当前位置:网站首页>Message queue: how to handle repeated messages?
Message queue: how to handle repeated messages?
2022-07-07 05:40:00 【Qin Tian】
Catalog
Two 、 There must be repetition of information
3、 ... and 、 Using idempotency to solve the problem of duplicate messages
1. Using the unique constraint of database to realize idempotent
2. Set preconditions for updated data
One 、 Preface
In the process of messaging , If the delivery fails , The sender will try again , In the process of retrying, duplicate messages may be generated . For business systems that use message queuing , If duplicate messages are not processed , There may be errors in the data of the system .
for instance , A consumer order message , Statistics of the amount of micro service orders , If duplicate messages are not handled correctly , There will be duplicate statistics , This leads to statistical errors .
You may ask , If the message queue itself can ensure that messages are not repeated , The implementation of the application is not simple ? Is there a message queue to ensure that messages are not repeated ?
Two 、 There must be repetition of information
stay MQTT Agreement , Three quality of service standards that can be provided when delivering messages are given , The three kinds of service quality from low to high are :
- At most once: One more time . When a message is delivered , It will be delivered at most once . To put it another way is , There's no guarantee of reliability , It's allowed to lose news . Generally, it is used in some monitoring scenarios that do not require high reliability of messages , For example, report the temperature data of the computer room once a minute , A small amount of data loss is acceptable .
- At least once: At least once . When a message is delivered , It will be delivered at least once . in other words , It's not allowed to lose news , But a small number of duplicate messages are allowed .
- Exactly once: Exactly Once . When a message is delivered , It will only be delivered once , No loss or repetition is allowed , This is the highest level .
This service quality standard is not only applicable to MQTT, It works for all message queues . The quality of service provided by most of the message queues we use now is At least once, Include RocketMQ、RabbitMQ and Kafka It's all like this . in other words , Message queuing is very difficult to ensure that messages do not repeat .
Speaking of this, I know that some students will refute me :“ You're not right , I have ever seen Kafka Documents ,Kafka It's supporting Exactly once Of .” I'm here to explain to these students , You're right ,Kafka It's really support Exactly once, But there's no problem with what I'm talking about , Why? ?
Kafka Supported by “Exactly once” And we just mentioned the quality of service standards for messaging “Exactly once” It's different , It is Kafka Another feature provided ,Kafka There are also some differences between the transactions supported in and the transactions we usually understand .
stay Kafka in , Business and Excactly once It is mainly for the characteristics used in flow calculation .
3、 ... and 、 Using idempotency to solve the problem of duplicate messages
The general solution to duplicate messages is , On the consumer side , Let's make the operation of consuming messages idempotent .
idempotent (Idempotence) It was originally a mathematical concept , It's defined as :
If a function f(x) Satisfy :f(f(x)) = f(x), The function f(x) Satisfy idempotence .
This concept has been extended to the computer field , Used to describe an operation 、 Method or service . The characteristic of an idempotent operation is , The impact of any multiple execution is the same as that of one execution .
An idempotent method , Use the same parameters , Make multiple calls to it and one call , The impact on the system is the same . therefore , For idempotent methods , Don't worry about any changes to the system due to repeated execution .
Let's give an example to illustrate . Without considering concurrency ,“ Put the account X The balance of is set to 100 element ”, The impact on the system after one execution is , Account X The balance becomes 100 element . Just provide the parameters 100 Yuan doesn't change , Then even if it's executed many times , Account X The balance is always 100 element , No change , This operation is an idempotent operation .
Another example ,“ Put the account X Plus the balance of 100 element ”, This operation is not idempotent , Every time , The account balance will increase 100 element , The impact of multiple and one executions on the system ( That's the balance of the account ) It's different .
If the business logic of our system's consumption message is idempotent , Then don't worry about the repetition of news , Because of the same message , Consumption once and consumption many times have exactly the same impact on the system . We can also think of , To consume many times is to consume once .
In terms of the impact on the system :At least once + Idempotent consumption = Exactly once.
So how to implement idempotent operation ? The best way is , Start with business logic design , Design the business logic of consumption into idempotent operation . however , Not all businesses can be designed as natural idempotent , Here we need some methods and techniques to realize idempotent .
