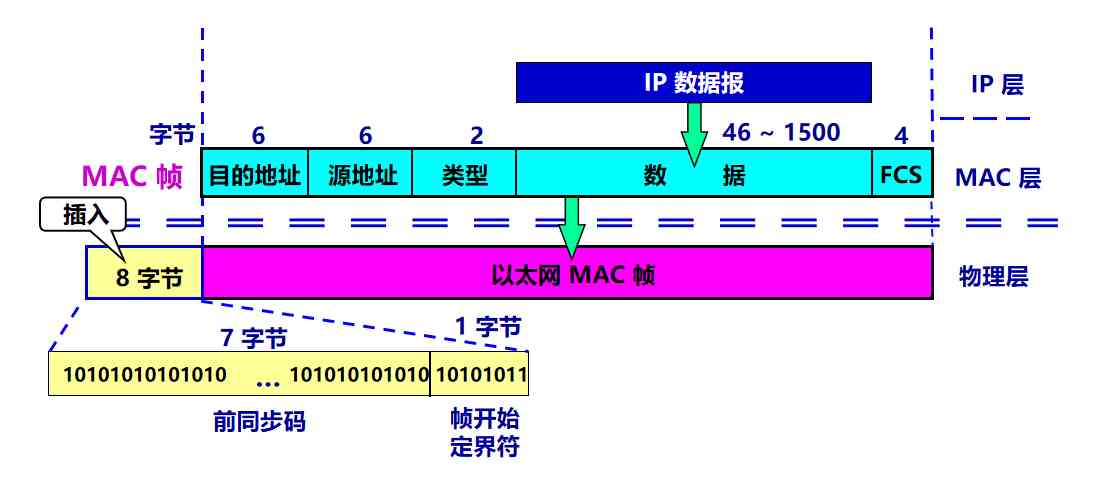
(3) MAC Frame format
Common Ethernet MAC There are two standard frame formats :
- DIX Ethernet V2 standard ( Commonly used )
- IEEE Of 802.3 standard
-
The type field is used to indicate what protocol is used in the upper layer , In order to receive MAC Frame data is handed over to the next layer of this protocol
-
The official name of the data field is MAC Customer data fields , Minimum length 64 byte - 18 The beginning and end of a byte = The minimum length of the data field (46 byte )
-
When the length of the data field is less than 46 Byte time , An integer byte filled field should be added after the data field , To ensure the Ethernet MAC Frame length not less than 64 byte
-
Insert... In front of the frame ( Hardware generation ) Of 8 In bytes , The first field consists of 7 Bytes , It's a preamble , For rapid implementation MAC Bit synchronization of frames . Second field 1 Bytes are the frame start qualifier , The following information is MAC frame .
invalid MAC frame
- The length of the data field does not match the value of the length field
- The length of the frame is not an integer byte
- Check the sequence with the received frame FCS Find out what's wrong
- The length of the data field is not 46 ~ 1500 Between bytes
- Effective MAC The frame length is 64 ~ 1518 Between bytes
Four Extended Ethernet
( One ) Extending Ethernet at the physical layer
Using optical fiber expansion
-
Host uses optical fiber ( It's usually a pair of fibers ) And a pair of fiber optic modems connected to the hub .
