当前位置:网站首页>Shell_ 05_ operator
Shell_ 05_ operator
2022-07-06 16:51:00 【Coke loving w】
Shell_05_ Operator
Operator
Operators are divided into : Arithmetic operator 、 Relational operator 、 Logical operators 、 String operators and file test operators
1) When using operators , You must add spaces on the left and right sides of the operator to separate other variables
Command operator
Association system command execution : There is a dependency between the two commands ( And 、 or )
| Command execution | |
|---|---|
| command 1 && command 2 | If command 1 Successful execution , Then start to execute the command 2 |
| If command 1 An error occurred during execution , Do not execute the order 2 | |
| command 1 || command 2 | If command 1 Successful execution , Do not execute the order 2 |
| If command 1 An error occurred during execution , Then start to execute the command 2 |
1) Whether the command is successfully executed depends on “$?” Is the variable 0 To judge
Such as : stay /root/test/abc Create files under folders test and test2
// Regardless of /abc Does the folder exist , Can be established
Arithmetic operator
Suppose there are variables a and b, The values are 10 and 20
| Operator | explain | give an example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Add | `expr $a + $b` The result is 30. |
| - | Subtraction | `expr $a - $b` The result is -10. |
| * | Multiplication | `expr $a \* $b` The result is 200. |
| / | division | `expr $b / $a` The result is 2. |
| % | Remainder | `expr $b % $a` The result is 0. |
| = | assignment | a=$b Will put the variable b The value is assigned to a |
| = = | Used to compare two numbers Same returns true( really ) | [ $a == $b ] return false( false ) |
| != | Used to compare two numbers If not, return to true | [ $a != $b ] return true |
1)bash It doesn't support arithmetic itself , It can be done by awk、expr and bc To achieve
2) Through the bracket operation form :[ $ Variable 1 Operator $ Variable 2 ]
// If you assign the result of the operation to other variables , It is also necessary to add $
expr command : Record the result of expression calculation
Command format :expr value 1 Operator value 2
1) Only integer level operations can be performed
Such as : Use expr Do four calculations 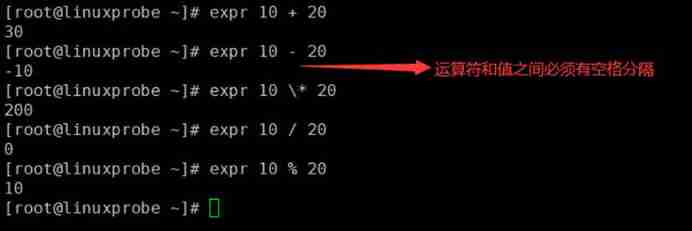
//“*” Operators need to pass “\” Transference
Bracket operators
Judging symbols : brackets “[ ]”
Command format :[ Detection expression ]
1)[ ] Belongs to operator , When using, you need to add spaces at the beginning and end
2) Variables in brackets , It is best to use double quotation marks
3) Constants in brackets , It's best to use a single / In double quotation marks
| Test parameters | meaning | analysis |
|---|---|---|
| 1. About file type detection | ||
| -e File path | Test files ( Including directory ) Whether there is If it is , Then return to true | [ -e $file ] return true |
| -d File path | Check if the file is a directory If it is , Then return to true | [ -d $file ] return false |
| -f File path | Check if the file is a normal file If it is , Then return to true | [ -f $file ] return true |
| -s File path | Check if the file is empty ( file size ) Not empty return true | [ -s $file ] return true |
| -p File path | Check whether the file is a pipeline file If it is , Then return to true | [ -p $file ] return false |
| -b File path | Check whether the file is a block device file If it is , Then return to true | [ -b $file ] return false |
| -c File path | Detect whether the file is a character device file If it is , Then return to true | [ -c $file ] return false |
| -S File path | Check whether the file is Socket file If it is , Then return to true | [ -c $file ] return false |
| 2. About file permission detection | ||
| -r File path | Check whether the file is readable If it is , Then return to true | [ -r $file ] return true |
| -w File path | Check whether the file is writable If it is , Then return to true | [ -w $file ] return true |
| -x File path | Check if the file is executable If it is , Then return to true | [ -x $file ] return true |
| -u File path | Check if the file is set SUID position If it is , Then return to true | [ -u $file ] return false |
| -g File path | Check if the file is set SGID position If it is , Then return to true | [ -g $file ] return false |
| -k File path | Check whether the file is set with the adhesive bit (Sticky Bit) If it is , Then return to true | [ -k $file ] return false |
| 3. About the detection of document comparison | ||
| -nt (new than) | Check whether the first file is newer than the second If new , Then return to true | [ $file1 -nt $file2 ] |
| -ot (old than) | Check whether the first file is older than the second If it's old , Then return to true | [ $file1 -ot $file2 ] |
| -ef | Check whether the two files are the same If the same file , Then return to true | [ $file1 -ef $file2 ] |
| 4. About integer detection | ||
| -eq (eaqul) | Check whether two numbers are equal Equal return true | [ $a -eq $b ] return false. |
| -ne (not equal) | Check whether two numbers are equal Unequal return true | [ $a -ne $b ] return true. |
| -gt (great than) | Check whether the number on the left is greater than that on the right If it is , Then return to true | [ $a -gt $b ] return false. |
| -ge | Check whether the number on the left is equal to or greater than the number on the right If it is , Then return to true | [ $a -ge $b ] return false. |
| -lt (less than) | Check if the number on the left is less than the number on the right If it is , Then return to true | [ $a -lt $b ] return true. |
| -le | Check whether the number on the left is less than or equal to the number on the right If it is , Then return to true | [ $a -le $b ] return true. |
| 5. About string detection | ||
| -z | Check if the string length is 0 by 0 return true | [ -z $c ] return false |
| -n | Check if the string length is 0 Not for 0 return true | [ -n $c ] return true |
| \> | Check whether the left string is larger than the right string Greater than return true( according to ASCII) | [ $c \> $d ] return true |
| \< | Check whether the left string is smaller than the right string Less than return true( according to ASCII) | [ $c \< $d ] return false |
| = = | Checks if two strings are equal Equal return true | [ $c = = $d ] return false |
| 6. About multiple condition detection | ||
| -a ( And operation ) | Both expressions are true To return to true | [ $a -lt 20 -a $b -gt 100 ] return false |
| -o ( Or operations ) | There is an expression for true Then return to true | [ $a -lt 20 -o $b -gt 100 ] return true |
| ! ( Non operation ) | Expression for true Then return to false | [ ! false ] return true |
1) Suppose there are variables a and b, The values are 10 and 20
2) Suppose there are variables c and d, The values are ‘abc’ and ‘efg’
3) The authority is judged as or : Only one of the three identities has , Think true
test command : The file / Data for specified detection
Command format :test Detection expression
1) The use method and effect are equivalent to the bracket judgment symbol
Such as : Compare sizes of integers 
//test And brackets do not directly print test results , Need to use “$?” see
Double parenthesis operation
Double parentheses can realize advanced mathematical expressions in Inner parentheses
1) Format :(( Mathematical expression ))
2) A mathematical expression can be any mathematical assignment or comparison expression ;
3) More used for for loop , The implementation is similar to C Linguistic for Circular format ;
| Operator | explain |
|---|---|
| ++ | Self increasing operation |
| – | Self built operation |
| ! | Logical negation |
| ~ | Position inversion |
| ** | Power operation |
| << | Left displacement |
| >> | Right displacement |
| & | Bit Boolean and |
| | | Bit Boolean or |
| && | And operation |
| || | Or operations |
边栏推荐
- 解决Intel12代酷睿CPU【小核载满,大核围观】的问题(WIN11)
- Chapter III principles of MapReduce framework
- Educational Codeforces Round 122 (Rated for Div. 2)
- ~69 other ways to use icon fonts
- 第6章 Rebalance详解
- Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of China's desktop capacitance meter
- Codeforces Round #771 (Div. 2)
- Business system compatible database oracle/postgresql (opengauss) /mysql Trivia
- Spark的RDD(弹性分布式数据集)返回大结果集
- Usage of insert() in vector
猜你喜欢