Now I'll introduce you to several common methods of designing idempotent operations :
1. Using the unique constraint of database to realize idempotent
For example, we just mentioned the example of transfer without idempotent property : Put the account X Plus the balance of 100 element . In this case , We can transform the business logic , Let it be idempotent .
First , We can limit , For each transfer document, only one change operation can be performed for each account , In distributed systems , There are many ways to limit implementation , The simplest thing is that we create a transfer statement in the database , This table has three fields : Transfer form ID、 Account ID And the amount of the change , Then give the transfer slip ID And accounts ID These two fields combine to create a unique constraint , So for the same transfer order ID And accounts ID, There can be at most one record in the table .
such , The logic of our message consumption can be changed to :“ Add a transfer record to the transfer daily report , Then according to the transfer record , Asynchronous operation to update user balance .” In the operation of adding a transfer record to the transfer daily report , Because we predefine in this table “ Account ID Transfer form ID” The only constraint , For the same transfer document, only one record can be inserted into the same account , Subsequent repeated insert operations will fail , In this way, an idempotent operation is realized . We just need to write one SQL, Just implement it correctly .
Based on this idea , Not only can you use relational databases , As long as it supports something like “INSERT IF NOT EXIST” Semantic storage class systems can be used to implement idempotent , such as , You can use it. Redis Of SETNX Command to replace the unique constraint in the database , To achieve idempotent consumption .
2. Set preconditions for updated data
Another way to achieve idempotence is , Set a precondition for data changes , Update data if conditions are met , Otherwise, refuse to update the data , When updating data , At the same time, change the data to be judged in the precondition . such , When you repeat this operation , Because the data that needs to be judged in the precondition has been changed when the data is updated for the first time , Does not meet the preconditions , The update data operation will not be repeated .
such as , We just said ,“ Put the account X The balance of increased 100 element ” This operation is not idempotent , We can add a precondition to this operation , Turn into :“ If the account X The current balance is 500 element , Add the balance to 100 element ”, This operation has idempotence . Corresponding to usage in message queue , You can bring the current balance in the message body when sending the message , In the database of judgment when consuming , Is the current balance equal to the balance in the message , Change operations are performed only if they are equal .
however , If the data we want to update is not numeric , Or we need to do a more complex update operation ? What should be used as a pre judgment condition ? A more general approach is , Add a version number attribute to your data , Before every data change , Compare the version number of the current data with that in the message , Refuse to update data if it is inconsistent , Update data with version number +1, The same can be achieved idempotent update .
3. Record and check operation
If neither of the two ways mentioned above can be applied to your scenario , We also have the most versatile , The most widely used method to realize idempotency : Record and check operation , Also known as “Token Mechanism or GUID( Globally unique ID) Mechanism ”, The idea of implementation is very simple : Before performing the data update operation , First check whether the update operation has been performed .
The specific implementation method is , When sending a message , Assign a globally unique... To each message ID, Consumption time , According to this ID Check if the message has been consumed , If you haven't consumed , To update the data , Then set the consumption status as consumed .
Is the principle and implementation very simple ? In fact, it's not simple at all , In distributed systems , This method is actually very difficult to implement . First , Assign each message a globally unique ID It's not that simple , There are many ways , But it's not so good, and it's simple 、 High availability and performance , It's more or less a sacrifice .
What's more troublesome is , stay “ Check consumption status , Then update the data and set the consumption status ” in , Three operations must be atomic as a set of operations , In order to realize idempotency , Otherwise, it will appear Bug.
for instance , For the same message :“ overall situation ID by 8, Operation for : to ID by 666 Account increase 100 element ”, It's possible that :
- t0 moment :Consumer A Got a message , Check message execution status , Found that the message has not been processed , Start execution “ Account increase 100 element ”;
- t1 moment :Consumer B Got a message , Check message execution status , Found that the message has not been processed , Because this moment ,Consumer A We haven't had time to update the message execution status .
This will cause the account to be wrongly increased twice 100 element , This is a very easy mistake to make in a distributed system , We must learn from it .
For this question , Of course, we can do it with transactions , It can also be done with locks , But in a distributed system , Both distributed transaction and distributed lock are difficult to solve .
