当前位置:网站首页>Deep understanding of cross entropy loss function
Deep understanding of cross entropy loss function
2022-07-08 02:17:00 【Strawberry sauce toast】
Preface
This article refers to torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() documentation 1, The cross entropy loss is deeply understood from the principle and implementation details .
One 、 Cross entropy
1.1 The definition of cross entropy
hypothesis X It's a discrete random variable , p ( x ) 、 q ( x ) p(x)、q(x) p(x)、q(x) by X Two probability distributions of , The definition of cross entropy is as follows :
H ( q , p ) = − ∑ x q ( x ) l o g p ( x ) H(q,p)=-\sum_xq(x)log\ p(x) H(q,p)=−x∑q(x)log p(x)
Cross entropy can be used to measure the similarity between two distributions . The smaller the cross entropy , p 、 q p、q p、q The more similar the two distributions are , When p = q p=q p=q when , H ( p , q ) H(p,q) H(p,q) To achieve the minimum .
1.2 Cross entropy loss
In the classification problem , Cross entropy loss (Cross Entropy Loss) For the definition of :
l ( y , y ^ ) = − ∑ j = 1 q y j l o g y ^ l(y,\hat y)=-\sum_{j=1}^qy_jlog\hat y l(y,y^)=−j=1∑qyjlogy^
In style , y y y Label the category of the sample ( The length is q q q Of one-hot Coding vector ; y ^ \hat y y^ The output probability predicted for the model .
Two 、 Maximum likelihood estimation
Likelihood : The form of the distribution function of a given population , Estimate the parameters of the model distribution function according to the probability of observed events .2
probability : When the population distribution function is known , Predict the probability of the next event .
2.1 Likelihood function
If overall X It belongs to discrete type , Its distribution law is P { X = x } = p ( x ; θ ) , θ ∈ Θ P\{X=x\}=p(x;\theta),\theta\in \Theta P{ X=x}=p(x;θ),θ∈Θ The form of is known , θ \theta θ Is the parameter to be estimated , Θ \Theta Θ by θ \theta θ Possible value range .
hypothesis x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , . . . , x n x_1, x_2, x_3,...,x_n x1,x2,x3,...,xn Is corresponding to the sample X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , . . . , X n X_1, X_2, X_3,...,X_n X1,X2,X3,...,Xn The sample values of , event X 1 = x 1 , X 2 = x 2 , X 3 = x 3 , . . . , X n = x n X_1=x_1, X_2=x_2, X_3=x_3,...,X_n=x_n X1=x1,X2=x2,X3=x3,...,Xn=xn The probability of that happening is zero :
L ( θ ) = L ( x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , . . . , x n ; θ ) = ∏ i = 1 n p ( x i ; θ ) L(\theta)=L(x_1, x_2, x_3, ...,x_n;\theta)=\prod_{i=1}^np(x_i;\theta) L(θ)=L(x1,x2,x3,...,xn;θ)=i=1∏np(xi;θ)
In style , p ( x i ; θ ) p(x_i;\theta) p(xi;θ) For events X i = x i X_i=x_i Xi=xi Probability of occurrence . L ( θ ) L(\theta) L(θ) along with θ \theta θ The value of , It is called the likelihood function of the sample .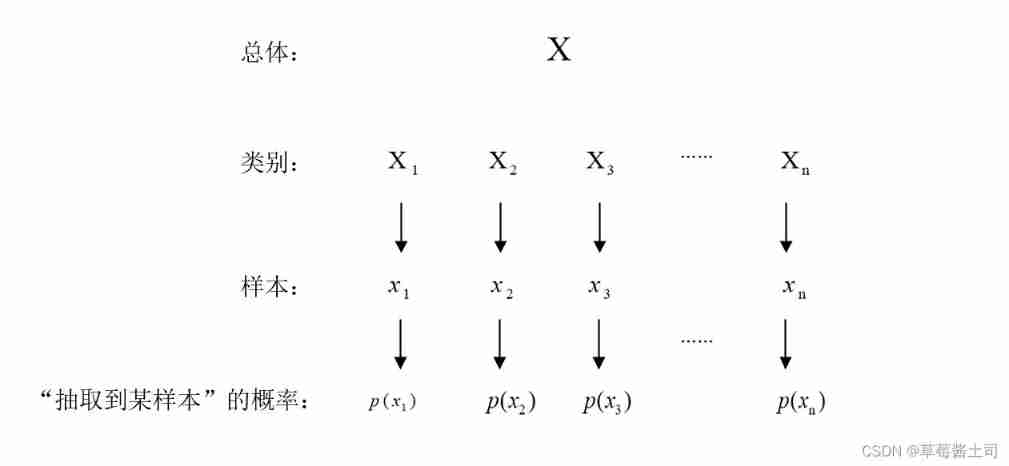
Show me your intention for easy understanding : Likelihood function L ( θ ) L(\theta) L(θ) For events { X 1 = x 1 , X 2 = x 2 , X 3 = x 3 , . . . , X n = x n } \{X_1=x_1, X_2=x_2, X_3=x_3,...,X_n=x_n\} { X1=x1,X2=x2,X3=x3,...,Xn=xn} Probability of occurrence .
2.2 Maximum likelihood estimation
The basic idea : Fixed sample observations x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , . . . , x n x_1, x_2, x_3,...,x_n x1,x2,x3,...,xn, stay θ \theta θ Select the estimation that maximizes the likelihood function within the possible range of values θ ^ \hat \theta θ^, namely :
L ( x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x n ; θ ^ ) = max θ ∈ Θ L ( x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x n ; θ ) L(x_1,x_2,...,x_n;\hat \theta)=\mathop{\max}\limits_{\theta \in\Theta} L(x_1,x_2,...,x_n;\theta) L(x1,x2,...,xn;θ^)=θ∈ΘmaxL(x1,x2,...,xn;θ)
The obtained parameter estimation θ ^ \hat \theta θ^ And sample value x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x n x_1,x_2,...,x_n x1,x2,...,xn of , Write it down as θ ^ ( x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x n ) \hat \theta(x_1, x_2,...,x_n) θ^(x1,x2,...,xn), It's called a parameter θ \theta θ Maximum likelihood estimate of .
2.3 Maximum likelihood estimation in classification problems
Assuming that K K K Classification problem , It is known that n n n Samples , For model parameters p ( x ( i ) , y ( i ) ) p(x^{(i)}, y^{(i)}) p(x(i),y(i)) Estimate , Then the likelihood function is :