-
It's easy to connect the mainframe to a hub a few kilometers away
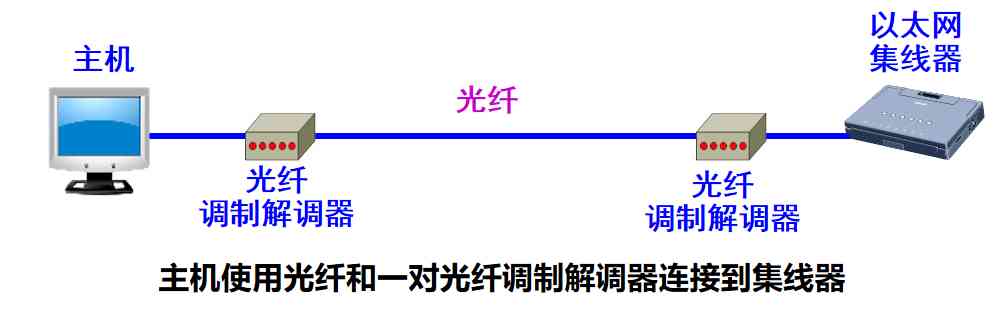
Using hub extensions : Connect multiple Ethernet segments into larger 、 Ethernet with multi-level star structure

advantage
- So that the computers on Ethernet belonging to different collision domains can communicate across collision domains
- Expand the geographical coverage of Ethernet
shortcoming
- The collision domain has increased , But the overall throughput has not improved
- If different collision domains use different data rates , Then you can't use hubs to interconnect them
Add
-
Collision domain (collision domain) It is also called conflict domain , It refers to the part of the network where the frame sent by one site will collide with the frame sent by other stations
The larger the collision domain is , The higher the probability of collision
( Two ) Extending Ethernet in data link layer
The more common way to expand Ethernet is at the data link layer
Early use of bridges , Now use Ethernet switches
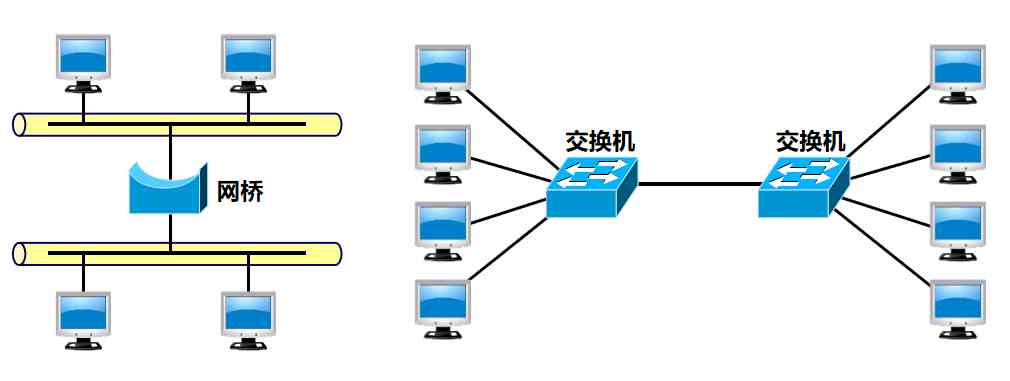
-
The bridge works at the data link layer
-
It is based on MAC The destination address of the frame forwards and filters the received frame
-
When the bridge receives a frame , This frame is not forwarded to all interfaces , But first check the purpose of this frame MAC Address , Then determine which interface to forward the frame to , Or throw it away
(1) Characteristics of Ethernet switch
-
Ethernet switch is essentially a switch with more than ten or more interfaces
- There are usually a dozen or more interfaces
-
Each interface is directly connected to a single host or another Ethernet switch , And generally Working in full duplex mode
-
Ethernet switch It has parallelism
- It can connect many pairs of interfaces at the same time , Enable multiple pairs of hosts to communicate at the same time
(2) Switching mode of switch
Store and forward mode
- The whole data frame is first cached and then processed .
Straight through (cut-through) The way
- At the same time of receiving data frame Immediately press the purpose of the data frame MAC The address determines the forwarding interface of the frame , Therefore, the frame forwarding speed is improved .
- The disadvantage is that it forwards the frame directly without checking for errors , therefore It is possible to forward some invalid frames to other stations .
summary :
Ethernet switch operation Self learning algorithm for automatic maintenance of exchange table
- After receiving a frame, the switch first conducts self-learning . Look for items in the exchange table that match the source address of the received frame .
- If not , Add an entry to the exchange table ( source address 、 Access interface and effective time ).