Four 、 Summary
This paper mainly introduces how to solve the problem of message duplication through idempotent consumption , Then it focuses on several methods to realize idempotent operation , You can use database constraints to prevent data from being updated repeatedly , You can also set one-time preconditions for data updates , To prevent duplicate messages , If neither method is suitable for your scene , You can also use “ Record and check operation ” To ensure idempotence , This method has the widest application , But the difficulty and complexity of implementation are also relatively high , Generally not recommended .
These methods of realizing idempotent , Not only can it be used to solve the problem of duplicate messages , The same applies to , Solve the problem of repeated requests or repeated calls in other scenarios . such as , We can HTTP Services are designed to be idempotent , Solve the front end or APP The problem of submitting form data repeatedly ; You can also design a microservice to be idempotent , solve RPC Repeated calls caused by automatic retrying of framework . These methods are universal , I hope you can do it by analogy , The lines .
边栏推荐
- 4. 对象映射 - Mapping.Mapster
- [reading of the paper] a multi branch hybrid transformer network for channel terminal cell segmentation
- 拼多多新店如何获取免费流量,需要从哪些环节去优化,才能有效提升店内免费流量
- 消息队列:消息积压如何处理?
- [JS component] date display.
- Two person game based on bevy game engine and FPGA
- 得物客服一站式工作台卡顿优化之路
- Photo selector collectionview
- AIDL 与Service
- Under the trend of Micah, orebo and apple homekit, how does zhiting stand out?
猜你喜欢

Use Zhiyun reader to translate statistical genetics books
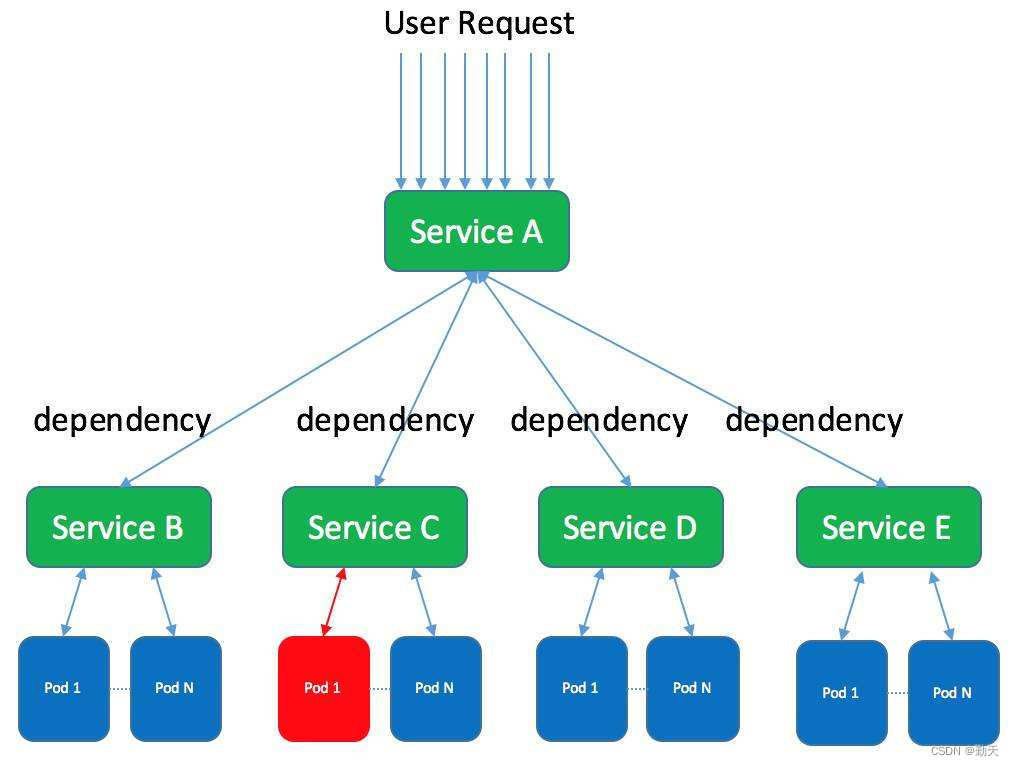
集群、分布式、微服务的区别和介绍
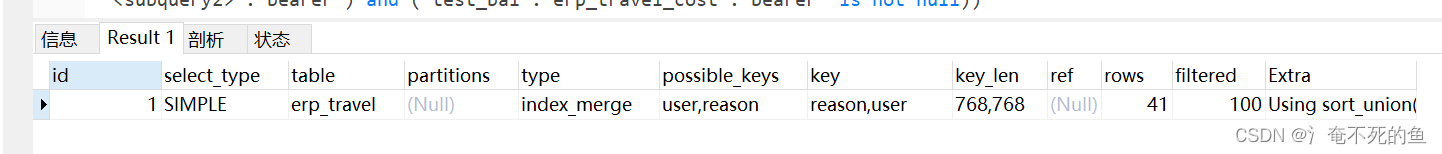
sql优化常用技巧及理解

【js组件】date日期显示。

论文阅读【Sensor-Augmented Egocentric-Video Captioning with Dynamic Modal Attention】
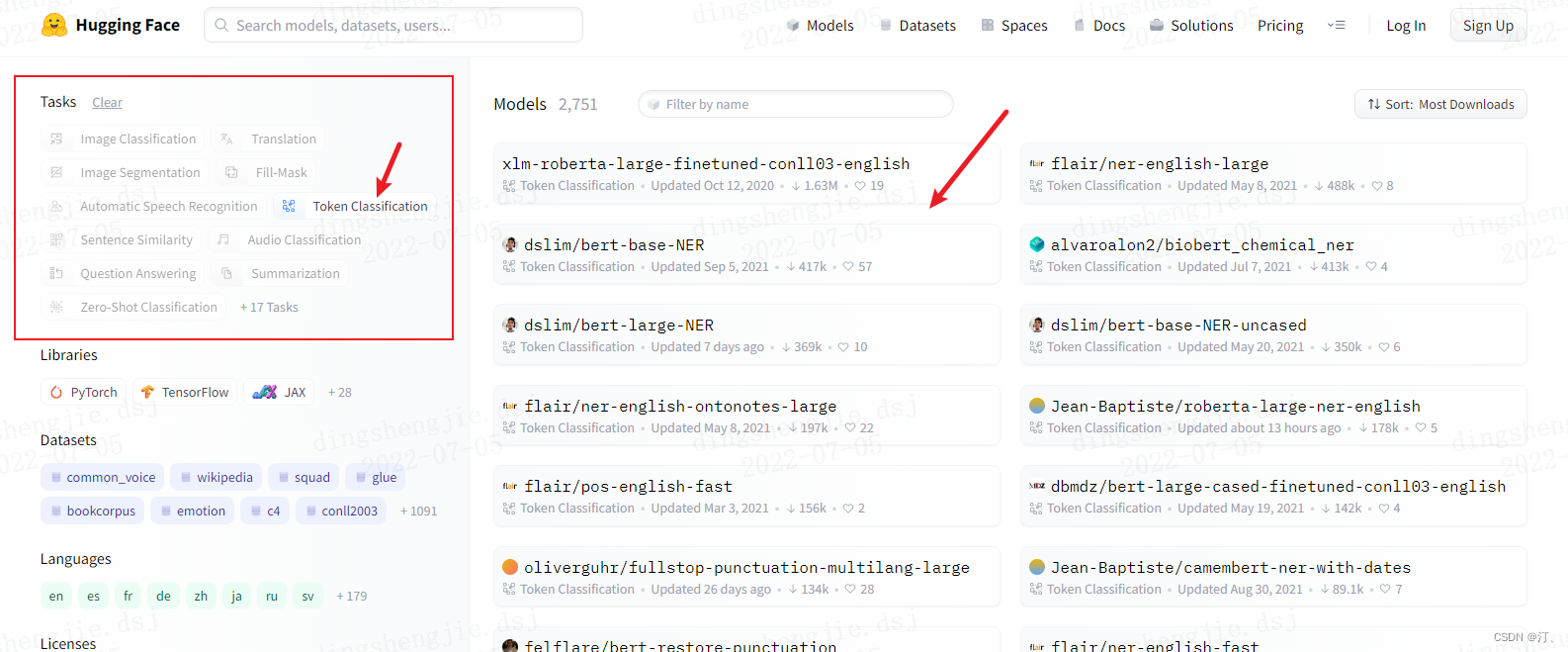
基于 hugging face 预训练模型的实体识别智能标注方案:生成doccano要求json格式
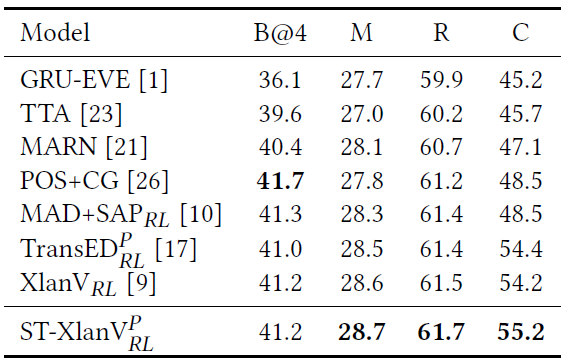
论文阅读【Semantic Tag Augmented XlanV Model for Video Captioning】

DOM node object + time node comprehensive case

How Alibaba cloud's DPCA architecture works | popular science diagram