L ( ( x ( i ) , y ( i ) ; p ) = ∏ i = 1 n ∏ k = 1 K p y ( k ) L((x^{(i)},y^{(i)};p)=\prod_{i=1}^n \prod_{k=1}^K p^{y(k)} L((x(i),y(i);p)=i=1∏nk=1∏Kpy(k)
Usually, the optimization problem is to take the minimum value instead of the maximum value , therefore Maximizing likelihood function Can be converted to Minimize the negative log likelihood function , Negative log likelihood (negative likelihood) Function is :
− l o g L ( ( x ( i ) , y ( i ) ; p ) = − ∑ i = 1 n ∑ k = 1 K y ( k ) l o g p k -log\ L((x^{(i)},y^{(i)};p)=-\sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{k=1}^Ky(k)log\ p_k −log L((x(i),y(i);p)=−i=1∑nk=1∑Ky(k)log pk
contrast 1.2 The definition of section cross entropy loss function is known : Minimizing cross entropy loss function and minimizing negative log likelihood function are equivalent in formula .
therefore , It can be downloaded from Maximize sample likelihood To understand the classification model, cross entropy is selected as the loss function .
3、 ... and 、 Realization of cross entropy loss function
torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() The description document mentions :
Note that this case is equivalent to the combination of LogSoftmax and NLLLoss.
Pytorch in log_softmax Has been implemented in blog 3 In detail .
here , Mainly through code understanding Negative log likelihood And Cross entropy The connection between ( Reference resources 4).
3.1 Negative log likelihood loss function (Negative Log Likelihood Loss)
Definition of negative log likelihood loss function :
n l l l o s s = − 1 N ∑ i = 1 N y i l o g y ^ = − 1 N ∑ i = 1 N y i ( l o g s o f t m a x ) nllloss=-\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N y_ilog\ \hat y=-\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N y_i\ (logsoftmax) nllloss=−N1i=1∑Nyilog y^=−N1i=1∑Nyi (logsoftmax)
In style , N N N Is the number of samples , y i y_i yi by one-hot Encoded real sample label , y ^ \hat y y^ Is the output probability vector of the model .
>>> import torch
>>> import torch.nn.functional as F
>>> import torch.nn as nn
>>> X = torch.randn(5, 5) # establish 5*5 The sample of ( Number of samples =5,5 Classification problem )
>>> label = torch.tensor([0, 2, 3, 4, 1]) # 5 Real tags for samples
>>> label_one_hot = F.one_hot(label).float()
>>> P = F.log_softmax(X, dim=1) # Convert the output into probability ( Anti overflow treatment is done here )
''' To achieve nll loss'''
>>> nllloss = -torch.sum(label_one_hot * P) / label.shape[0]
tensor(1.9052)
''' call pytorch API Find the negative log likelihood loss '''
>>> nllloss_1 = F.nll_loss(P, label) # There is no need to make one-hot Encoding processing
tensor(1.9052)
''' call pytorch API Find the cross entropy loss '''
>>> cross_entropy_loss = F.cross_entropy(X, label)
tensor(1.9052)
The final implementation results are consistent .
3.2 To achieve CrossEntropyLoss function
Finally, the self - implemented code is given :
''' Customize log-softmax function , Normalize the model output and prevent overflow '''
def log_softmax(X):
c, _ = torch.max(X, dim=1, keepdim=True)
log_sum_exp = c + torch.log(torch.sum(torch.exp(X - c), dim=1, keepdim=True))
return X - log_sum_exp
''' Custom negative log likelihood function '''
def nll_loss(P_k, label):
label_one_hot = F.one_hot(label)
return -torch.sum(label_one_hot * P_k) / label.shape[0] # Here, take the mean value of all samples ( because cross_entropy Default 'reduction=mean')
>>> X = torch.randn(5, 5)
>>> label = torch.tensor([0,2,3,4,1])
>>> nll_loss(log_softmax(X), label) == F.cross_entropy(X, label)
tensor(True)
The final output is True, explain torch.nn.CrossEntropy() The implementation process of is consistent with the customized implementation .
边栏推荐
- Semantic segmentation | learning record (2) transpose convolution
- Introduction to Microsoft ad super Foundation
- 文盘Rust -- 给程序加个日志
- Ml backward propagation
- Vim 字符串替换
- Thread deadlock -- conditions for deadlock generation
- Many friends don't know the underlying principle of ORM framework very well. No, glacier will take you 10 minutes to hand roll a minimalist ORM framework (collect it quickly)
- 谈谈 SAP iRPA Studio 创建的本地项目的云端部署问题
- Semantic segmentation | learning record (1) semantic segmentation Preface
- Ml self realization / logistic regression / binary classification
猜你喜欢
Nacos microservice gateway component +swagger2 interface generation