- if there be , The original project will be updated ( Entry interface or valid time ).
- Forward frame . Look for items in the exchange table that match the destination address of the received frame .
- If not , To all other interfaces ( Except for the incoming interface ) forward .
- if there be , Then forward according to the interface given in the exchange table .
- If the interface given in the exchange table is the interface that the frame enters the switch , The frame should be discarded ( Because there is no need to forward through the switch ).
This self-learning method of Ethernet switch makes Ethernet switch plug and play , No manual configuration is required , So it's very convenient .
( 3、 ... and ) Virtual LAN
The use of Ethernet switch can be very convenient to achieve virtual LAN VLAN (Virtual LAN)
IEEE 802.1Q For VLAN VLAN The definition of :
- Virtual LAN VLAN It is a logical group composed of some LAN segments that are independent of the physical location , These network segments have some common features - The needs of . every last VLAN All frames of have an explicit identifier , Indicates which computer is sending this frame to VLAN
Virtual LAN is just a service provided by LAN to users , It's not a new kind of LAN
Because VLAN is a logical combination of users and network resources , Therefore, the relevant equipment and resources can be easily recombined as needed , Enables users to access the required resources from different servers or databases
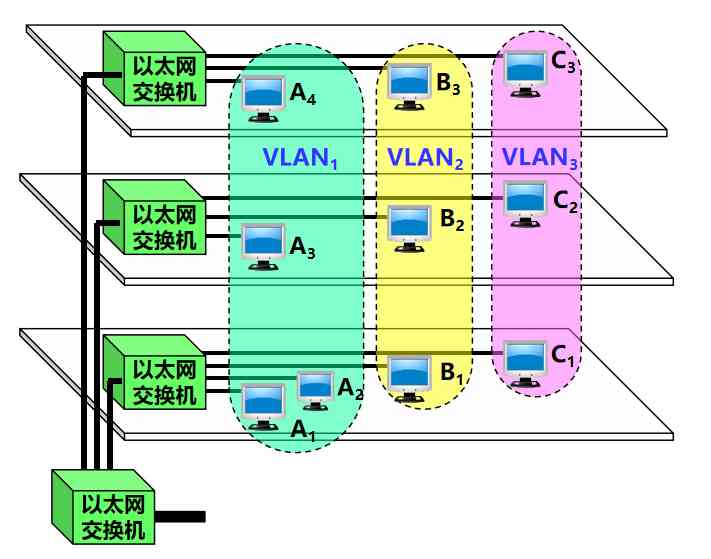
-
10 Computers are divided into three VLANs : VLAN1, VLAN2 and VLAN3
-
Each VLAN is a broadcast domain ,VLAN1, VLAN2 and VLAN3 It's three different broadcast domains
-
When B1 towards VLAN2 When members of a team send data , The workstation B2 and B3 It will receive its broadcast message
-
B1 When sending data ,VLAN1 and VLAN3 Workstation in A1,A2 and C1 I won't even receive it B1 Broadcast messages sent
-
VLAN limits the number of workstations that receive broadcast information , So that the network will not spread too much broadcast information ( namely “ Broadcast storm ”) And cause performance deterioration .
Virtual LAN (VLAN) The technology has the following main advantages :
- Improved performance
- Simplified management
- Reduced cost
- Improved security
5、 ... and PPPoE
-
PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) It means “ Running on the Ethernet PPP”, It is the PPP Protocol combined with Ethernet protocol —— take PPP Frames are then encapsulated in Ethernet for transmission
-
Today's fiber broadband access FTTx All use PPPoE The way to access . stay PPPoE In the pop-up window, type the user name and password purchased by the network operator , You can use broadband Internet
-
utilize ADSL For broadband access , From the user's personal computer home ADSL Between modems , Is also used RJ-45 and 5 Quasilinear ( That is, the Ethernet cable ) To make a connection , And it also uses PPPoE Pop up window for dial-up connection