The most lost road I have ever walked through is the brain circuit of ByteDance programmers
Hbuilder x format shortcut key settings
The 116 students spent three days reproducing the ByteDance internal real technology project

LeetCode 1584. Minimum cost of connecting all points
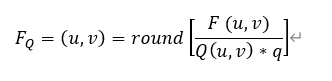
Basic principles of video compression coding and audio compression coding
~81 long table

100张图训练1小时,照片风格随意变,文末有Demo试玩|SIGGRAPH 2021

字节跳动技术新人培训全记录:校招萌新成长指南
Chapter 6 datanode
Solve the single thread scheduling problem of intel12 generation core CPU (II)
随机推荐
Spark独立集群动态上线下线Worker节点
LeetCode 1557. The minimum number of points that can reach all points
Eureka single machine construction
谢邀,人在工区,刚交代码,在下字节跳动实习生
7-4 harmonic average
Eureka high availability
~87 animation
第5章 NameNode和SecondaryNameNode
第5章 消费者组详解
腾讯面试算法题
LeetCode 1641. Count the number of Lexicographic vowel strings
LeetCode 1562. Find the latest group of size M
Basic principles of video compression coding and audio compression coding
字节跳动新程序员成长秘诀:那些闪闪发光的宝藏mentor们
Codeforces Round #771 (Div. 2)
~82 style of table
亮相Google I/O,字节跳动是这样应用Flutter的
两个礼拜速成软考中级软件设计师经验
~72 horizontal and vertical alignment of text
Li Kou leetcode 280 weekly match