Semantic segmentation | learning record (5) FCN network structure officially implemented by pytoch
Introduction à l'outil nmap et aux commandes communes

Popular science | what is soul binding token SBT? What is the value?

Completion report of communication software development and Application

Keras深度学习实战——基于Inception v3实现性别分类

ClickHouse原理解析与应用实践》读书笔记(8)
Leetcode featured 200 channels -- array article
咋吃都不胖的朋友,Nature告诉你原因:是基因突变了

Many friends don't know the underlying principle of ORM framework very well. No, glacier will take you 10 minutes to hand roll a minimalist ORM framework (collect it quickly)
随机推荐
leetcode 865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes | 865.具有所有最深节点的最小子树(树的BFS,parent反向索引map)
力扣4_412. Fizz Buzz
Emqx 5.0 release: open source Internet of things message server with single cluster supporting 100million mqtt connections
Strive to ensure that domestic events should be held as much as possible, and the State General Administration of sports has made it clear that offline sports events should be resumed safely and order
生命的高度
Cross modal semantic association alignment retrieval - image text matching
Semantic segmentation | learning record (5) FCN network structure officially implemented by pytoch
Infrared dim small target detection: common evaluation indicators
Random walk reasoning and learning in large-scale knowledge base
The way fish and shrimp go
Leetcode featured 200 channels -- array article
Height of life
Literature reading and writing
Alo who likes TestMan
Leetcode question brushing record | 283_ Move zero
Exit of processes and threads
WPF custom realistic wind radar chart control
Le chemin du poisson et des crevettes
Completion report of communication software development and Application
leetcode 869. Reordered Power of 2 | 869. 重新排序得到 2 的幂(状态压缩)