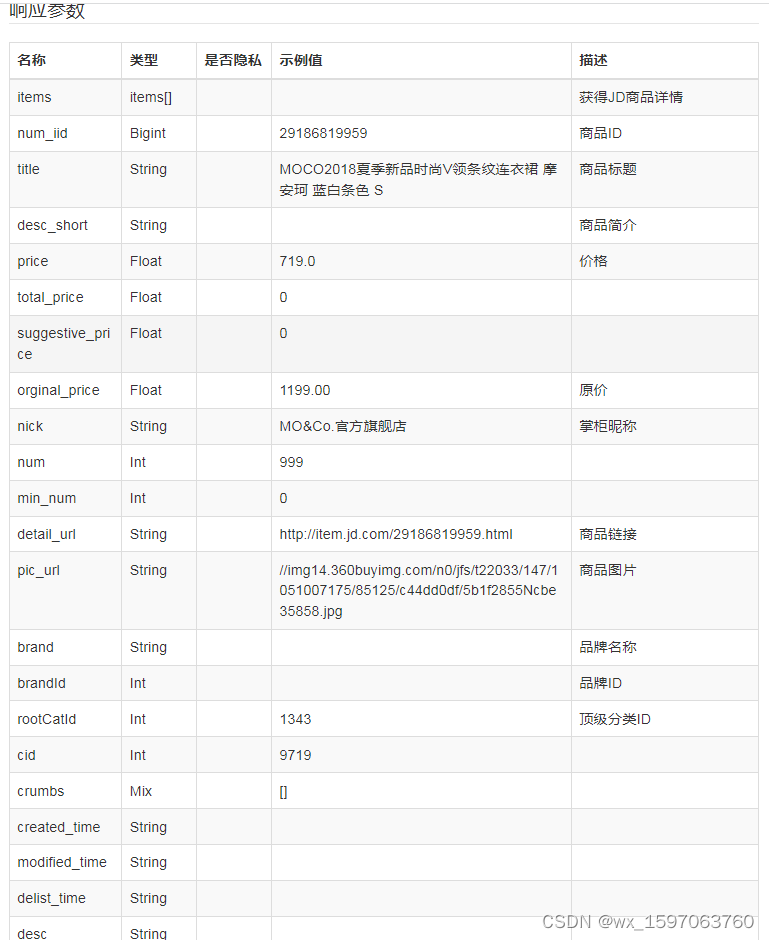
JD commodity details page API interface, JD commodity sales API interface, JD commodity list API interface, JD app details API interface, JD details API interface, JD SKU information interface
随机推荐
A cool "ghost" console tool
JVM(十九) -- 字节码与类的加载(四) -- 再谈类的加载器
Web architecture design process
拼多多新店如何获取免费流量,需要从哪些环节去优化,才能有效提升店内免费流量
ForkJoin最全详解(从原理设计到使用图解)
Design, configuration and points for attention of network specified source multicast (SSM) simulation using OPNET
Most commonly used high number formula
Distributed global ID generation scheme
[reading of the paper] a multi branch hybrid transformer network for channel terminal cell segmentation
Web Authentication API兼容版本信息
张平安:加快云上数字创新,共建产业智慧生态
5阶多项式轨迹
不同网段之间实现GDB远程调试功能
C nullable type
【js组件】自定义select
Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) D. Vladik and Favorite Game
Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) D. Vladik and Favorite Game
AI人脸编辑让Lena微笑
随机生成session_id
Intelligent annotation scheme of entity recognition based on hugging Face Pre training model: generate doccano request JSON format